Topic 2- Genes and Health
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
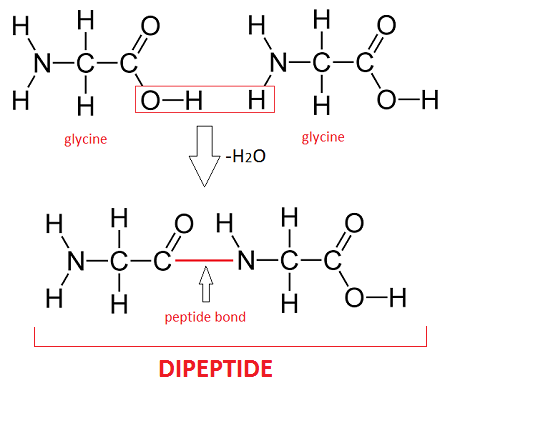
formation of a peptide bond
condensation reactions occur between amine groups on one amino acid and carboxyl groups on other amino acids. a molecule of water is lost for the formation of each peptide bond.
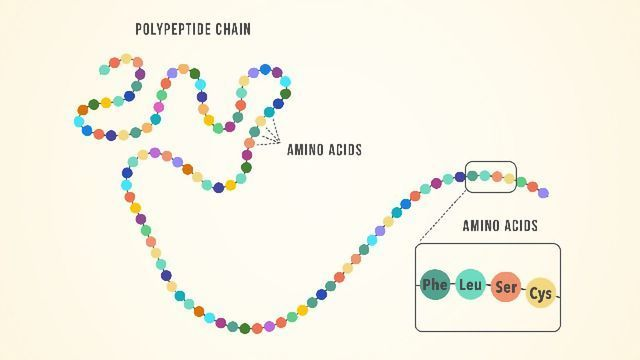
primary structure
the specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
formed by condensation reactions
involves formation of peptide bonds
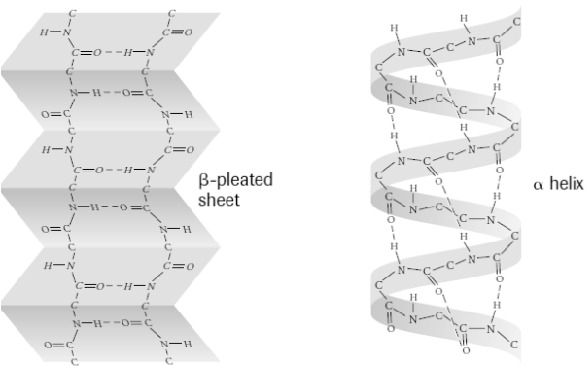
secondary structure
interactions of amino acids in polypeptide chains to form α-helices or β-pleated sheets.
involves the formation of hydrogen bonds (between C=O and N-H groups in different amino acids)
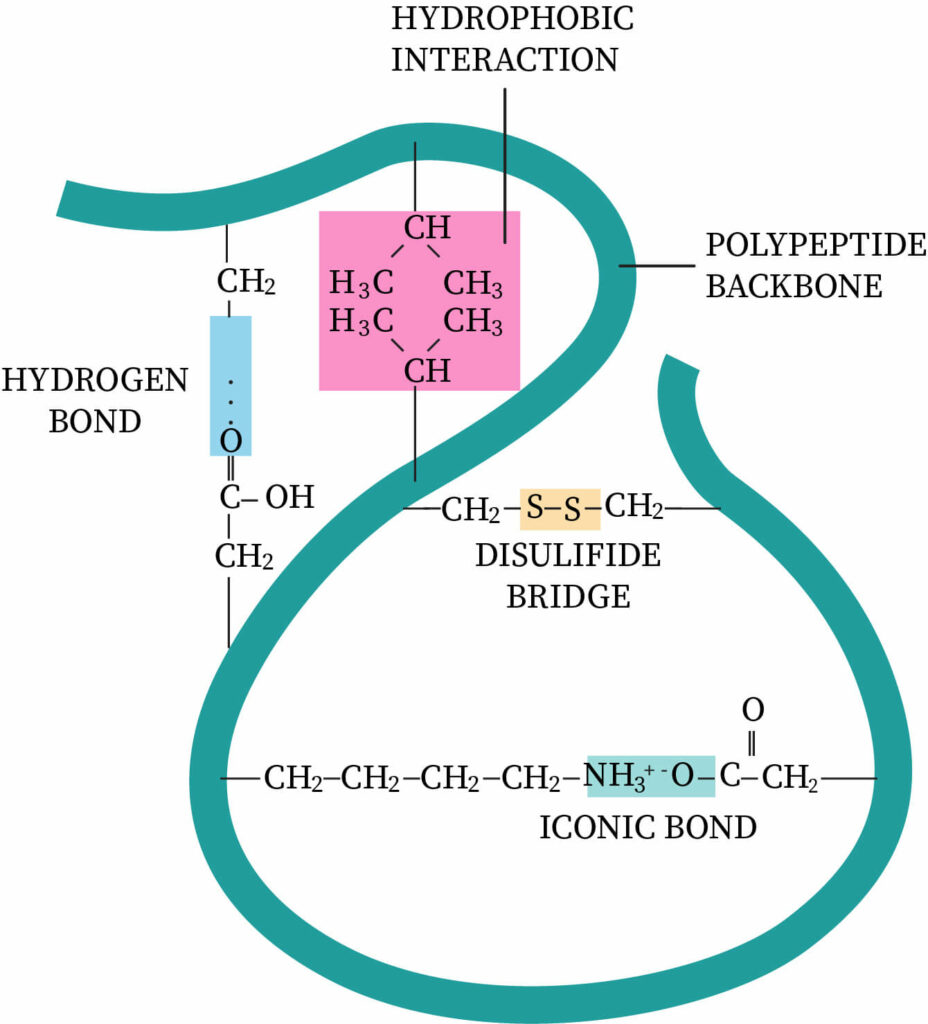
tertiary structure
further folding of the secondary structure into a precise/specific 3D shape.
involves hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, and formation of disulphide bridges between R groups
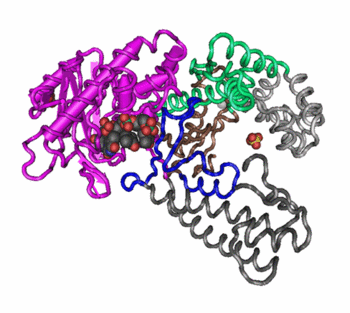
quaternary structure
3-dimensional arrangment involving more than one polypeptide chain.
involves hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, and formation of disulphide bridges between R groups
the importance of primary structure
the sequence of amino acids in a protein determine the position of R groups, which are responsible for hydrogen, disulfide, and ionic bonding present in the polypeptide chain. the bonds determine the folding and shape of the protein, which gives rise to specific properties that allow is to carry out specific functions
conjugated proteins
proteins with a non-protein group associated with their polypeptide chain
e.g. glycoproteins, lipoproteins, haemoglobin
fibrous protiens
polypeptide chains remain elongated
little or no tertiary structure
repetitive sequences of amino acids
hydrophobic R groups on the outside- insoluble
has structural roles in organisms e.g. collagen, fibrin, keratin
globular proteins
polypeptide chains folded into a spherical shape
tertiary structure and some have quaternary structure
does not have repetitive sequences
hydrophillic R groups on the inside- soluble
important metabollic roles, e.g. enzymes, thrombin, fibrinogen and prothrombin, haemoglobin
haemoglobin
globular and conjugated
contains haem (iron containing) groups
4 polypeptide chains
has tertiary and quaternary structure
soluble due to hydrophillic R groups on the outside
required for binding and transport of oxygen in red blood cells
collagen
fibrous
3 polypeptide chains
has quaternary structure
insoluble due to hydrophobic R groups on the outside
provide structural strength and support in skin, artery walls
fluid mosaic model definition
described and fluid because the phospholipid tails move slightly and proteins are described to move through the sea of phospholipids
described as mosaic because of the random assortment of proteins, phospholipids, cholestrol- different shapes and sizes within the membrane
the fluidity of membranes allow them to fuse together- determined by the phospolipids; unsaturated fatty acids that make up phospholipids have kinks that disrupt the close packing to allow for more movement and therefore more fluidity
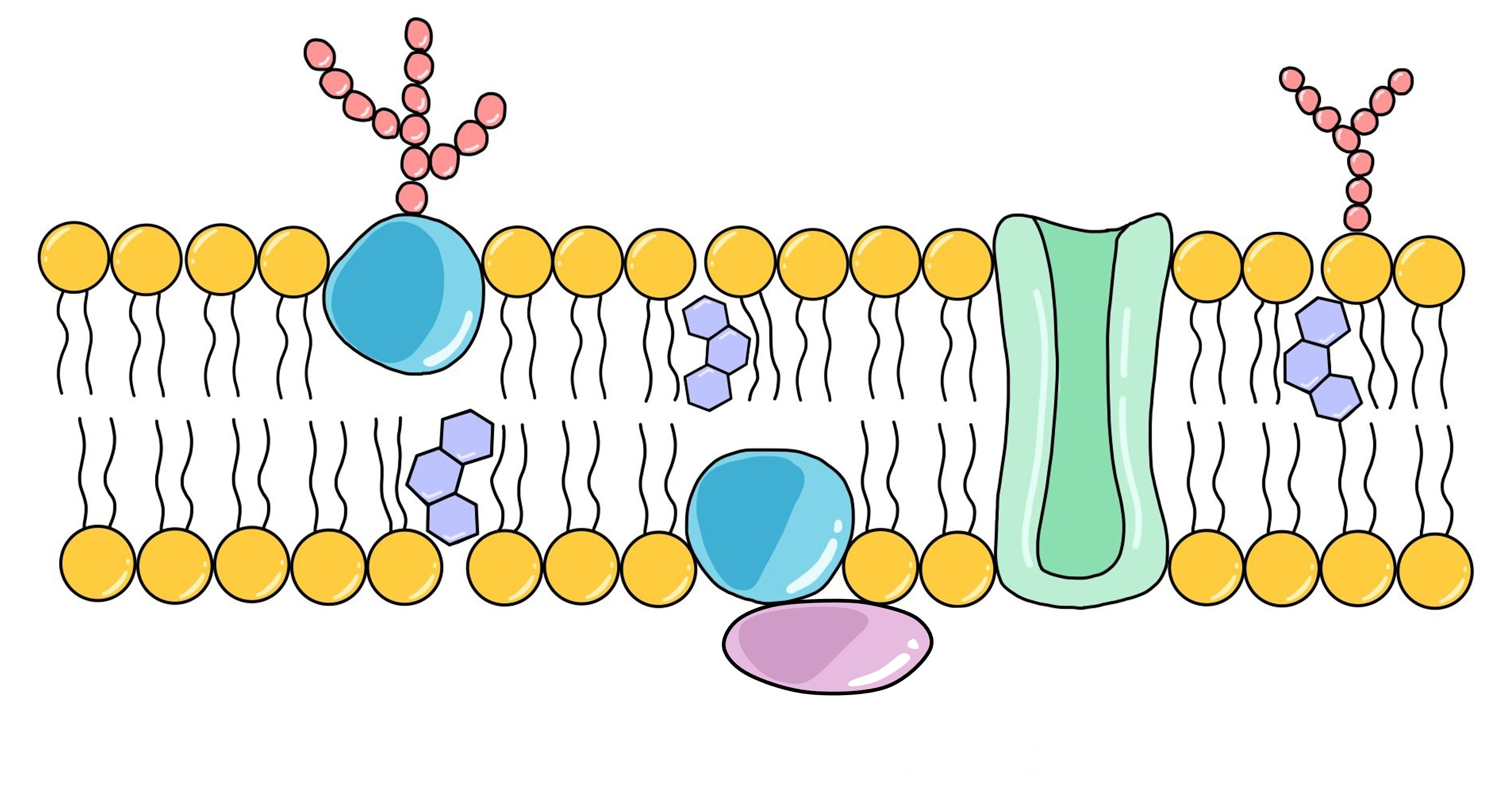
cell membrane structures and their functions
glycolipids- act as receptors and stabilise membrane structure
(extrinsic/peripheral) or (intrinsic/transmembrane) proteins- sit on top of the bilayer or completely span it, and can have a role in cell signalling pathways and stabilising membrane structure
glycoproteins- role in cellular recognition and the immune response, act as receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters
phospholipids- form the bilayer
channel proteins- span the bilayer and control movement of molecules in and out of the cell
cholestrol- disturbs the close packing of the phospholipids to regulate membrane fluidity- essential for membrane stability
Gorter and Grendel
red blood cell membranes contain enough phospholipids to cover the cell twice- the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer
Davidson and Danielli
electron microscope showed more detailed images of the cell membrane- darker outer layers (protein) and lighter inner layers (lipid) could be seen
freeze fracture
freeze fracture showed ‘bumps’ in the middle of the cell membrane- proteins are found embedded in the bilayer
Frye and Edinin
the proteins of two different cells were labelled with flourescent markers and fused, and the colours were seen to mix- the membrane is fluid as it allows proteins to move
Unwin and Henderson
some proteins release from the membrane easily by increasing ionic strength whereas others require strong detergents- intrinsic/integral proteins are fully embedded within the membrane whereas extrinsic/peripheral proteins are only loosely associated with the membrane
lectins
lectins (that only bind to carbohydrates) only bound to the outside of the cell membrane- carbohydrate is only found on the outside/tissue fluid side of the cell membrane
diffusion
the net movement of molecules down a concentration gradient- region of high to low
continues until equilibrium is reached
is passive
facilitated diffusion
passive movement of larger molecules down a concentration gradient via channel/carrier proteins
movement can be either direction
osmosis
the net movement of water molecules from a solution of low solute concentration to a solution of high solute concentration through a partially permeable membrane
active transport
movement of molecules across a membrane against a concentration gradient, usually using energy from ATP to drive pumps (eg carrier proteins) in the membrane
is active
one way direction
exocytosis
active bulk transport out of a cell: membrane bound vesicle containing substance fuses with the cell membrane and releases its contents- relies on the fluid nature of the membrane
endocytosis
active bulk transport into a cell: the cell membrane invaginates (bulges inwards) to form a vesicle that pinches off whilst enclosing the substance inside- relies on the fluid nature of the membrane
factors that affect rate of diffusion
temperature- increasing temperature increases kinetic energy and therefore rate of successful collisions, so rate of diffusion increases
concentration gradient- steeper concentration gradient increases rate of diffusion due to accumulation of molecules on one side
stirring movement- increases kinetic energy
surface area- larger surface area increases rate of diffusion
distance thickness- shorter diffusion pathways will increase rate of diffusion
size of molecule- smaller molecules diffuse faster as they have more kinetic energy
facilitated diffusion: carrier proteins
molecule or ion binds to specific site on the protein, which then changes shape as the molecule crosses the membrane
active transport: carrier proteins
substance binds to the carrier protein. ATP changes the shape of the carrier protein causing the substance to be released on the other side of the membrane
facilitated diffusion: channel proteins
they are specific to the molecule or ion that needs to be transported. gated channel proteins can be open or closed depending on the presence of a signal
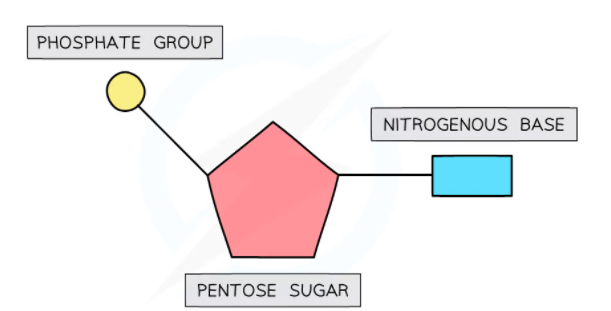
mononucleotide structure
the pentose sugar is deoxyribose
organic base can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thyamine
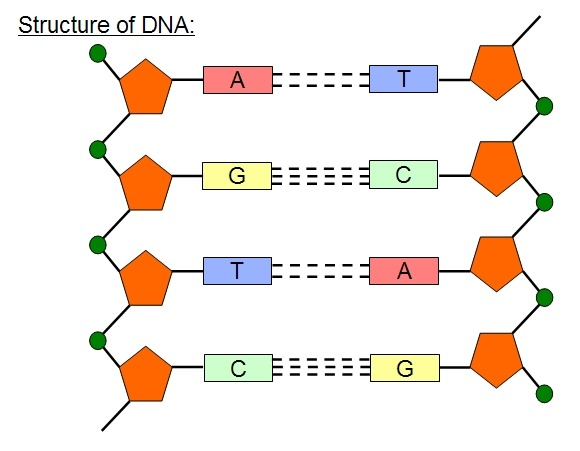
DNA structure
DNA nucleotides are joined by phosphodiester bonds in condensation reactions to form two polynucleotide chains- the two DNA strands that twist around each other to form double helix. the strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between bases. the sugar and the phosphate group form the ‘sugar-phosphate backbone’ with the hydrophillic phosphate groups on the outside.
DNA replication
when a DNA molecule copies itself to make two identical new DNA molecules in order to pass down genetic information from cell to cell
DNA polymerase
acts as an enzyme to join adjacent mononucleotides with phosphodiester bonds, in condensation reactions to form the new DNA strand
compare and contrast structures of DNA and RNA
similarities:
both made of nueclotides with structure of phosphate, pentose sugar, and organic base
both contain adenine, guanine, and cytosine
mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds
differences:
DNA contains deoxyribose sugar whereas RNA contains ribose sugar
RNA contains uracil whereas DNA contains thyamine
RNA is single stranded whereas DNA is double stranded
gene
a sequence of bases on a DNA molecule that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
how do mutations arise
mutations can arise due to errors in the process of DNA replication which happen randomly. risk of mutations can be increased by exposure to ionising radiation or carcinogenic chemicals
substitution mutations
base is substituted for another- changes one triplet in DNA
addition mutation
bases added into the DNA- usually causes a frameshift that changes all subsequent triplets
deletion mutation
bases in DNA deleted- usually causes a frameshift that changes all subsequent triplets
types of mutations that can result in the cystic fibrosis gene
addition or deletion- frameshift changes the amino acid sequence, and CFTR protein may not be made especially if the mutation is at the start of the gene
substitution- change in one codon may cause a specific amino acid to be missing and the CFTR protein may not fold correctly and its shape/structure may change, or it may change due to a shorter polypeptide chain if the mutation creates a stop codon
substitution may not change it due to the degenerate nature of the genetic code, the changed codon may still code for the same amino acid
germ line mutations vs somatic mutations
germ line mutations occur in replicating DNA of ovaries or testes in the creation of gametes whereas somatic is in body cells after conception
germ line mutations are passed onto offspring whereas somatic are not
information about the CFTR protein
channel protein in the apical membrane of mucus producing (epithelial) cells of respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems
its responsible for transporting chloride ions Cl- through cell membranes
cause of cystic fibrosis
mutation results in change of the tertiary structure of a CFTR protein to make it faulty
faulty CFTR protein cannot transport chloride ions so cannot move out of epithelial cells to enter mucus
sodium ions do not move out of cells into the mucus and watter cannot move out of cells into mucus by osmosis
mucus becomes sticker, thicker, and more viscous than normal, blocking parts of the body and impairing the function of certain systems
mucus: people without CF vs people with CF
without: the water in the mucus is regulated to maintain a constant viscosity, as it must be runny enough to be moved by beating cillia but not flood the airway
with CF: CFTR protein does not work properly and mucus becomes stickier than normal
regulation of water
water content is regulated by movement of sodium ions and chloride ions across the epithelial cells in the airways, where water follows the ions due to osmosis
effect of CF on digestion and absorption of digested food
thick mucus blocks the pancreatic duct
pancreatic digestive enzymes cannot leave the panreas and enter the small intestine- lower concentration of enzymes causes less efficient digestion and less products are absrobed into the blood
lack of glucose for respiration results in a lack of energy for cell activity causing tiredness
effect of CF on pancreas function
sticky mucus blocks the pancreatic duct so pancreatic enzymes are trapped behind the mucus and damage the pancreas to cause cysts of hard fibrous tissue
if cells that produce insulin are damaged it can result in diabetes
effect of CF on the male reproductive system
thick mucus blocks sperm ducts as sperm cannot leave the testes, decreasing chance of sperm fertilising an egg
effect of CF on femal reproductive system
thick mucus forms a mucus plug which blocks the cervix and prevents sperm from reaching the ovum in the oviduct to reduce chances of fertilisation
fick’s law of diffusion

role of mucus in the lungs
traps dust, debris, and microorganisms
cillia in the epithelial cells of the trachea and bronchi remove mucus by a wave-like beating, which is then coughed up or removed or swallowed, where the acid in the stomach destroys pathogens
adaptation of the mammilian lung for gas exchange
many alveoli- larger surface area for gas exchange
thin alveoli walls, one cell- short diffusion distance
capillary walls are thin, one cell- short diffusion distance
ventilation of alveoli- maintains steep concentration gradient
blood flow in capillaries- maintains steep concentration gradient
effect of CF on the respiratory system
thick mucus cannot be removed by cilia, which remains in the lungs and blocks the bronchioles, restricting airflow and prevents ventilation of the alveoli. this reduces the number of alveoli involved in gas exchange, reducing the surface area and concentration gradient for gaseous exchange
blockages can also cause over-inflation of the alveoli and damage the elasticity of the lungs
reduction in gas exchange reduces oxygen supply to cells and tissues- during exercise muscle cells recieve less oxygen
lung infections
mucus build up in the lungs allows rapid multiplication of anaerobic bacteria due to the lack of oxygen in the mucus, causing a lung infection
white blood cells die and break down to release DNA which makes the mucus even stickier
repeated infections damage the lung tissue
enzymes
biological catalyst- produced by organism to speed up rate of biological reaction by reducing the activation energy
mechanism of en enzyme
the substrate fits into and binds to the enzyme active site
the shape of the active site fits the shape of the substrate
an enzyme-substrate complex forms and reaction occurs- the activation energy is owered as the substrate is held in the correct position
product is released from the active site and enzyme is unchanged
enzyme specificity
enzyme has specific tertiary structure
due to shape of active site
only substrate will fit- lock and key theory
forms enzyme-substrate complex
types of enzymes
intracellular enzymes catalyse reactions inside cells
exracellular enzymes catalyse reactions outside of cells
homolohous chromosomes
every human cell nucleus has 22 pairs +1 pair of sex chromosomes
in each pair, one from mother one from father
homologous chromosomes are the same length, same position of centromeres, and genes in the same position
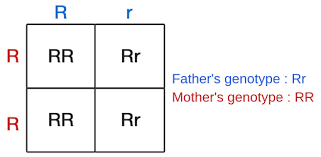
punnet squares
illustrate all the possible ways in which two types of allele can combine to show all the genotypes
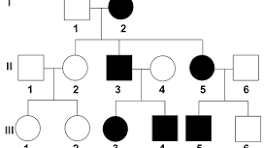
pedigree diagrams
show family inheritence
genetic screening- screening to confirm diagnosis
blood sample taken (WBCs or cheek cells)
DNA tested for presence of defective gene to confirm diagnosis
disadvantages include emotional stress of genetic abnormalities, flase positives or negatives, screening does not test for all possible mutations
genetic screening- pre-conception screening to identify carriers
blood sample or cheek cells taken, DNA tested for presence of defective gene
disadvantages- same as testing for disorder
advantages- couples can make informed decision about having children, can have IVF and embryos screened
genetic screening- pre-implantation genetic diagnosis
8 cell embryos have one cell tested for presence of defetive gene and only unaffected ones are implanted into the uterus
disadvantages- false negative means parents could still have child with disorder, IVF is expensive, low success rates
advantages- affected embryos not implanted, disease not passed on, avoids need for prenatal testing, miscarriage, or abortion
amniocentesis
when fetus is in uterus, 15-17 weeks
foetal cells collected from amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus using a needle to the abdomen
DNA is extracted and analysed to detect defective gene
implications: risk of miscarriage, false positive could result in abortion of healthy foetus, stress
chrionic villus sampling
when the fetus is in uterus, 8-12 weeks
fetal cels collected from the placenta using needle to abdomen or vagina
disadvantages- false positive, stress, risk of misscariage
non-invasive prenatal diagnosis
when fetus is in the uterus, 7-9 weeks
analyses cell free detal DNA from mothers blood plasma
DNA is extracted and analysed to detect defective gene mutation
disadvantages- false postives, stress
social and ethical issues related to genetic screening
fetus is living, abortion is murder
who ha the right to decide if tests should be performed, implications of medical costs, disagreements over next steps
abnormalities found may result in discrimination by employers or insurance
fetus has right to live
issues with confidentiality of parents and child
risks of prenatal tests are not fully understood- risk of miscarriage