Genetics - Exam 3
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
2 mechanisms of inheritance
DNA replication
Cell Division
2 types of cell division
Mitosis
Meiosis
What is reproduction?
To produce more individual cells or organisms
What is sex?
To produce new combo of alleles, recombination, allowing for genetic diversity
Examples of asexual reproduction
Binary fission in bacteria
Mitosis in eukaryotic organisms
Examples of sexual reproduction
Meiosis and union of gametes (sperm and ova)
In order for a population to adapt to a new environment, _______ in our traits must be present
Variation
What are the 2 origins of genetic diversity?
Mutation
Sex
What are the basics of DNA replication?
Each strand serves as a template
Base pairing rules allow replication
What is the team of DNA replication?
Helicase
Topoisomerase
SSB’s
DNA polymerase
Primase
The function of helicase is to…
Unwinds DNA
The function of topoisomerase is to…
Release mechanical stress of unwinding
The function of SSB’s are to…
Keep DNA single stranded
What does SSB stand for?
Single-stranded binding proteins
The function of DNA polymerase is to…
Add base pairs to template strand
What are the 2 restrictions of DNA polymerase?
Only can occur in 5’to 3’ direction
Primer is needed to begin synthesis
The function of a primase is to…
Make primers made of RNA
DNA replication is semi-__________ (daughter strand)
Conservative
What does it mean when we say DNA replication is semi-conservative?
Daughter molecules are half old, half new
Daughter molecules are half old, half new. This means…
One strand is used as a template to make a new one, which is then retained in the daughter molecule
DNA replication is semi-________ (5’ to 3’)
Discontinuous
DNA replication is semi-discontinuous, meaning that…
one strand is made continuously while the other is made in short, discontinuous fragments.
Leading strand is made…
continuously in the same direction as the replication fork moves.
Lagging strand is made…
discontinuously in short fragments (called Okazaki fragments) in the opposite direction of the fork movement.
Short fragments of the lagging strand are called ________ ________
Okazaki fragments
DNA ligase is an enzyme, which function is to…
Link DNA by phosphodiester bonds
DNA replication is bi-_______
Directional
DNA replication is bi-directional, meaning…
It proceeds outward from the origin in 2 opposite directions
Replication forks
Regions that form when the double-helix unwinds during replication
The problem with linear DNA is…
Incomplete replication of telomeres
What solves the problem with linear DNA?
Telomerase
Telomeres get shorter and shorter with each _________
replication
Telomerase function is to…
facilitate replication of telomeres
Telomerase are turned ____ in most body cells
Off
Telomerase are turned ___ in gamete producing cells
On
What is happening during interphase?
Cell not dividing
Working its ass off
3 stages of interphase
G1
S
G2
What happens during G1 of Interphase?
Cell growth
What happens during S of interphase?
Replication
What happens during G2 of interphase?
Further prep for cell division
2 types of cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis
What is the goal of mitosis?
Produce 2 genetically identical daughter cells from one parent
What is the role of mitosis in unicellular organisms?
Asexual reproduction
What is the role of mitosis in multicellular organisms?
(HINT: 3 R’s)
Repair, regeneration, reproduction?
______ and ______ cells can undergo mitosis
Haploid and Diploid
Steps of mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
What occurs during prophase?
Condensing of chromosomes
What occurs during Metaphase?
Chromosomes line up
What occurs during anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate
What occurs during Telophase?
New nuclei form
_____ ______ hold sister chromatids from centromeres
Spindle fibers
Between Interphase and Prophase, what occurs?
Condensation
Between Anaphase and Telophase, what happens?
Cell divides
Meiosis is…
Separation of homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids
What is the main goal of meiosis?
Create genetic diversity
Only _____ cells can undergo meiosis
Diploid (or higher ploidy)
There must be at least _ sets of chromosomes for meiosis to occur
2
What occurs during meiosis 1?
Homologous pairs separate
Tetrads align
Tetrads are…
pairs of homologous chromosomes
What occurs during prophase 1?
Synaptonemal complexes form tetrads
Crossing over occurs
Condensation occurs
Chiasmata can be seen
What is a chiasmata?
Visual evidence that crossing over has occurred
What happens during metaphase 1?
Tetrads align
What happens during anaphase 1?
homologous pairs separate
Equal segregation
Independent assortment
What is equal segregation?
homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles.
Each daughter cell gets one chromosome from each pair, keeping the genetic material balanced.
What is Independent assortment?
Random alignment and separation of genes on different chromosomes
In meiosis 1, how are resulting cells different from original cell?
½ the number or chromosome sets
½ the amount of DNA
In meiosis 2, how are resulting cells different from original cell?
Same number or chromosome sets
½ the amount of DNA
What is Crossing over?
homologous chromosomes exchange DNA segments at chiasmata.
Each gamete will be unique because of ______ _______ and ______ _______
Independent assortment and Crossing over
Meiosis produces…
Gametes and spores
Gametic meiosis is a ________ dominant life cycle
diploid
Who uses gametic meiosis?
Animals and some protists
Zygotic meiosis is a _____ dominant life cycle
haploid
What uses zygotic meiosis?
Fungi and some protists
Sporic meiosis is _________ __ _______ life cycle
Alternation of generations
What uses sporic meiosis?
Plants
Results of equal segregation are ___ between sexes
Same
Agouti fur
Strand of hair containing multiple colors
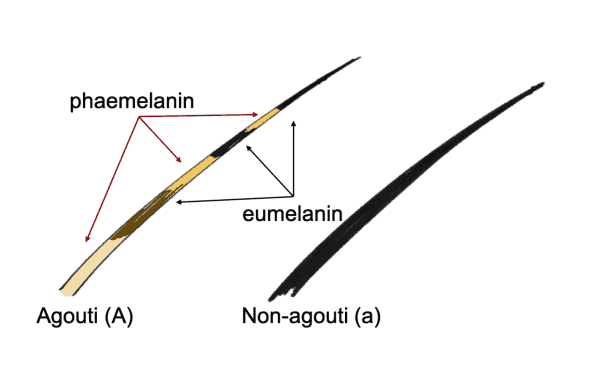
The likelihood of 2 or more events is found by _______ the probabilities
Multiplying
The likelihood of 1 our of 2 or more events is found by _______ the probabilities
Adding