PULMONARY REHAB FINAL
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Definition of pulmonary rehabilitation
A comprehensive intervention based on a
thorough patient assessment followed by patient-
tailored therapies that include, but are not limited
to, exercise training, education, and behavior
change, designed to improve the physical and
psychological condition of people with chronic
respiratory disease and to promote the long-term
adherence to health enhancing behaviors
COPD Facts
COPD is 3rd leading cause of death in U.S
COPD costs U.S economy 32.1 billion/ year- 18 direct and 14.1 indirect
In 2000, the number of women dying of COPD was greater than men
In 2001, 12.1 million adults diagnosed with COPD
About 24 million have impaired lung function and are undiagnosed
85% caused by cigarette smoking
The other 15% is due to factors such as occupational and environmental exposures previous serious lung infections or genetic abnormalities such as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
What % of smokers develop COPD
15-20%
can lay dormant for 20 years before the patient becomes symptomatic
50% of patients die within 10 years of a diagnosis of COPD
in 1965 smoking statistics revealed that for individuals aged 18 years and older
52% of men were smokers
34% of women were smokers
in 2006 smoking statistics revealed that for individuals aged 18 years and older
23% of men were smokers
18% of women were smokers
Essential components of pulmonary rehab
promotion of long term adherence
education and training
assessment
exercise
psychosocial intervention
prevention and outcomes ( In middle)
Patient goals and program goals
Staff should be consistent in their understanding of the goals
patient goals need to be established and reviewed with the patient significant other at the beginning of the program
goals should be realistic and readily achievable
goals may be altered as program progresses
Patient goals
Breath better
more active- return to work and participate in hobbies
improve quality of life
improve activities of daily living
be able to travel with greater ease
Program goals
increase exercise tolerance
increase patient compliance
decrease psychological symptoms
education
infection control
treatment plan ( smoking cessation, weight loss or gain)
return the pt to gainful employment or active retirement if applicable
Demonstrated outcomes of pulmonary rehab
Reduced resp symptoms ( dyspnea and fatigue )
increased exercise tolerance and endurance
increased knowledge of pulmonary disease
enhanced ability to perform activities of daily living
improved health related quality of life
improved psychosocial symptoms ( anxiety and depression)
reduced hospitalizations
return to work for some patients
Physiologic impairment
Abnormal PFT’s
FEV1/FVC < 70% of predicted
FEV1 < 80% of predicted
DLco < 65% of predicted
Resting hypoxemia SpO2< 90%
Oxygen desaturation with exercise: SpO2< 90%
Functional impairment
Dyspnea
Occupational performance
increased use of medical resources
reduction in activities of daily living
reduction in physical activity
Chronic lung conditions appropriate for pulmonary rehab
Obstructive diseases
Emphysema
persistent asthma
bronchiectasis
chronic bronchitis
cystic fibrosis
Chronic lung conditions appropriate for pulmonary rehab
Restrictive diseases
interstitial fibrosis
sarcoidosis
occupational lung disease: asbestosis and silicosis
Chronic lung conditions appropriate for pulmonary rehab
Neuromuscular diseases
myasthenia gravis
diaphragmatic dysfunction
postpolio syndrome
Chronic lung conditions appropriate for pulmonary rehab
Chest Wall Diseases
kyphoscoliosis
ankylosing spondylitis
Chronic lung conditions appropriate for pulmonary rehab
Other lung conditions
lung cancer
pre / post lung transplantation
pre / post lung volume reduction surgery
pulmonary hypertension
post COVID-19 infection
Conditions that exclude a patient from pulmonary rehab
unstable cardiac disease
severe pulmonary hypertension
metastatic cancer
severe cognitive defect
severe psychiatric disease
significant orthopedic impairment
tobacco abuse
pt motivation
financial situation
transportation
The Gold spirometric criteria ( post- bronchodilator FEV1) for COPD severity
MILD
MODERATE
SEVERE
VERY SEVERE
The Gold spirometric criteria ( post- bronchodilator FEV1) for COPD severity for Mild COPD
FEV1/ FVC < .70
FEV1> 80% predicted
The Gold spirometric criteria ( post- bronchodilator FEV1) for COPD severity of Moderate COPD
FEV1/FVC < .70
50% < FEV1 < 80% of predicted
The Gold spirometric criteria ( post- bronchodilator FEV1) for COPD severity of Severe COPD
FEV1/FVC < .70
30% < FEV1 < 50% of predicted
The Gold spirometric criteria ( post- bronchodilator FEV1) for COPD severity of Very Severe COPD
FEVI/FVC < .70
FEV1< 30% predicted or FEV1 < 50% predicted plus chronic resp failure
Medicare Law HR 6331 requieres
Stage 2, 3 and 4 COPD to be approved for pulmonary rehab
Components of initial patient interview
Observation skills
Listening skills
Ability to ask the right questions
Characteristics of the patient in pulmonary rehab
Developmental Stage
Includes the physical cognitive and psychosocial elements
some patients experienced successful learning in the past ( formal education or a non traditional setting )
other patients experienced frustrations and conflict in dealing with school settings
physical changes may have a negative influence, such as a decreased hearing or vision
life changing events such as “ empty- nest syndrome” may serve as a stressor in learning
shortness of breath, denial and depression all act to decrease the effectiveness of the learning environment
Characteristics of the patient in pulmonary rehab
Motivation Stage
The capacity to learn
the readiness to learn
the presence of moderate anxiety
previous successful experiences
a positive teacher learner relationship
a social support system
Characteristics of the patient in pulmonary rehab
Compliance
Elements consistent with patients adherence to behaviors requested of them include:
the pt must value the healthy state that pulmonary rehab promotes
the pt believes that the actions occurring in rehabilitation will help them attain a healthy state
the pt sees how others cope with chronic lung disease and better understand and accept the rehab process
Characteristics of the patient in pulmonary rehab
Health Literacy
The degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions
Research show the strongest predictor of an individuals health status is health literacy
other factors that may predict an individuals health status are:
age
income
employment status
education level
racial or ethnic group
Health literacy
adults with no insurance are more likely to have basic or below basic health literacy
a higher percentage of adults with low literacy receive their info about health issues from radio and TV than through written sources, the internet or social contacts
avg handout of health information is written at the 10th grade level and the avg american reads at only a 5th grade level
low health literacy exacerbates further the negative health impact of the social determinants of health
Characteristics of the patient in pulmonary rehab
Deficits and Disabilities
Hearing problems- pts may not use their hearing aids or they may use them improperly
vision difficulties- may be overcome with corrective lenses or contacts
learning disabilities- usually plague individuals from childhood
Education sessions taught in pulmonary rehab
normal pulmonary anatomy and physiology
pathophysiology of lung disease
description and interpretation of medical tests
breathing training
bronchial hygiene
medication delivery devices
medications, including oxygen
Educational materials
Education materials utilized in pulmonary rehab classes should
be printed in large font
be written at a low education level ( 5th grade level)
utilize terms and expressions that patients can understand ( do not use medical jargon )
Medical Director qualifications
Must be under the direction of a licensed physician ( M.D or Doctor if Osteopathy
Medical Director responsibilities
training or experience in the care of patients with chronic resp disease
ultimate responsibility for the safety and quality of care provided
provides supervision of the rahab process
responsible for determining the appropriateness of the pulmonary rehab plan of care for the pt
Administrative- review policies, protocols and procedures
Education- training of healthcare professionals ( RT’s, residents, pulmonary fellows)
Clinical- patient evaluations, exercise prescription and treatment plans
responsible and accountable for the PR program including overshight of the PR staff
must re-avulaute each pt and revise the plan of care for each pt at least every 30 days
is involved substantially in consultation with staff, in directing the progress of the individuals in the PR program.
Program director qualifications
the american association of cardiovascular and pulmonary rehab- recommends the programs coordinator have graduated from an accredited program such as RT, PT, RN, OT or exercise physiologist and hold a national certification or licensure
AACVPR recommends that the coordinator has a minimum of 3 years of clinical pulmonary rehab experience after a BS degree or
five years of pulmonary rehab experience after an associates degree
Program director is responsible for
coordinator needs to be competent in reimbursement, documentation and marketing strategies
duties include clinical, administrative, educational and advocacy
serves as the liaison among the pt, medical director , referring physicians and rehab staff
Physician oversight of pulmonary rehab exercise sessions
Physician must be in close proximity to the rehab area
supervising physician does not have to be the medical director
direct supervision of pulmonary rehab must be established by each program and documented in the protocol manuals
Common symptoms observed of patients in pulmonary rehabilitation
Psychological
Depressed mood- up to 59% have depression
Anxiety- among COPD patients ranges from 30% to 40%
Anger
Guilt
Embarrassment
Common symptoms observed of patients in pulmonary rehabilitation
Cognitive
mild deficits
impaired psychomotor speed
impaired problem solving
impaired attention
Common symptoms observed of patients in pulmonary rehabilitation
Social
reduced social activity
change in family roles
reduced independence
Common symptoms observed of patients in pulmonary rehabilitation
Behavioral
impaired ADL’s
smoking
malnourishment
decreased exercise capacity
medication noncompliance
Psychological functioning
evaluation of psychological functioning includes tools to assess symptom specific indicators such as
brief symptoms inventory
beck depression inventory
the COPD coping questionnaire
the COPD self efficacy scale
Beck Depression Scale
The BDI is a self report rating inventory introduced in 1961 that measures characteristics attitudes and symptoms of depression
BDI uses 21 items to measure the severity and depth of depression symptoms as listed in the american psychiatric association diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders
Scoring of the beck depression inventory
Patients rate 21 symptoms and attitudes of
depression on a scale of zero to three to best
reflect their level of intensity.
Each of the symptoms in the Beck Depression
Inventory fit the diagnostic criteria of the DSM-V.
- An example of a question and rating scale:
0. I do not feel sad
1. I feel sad
2. I am sad all the time, and I can’t snap out of it
3. I am so sad and unhappy that I can’t stand it
Beck scoring
Score of 1-10: These ups and downs are considered
normal
Score of 11-16: Mild mood disturbance
Score of 17-20: Borderline clinical depression
Score of 21-30: Moderate depression
Score of 31-40: Severe depression
Score of 40+ Extreme depression
The COPD self efficacy scale
Used to measure the degree of
confidence patients with COPD have
regarding their ability to avoid breathing
difficulty while participating in specific
activities.
This scale rates the strength of
expectations of managing or avoiding
breathing difficulties in 34 situations such
as . . . .
o physical exertion
o weather/environmental
o behavioral factors
o intense emotional situations
Treatment if psychological distress
counseling
psychotherapy
exercise, rehab
support groups
The three commonly used QOL measures:
SF 36
St Georges Respiratory Questionnaire
CAT assessment
Gold definition of COPD
COPD is a heterogeneous lung condition
characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms
(dyspnea, cough, sputum production and/or
exacerbations) due to abnormalities of the
airways (bronchitis, bronchiolitis) and/or alveoli
(emphysema) that cause persistent, often
progressive, airflow obstruction.
Arterial hypoxemia ranges
35 to 45 mmHg
Airflow limitations in COPD ( FEV1 post bronchodilator )
If airflow obstruction is minimally improved, then
chronic airflow obstruction is considered.
If airflow obstruction has a high improvement, then
Asthma is considered.ATS states that improvement of airflow is considered
significant for increases > 10% for either FEV1 or FVC
(use of GLI 2012 reference equation is required for this
calculation)
Static Hyperinflation
is a permanent elevation of the
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) at rest due to the
loss of elastic recoil
Dynamic Hyperinflation
occurs with exercise and is due
to expiratory airflow limitation when ventilatory demands
are increased and expiratory times are reduced.
Hyperinflation
An increased RV/TLC ratio in the presence of
increased TLC equals hyperinflation
Air Trapping
An increased RV/TLC ratio with a normal TLC equals
Purpose of the MRC dyspnea scale
to measure the severity of breathlessness (dyspnea) and its impact on a patient's daily activities and mobility
How is CAT score range
5-40
CAT score impact level
> 30 Very High
• > 20 High
• 10-20 Medium
• < 10 Low
• 5 (Upper limit of normal
in healthy non-smokers)
CAT is a tool used to
measure health status
Involuntary weight loss criteria:
Weight loss > 10% of usual body weight in the past 6 months
or
Weight loss > 5% in the past month
BMI calculation
Weight in kilograms divided by height in meters x height in meters= kg/m2
Carbohydrate oxidation produces an RQ near
1.0
Fat oxidation produces an RQ near
0.71
Protein oxidation produces an RQ of
.82
Depletion of fat free mass in males
FFM < 16 kg/m2
Depletion of fat frass mass in females
FFM < 15 kg/m2
cachexia
underweight and low FFM
Semistarvation
underweight and relative preservation of FFM
Sarcopenia
normal weight and depletion of FFM
Modified Borg Scale is considered
subjective
10 point category ratio scale with descriptive terms
Unidimensional instruments
visual analog scale
modified borg scale for breathlessness
medical research council breathlessness scale
Multidimensional instruments
Chronic resp disease questionnaire
san diego shortness of breath questionnaire
Critical strategy for decreasing dyspnea
exercise
BODE index
B- body mass index
O- degree of obstruction
D- dyspnea
E- exercise endurance ( 6 min walk test )
A higher BODE score correlates with an increased
risk of death.
• Improvement in the BODE score is associated with
better survival over time
The primary outcome is 6 minute walk distance is
feet or meters
A 6 minute walk test with a value of less than 350 meters is considered
abnormal
Minimum clinical important distance is
30 meters for adults with chronic resp disease
Calculate predicted max HR
220- age in years = max HR
the target HR range for exercise
60%- 85% of max HR
Average 6 MWT walking speed
speed= total distance / time x 0.01136
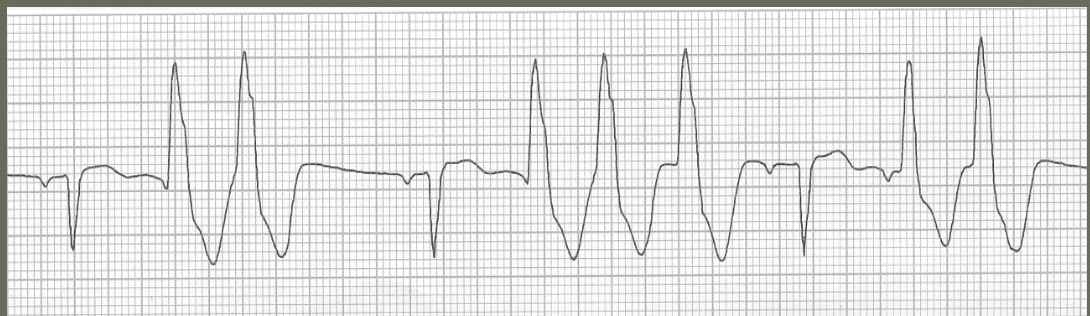
Premature Ventricular Contractions
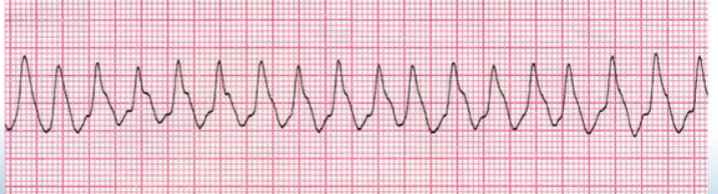
V-tach
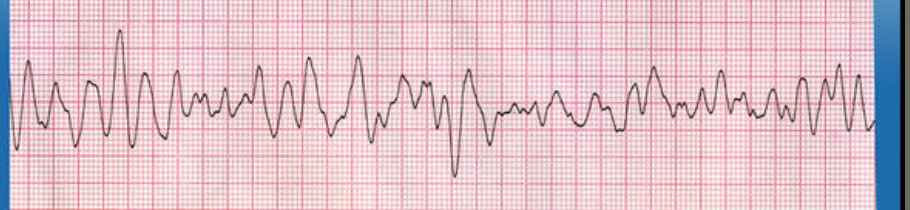
V-Fib
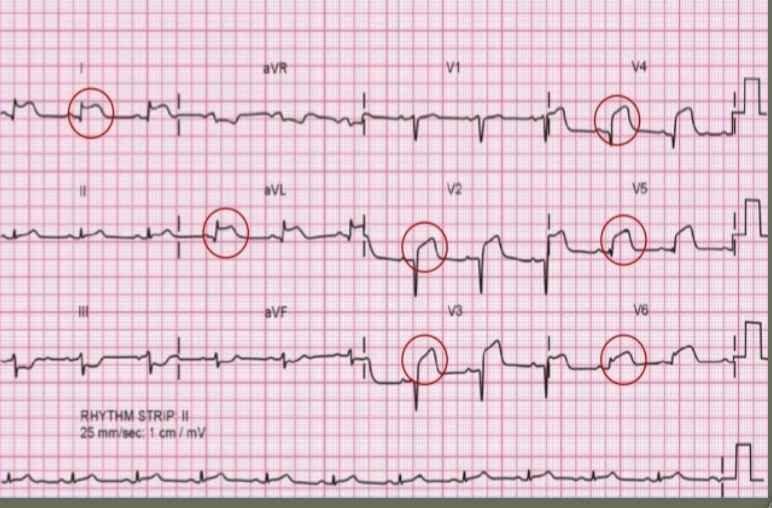
STEMI
Determining Limitations During Graded Exercise testing
dynamic hyperinflation
excerise-induced bronchospasm
rising VD/VT
rising PaCO2
failling SpO2
falling blood pressure
chest pain
arrhythmias
musculoskeletal
deconditioning
Purpose of the tinetti gait and balance instrument
used to predict the risk of a fall of an elderly patient
Who is a candidate for home care
patients that
are newly diagnosed with a disease that requires education and training
have a terminal disease and desire to be treated at home
require medical devices that necessitate monitoring and maintenance
have repeated hospitalizations
Candidates for home care part 2
patients with functional limitations- cognitive disabilities, inability to perform ADL’s and inability to monitor and administer medications
patients with physical limitations- dyspnea that limits ADL’s, ambulatory limitations and difficulties with speech, vision or hearing
Benefits of home care
improves quality of life
is cost effective
encourages self- management and independence
allows for ongoing monitoring of patient response to treatment
reduces the need for clinic visits, ER visits, and hospital admissions
reduces risk of nosocomial infections
Role of the home care RT
teach patients how to correctly and safely use resp care equipment
pt evaluation and assessment
train the caregivers to perform reps care procedures
provides education and training to other member of the home care team
Part A
covers inpatient care in hospitals , skilled nursing
facilities, hospice care, and some home health care
Part B
is an optional coverage of doctor’s services,
outpatient care, services of PT, OT, and some home health
care.
◦ Patients pay a monthly premium to cover the cost of Part B.
2024 Medicare premium is $185 per month;
Increases every year; 2026 premium is estimated to be
$206.50
Medicare provides reimbursement for Nursing, Physical
Therapy, Occupational Therapy, Speech Therapy, Social
Workers, and Home Health Aides.
Current Medicare law does not provide direct
reimbursement for Respiratory Therapy services in the
H.R 941 Medicare Resp Therapy initiative act of 2011
To amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide for
Medicare coverage of services of qualified respiratory
therapists performed under the general supervision of a
physician.Representatives of the AARC proposed to revise the Medicare
statute to add recognition of respiratory therapy services as a
separate Medicare Part B benefit and to permit qualified
respiratory therapists to provide respiratory therapy services
under the general supervision of a physician.
Reimbursement for DME equipment and supplies
DMEPOS
Reimbursement for most Durable Medical Equipment
Prosthetic/Orthotics and Supplies (DMEPOS) is
established by fee schedules.
Reimbursement for DME equipment and supplies
DMEPOS competitive bidding program
Mandated by Congress through the Medicare
Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act
of 2003 (MMA).
There is no active competitive-contract round right
now for respiratory DME - CMS has a temporary gap
period while it finishes rulemaking
FDA definition of a tobacco product
A “tobacco product” is defined by the FDA as a
product made or derived from tobacco and intended
for human consumption, including any component,
part or accessory of a tobacco product
How an individual becomes tobacco dependent
For a patient to be tobacco dependent, two
independent processes must occur:
Nicotine in cigarette smoke must activate the
CNS genetic systems, creating the cellular
substrate for nicotine dependence.The development of classic conditioned
responses to cigarettes.
Nicotine in a cigarette
11.9 mg to 14.5 mg
Smokers nicotine yield is up to
2mg per cig