8: Project Management
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Critical Path Method
A single, or deterministic, estimate for activity time was used
Nodes or circles
In critical path method (CPM), activities were represented as the __________
Project Evaluation and Review Technique
Probabilistic time estimates were employed
arcs, or arrowed lines, between two nodes, or circles
In project evaluation and review technique (PERT), activities were represented as ______________________
Critical Path Method
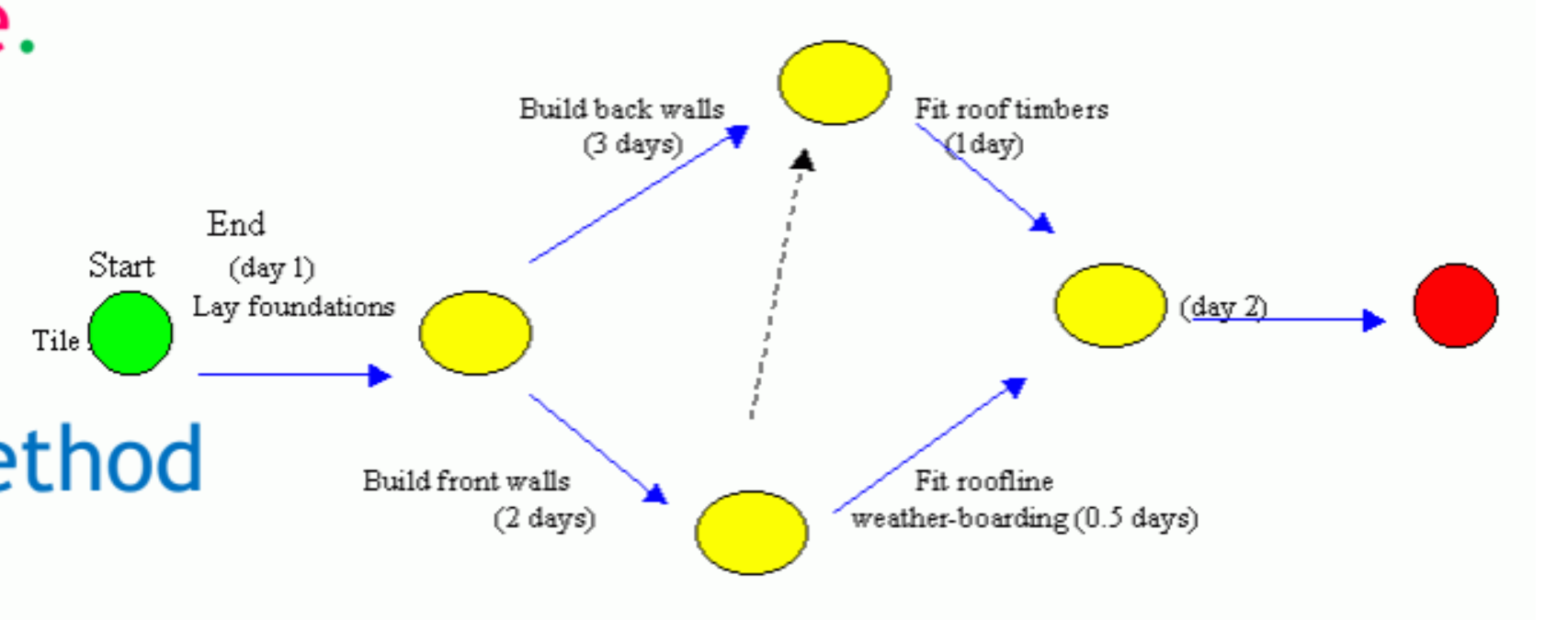
Project Evaluation and Review Technique
Management
is generally perceived to be concerned with the planning, organization, and control of an ongoing process or activity such as the production of a product or delivery of a service.
Project Management
reflects a commitment of resources and people to a typically important activity for a relatively short time frame, after which the management effort is dissolved.
Projects
do not have the continuity of supervision that is typical in the management of a production process.
Planning, Scheduling, Control
Project Management Process are composed of:
Planning
This is the foundational phase of a project where the groundwork is laid
Planning
Manager and Team
Scope
WBS (Work Breakdown Structure)
RAM (Responsibility Assignment Matrix)
ROI (Return on Investment)
Scheduling
This phase focuses on when and how the tasks will be executed.
Scheduling
Gantt Chart
CPM/PERT
Resources
Control
This phase ensures the project stays on track.
Control
Stay on Schedule
EVA (Earned Value Analysis)
Cost Control
Objectives, Project Scope, Contract Requirements, Schedules, Resources, Personnel, Control, Risk and Problem Analysis
The elements of project planning are:
Objectives
A detailed statement ofwhat is to be accomplished by the project, how it will achieve the company’s goals and meet the strategic plan, and an estimate of when it needs to be completed, the cost, and the return.
Project Scope
A discussion of:
how to approach the project
the technological and resource feasibility
the major tasks involved
a preliminary schedule;
it includes a justification of the project and what constitutes project success.
Contract Requirements
A general structure of managerial, reporting, and performance responsibilities including:
a detailed list of staff, suppliers, sub-contractors
managerial requirements and agreements, reporting requirements,
a projected organizational structure
Schedules
A list of all major events, tasks, and sub-schedules, from which a master schedule is developed.
Resources
The overall project budget for all resource requirements and procedures for budgetary control.
Personnel
Identification and recruitment of personnel required for the project team, including special skills and training.
Control
Procedures for monitoring and evaluating progress and performance, including schedules and cost.
Risk and Problem Analysis
Anticipation and assessment of uncertainties, problems, and potential difficulties that might increase the risk of project delays and/or failure and threaten project success.
Return on Investment
is a measure used to evaluate projects calculated by dividing the dollar gain minus the dollar cost of a project by the cost
Return on Investment
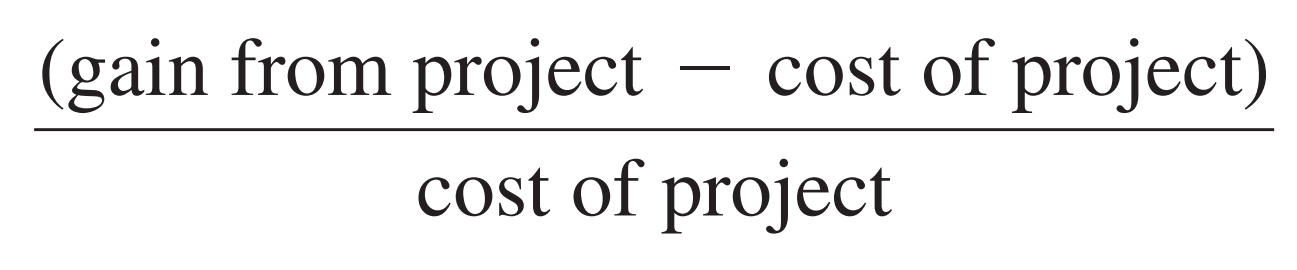
The project might not be undertaken
If a project does not have a positive ROI
If another project has a higher ROI
Return on Investment
a very popular metric for project planning because of its versatility and simplicity
Soft Returns
projects sometimes have benefits that cannot be measured in a tangible way with something like an ROI
Soft Returns
Example:
A project that has raising employee satisfaction as its goal can result in real benefits—increased productivity, improved quality, and lower costs—that are difficult to measure monetarily in the short run
Project teams
are made up of individuals from various areas and departments within a company.
Project Team
consists of a group of individuals selected from other areas in the organization, or from consultants outside the organization, because of their special skills, expertise, and experience related to the project activities
Project Team
includes various managers and staff personnel from specific areas related to the project.
and also workers, if their jobs are a function of the project activity
Project Team
Example as for the construction of a new loading dock facility at a plant might logically include:
truck drivers
forklift operators
dock workers
and staff personnel and managers from purchasing, shipping, receiving, and packaging
as well as engineers to assess vehicle flow, routes, and space considerations.
Assignment to a project team
is usually temporary and thus can have both positive and negative repercussions.
Project Manager
The most important member of a project team
Project Manager
is often under great pressure.
Uncertainty, Failure
The job of managing a project is subject to a great deal of __________ and the distinct possibility of ______.
Scope Statement
a document that provides a common understanding of a project
Scope Statement
includes a justification for the project that describes what factors have created a need within the company for the project.
includes an indication of what the expected results of the
project will be and what will constitute project success.
a list of the types of planning reports and documents that are part of the project management process
Statement of Work
is often prepared for individual team members, groups, departments, subcontractors, and suppliers in a large project
Statement of Work
It describes the work in sufficient detail so that the team member responsible for it knows what is required and whether he or she has sufficient resources to accomplish the work successfully and on time
Statement of Work
Some companies require that an _________ be part of an official contract with a supplier or subcontractor
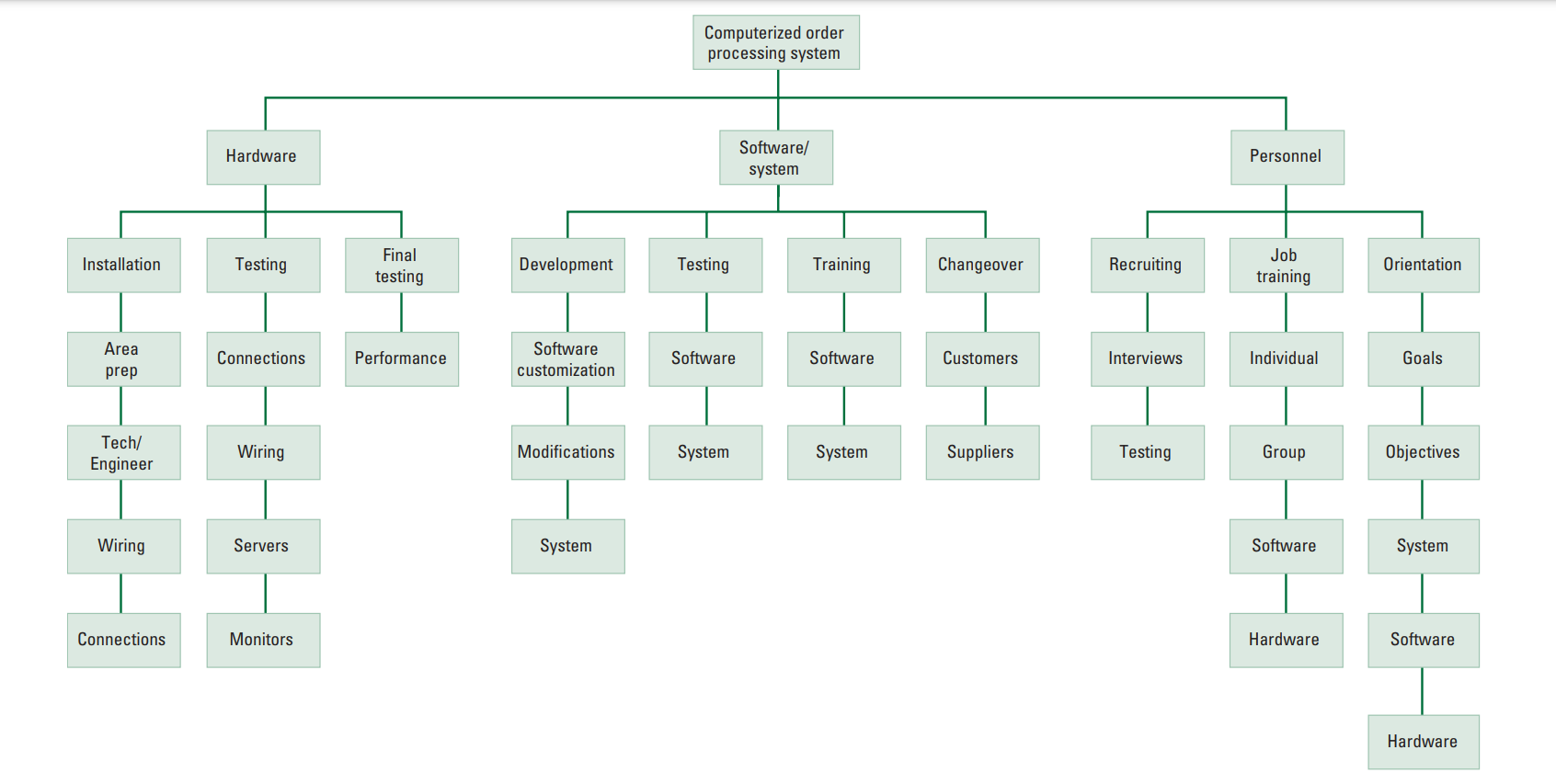
Work Breakdown Structure
an
organizational chart
that breaks down the
project into modules
for planning
Modules
are further broken down into activities, and, finally, into individual tasks
Work Breakdown Structure
Identifies activities, tasks, resource requirements and relationship between modules and activities
Helps avoid duplication of effort
Work Breakdown Structure
Basis for project development, management, schedule, resources and modifications
is most often in the form of a chart or a table
Top Down Process, Brainstorm Entire Project
These are approaches for WBS development
Top Down Process
An approch for WBS development wherein it start at the top and work your way down, asking “What components constitute this level?” until the WBS is developed in sufficient detail.
Brainstorm Entire Project
An approch for WBS development wherein it involves writing down each item on a sticky note and then organizing the sticky notes into a WBS.
The upper levels of the WBS tend to contain the summary activities, major components or functional areas involved in the project that indicate what is to be done.
The lower levels tend to describe the detailed work activities of the project within the major components or modules. They typically indicate how things are done.
Work Breakdown Structure
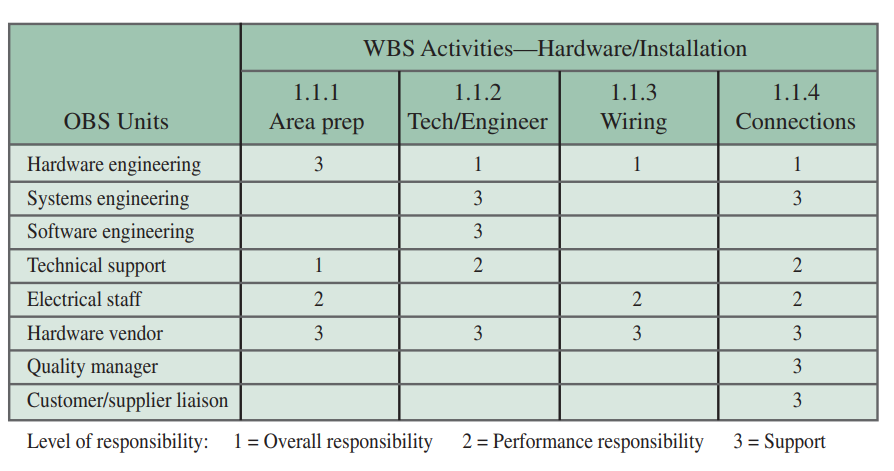
Responsibility Assignment Matrix
is a table or chart that shows who is responsible for project work
Organizational Breakdown Structure
is a table or a chart showing which organizational units are responsible for work items
Organizational Breakdown Structure
It is used in Responsibility Assignment Matrix
Responsibility Assignment Matrix
shows who is responsible for doing the necessary work in the project
Responsibility Assignment Matrix
Project manager assigns work elements to organizational units, departments, groups, individuals or subcontractors
Responsibility Assignment Matrix
Project Scheduling
is typically the most critical element in the project management process, especially during the implementation phase (i.e., the actual project work), and it is the source of most conflict and problems.
Project Scheduling
Example:
If a stadium is supposed to be finished in time for the first game of the season and it’s not, there will be a lot of angry ticket holders
If a school building is not completed by the time the school year starts, there will be a lot of angry parents
If a shopping mall is not completed on time, there will be a lot of angry tenants
If a new product is not completed by the scheduled launch date, millions of dollars can be lost
If a new military weapon is not completed on time, it could affect national security.
Project Scheduling
One reason is that frequently the single most important criterion for the success of a project is that it be finished on time.
Time is an absolute with little flexibility; you can spend less money or use fewer people, but you cannot slow down or stop the passage of time.
Define the activities, Sequence the activities, Estimate the time, Develop the schedule
Steps in Project Scheduling
1st Step in Project Scheduling
define the activities that must be performed to complete the project
2nd Step in Project Scheduling
sequence the activities in the order in which they must be completed
3rd Step in Project Scheduling
estimate the time required to complete each activity
4th Step in Project Scheduling
develop the schedule based on the sequencing and time estimates of the activities
Gantt Chart
a traditional management technique for scheduling and planning small projects that have relatively few activities and precedence relationships.
Gantt Chart
a graph or bar chart with a bar for each project activity that shows the passage of time.
Henry Gantt, 1914
Gantt Chart (also called a bar chart) was developed by _________, a pioneer in field of industrial engineering at the artillery ammunition shops of the Frankford Arsenal in _____.
Gantt Chart
the direct precursor of the CPM/PERT technique
Gantt Chart
provides a visual display of a project schedule, indicating when activities are scheduled to start and to finish and where extra time is available and activities can be delayed
Gantt Chart
indicates the precedence relationships between activities; however, these relationships are not always easily discernible.
limits the chart’s use to smaller projects with relatively few activities.
Slack
is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project.
Project Control
is the process of making sure a project progresses toward successful completion.
Project Control
It requires that the project be monitored and progress measured so that any deviations from the project plan, and particularly the project schedule, are minimized.
Project Control
If the project is found to be deviating from the plan (i.e., it is not on schedule, cost overruns are occurring, activity results are not as expected), corrective action must be taken.
Time Management
is the process of making sure a project schedule does not slip and that a project is on time
Time Management
This requires monitoring of individual activity schedules and frequent updates.
If the schedule is being delayed to an extent that jeopardizes the project success, it may be necessary for the project manager to shift resources to accelerate critical activities.
Time-cost Trade-off
Some activities may have slack time, so resources can be shifted from them to activities that are not on schedule
Cost Management
is often closely tied to time management because of the time–cost trade-off occurrences
Cost Management
If the schedule is delayed, costs tend to go up in order to get the project back on schedule.
Cost Management
Also, as a project progresses, some cost estimates may prove to be unrealistic or erroneous.
Therefore, it may be necessary to revise cost estimates and develop budget updates.
If cost overruns are excessive, corrective actions must be taken.
Performance Management
is the process of monitoring a project and developing timed (i.e., daily, weekly, monthly) status reports to make sure that goals are being met and the plan is being followed.
Performance Management
It compares planned target dates for events, milestones, and work completion with dates actually achieved to determine whether the project is on schedule or behind schedule
Earned Value Analysis
a specific system for performance management. Activities “earn value” as they are completed.
Earned Value Analysis
is a recognized standard procedure for numerically measuring a project’s progress, forecasting its completion date and final cost, and providing measures of schedule and budget variation as activities are completed
Schedule Variance
compares the work performed during a time period with the work that was scheduled to be performed
Negative Schedule Variance
means the project is behind schedule.
Cost Variance
is the budgeted cost of work performed minus the actual cost of the work
Negative Cost Variance
means the project is over budget
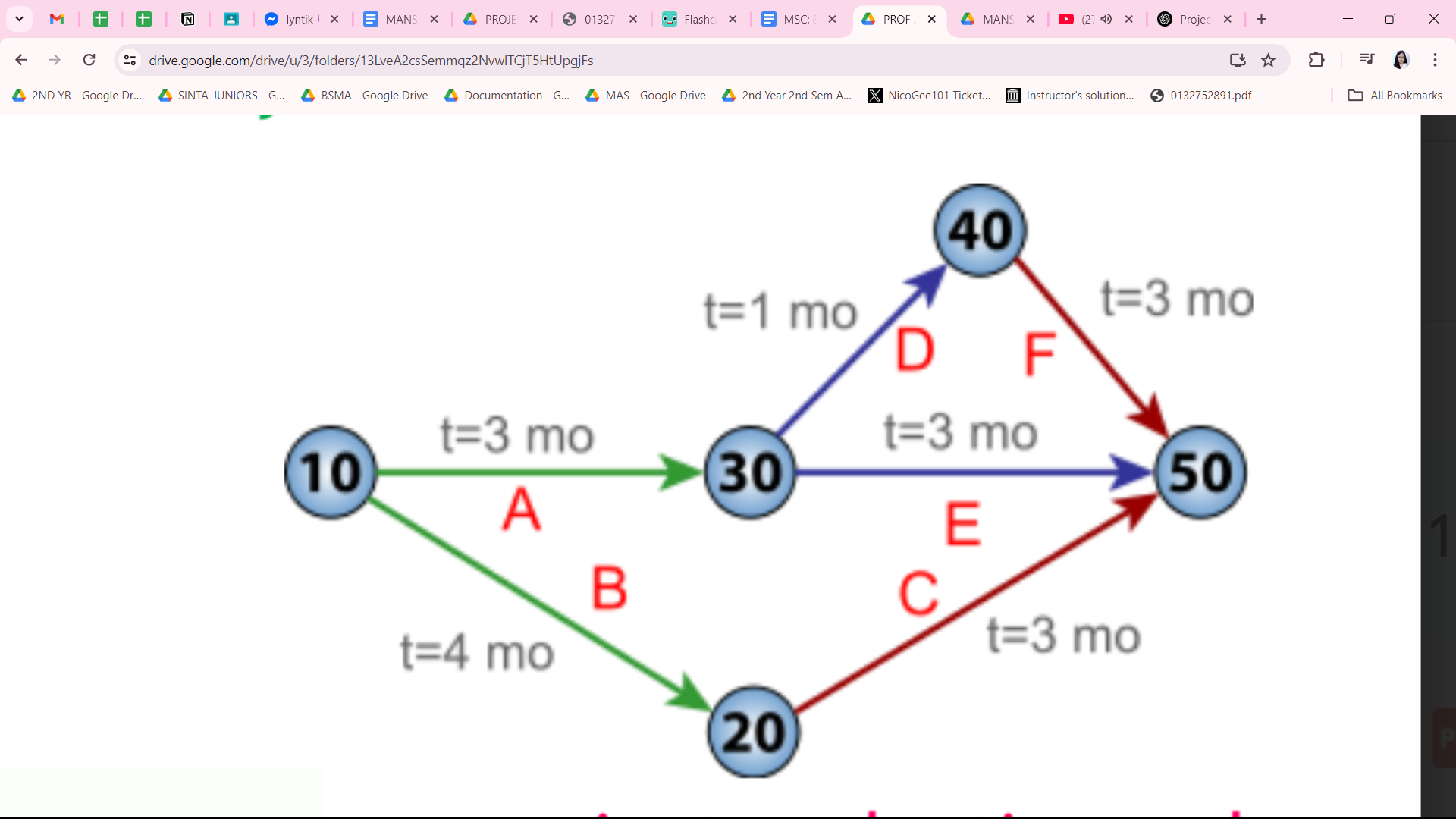
Critical Path Method
used a single activity time estimate, and in the network, activities were nodes
Project Evaluation and Review Technique
used multiple activity time estimates, and in the network, activities were lines between nodes.