Dental Terminology
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
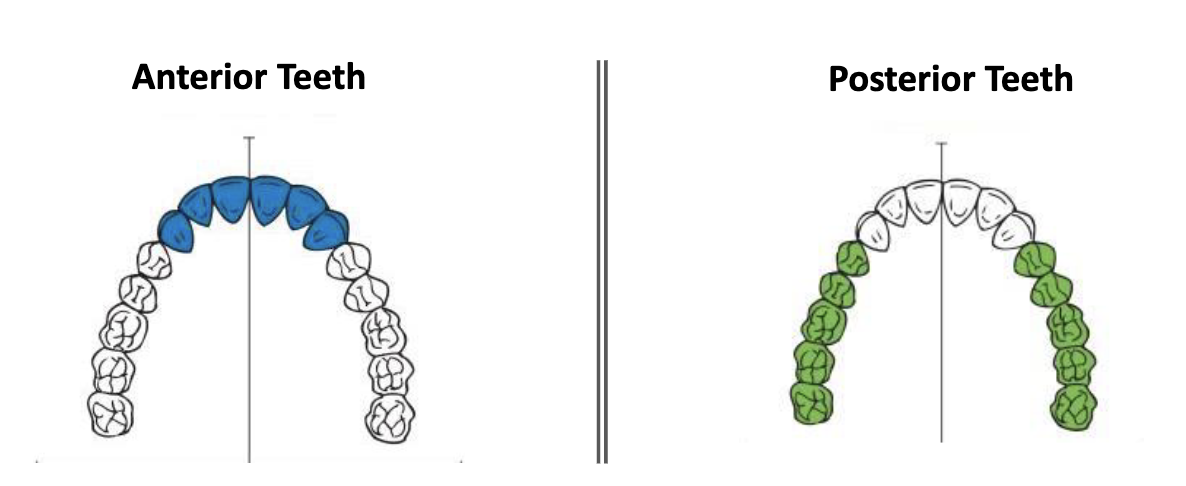
which teeth are considered anterior? posterior?
anterior = incisors + canines
posterior = premolar + molars
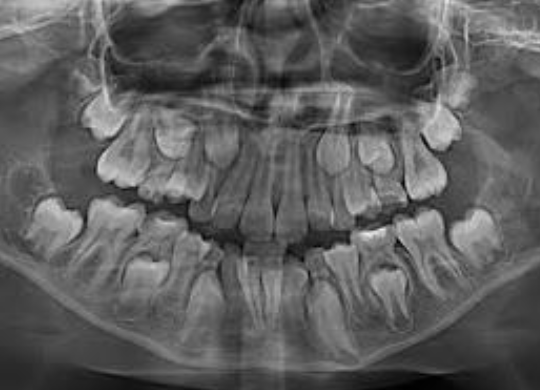
How many decidious teeth are there?
20
primary dentition average age and type of teeth present?
6 months to 6 years
primary teeth
mixed dentition average age and type of teeth present?
6 years to 12 years
primary AND permanent teeth
permanent dentition average age and type of teeth present?
12 years until loss of teeth
permanent teeth
dental formula for primary dentition
I 2/2 (incisors)
C 1/1 (canine)
M 2/2 (molar)
t/f there are no premolars in primary dentition
true
3rd molar is also known as
wisdom teeth
function of molars/premolars
grinding, chewing, crunching
dental formula for permanent dentition
I 2/2 (incisor)
C 1/1 (canine)
P 2/2 (premolar)
M 3/3 (molar)
how many permanent dentition
32
how many primary dentition?
20
what are succedaneous teeth
Permanent teeth that replace primary teeth
T/F: the permanent molars are succedaneous
false, molars do not replace primary teeth (nonsuccedaneous)
the permanent premolars replace the decidous molars
which teeth are considered succedaneous teeth?
permanent incisors, canines, and premolars
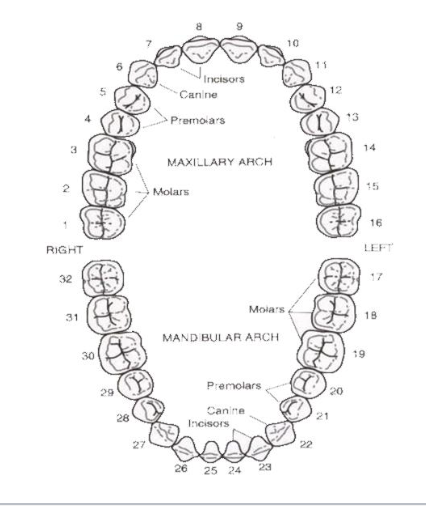
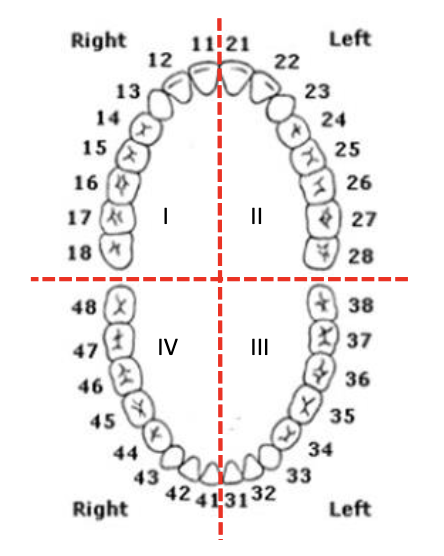
universal numbering system the upper right quadrant is # ___ - ___
1-8
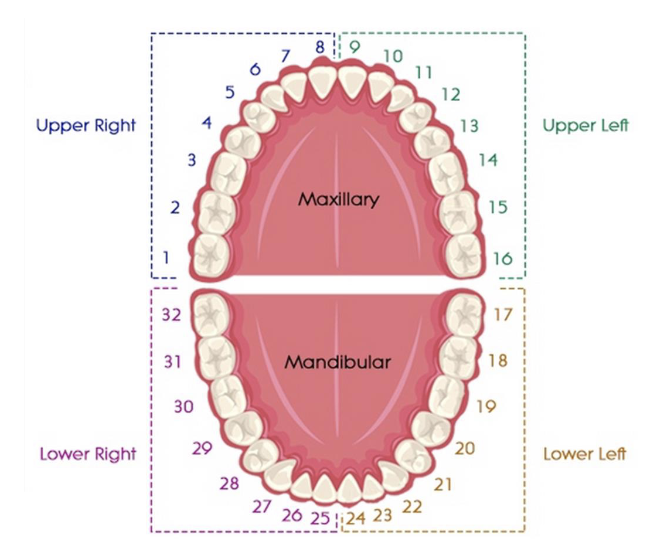
universal numbering system the upper left quadrant is # ___ - ___
9-16
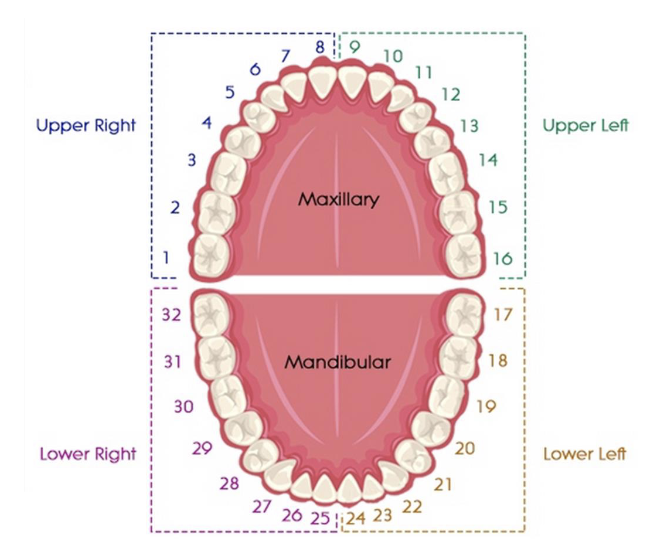
universal numbering system the lower left quadrant is # ___ - ___
17-24
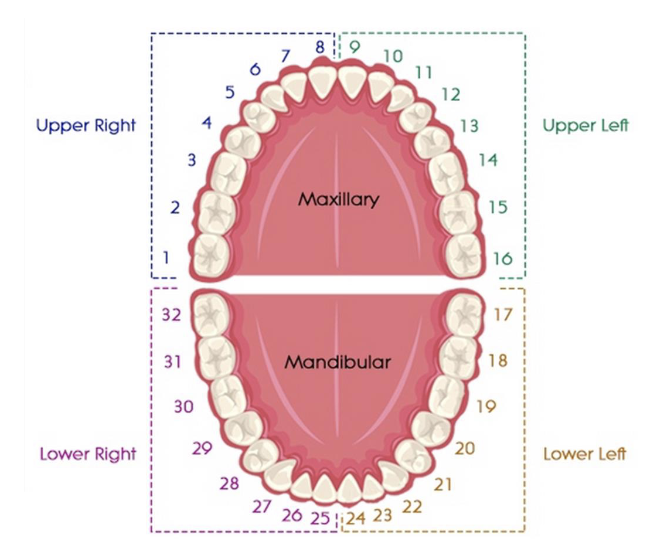
universal numbering system the lower right quadrant is # ___ - ___
25-32
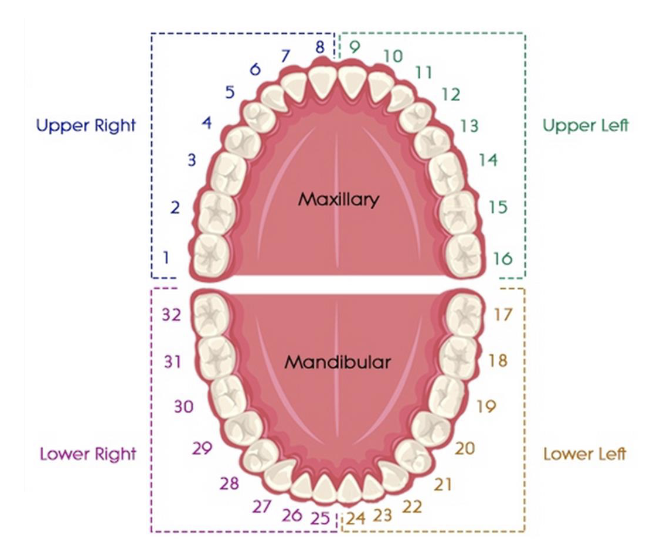
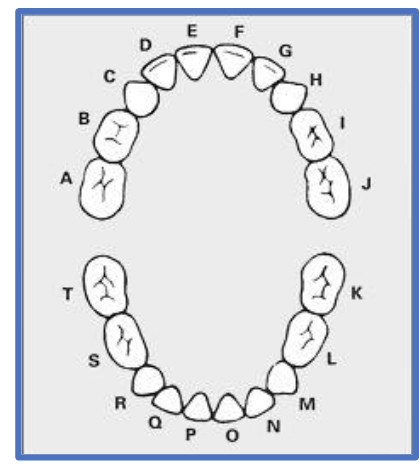
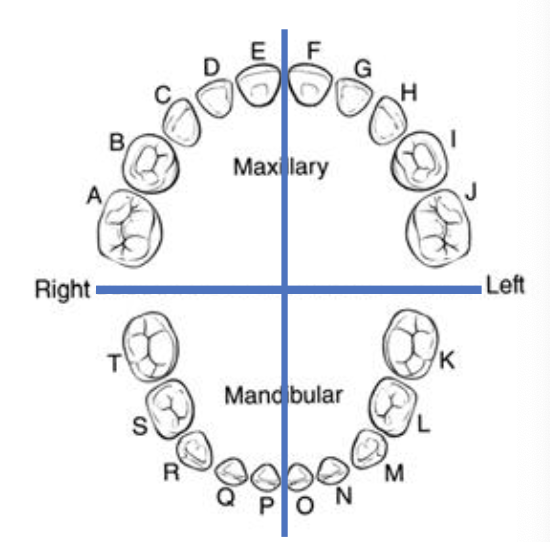
primary dentition are labelled
A-T
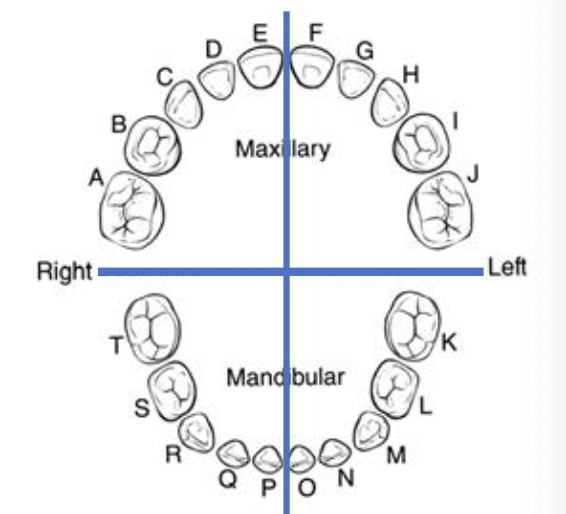
universal numbering system, primary dentition, the upper right quadrant is letter ___ - ___
A-E
universal numbering system, primary dentition, the upper left quadrant is letter ___ - ___
F-J
universal numbering system, primary dentition, the lower right quadrant is letter ___ - ___
T-P
universal numbering system, primary dentition, the lower left quadrant is letter ___ - ___
O-K
Zsigmondy/palmer notation system uses ___ and ___
quadrants (right angle) and #1-8 per quadrant.
the most medial/anterior is #1 for each quadrant

FDI Notation system (Federation Dentaire Internationale) uses
XY
X: quadrant # (1-4)
Y: tooth number in each quadrant (1-8)
all teeth have __ surfaces
5
Anterior: incisal, medial, distal, labial, lingual
posterior: occlusal, mesial, distal, buccal, lingual
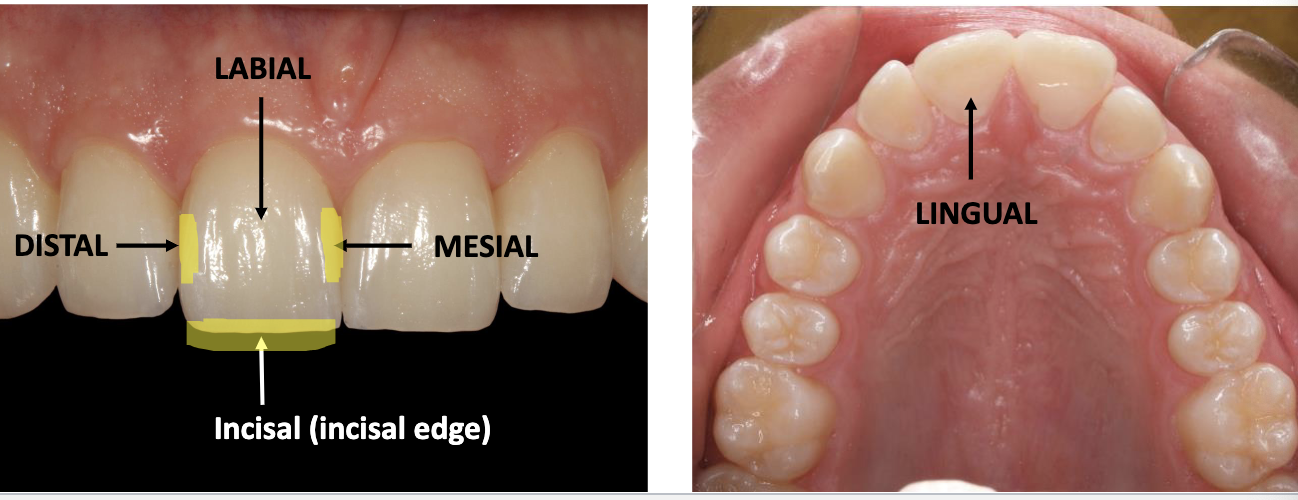
labial and buccal surfaces are also considered
facial surfaces
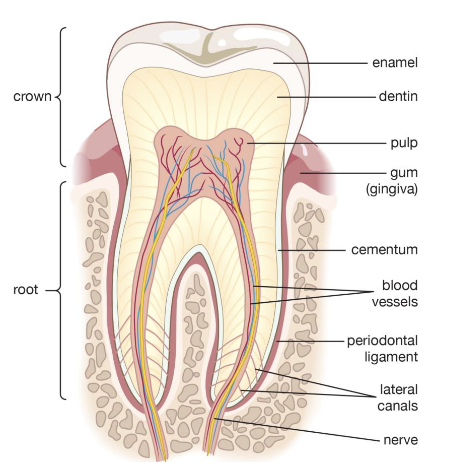
what are the 4 major tissues of a tooth?
enamel
dentin
pulp
cementum
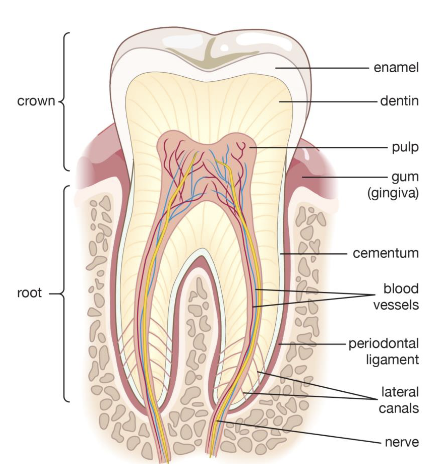
what are the 3 major periodontal structures?
periodontal ligament (PDL)
alveolar bone
gingiva
what is the hard tissue covering dentin of anatomical root of tooth
cementum
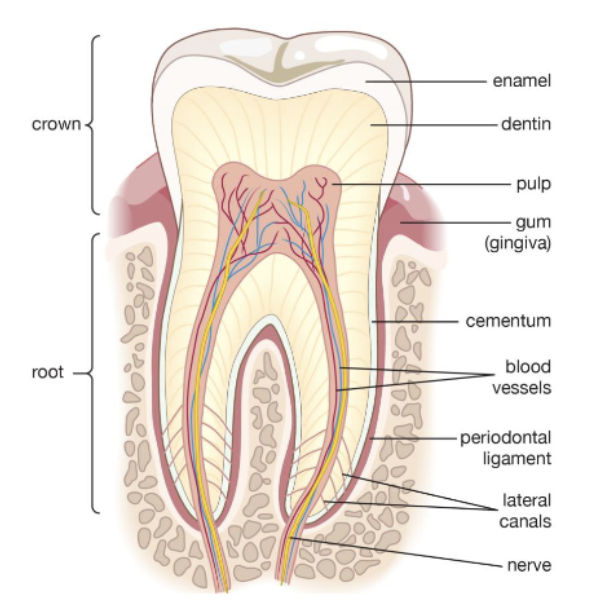
what is the outer most layer of a tooth surrounding the entire anatomical crown?
enamel
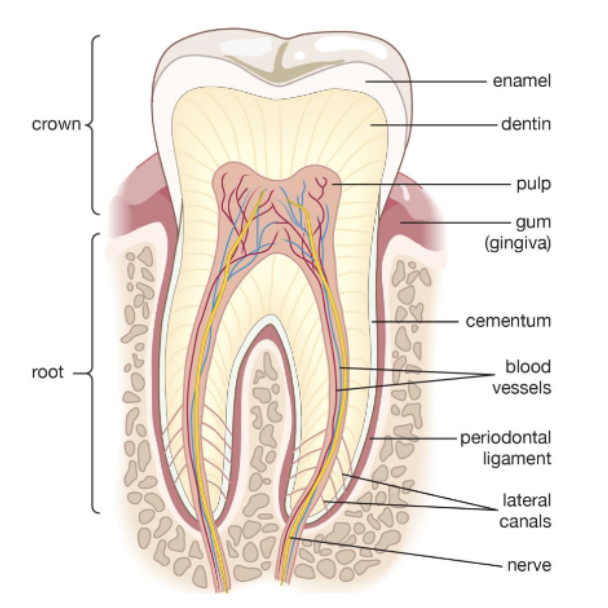
t/f: cementum is cellular
cementum can be cellular or acellular depending on location of cementum along the root
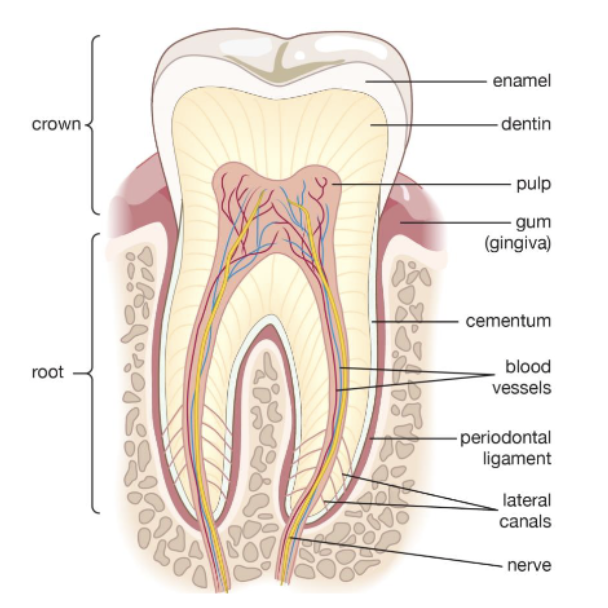
the bone into which the teeth are set. this structure forms to house the developing tooth buds and, once erupted, the roots of the teeth. Provides structural support for dentition
alveolar bone
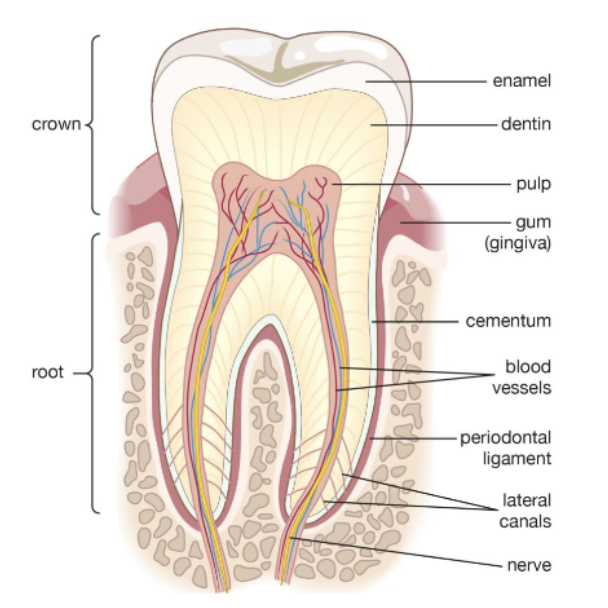
the mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes and surrounds the teeth
gingiva (gums)
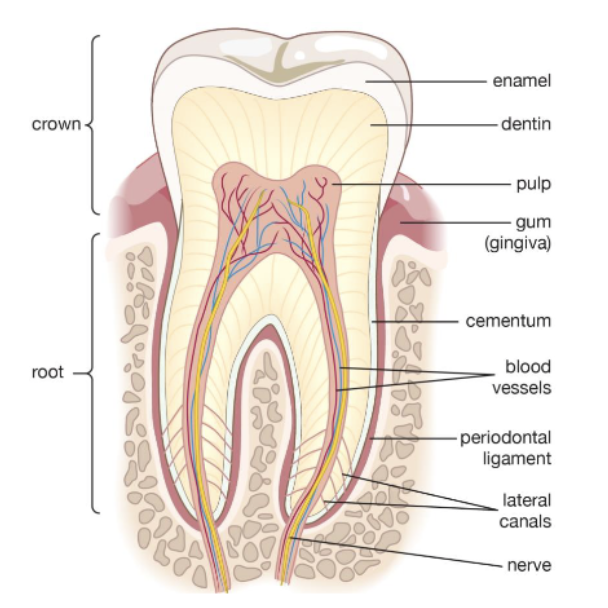
what is the hard, vital tissue that is cellular and forms the bulk of a tooth and is covered by enamel in the anatomical crown and by cementum in the anatomical root?
dentin
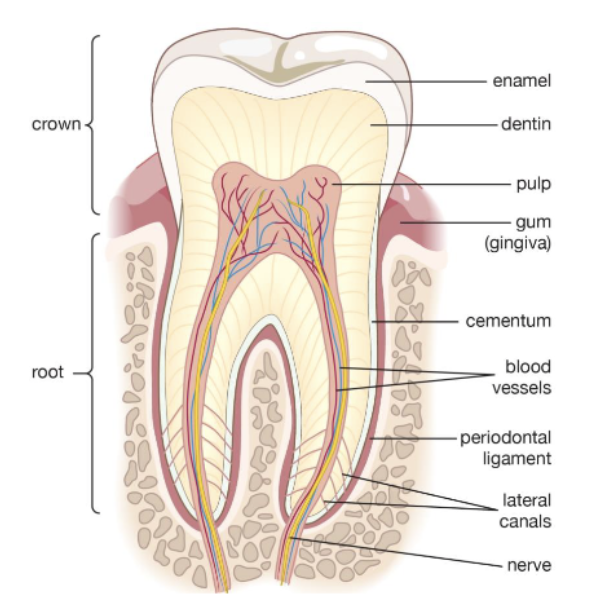
t/f enamel is vital and cellular
false. enamel is non-vital and acellular
96% inorganic materla and 4% organic/water
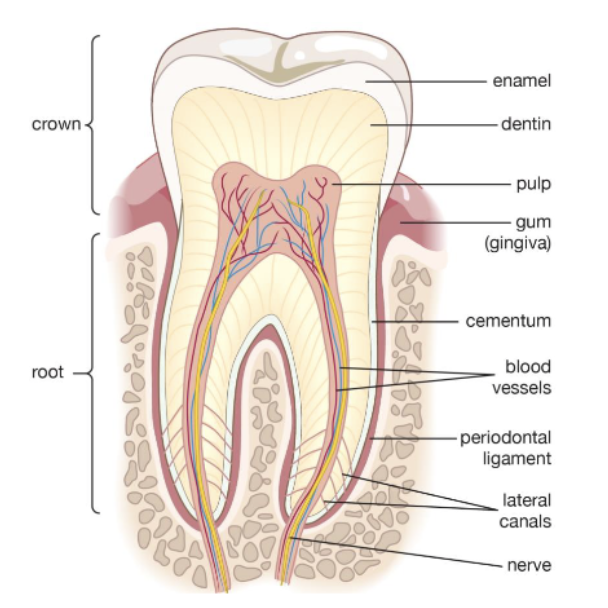
what percent of dentin is inorganic/organic material
70% inorganic (calcium, phosphate ions, etc.)
30% organic (+water)
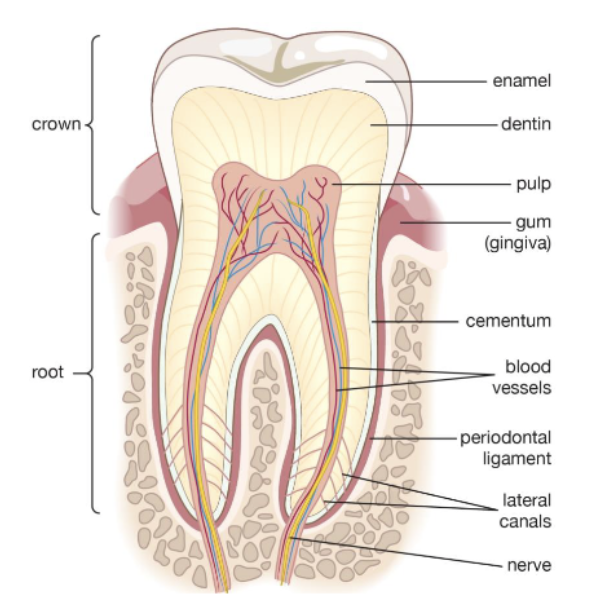
what is the periodontal ligament (PDL)? what is it’s function?
connective tissue fibers that attach cementum of tooth to the alveolar bone that surrounds it
it acts as a cushion to protect teeth while chewing.
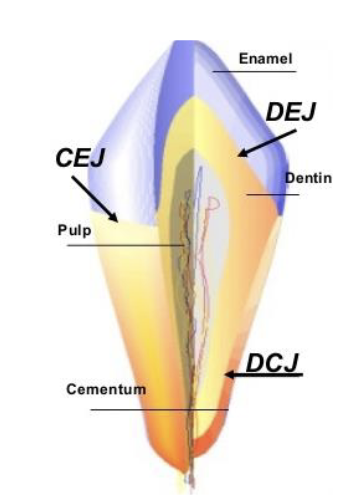
meeting of dentin and enamel within the anatomical crown of a tooth
dentinoenamel junction DEJ
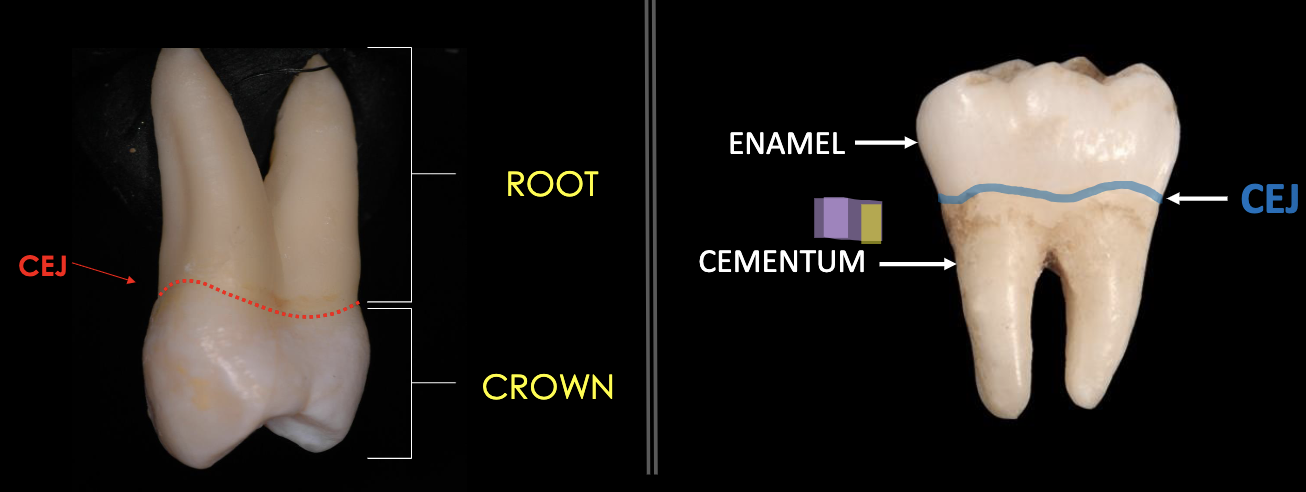
The junction line between the enamel layer and the cementum layer of the tooth.
Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ) also called the cervical line
cervical line is also called
cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
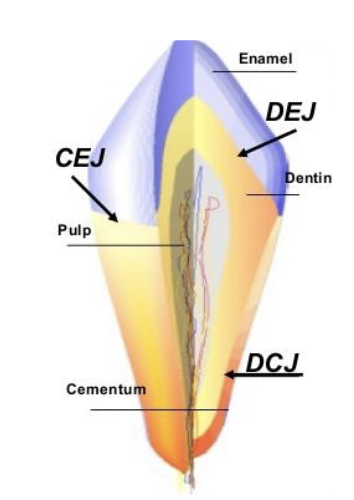
the junction of the dentin and cementum along the anatomical root structure
dentinocemental junction (DCJ)
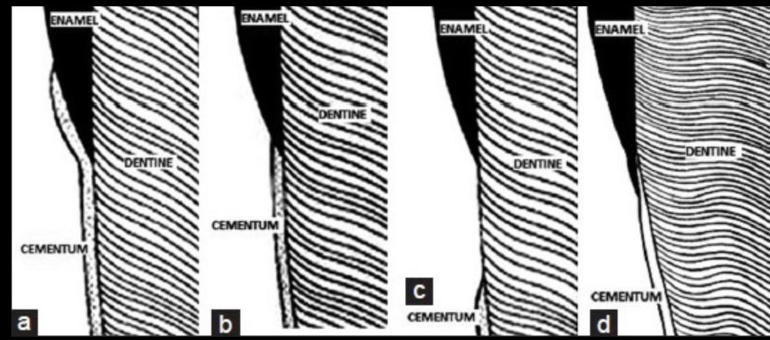
Type I CEJ
cementum overlapping enamel
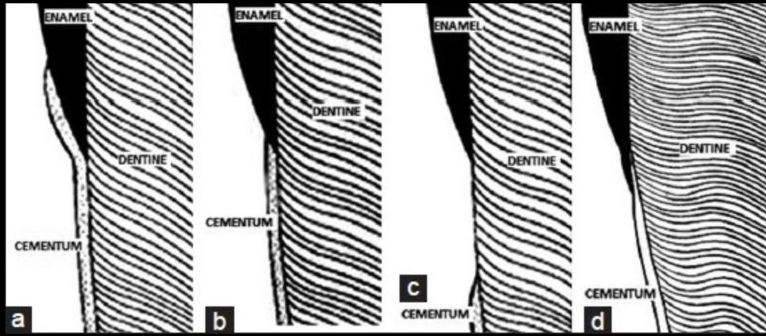
Type II CEJ
end-to-end (enamel meets cementum)
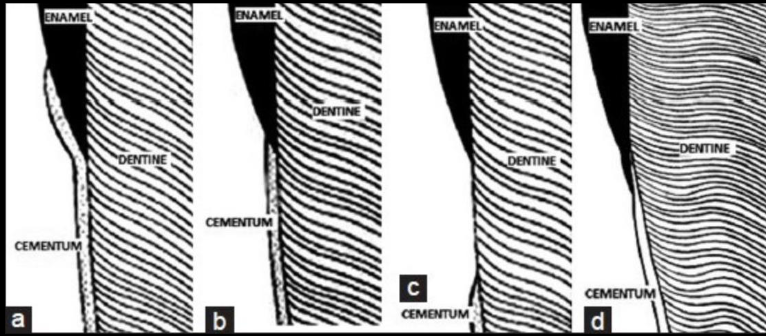
Type III CEJ
gap (absence of enamel meeting the cementum)
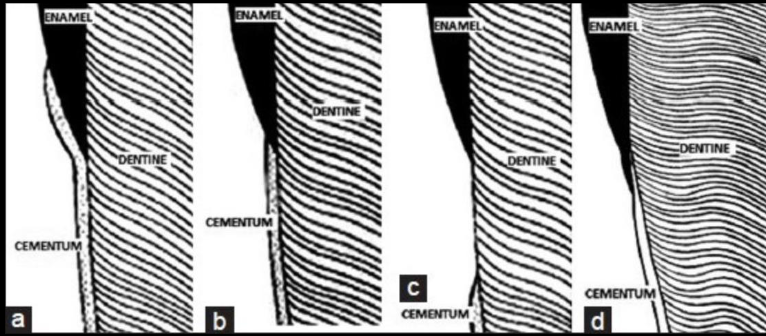
Type IV CEJ
enamel overlapping the cementum
odontoblasts secrete _________, have ________ cells, and protect the _______. Secondary dentin is secreted after ___________ to protect the pulp.
odontoblasts secrete dentin, have sensory cells, and protect the pulp. Secondary dentin is secreted after trauma to protect the pulp.
if a patient has pain without a clear cause (cavity), this could be what pattern of CEJ
Type I, where cementum overlaps the enamel
this is because the cementum is vital. if it is overlapping the enamel it isn't protected and therefore is exposed and causes pain.
Type III, where there is a gap between the enamel and the cementum. If the dentin is exposed it's vital so pain.
the mesial surface of a tooth has a _______ than distal
greater curvature of CEJ than distal
the more anterior a tooth, the ________ curvature of the CEJ
greater curvature of the CEJ
what has greater curvature of CEJ, maxillary or mandibular tooth (same tooth just on different part)
the CEJ curvature of maxillary teeth are higher than its counterpart on the mandibular arch
difference between anatomical and clinical root/crown
anatomical:
crown is covered by enamel. Does not matter if it has erupted or not.
root is covered by cementum.
clinical:
crown is above gingiva
root is below gingiva
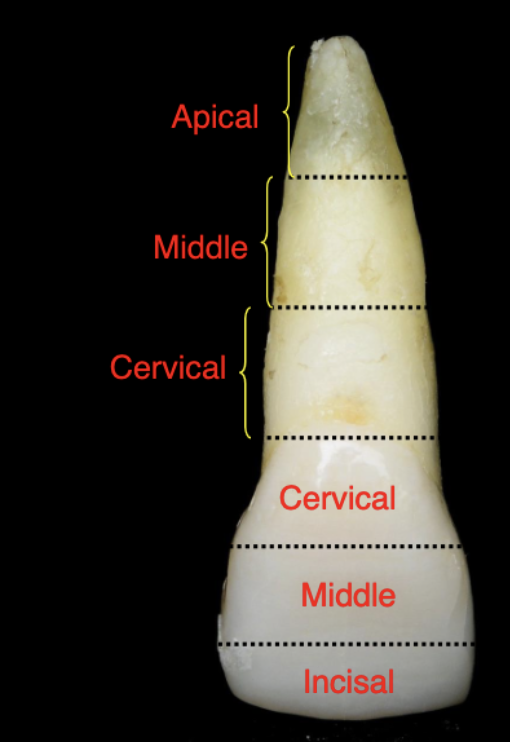
root thirds
cervical, middle, apical
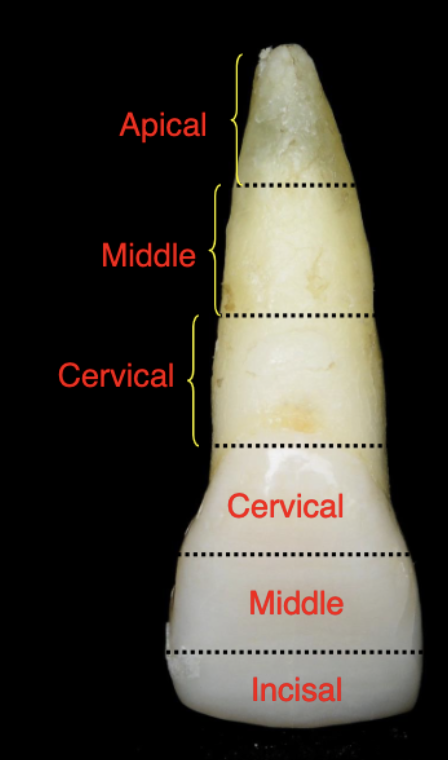
crown thirds
cervical, middle, and occlusal/incisal
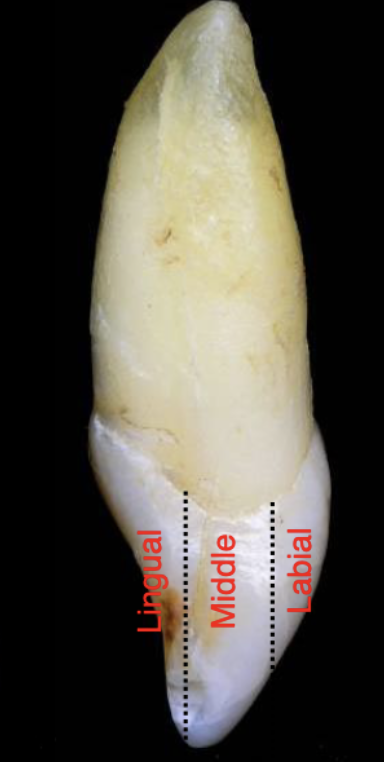
proximal tooth thirds
lingual, middle, labial/buccal
all teeth develop from
4 or 5 lobes
what do lobes form?
cusps and mamelons
one of the primary centers of formation in the development of a crown?
lobe
what is the height of contour?
widest part of the tooth
lobes are separated by
developmental grooves
HOC increases as you go in what direction?
HOC (height of contour) increases as you go distal in the mouth
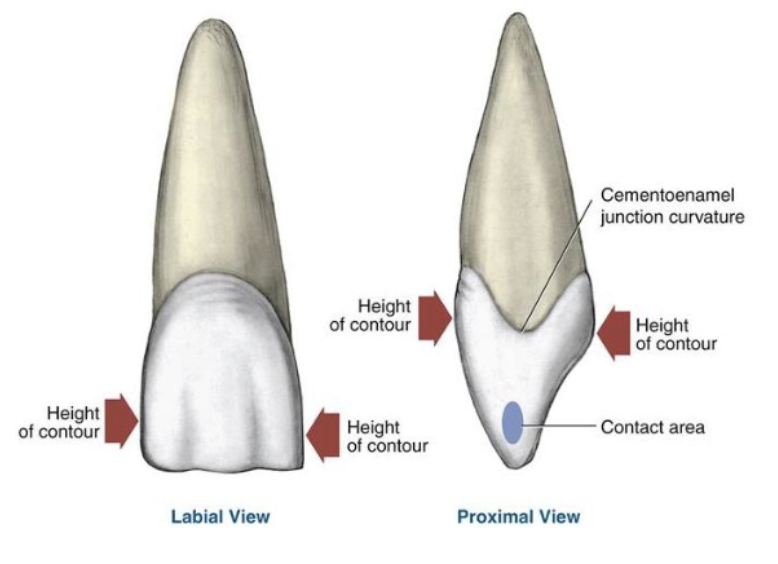
the mesial/distal HOC is seen from which view? what about facial/lingual HOC?
mesial/distal → facial/lingual view
facial/lingual → proximal
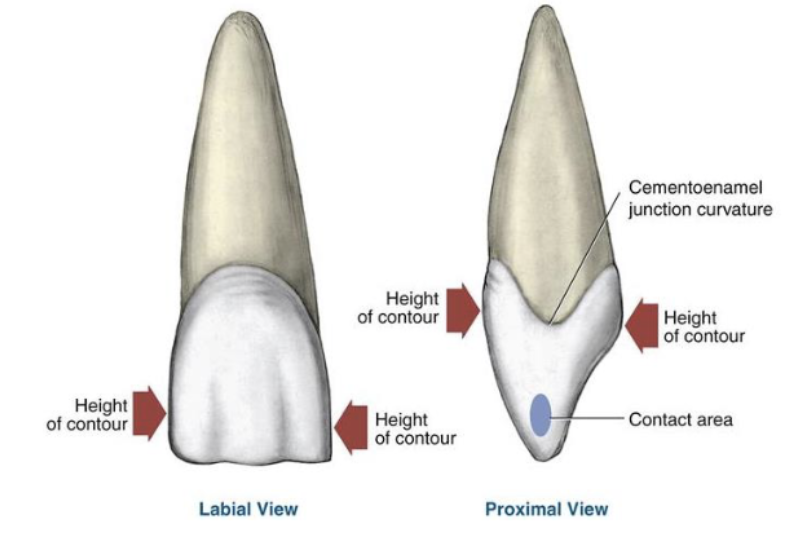
function of proximal contact areas
prevent food impaction between two teeth
all teeth have __ contact areas, except?
2
except the most distal tooth in each arch
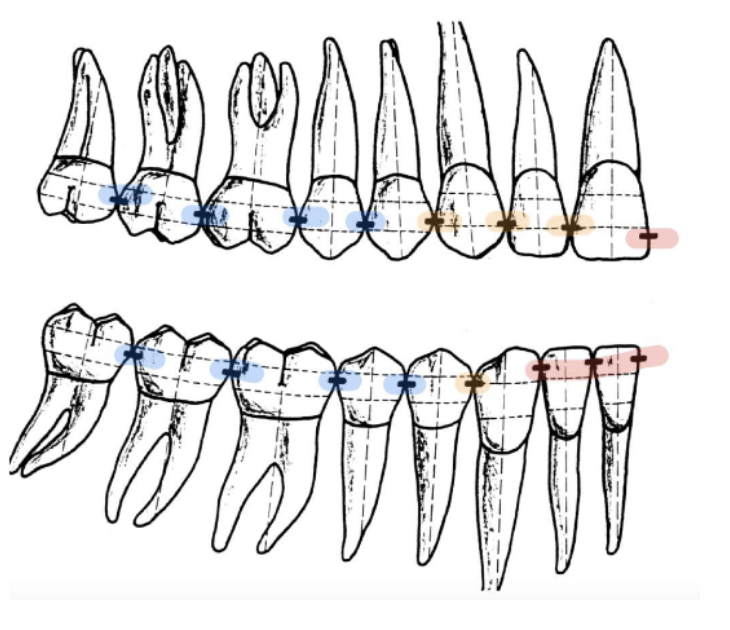
contact areas move more __________ from anterior to posterior
cervically
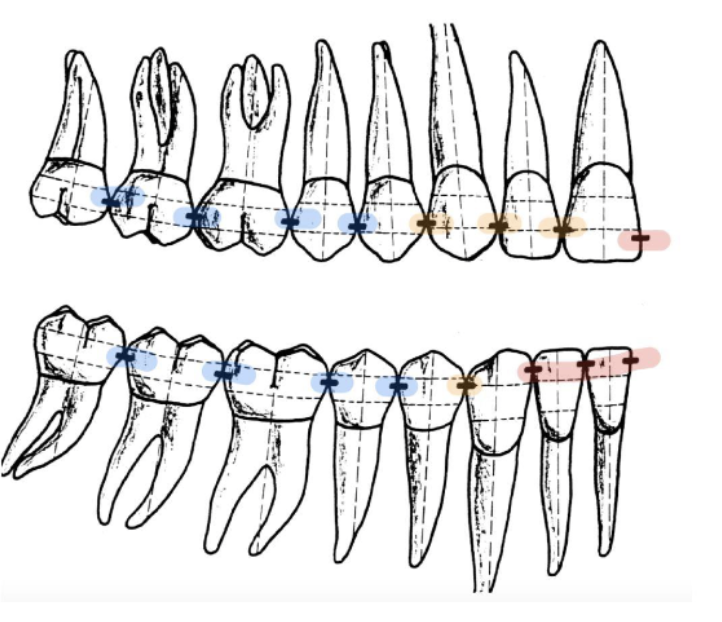
distal contact area is usually located more _________ than the mesial contact area
cervically
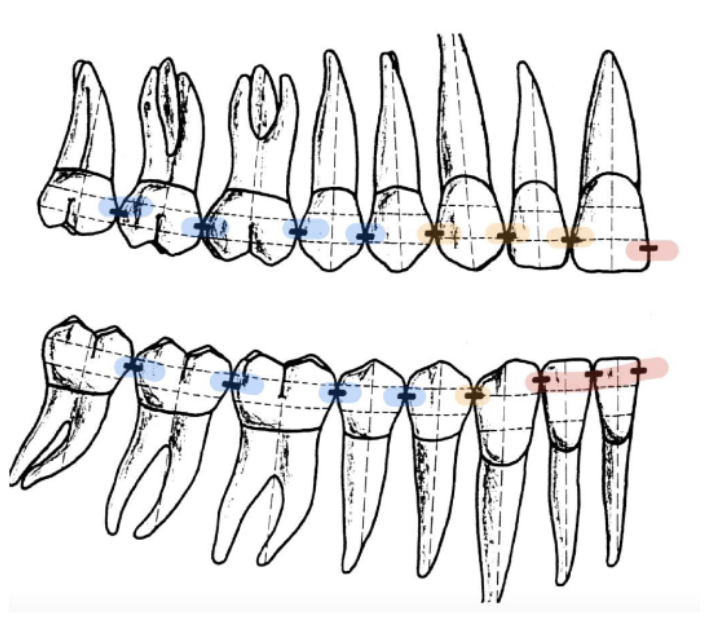
triangular spaces that surround the contact area of two adjacent teeth
(very important for self cleaning process of teeth)
embrasure spaces
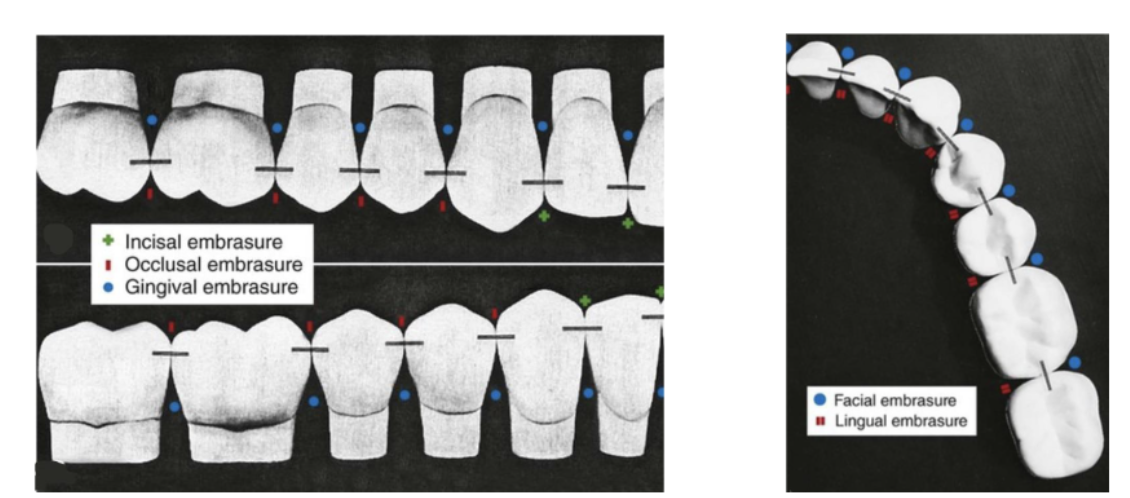
four types of embrasure spaces
incisal/occlusal
gingival (cervical)
facial (buccal)
lingual
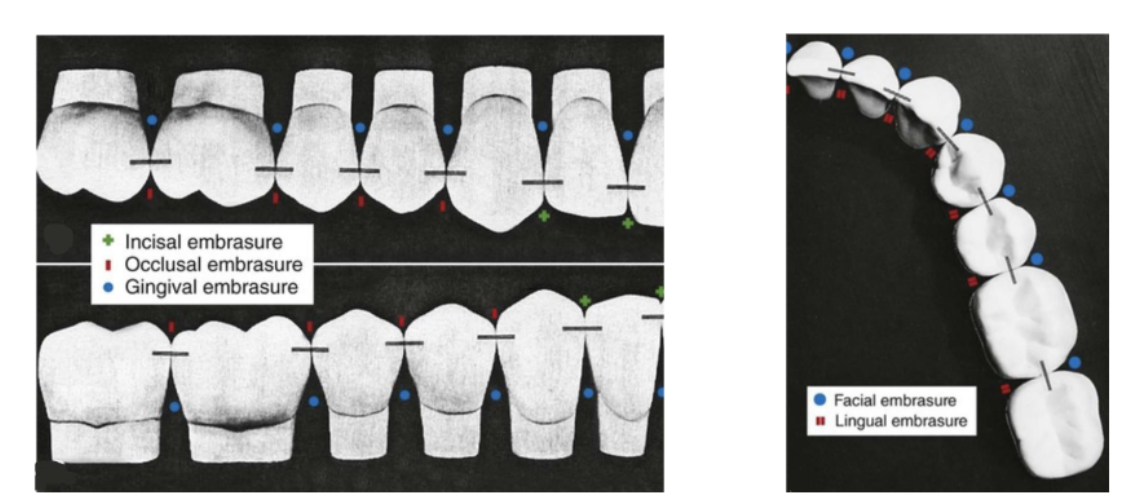
function of embrasure spaces
serves as a spillway for food during mastication
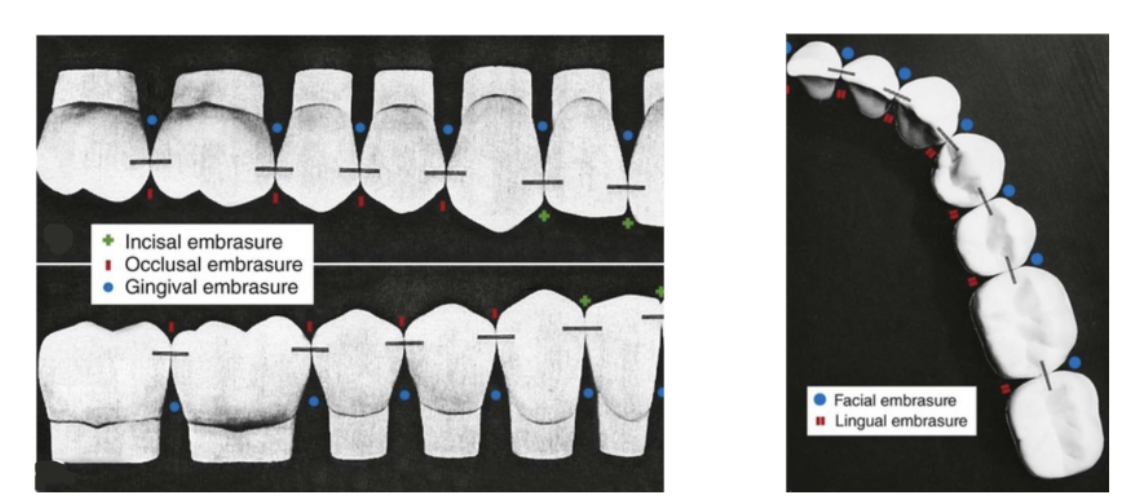
smallest incisal embrasure
between mandibular central incisors (1)
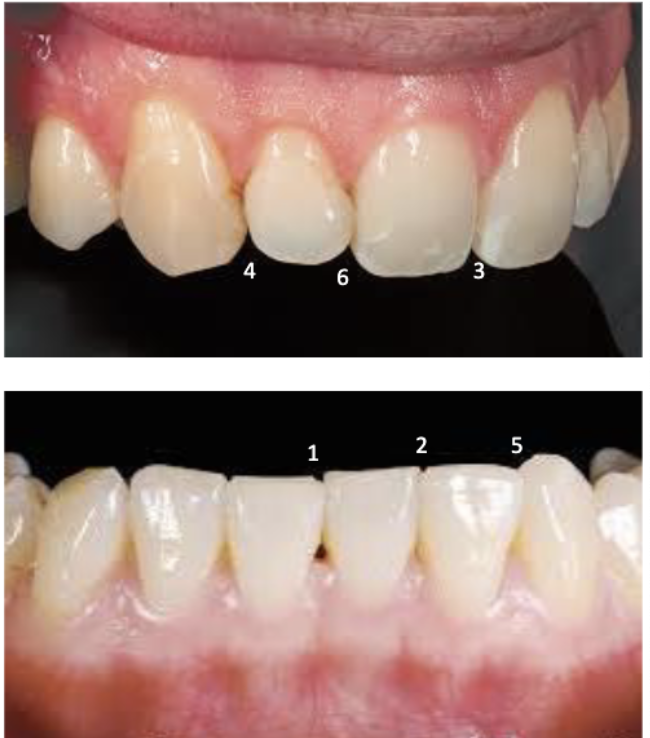
2nd smallest incisal embrasure
between mandibular central and lateral incisors (2)
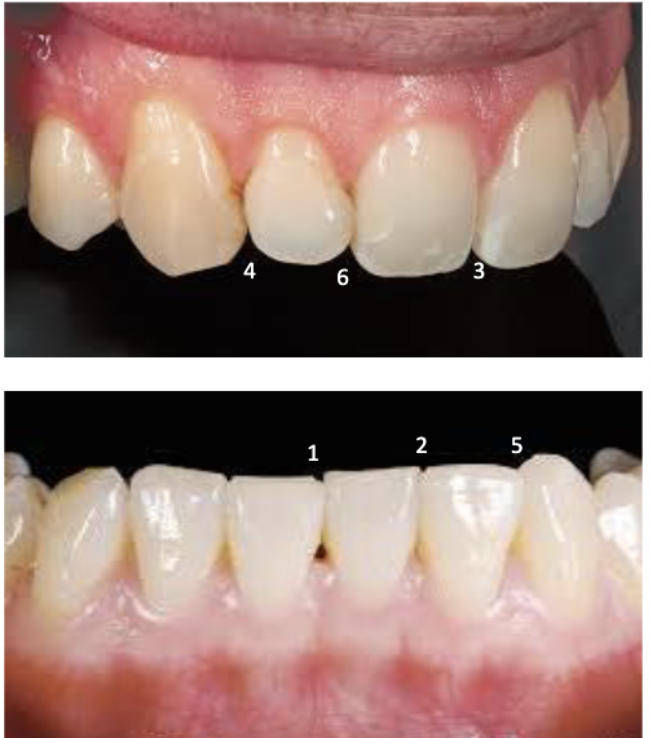
3rd smallest incisal embrasure
between maxillary central incisors (3)
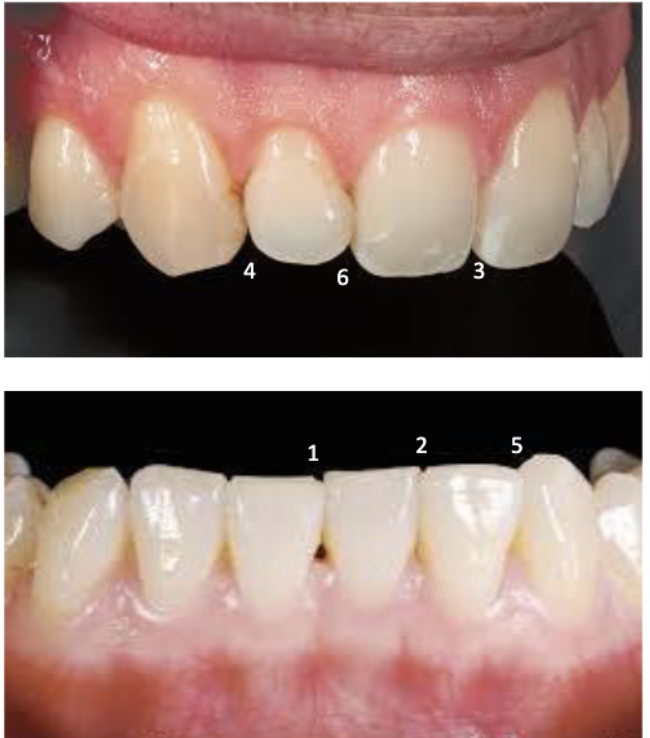
largest incisal embrasure
between maxillary lateral and maxillary canine (4)
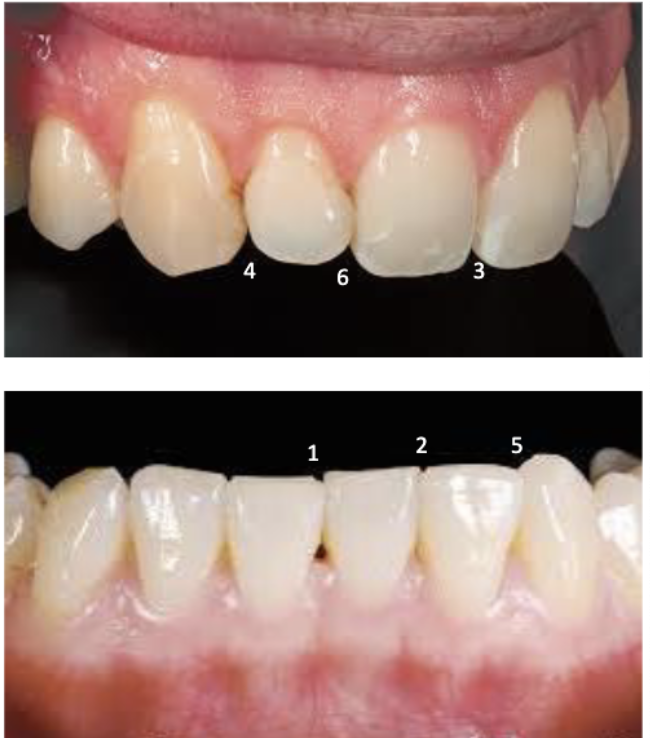
2nd largest incisal embrasure
between mandibular canine and mandibular lateral incisor (5)
#22 and #23
#26 and #27
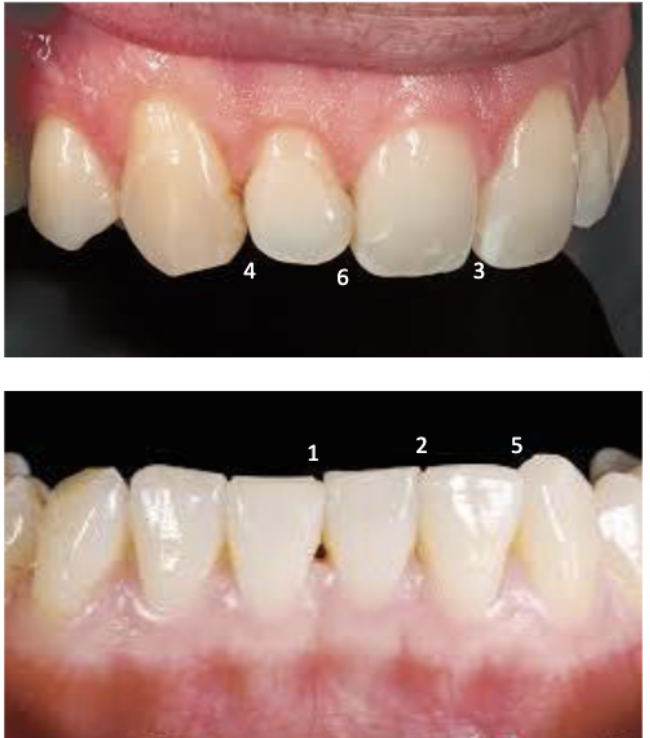
3rd largest incisal embrasure
between maxillary central incisor and maxillary lateral incisor (6)
#7 and #8
#9 and #10
shallow midline V-shaped depression from under the nose to the midline of the upper lip
philtrum
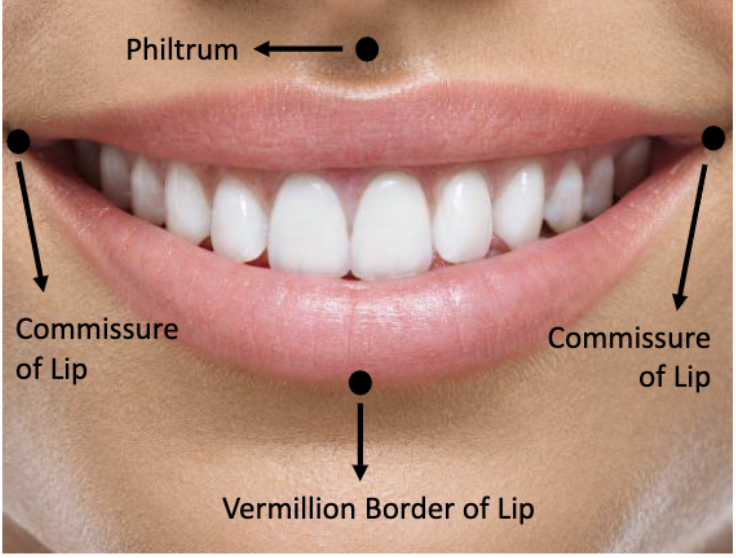
union between the upper and lower lip at the corner of the mouth
commissure of lips
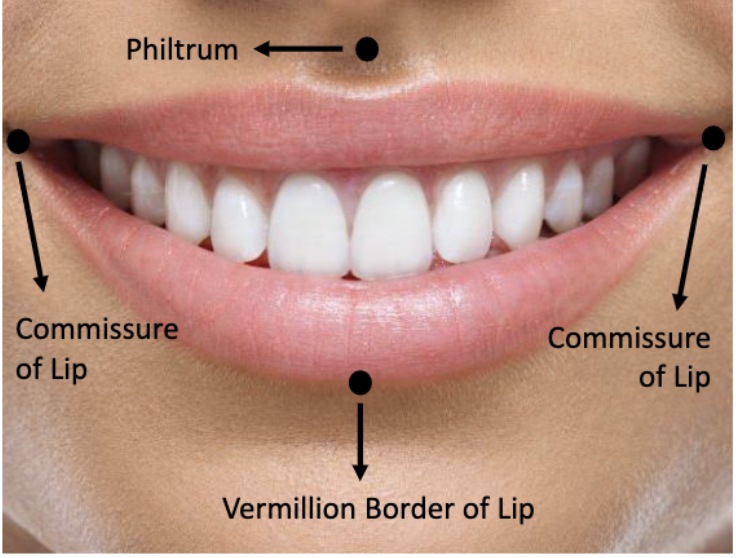
Transitional zone between the skin of the face and the mucous membrane of the oral cavity
aka midline of lower lip
Vermillion border of the lips
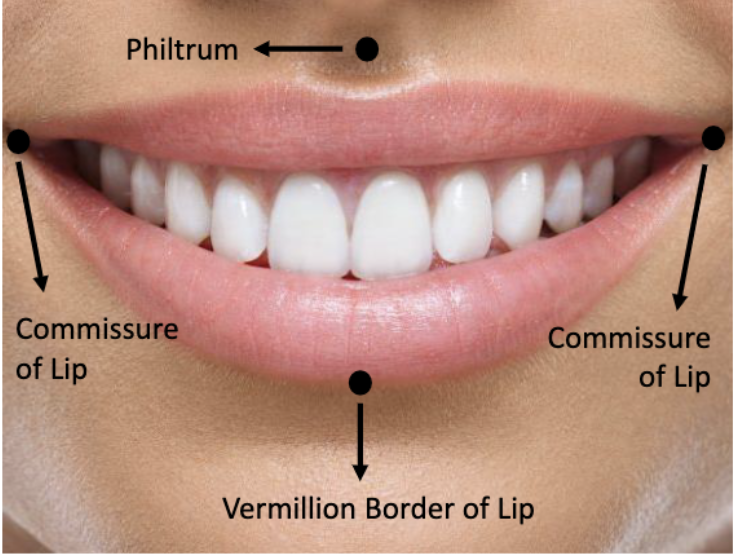
muscular attachment that gives stability to oral structures such as cheeks and lips
frenum (labial and lingual)
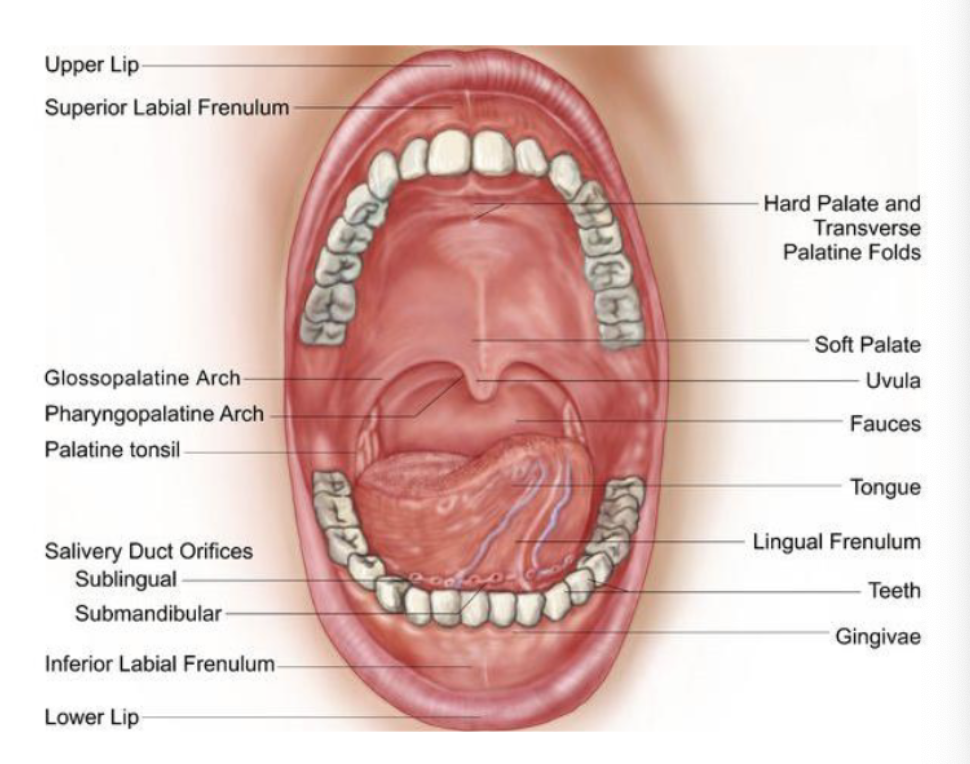
tissue that connects your gum to the top lip
labial frenulum
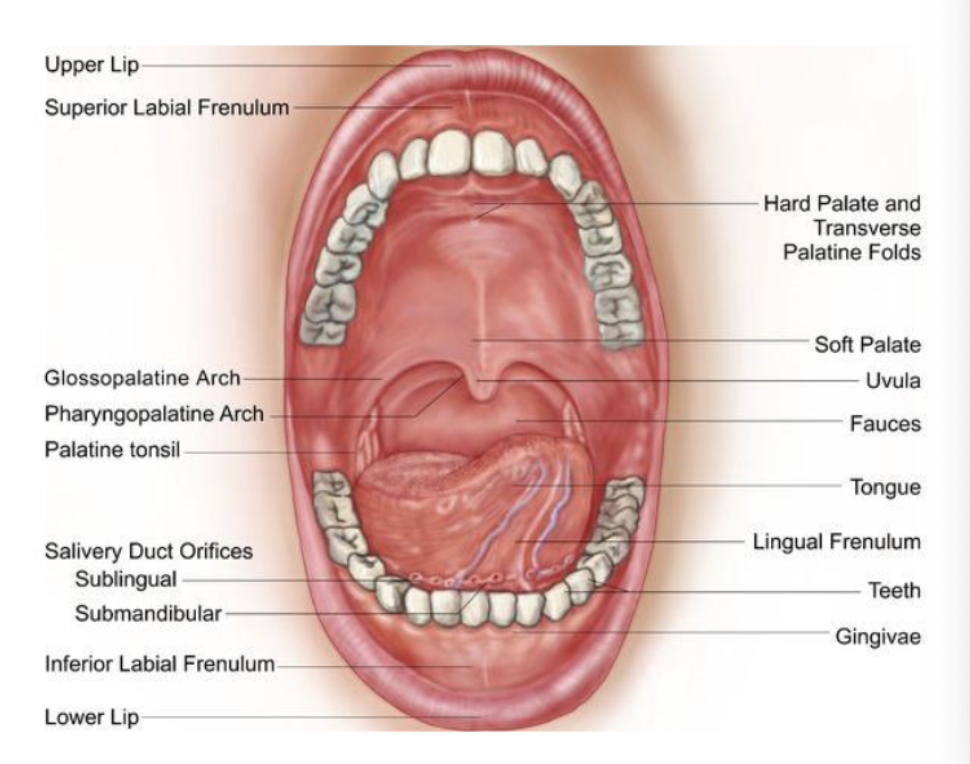
connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth
lingual frenum
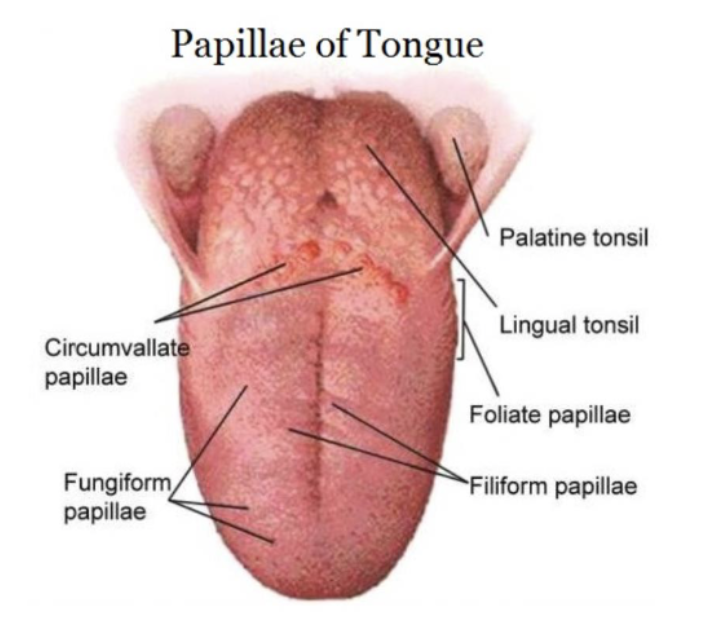
irregularly arranged folds or projections containing numerous taste buds found on lateral borders of tongue in the posterior 1/3
foliate papillae
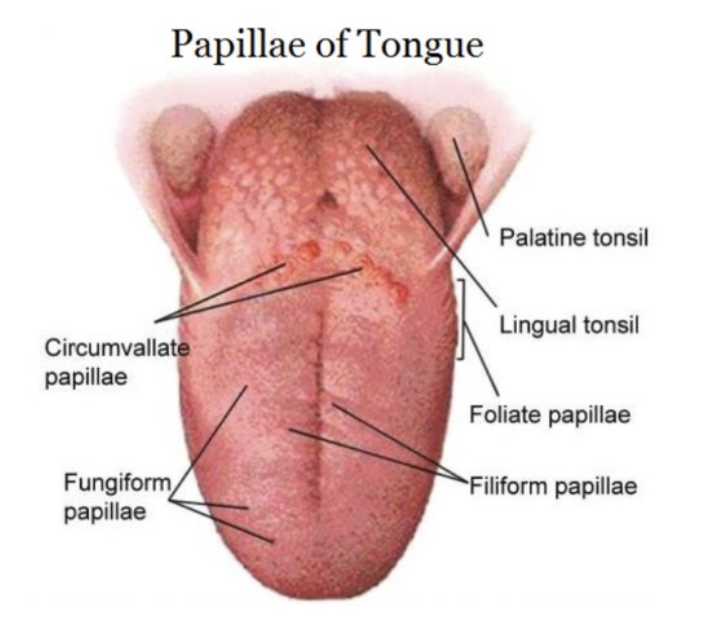
most numerous type of papillae, densely arranged, hair-like, highly keratinized papillae on dorsal surface of tongue (do NOT contain taste buds)
filiform papillae
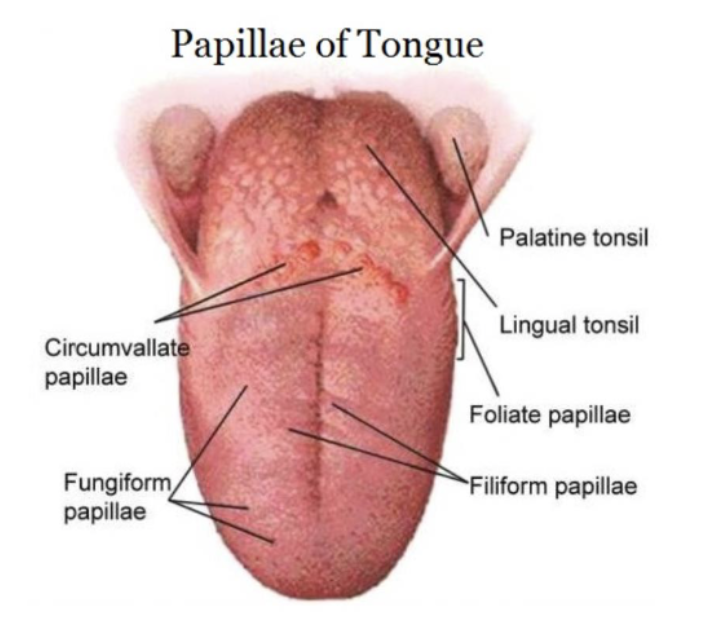
dorsum of tongue, contains 1-3 taste buds (taste buds on dorsal surface of papillae)
fungiform papillae
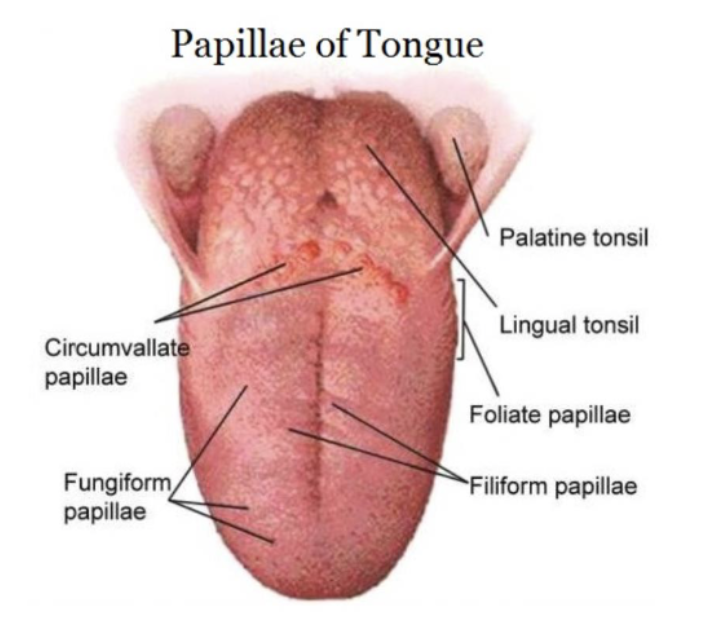
large, flat, round prominences on posterior of tongue, arranged in V-shaped row on dorsum of tongue (8-10 each containing many taste buds)
circumvallate (vallate) papillae
Describe the four patterns of CEJ. Which two cause the most sensitivity?
Type I - Cementum overlapping enamel *
Type II - Cementum and enamel meet end-to-endT
ype III - Gap (exposed dentin between cementum and enamel) *
Type IV - Enamel overlapping cementum
Which hard tissues of the tooth are vital?
dentin and cementum
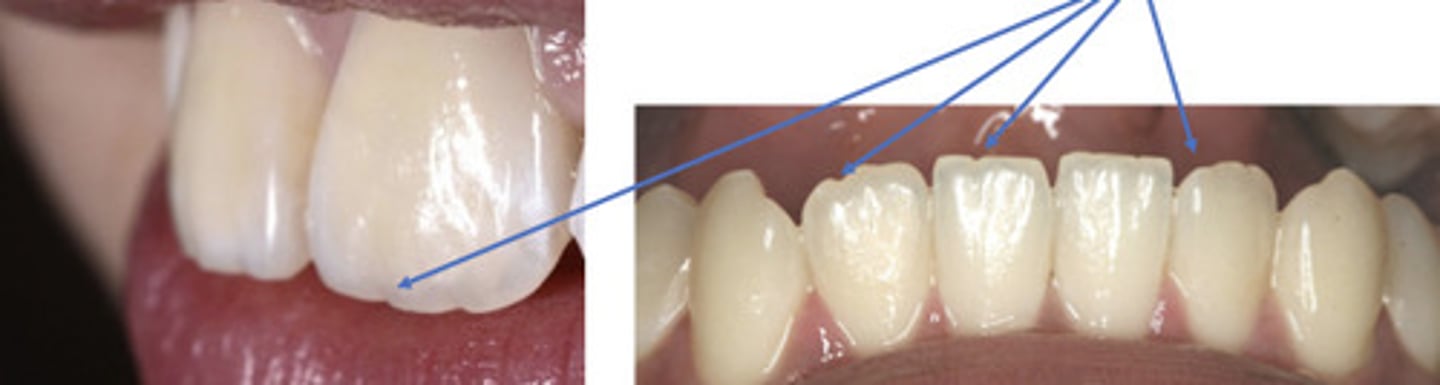
mamelon
Space between the cheeks and tissue covering the bone of the upper and lower jaw
vestibule
function of incisors in mastication
cutting and incising
canine function in mastication
cutting, tearing, piercing, holding (also called a cuspid)
premolars function in mastication
tearing, holding, grinding (also called bicuspids)
the pulp cavity is the entire central cavity of a tooth, which contains
pulp
pulp canal
pulp chamber
pulp horns

the cervical line seperates what…? it is a _______
anatomical crown and anatomical root
constant entity
the general area of the tooth where the cervical line is located is also called
the nock or cervix