Physics 1004- Final
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What do all EM waves have in common?
Speed in a vacum
When does total internal reflection occur?
theta initial > critical angle
Does wave length increase or decrease from Red-Violet?
Decrease
Rank Glass, water and air from faster to slowest material for light to travel through?
air>water>glass
What is the n value for air?
1.00
How does the energy associated with the magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave compare to the energy associated with the electric field?
One half of the energy is caried by the magnetic field component
One half by the electric field component
What happens to the intensity when it is initially polarized?
The intensity is halved
Which way does light refract when it travels from a slower to faster medium?
Away from the normal
Which way does light refract when it travels from a faster to slower medium?
Towards the normal
If a material has a large n value then light travels _____ through it?
Slower
If a material has a small n-value then light travels ____ through it.
Faster
Light is _____ times faster than sound.
1 000 000
T/F A beam of light will exit a material at the same angle it entered
True
When does the angle of incidence not equal the angle of refraction?
There are no practical studied that it doesn’t. Therefore the angle of incidence always equals the angle of refraction.
How to go to the root mean square version of a variable?
Divide by root(2)
What formula can you use to determine the direction of an em waves E comp, B comp or direction?
s = ExB (use simple vector algebra)
Definition of an emf?
Work required to move a charge from one end of the circuit to the other.
(Positive-Negative terminal)
How does a capacitor act at t=0
Acts as an short circuit.
How does a capacitor act at t= infinity?
Acts as an open circuit.
How can you sum an unknown amount of equivalent resistances in parallel?
R_eq = Ri/n (n= number of resistors)
When is the force on a particle (positive or negative) equal to zero in a magnetic field?
If the particle is stationary, parallel or anti parallel.
This is because the force on a particle within a magnetic field is given by the perpendicular components of its velocity.
What is the direction of the electric force in relation to the electric field?
The electric field’s force points in the direction of the field.
What is the direction of the magnetic force in relation to the magnetic field?
The magnetic force is perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Magnetic fields can not cause a change in speed but can cause acceleration, why?
Magnetic fields can cause a change in direction which is considered a change acceleration.
T/F electric fields can cause a change in speed?
True!
If two wires carrying the same current both flow out of the page do they attract or have zero net force?
They still attract .
Zero net force directly between them but the wires still attract.
Do wires that are carrying parallel currents attract or repel?
Attract
There are two identical currents one is traveling in the page the other is traveling out of the page is there a force in the center?
Yes, there is a force in the center as both of their forces will add and point downwards.
(use RHR where you wrap your fingers around the wires)
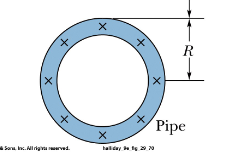
What is the magnetic field at the center of the pipe. The outer radius is current carrying
Zero, because there is no current enclosed inside if you were to draw an amperian loop.
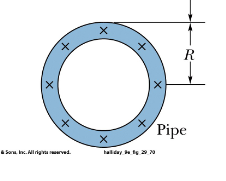
What B equation do you use for the outside of the pipe?
B for a circular loop.
When is flux at its max through an area?
When B is parallel to the normal of the area
Where is the magnetic field of a wire at its maximum?
At the surface/ at its radius ie. r=R
Define Faraday’s Law
If magnetic flux through an area changes with time than an emf and a current will be induced.
If the change in magnetic flux is constant through a loop then what does that mean for the current?
the current will be constant because the emf will be constant.
What is Lenz’s law
An induced current direction will oppose the change in flux that caused it.
(This means that when you use the right hand rule for current you need to reverse, the current direction)
T/F For there to be an induced emf the flux/magnetic field must vary over time.
True
When working with RL circuits and you need to use i in an equation what should you use?
Make sure to either use i(t) charging or i(t) discharging
How does an LC circuit work?
Energy is shuttled between the electric field of the capacitor and the magnetic field of the inductor. The energy within the circuit always stays the same so U_E = U_B.
What dampens oscillations?
When a resistor in added to an LC circuit, creating an RCL circuit.
At t=0 how does an inductor act vs a capacitor
inductor: Broken wire/open circuit (not enough current)
capacitor: Acts like a wire/ short circuit (no voltage yet so just acts like wire)
At t=infinity how does an inductor act vs a capacitor
inductor: Acts like a wire/ short circuit (constant i no change to oppose)
capacitor: Broken wire/open circuit (capacitor is full)
Inductors oppose a change in current
Capacitors oppose a change in voltage
What does this statement mean?
The current can not change instantly through an inductor
The voltage can not change instantly across a capacitor
When current equals zero in an LC circuit what does this mean for the capacitor?
The capacitor is fully charged.
What happens if you break a magnet?
Each fragment will become a separate magnetic with its own poles.
What law/equation confirms that there are no magnetic monopoles
Gauss’ Law for magnetic flux