AP Environmental Science-Unit 7
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What is the defintion of air pollution?
The introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere in concentrations high enough to harm plant, animals, and materials, or to alter ecosystems
What system is air pollution considered? What does it mean?
Global system, and this means that pollution in one area can affect anywhere in the world due to the atmosphere being a common and is shared
What are primary pollutants?
They come directly from source/emission source, like a smockstack or exhaust pipe
What are six examples of primary pollutants?
CO2, SO2, CO, NOx, VOCs, and most particulates
What are secondary pollutants?
Primary pollutants that have undergone tranformation in the prescence of water, sunlight, oxygen, and other compounds
In what conditions to secondary pollutants occur in? (what conditions do most transformations occur in?)
During the daytime and with wet conditions
What are six examples of secondary pollutants?
Ozone (reacts with oxygen, VOCs, and moisture), H2SO4, H2O2, SO3, HNO3, NH4
What did the Clean Air Act (1970) do?
It identified 6 pollutants that jeopardize the environment and humans; states the standard amount of those pollutants and how much can be emitted and exist in the atmosphere
What are the six criteria pollutants? (acronym)
N-Nitrogen oxides
O-ozone (troposheric ozone NOT stratospheric)
S-sulfur dioxide
C-carbon monoxide
L-lead
P-particulate matter
How is sulfur dioxide emitted anthropogenically and naturally (2)?
-combustion of oil and coal
-volcanoes and forest fires
How does sulfur dioxide harm organisms?
It is a respiratory irritant, and it affects plant tissues
What symbol are nitrogen oxides called?
NOx
How are nitrogen oxides released anthropogenically (2) and naturally (3)?
-fossil fuels combustion and biomass and wood burning
-forest fires, soil microbes, and lightning
How are nitrogen oxides harmful? What do they cause (2)?
They are respiratory irritants; they cause smog and acid rain
How is carbon monoxide formed? How is it emitted?
It is formed during incomplete combustion of most matter; Carbon monoxide is emitted by vehicle exhaust and other forms of combustion
How is carbon monoxide dangerous? Where can it be seen (3)?
It is dangerous in indoor areas with poor ventilation, and it can be seen in charcoal, kerosene, and manure. Carbon monoxide can cause humans to suffocate and die because their red blood cells are attracted to carbon monoxide instead of oxygen
What are particulates?
liquid or solid particles suspended in air
How are particulates formed?
By the combustion of fossil fuels and biomass
Which substance produces more particulates: gasoline? diesel?
diesel
What are five sources of particulates?
Road dust, volcanoes, dust storms, rock-crushing, and fires
What is unique about particulate?
They can vary in size-the smaller they get (PM2.5) the more dangerous they can be (can go through all the body's filters)
What problems do particulates (or particulate matter) cause? (2)
-Respiratory irritant (coughing and shortness of breath)
-Blocks sunlight, which prevents photosynthesis if it is heavy enough
How is ground level ozone formed?
By sunlight and water reacting with VOCs, O2, and NOx
What is the molecule of good ozone and where can it be found?
O3, and it can be found in the stratosphere (6-30 miles up)
What is the molecule of bad ozone and where can it be found?
O3, and it is found in the troposphere (0-6 miles)
What does ozone cause? (2)
-all problems that stem from respiratory irritants
-damages plants
What does VOC stand for?
Volatile organic compounds
What is the source of VOCs?
Hydrocarbons from household products and building supplies
What are three examples of VOCs? What organism produces VOCs naturally?
Toluene, benzene, and formaldhyde
Plants release VOCs naturally
What is lead?
A trace metal found naturally in rocks
What are three sources of lead?
Gasoline, old pipes (Flint), and paint in older buildings
When was gasoline phased?
1996
What is lead toxic too?
CNS (central nervous system) of living organisms
Where can mercury be found in? (3)
Coal, oil, and fish
What happened to the mercury concentrations in air and water?
They have increased dramatically
What are the two main categories of smog?
Industrial and photochemical smog
What are the five names of industrial smog?
Sulfurous smog, gray smog, London smog, pea soup smog, and winter smog
How is industrial smog caused?
It is caused by SO2 and particulates reacting with water vapor
What is the biggest cause industrial smog?
Coal
What conditions is industrial smog common occur in? Why does this happen?
Humid, cool conditions (prevents is from spreading out)
What are the four names of photochemical smog?
Yellow smog, brown smog, Los Angeles smog, and summer smog
How is photochemical smog caused? (2)
VOCs and NOx reacting with sunlight, water vapor, and heat
What is the biggest cause of photochemical smog? What conditions is photochemical smog common in?
-Cars (NOx)
-Dry, warm conditions
What should be done to reduce photochemical smog?
Reduce production of anthropogenic VOCs and NOx
How do we reduce VOCs and NOx?
Paint with low VOCs, less use of fireplaces, less use of ICVs, and pump gas at night
What are some of the health effects of photochemical smog? (roughly three)
-Respiratory irritant
-mucus membranes (eyes)
-coughing, wheezing, asthma, and an increase chance in a heart attack
What are VOCs (not what it stands for)?
Can easily become vapors and anything with a strong smell
What is the relationship between temperature and altitude?
As altitude increases, temperature decreases
Describe what happens to warm air?
It is less dense, so it rises
What problem does this cause for pollutants?
This allows pollutants to be reduced or diluted through circulation
What is thermal inversion?
A warm layer of air of air gets trapped between the two cooler layer
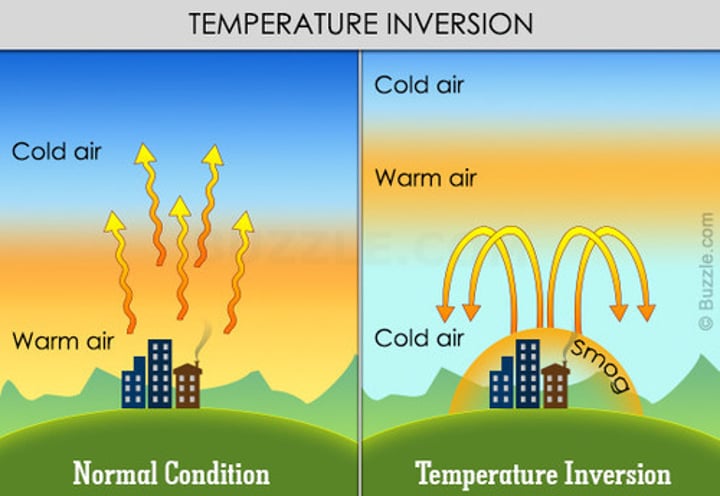
What is the warm layer called in thermal inversion?
inversion layer
What problem does thermal inversion cause?
Emmissions accumulate beneath the inversion layer
What two situations or factors lead to thermal inversion? (expand and what conditions are within those factors?)
Topography (valleys and coastal areas) (cool air comes in and sits in the bowl area)
Weather (more likely on cold nights, during winter, and in snowy areas)
What are four carbon dioxide sources?
Ocean-atmosphere exchange, plant and animal respiration, soil respiration and decomposition, and volcanic eruptions
What percentage of carbon dioxide comes from ocean-atmosphere exchange?
~40%
What percentage of carbon dioxide comes from plant and animal respiration?
~30%
What percentage of carbon dioxide comes from soil respiration and decomposition?
~30%
What percentage of carbon dioxide comes from volcanic eruptions?
~0.03%
What are five natural sources of particulates?
-Sea salt
-Dust (airborne soil)
-Pollen
-Black carbon from wildfires
-Volcanic ash
what is a natural source of air pollution (3)?
Radon, mold (airborne spores), and dust
What is radon? What is it most stable isotope?
It is a naturally occuring gas; Radon-222 (half life of 4 days)
How is radon produced? Where is that element found?
Through the decay of uranium, which is found in soils and rocks
How does radon enter homes? (3) What is an essential criteria?
1. the soil in the area has to have a high level of radon
It enters homes through the basement; goes through cracks and walls in the foundation
Can also enter homes through wells once it has been dissolved in groundwater
What are three anthropogenic sources of particulates?
-insulation
-lead from paint
-VOCs
What specific form of VOCs is a source of particulates?
-Formaldehyde from materials, furniture, buildings, carpeting, and upholstery
What are five chemicals and substances that are combusted to cause indoor air pollution?
-carbon monoxide
-SO2
-NOx
-tobacco smoker
-particulate matter
What do developing countries due to cause indoor air pollution? (5 items are used) What group of people suffer the most?
Burn charcoal, wood, dung, crop resiude, and coal indoors
The less fortunate suffer the most
Is indoor or outdoor pollution a bigger problem in developed countries? Why? (3 main points)
Indoor pollution
-We spend 90% of our time indoors or in a car
-More chemicals are being trapped inside due to improved insulation
-There has been an increase in plastics and additional petroleum-based materials in offices and homes that emit harmful chemicals and particulaes
What are three main categories of methods to prevent the emission air pollutants?
Industrial regulatory practices, alternative fuels, and non-industrial regulatory practices
What are two examples of industrial regulatory practices?
Scrubbers and electrostatic precipitators
What are scrubbers? What is the difference between the two types?
They remove particulates and/or gases from exhuast streams from factories
Wet scrubbers use a spray to remove the particulates and/or gases and eventually produce a slurry that has to be disposed
Dry scrubbers use a powder, commonly limestone, to discard of the gases and/or particulates
What four gases are removed through scrubbers?
NOx, SO2, CO2, and CO
How do electrostatic precipitators work?
The particulates pass through electrically charged rods, wires, or plates and gain a negative charge; they are attracted to an additional plate or wire that has a positive electric charge, which results in the collection and disposal of particulates
What two substances are discarded through electrostatic precipitators?
Smoke and other particulates; NO GASES (scrubbers would be paired with electrostatic precipitators to discard the gas)
What are two examples of non-industrial regulatory practices?
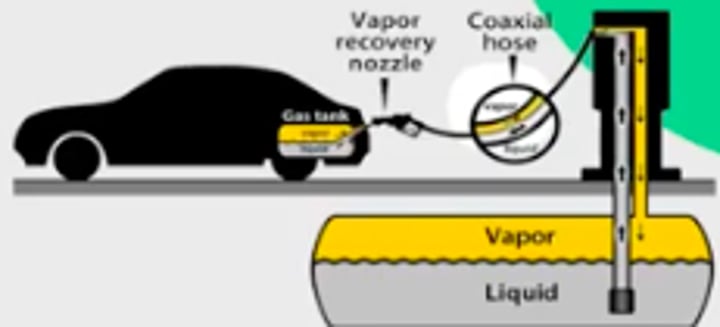
Vapor recovery nozzle (gasoline) and catalytic converters
What do vapor recovery nozzles do?
They prevent fumes from being released into the atmosphere while fueling a motor vehicle (not all fumes are prevented)
How do catalytic converters function?
A device utilizing precious metals to convert pollutants in car exhaust into less harmful molecules; within internal combustion vehicles
What should be done with lighter and dry-cleaning fluid to reduce VOCs?
control the use of dry-cleaning fluid and restrict the use of lighter fluid
What should be done with wood-burning stoves and trash to reduce VOCs?
there needs to a reduction in the use of wood-burning stoves; the bruning of trash needs to be terminated
What are three actions regarding internal combustion vehicles to reduce VOCs?
-only allowing people to drive on odd days
-improvement in use and quality public transportation
-tolls and carpooling
What is wet acid deposition? (3) (the conditions)
Rain, fog, and snow
What is dry acid deposition? (2)
Gases and aerosol particles
What is at major risk from acid deposition?
Downwind communities
What are three consequences created from acid deposition?
1. acidification of soils and bodies of water, which can harm organisms in those habitats do to optimal pH levels
2. corrosion of human-made structures and statues
3. the leaves of plants will deteriorate and ruin the plant's photosynthesis capabilties
What affects the intensity and impactful capabilities of acid deposition?
The differences in bedrock and soils in different region (ex: soil with more limestone will not be impacted as badly with acidification)
What does limestone do to acid rain?
Limestone in bedrock can neutralize acid rain and prevent acidification
What two majr consequebces are sesulted from televisin? What group is mainly affected? How is the human body affected?
Hearling loss and physiologicsl stress (mainy children); damages the special hair cells, which play an essential role in the hearing process
What are three sources of air pollution? (broad)
transportation, domestic and individual flight, and tranpsortation
What are four harmful effects on other organisms?
-stress
-covering sounds for hunting or communicating
-damaged hearing
-alters their migratory routes
What group of animals are harmed by sonar?
Marine mammals
How are those organisms harmed by noise pollution?
The use of sonar and boats covers their form of communication, which is sonar. If they can not hear it, those organisms can not mate, feed, or warn each other
What are three pros of wet scrubbers? (cost, space, and efficiency?)
-initial cost is low
-do not require much space
-efficient at getting rid of corrosive, harmful gases and particulates
What are four cons of wet scrubbers? (maintenance, build up, technology, and temperature)
-maintenance costs are high
-slurry, water, and solids can build up to make the strucuture heavy and would need to be disposed
-somewhat high technology with horsepowerand pressure-drop requirements
-ensure that substances will not freeze
What are four pros to dry scrubbers? (product, space, costs, efficiently, and pollutants)
-does not produce a sludge
-low space
-barely any maintenance costs
-can somewhat efficiently collect acid gases; particulates need a fabric filter
What are four cons of dry scrubbers? (efficiency, build up, costs, and removal process)
-not as efficient as a wet scrubber
-residual powder can build up and has to be disposed
-expensive and high initial cost
-can not remove all types of contaminants (ex: can not remove particulates unless a fabric filter is used)