Geography SL - Climate Change (Core Unit)
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Atmospheric System
Gases that form 4 distinct layers around the Earth
Name the 4 atmospheric layers (from top to bottom)
Thermosphere
Mesosphere
Stratosphere
Troposphere
Thermosphere (function & temperature)
Protects Earth from sun’s harmful radiation, x-rays and ultraviolet rays
Temp. = 500 to 2000 degrees celcius (hottest layer)
Mesosphere (function & temperature)
Protects earth from comets and meteorites
Temp. = -2.5 to 90 degrees celcius (2nd hottest layer)
Stratosphere (function & temperature)
holds ozone layer and protects from sun’s ultraviolet rays (UV)
Temp. = -51 to -15 degrees celcius (coldest)
Troposphere (function & temperature)
Provides oxygen & keeps Earth at habitable temperature. Allows weather to occur
Temp. = -51 to 17 degrees celcius (decreases as you climb)
Tropopause
Boundary between troposphere and stratosphere
Stratopause
Boundary between stratosphere and mesosphere
Mesopause
Boundary between mesosphere and thermosphere
Atmosphere
Open energy system receiving energy from the sun and earth
Insolation
Incoming solar radiation
Energy flow in the atmosphere
balance between inputs, outputs and transfers of energy. Earth is neither heating up or calling down
Short wave radiation
radiation and wavelengths of less than 4 microns. Enters Earth by reflecting off clouds being absorbed by the atmosphere
Long wave radiation
electromagnetic energy radiated outwards by Earth when the atmosphere warms and heat is emitted, partly radiating into space
How short wave radiation is used
Given out by the sun. The hotter the energy-supplying body, the shorter the wavelength.
Can be absorbed at:
- Surface
- Reflected back from surface
- Reflected to space from cloud & gases
- Reflected to surface as diffused radiation
How long wave radiation is used
Given out by surface to eventually leave the atmosphere. Transferred back to surface if there is a cloud cover or greenhouse gases that trap it
Factors affecting earth-atmosphere energy balance
Short-wave radiation reaching surface
Long-wave radiation leaving atmosphere
How the factors affect earth-atmosphere energy balance
Latitude (solar radiation) & albedo
Cloud cover (solar & long-wave radiation)
Atmosphere characteristics → gas, water vapour, dust/sand (solar & long wave radiation)
Latitude
Measures distance North/South of equator
Latitude effects on solar radiation
Energy distributed unevenly
Far away from equatorial line = lower energy input
If long distance, short waves may be reflected or not reach surface. Lost heat-energy
Albedo effect
ability of surfaces to reflect sunlight. Depends of colour of surface (rainforest/desert) & characteristics (thin/thick clouds)
Clouds
reduces solar (short wave) radiation reaching the surface & long wave leaving the atmosphere
Clouds + Albedo
Clear sky albedo → albedo without clouds
Total albedo → albedo with clouds
Cloud cover impact on albedo
the lighter the colour, the more solar radiation reflected to space
Atmosphere characteristics
Gases → can reflect and absorb solar radiation. Also reflects long-wave radiation (Greenhouse effect)
Water vapour → absorbs & reflects solar radiation. Is the cause of 36-66% of the greenhouse effect
Dust/sand → particles in suspension lead to reflection and scattering of solar radiation
Greenhouse gases
gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. It is re-emitted as heat energy into space
e.g. water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, etc.
Anthropogenic gases
Greenhouse gases that are human induced
Greenhouse effect
a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface
Greenhouse effect process
When the sun’s energy reaches the atmosphere, some is reflected back to space. The rest is absorbed & re-radiated by greenhouse gases. This keeps Earth 33 degrees warmer than it would be otherwise.
Cause of climate change
increase in greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide
increasing due to fossil fuels being burned for energy. Human induced CO2 has risen by 50% since the 18th century. Human emissions could reach 75 billion tons per year by end of century. China emits the most. Without CO2, the greenhouse effect would be too weak to keep global average temperature above freezing
Methane
increasing due to agriculture, fossil fuels and landfill waste. Concentration doubled over the past 200 years. Projected 9 million tonnes per year by 2030. China emits the most. Responsible for +25% of global warming. Traps more heat in atmosphere than CO2
CFC’s
increasing due to aerosols and waste (air conditioners & fridges). CFCs were banned a decade ago but production has been increasing. China emits the most. CFCs enhance atmospheric greenhouse effects
Nitrous oxide
increase due to agriculture, fuel combustion, wastewater management & industrial processes. Reached new high of 334 ppb in 2021. China emits the most. Contributes to greenhouse effect due to positive radiative forcing effect
Natural factors of climate change
Variations in solar energy (sunspots release increased solar radiation)
Volcanic eruptions → short-term (1-3 years) cooling effect
Variation in Earth’s orbit (distance from sun changing)
Clouds/water vapour → absorbs/reflects solar (short wave) radiation
Human factors of climate change
Burning fossil fuels (coal, gas, oil)
Deforestation (effects carbon dioxide)
Increased cattle ranching (methane)
Fertilisers in agricultural systems (higher nitrous oxide (N2O) concentrations)
Milankovitch Cycle
periodic changes in the orbital characteristics of a planet that control how much sunlight it receives
Eccentricity
changes in orbit shape. Earth’s rotation is not perfectly circular (more elliptical). When more elliptical, more solar radiation enters the atmosphere. Cycle = 100,000 years
Obliquity
most important, the earth’s tilt. Varies between 22.1 to 24.5 degrees. The more tilt, the more extreme seasons. Is the main reason for seasons. Cycle = 41,000 years
Precession
Axial precession. As earth rotates, it wobbles slightly upon its rotational axis. Due to tidal forces caused by gravitational influences of the sun & moon. Cycle = 23,000 years
Long-term changes in energy balance
Ice age → expansion of ice sheets and alpine glaciers due to long period of reductions in Earth’s surface & atmosphere temperature. 110,000 - 10,000 years ago
Jurassic period → atmosphere was warmer and thicker than today. Carbon dioxide levels were likely 4x higher. 119.6 - 145.5 million years ago
Short-term changes in energy balance
Volcanic eruptions → ash & sulfric acid prevent sunlight from reaching surface. Creates cooling affect
Short-term carbon cycle → Plants “fix” carbon out of atmosphere through photosynthesis
Sunspots
Short-term variation in solar energy. Huge magnetic storms on sun’s surface which increases solar radiation to earth
Negative feedback
system that returns to the original “balanced” situation through a self-regulating method of control. Same state of equilibrium.
e.g. global cooling, ice growth, increased albedo, less insolation absorbed
Positive feedback
System that takes a new “balanced” situation through permanent changes in the state of the system. New state of equilibrium
e.g.
Carbon cycle
series of processes by which carbon compounds are interconverted in the environment, involving incorporation of CO2 into living tissue by photosynthesis and its return to atmosphere through respiration, the decay of dead organisms and burning fossil fuels
MEDC Economy & emissions
Portugal:
emissions per capita = 4.05 metric tons
GDP per capita = $26,878.87
Trade balance of goods = -$32.31 billion
LEDC Economy & emissions
Kenya:
emissions per capita = 0.46 metric tons
GDP per capita = $2,187.65
Trade balance of goods = -$14.03 billion
Implications of climate change
rising sea levels
increasing storm activity
agricultural patterns will change
less rainfall
up to 40% of species will go extinct
Atmosphere
thin layers of gases surrounding earth. protects from UV radiation, monitor temperatures & provides animals with CO2 and oxygen. Climate change worsens air quality within the atmosphere
Hydrosphere
all water covering earth; liquid & solid. 71% of earth is covered in water. Climate change melts glaciers and ice sheets
Biosphere
all life on earth; humans, plants and animals. Climate change causes some habitats to be too warm or dry for animals to survive
Atmosphere/hydrosphere case study
Shishpar glacier in North Pakistan was thawing due to a record heat-wave which flowed into a nearby lake. Water levels grew too high and triggered a flood that destroyed a nearby village
Changes to atmosphere
increased greenhouse gases = warmer air
More atmospheric energy = increased storm activity
Change in temperature, wind, pressure, precipitation & humidity
Changes to hydrosphere
rising sea levels could displace 200 million people
Floods from glacial melt threaten 4 million sq/km (5% of population home)
Changes in sea ice
Acidification → changes in carbon stored in ice & oceans
Changes to biosphere
vegetation could increase or decrease
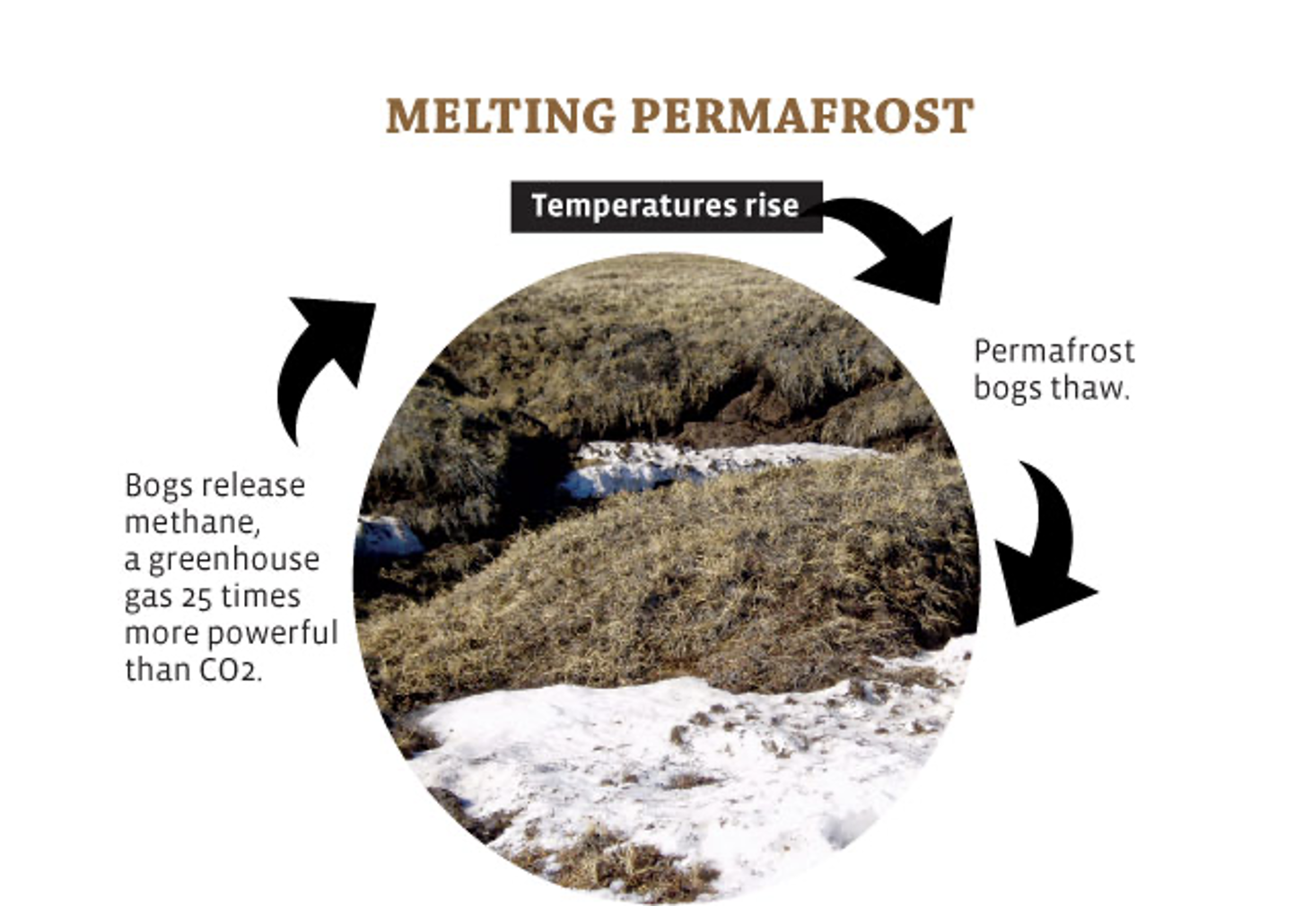
Thawing of permafrost
Changes in biomes (too fast = migration/extinction)reduction in biodiversity
Consequences of climate change
75-250 million projected to be exposed to increase in water stress by 2020
Agricultural production projected to be compromised by climate variability and change. Affects food security exacerbate malnutrition
Some African countries, yields from rain-fed agriculture reduced by 50% by 2020
Consequences of climate change case study: Asia
Freshwater availability across Asia projected to decrease. Could affect +1 billion people by the 2050s. Coastal areas, especially heavily populated mega-delta regions will be at greatest risk due to regions rapid urbanisation, industrialisation and economic development
Consequences of climate change case study: America and hurricanes
Caused by thunderstorms (use ocean heat as fuel) and warming oceans (storms pull in more water vapour & heat) which makes stronger winds, rainfall and flooding. Some hurricanes cause up to $1 billion in damage and displacement due to damage of housing. Hurricanes spread bacteria which leads to mini outbreaks of diseases
Risk
both the possibility of danger and simultaneously its potential consequences
Vulnerability
conditions determined by physical, social, economic and environmental factors which increase susceptibility to the impacts of hazards
Adaptation
anticipating adverse effects of climate change and taking appropriate action to prevent or minimize the damage
e.g. America invest in robust coastal defence infrastructure to minimize damage caused by hurricanes
Mitigation
reducing climate change by reducing sources of the problem
e.g. America build energy-efficient, green building techniques to reduce emissions from electricity generation
Exposure
the degree to which people are exposed to climate change
Sensitivity
the degree to which they could be harmed by exposure to climate change
Disparities in exposure case study
Netherlands = MEDC, HIC. Located in Europe. One of the most flood-prone countries in the world. exposed = land captured by the sea. vulnerable = lives &homes at risk from flooding. Dutch adapt by reinforcing dikes and dunes. Dutch want to reduce greenhouse emissions by 49% by 2030
Bangladesh = LEDC, LIC. Located in Asia. one of the most flood-prone countries in the world. exposed = losing land due to rising sea levels. vulnerable = flat topography causes more extreme flooding, destroying infrastructure. government has implemented 726km of river-bank protection. Wants to increase tree cover from 22% to 25% by 2030
COPs
conference of the parties. Members make plans for their countries on how to reduce emissions and impacts of climate change. They meet every year to review each country’s progress. formed 1995
Paris Climate agreement
Keep warming below 2 degrees celcius
Rich countries must invest $100 billion from 2020
Developing countries encourages to “enhance efforts”
Developed countries must provide financial support
Review progress every 5 years
Mitigation strategies
reducing energy consumption
reducing emissions of Nitrous Oxide and methane from agriculture
geo-engineering
using alternatives to fossil fuels
using biomass as a fuel source
Carbon sinks
anything that absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases
e.g. trees
geo-engineering
deliberate large-scale intervention of earth’s natural system to counteract climate change
e.g. sunshades in earth’s orbit that reflects sunlight back into space
pollution management/control
stopping forest clearance
improving public transport
setting national limits on carbon emissions
Carbon taxes
taxes levied on the carbon emissions required to produce goods and services
Carbon trading
use of a marketplace to buy and sell credits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of CO2 per year
Carbon offset schemes
reduction/removal of emissions to compensate for emissions released elsewhere
Civil society
aggregate of NGOs and institutions that manifest interests and will of citizens
TNC climate change action
McDonalds → committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions caused by its restaurants and offices by 36% by 2030
Civil society climate change action
Save the Children → committed to reducing their own greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impacts