JC Science - earth and space
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:34 PM on 5/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
The Universe
All of space and everything in it
2
New cards
the Universe includes:
-Stars
-Planets
-Satellites
-Moons
-Asteroids
-Comets
-Planets
-Satellites
-Moons
-Asteroids
-Comets
3
New cards
Star
-A big ball of gas that gives off light + heat
-Hot star: blue
-Cool star: red
-Hot star: blue
-Cool star: red
4
New cards
SUn
-A star
-Our closest star which is why it looks different
-Yellow star
-Our closest star which is why it looks different
-Yellow star
5
New cards
Sun temperature
Surface: 5500
Inside: 15,000,000
Inside: 15,000,000
6
New cards
Galaxy
A collection of millions of stars
7
New cards
Solar systems
A solar system is made up of a star + all the objects that orbit around it
8
New cards
Planets
A large round space object that circles a star in an orbit
9
New cards
Atmosphere
Layer of gas around a planet
10
New cards
Dwarf planet
A round space object that circles a star but has not cleared its own orbit
11
New cards
Satellite
An object that orbits a larger object or planet
12
New cards
Moon
A naturally occurring satellite
13
New cards
Man made satellite
Made by humans
14
New cards
Comet
-Huge balls composed of frozen gases, ice, rock + dust
-Glows + produces a tail when the icy layer burns
-Orbits the sun
-Glows + produces a tail when the icy layer burns
-Orbits the sun
15
New cards
Asteroids
-Small rocky object that orbits the sun
-Found in the Asteroid Belt between Mars + Jupiter
-Found in the Asteroid Belt between Mars + Jupiter
16
New cards
Meteor
A piece of burning rocky space debris entering the earths atmosphere
17
New cards
Meteorite
Meteors that successfully pass through earths atmosphere + collide with earth
18
New cards
Gravity
-A force that pulls objects towards each other
-The bigger the object, the bigger the gravitational pull
-The bigger the object, the bigger the gravitational pull
19
New cards
Gravitational force
When scientists compare gravity of different planets, they refer to the force of gravity on the surface of the planet
20
New cards
Big Bang Theory
It suggests the universe began with an explosion that allowed all of the universes known matter + energy + space + time to form
21
New cards
Big bang theory diagram

22
New cards
Planet rhyme
My
Very
Educated
Mother
Just
Served
Us
Nandos
Very
Educated
Mother
Just
Served
Us
Nandos
23
New cards
Mercury
-Smallest planet
-No atmosphere
-Lots of craters
-No atmosphere
-Lots of craters
24
New cards
Venus
-Very bright + cloudy
-No life can exist
-No moons
-No life can exist
-No moons
25
New cards
Earth
-Only planet with life
-Has atmosphere
-15C
-Has atmosphere
-15C
26
New cards
Mars
-Iron oxide making it red
-No surface water
-2 moons
-No surface water
-2 moons
27
New cards
Jupiter
-Red spot which is a storm
-79 moons
-79 moons
28
New cards
Saturn
-53 moons
-Yellow from Ammonia
-Rings
-Yellow from Ammonia
-Rings
29
New cards
Uranus
-2nd coldest planet
-27 moons
-27 moons
30
New cards
Neptune
-Furthest away from the sun
-3rd largest planet
-3rd largest planet
31
New cards
Rocky planets
-Mercury
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
32
New cards
Gaseous planets
-Jupiter
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
33
New cards
Hottest planet
Venus
34
New cards
Coldest planet
Neptune
35
New cards
Planets in the solar system
-Mercury
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
-Jupiter
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
-Jupiter
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
36
New cards
Terrestrial planets
-Mercury
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
-Venus
-Earth
-Mars
37
New cards
Gaseous planets
-Jupiter
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
-Saturn
-Uranus
-Neptune
38
New cards
Compare
To give an account of the similarities and differences between two or more items
39
New cards
Mass
How much matter is in an object
40
New cards
Acceleration due to gravity on earth
10 m/s^2
41
New cards
How do we compare space objects
-Mass
-Size
-Composition
-Gravity
-Size
-Composition
-Gravity
42
New cards
Comparing mass of planets
To compare the mass of planets we use relative mass
43
New cards
Relative mass
The mass of one object compared to the other
44
New cards
Relative mass equation
Mass of planet / mass of earth
45
New cards
Planet has relative mass less than 1.0
Its mass is less than earth
46
New cards
Planet has relative mass more than 1.0
Its mass is more than earth
47
New cards
Planets in order of diameter small to big
-Mercury
-Mars
-Venus
-Earth
-Neptune
-Uranus
-Saturn
-Jupiter
-Mars
-Venus
-Earth
-Neptune
-Uranus
-Saturn
-Jupiter
48
New cards
Planets in order of mass small to big
-Mercury
-Mars
-Venus
-Saturn
-Earth
-Jupiter
-Uranus
-Neptune
-Mars
-Venus
-Saturn
-Earth
-Jupiter
-Uranus
-Neptune
49
New cards
Why are the 4 outer planets less dense
They're gaseous planets so the molecules that make up gas are very far apart therefore they're less dense
50
New cards
Comparing size
We use relative radius
51
New cards
Relative radius equation
Radius of an object / radius of earth
52
New cards
Composition
What an object is made of
53
New cards
Comparing composition: Earth
-Rock
-Thin atmosphere
-Thin atmosphere
54
New cards
Comparing composition: Mercury
-Rock
-Thin atmosphere
-Thin atmosphere
55
New cards
Comparing composition: Venus
-Rock
-Thin atmosphere
-Thin atmosphere
56
New cards
Comparing composition: Mars
-Rock
-Thin atmosphere
-Thin atmosphere
57
New cards
Comparing composition: Jupiter
Gas
58
New cards
Comparing composition: Saturn
Gas
59
New cards
Comparing composition: Uranus
Gas
60
New cards
Comparing composition: Neptune
Gas
61
New cards
Comparing gravity
Compared using relative surface gravity
62
New cards
Relative surface gravity
The surface gravity of one object compared to another
63
New cards
Relative surface gravity equation
Surface gravity of space object / surface gravity of earth
64
New cards
Gravity
Force generated by all objects that have mass
65
New cards
Weight
Force of gravity acting on an object
66
New cards
Weight equation
mass x gravity
67
New cards
Force equation
mass x acceleration
68
New cards
Other comparisons
-Distance from sun
-Rotation period
-Orbit period
-Maximum surface temperature
-Number of moons
-Rotation period
-Orbit period
-Maximum surface temperature
-Number of moons
69
New cards
Sun
The star at the centre of our solar system
70
New cards
Earth
One of the 8 planets in our solar system
71
New cards
Moon
Natural satellite that orbits the earth
72
New cards
Phenomenon
Any event that can be observed happening
73
New cards
Day + night
-Caused by the rotation of earth around its own axis
-The half facing the sun experiences daylight
-The half facing away experiences night
-The half facing the sun experiences daylight
-The half facing away experiences night
74
New cards
Amount of daylight depends on
Latitude + time of year
75
New cards
Diagram of day + night
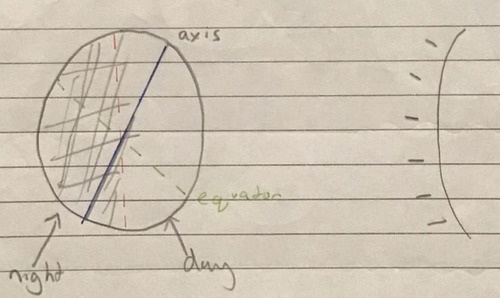
76
New cards
How long does it take for earth to rotate on its own axis
24 hours
77
New cards
Latitude of Dublin
53.3 North
78
New cards
Day with the most sunlight
21st June
79
New cards
How long does it take for the earth to revolve around the sun?
365 1/4 days
80
New cards
Rotate
Spins on its own axis
81
New cards
Latitude
A measure of distance north or south of the equator
82
New cards
Revolve
Something moving around something else
83
New cards
4 seasons
-Spring
-Summer
-Autumn
-Winter
-Summer
-Autumn
-Winter
84
New cards
How long do each season last
3 months
85
New cards
What are seasons called near the equator
Wet season + dry season
86
New cards
How many weeks are in a year?
52 weeks
87
New cards
Seasons diagram
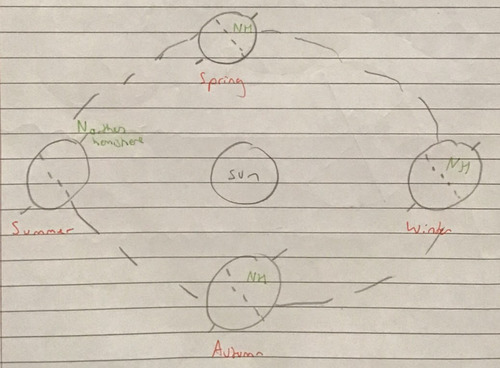
88
New cards
Summer
The side of the earth that is experiencing summer is tilted towards the sun
89
New cards
Winter
The side of the earth that is experiencing winter is tilted away from the sun
90
New cards
8 phases of the moon
1. New Moon
2. Waxing Crescent
3. First Quarter
4. Waxing Gibbous
5. Full Moon
6. Waning Gibbous
7. Third Quarter
8. Waning Crescent
2. Waxing Crescent
3. First Quarter
4. Waxing Gibbous
5. Full Moon
6. Waning Gibbous
7. Third Quarter
8. Waning Crescent
91
New cards
Phases of the moon
-The moon doesn't generate its own light, it reflects the light of the sun
-How much of the earth is illuminated depends on where the moon is in relation to the earth
-How much of the earth is illuminated depends on where the moon is in relation to the earth
92
New cards
Lunar cycle
-It takes 29.5 days for the moon to go around the earth once
-The moon is illuminated by the sun
-The moon is illuminated by the sun
93
New cards
Phases of the moon diagram
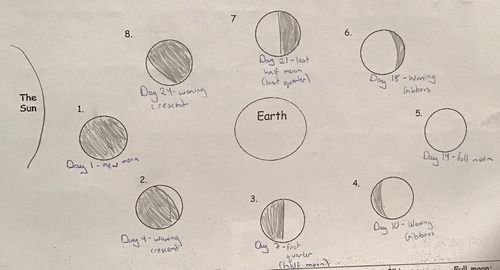
94
New cards
Solar eclipse
-Occurs when the moon blocks out the light of the sun
-It occurs during a new moon
-They are very quick + short because the moon is much smaller than the sun
-It occurs during a new moon
-They are very quick + short because the moon is much smaller than the sun
95
New cards
Solar eclipse diagram
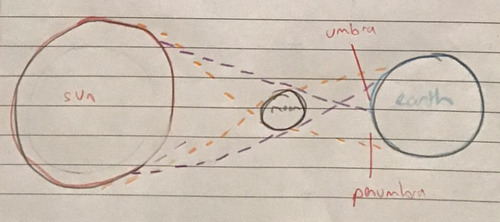
96
New cards
Umbra
Total solar eclipse
97
New cards
Penumbra
Partial solar eclipse
98
New cards
Lunar eclipse
-Occurs when the earth casts a shadow on the surface of the moon
-They are more common as more people see them
-Occurs during a full moon
-They are more common as more people see them
-Occurs during a full moon
99
New cards
Lunar eclipse diagram

100
New cards
How long between each high tide
12 hours 25 minutes between consecutive high tides