Social Psychology & Personality
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
15-25% of the AP Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Attribution theory
How we attribute or explain the cause of our own behavior and the behavior of others.
Dispositional attribution
The tendency to attribute a person's behavior to their internal characteristics, such as their personality traits, attitudes, or abilities
Situational attribution
The tendency to attribute a person’s behavior to external factors, such as the situation or environment.
Explanatory style(s)
Optimistic: positive; brighter outlook on life
Pessimistic: negative outlook on life
Fundamental Attribution Error
Human tendencies to explain someone's behavior based on internal factors (personality/dispositional), and underestimate the possibilities of any situational, or external factors
Actor-Observer Bias (others v. ourselves)
A cognitive bias where humans tend to attribute their own actions to external or situational factors, while attributing others’ actions to internal characteristics or personality traits in order to excuse/feel better about our mistakes.
Self-Serving Bias (judging ourselves)
A cognitive bias that explains our behavior depending on whether the outcome of our behavior is positive or negative.
Individuals will attribute their success to internal factors like talent or effort, while blaming their failures on external factors like luck, others, environment.
This bias serves to maintain self-esteem and protect one's ego.
Social Comparison
Comparing yourself to others to evaluate your abilities, opinions, and overall self-worth:
Upward Comparison: Comparing yourself to someone who you perceive as superior to you. This can inspire someone to improve their quality of life or create a sense of inferior complex.
Downward Comparison: Comparing yourself to someone who you perceive as less fortunate or inferior than you in order to feel better about yourself.
Attitude
Feelings often influenced by our beliefs that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events.
Factors:
Experience
Social roles & norms
Classical & operant conditioning
Observing others
Mere-Exposure Effect
The phenomenon where people tend to develop a preference for things merely because they are familiar with them. This effect suggests that repeated exposure to a stimulus increases our liking for it.
Peripheral Route Persuasion (ethos/pathos)
A method of persuasion that relies on superficial cues rather than the content of the message, often influencing attitudes through emotional appeal or attractiveness. This approach focuses on factors such as endorsements, visual, and emotional appeals.
Lacks depth and logic
Surface level information
Uses positive association
Attitude change is weak and short-lived
Requires little conscious effort
Central Route Persuasion (logos)
Offers evidence and arguments that aim to trigger favorable thoughts.
Long-lasting attitude change
Audience must be motivated to listen
Uses logic and facts to convince people to change their attitudes or behaviors
Foot-in-the-Door Technique
People who agreed to smaller requests are more likely to comply later with a larger request based on the idea of maintaining consistency in their behavior.
Door-in-the-Face Technique
Where a person makes a large request that is likely to be rejected, but follows up with a smaller, and more reasonable request that’s more likely to be agreed upon.
Role
A set of expectations/norms about a social positioning defining how those in position must behave.
Belief Perseverance
Maintaining a belief even when presented information that refute against your beliefs or opinions.
Confirmation Bias
Search, interpret, or recall information that supports/confirms one’s beliefs or opinions.
Cognitive Dissonance
A nagging feeling of discomfort feeling when your beliefs and actions don't quite line up.
Conflicting beliefs, values, or attitudes
Discomfort feeling comes from inconsistency/contradictions
Attempt to relieve discomfort by rejecting, explaining away, or avoiding new information
Prejudice
Unjustifiable and negative behavior or attitude towards a specific group.
Explicit Attitude (directly)
Aware of the negative/harmful attitude and behavior towards the specific group.
Implicit Attitude (indirectly)
Unconscious belief or attitude towards a group or individual.
Just-World Phenomenon
The belief that the world is “just” and people will get what they deserve → karma
Good people will be rewarded
Bad people will be punished
Out-group Homogeneity
The tendency to assume that the members of other groups are very similar to each other, while your group are all individually different from one another.
Ex:
A white person might think that all Asian people are similar to each other.
A basketball player might think that all cheerleaders are the same, but that the people on their team are all different.
In-group Bias
A cognitive bias that causes people to favor their own group over other groups. The tendency to favor someone whom we can relate to share a common trait or interest with.
Normative Social Influence
Influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval. Conforms; agrees with others’ opinions because they feel the need to belong and to feel accepted.
Informational Social Influence
Influence resulting from one’s willingness to accept others’ opinion about reality. Conforms to gain knowledge or because they think that person knows better, therefore, they are right, and they should obey.
Factors of Conformity
Appealing to societal standards; fear rejection & being different
Blending in with the majority
Feels incompetent or insecure
Peer pressure
Being observed
Admire the group’s status and attractiveness
No prior commitment/collaboration
Obedience
Complying to direct orders from an authority figure.
Factors:
The authority figure was present in the room with the subject.
Prestigious institution
Authority holds high status
No one else is disobeying
Intimidation/fear tactics; avoid consequences
No sense of self-responsibility; assigning responsibility to the authority
Social Facilitation
Strengthened performance in other’s presence; do well when people are watching.
Social Inhibition
Performance worsens in other’s presence.
Social Loafing
When in a group setting, your performance effort decreases due to not holding your actions accountable; decreased self-responsibility. Because you’re in a group setting, you believe that you do not have a lot of impact, and slack off.
Loaf —> cat loafing (loaf bread position = chill)
Deindividuation
Losing one’s self-identity, individuality, self-awareness, and self-restraint when participating in a group. It can lead to people acting in ways they might not otherwise, such as engaging in impulsive, deviant, or violent behavior.
Ex:
Anonymity: Feel less accountable for their actions because they’re unidentifiable and can get away with it
Group size: “Everyone else is doing it, so I can do it too.”, “The crowd is too big, I won’t get caught.”
Group Polarization
The belief and attitudes we bring to a group grow stronger as we discuss them with like-minded others. Occurs when like-minded people reinforce each other’s opinions and they become/grow more extreme as they’re discussed.
Us v. Them mentality; isolate group from “outsiders" (those with opposing opinions and beliefs)
Ex:
Political discussions
Extremist groups
Terrorist organizations
Cults
Groupthink
Fed by overconfidence, conformity, self-justification, and group polarization. It is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when a group of people make irrational decisions due to a desire for harmony or conformity.
Lack of critical thinking
Poor decision making by dismissing/suppressing differing opinions and not exploring alternative solutions
Lack of perspective
Ignore warning signs & doesn’t reconsider beliefs
Altruism
Selfless, prosocial behavior.
Bystander Effect
A social psychological theory that describes how an individual is less likely to intervene in a conflict when there are multiple witnesses/bystanders present.
Social Exchange Theory
A sociological and psychological theory that explains how people make decisions based on the costs and benefits of their actions and relationships.
Ex: “If I help them, what will I gain from it? Will it benefit me? What will I get in return?”
Social Reciprocity Norm
Repaying what another has provided - mutual benefits and cooperation.
Ex: Treat people how they treated you
Social Responsibility Norm
A belief that people have a moral obligation to help others, even if they are not directly benefiting from it; no personal gains. Act in ways that benefit others and contribute to the community.
Conflict
A state of opposing forces, such as desires, emotions, or behaviors. It can occur between individuals, groups, or within an individual.
Social Traps
A conflict of interest or perverse incentive where individuals or a group of people act to obtain short-term individual gains, which in the long run leads to a loss for the group as a whole.
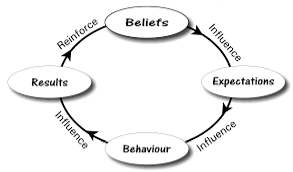
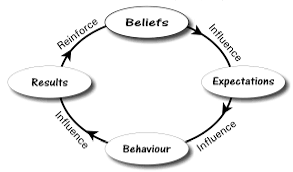
Self-fulfillment
A prediction that becomes true because someone believes it will.
A person's belief or expectation influences their actions
Expectation leads to fulfillment
Peace
Attained through the following:
Contact: Involve equal status between individuals and a shared goal requiring cooperation.
Cooperation: With people towards a shared goal – superordinate goals; Overcoming differences in order to achieve a shared goal.
Communication: Promote understanding, and foster peaceful relationships between individuals and groups.
Conciliation: Facilitating communication and reaching an agreement between conflicting parties, often through the involvement of a neutral third party, with the goal of resolving conflict peacefully, and promoting reconciliation.
Personality
Characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting.
Psychodynamic theorists view personalities
Conscious
The state of being aware of your thoughts, desires, feelings, memories, and surroundings.
Unconscious
Unaware thoughts, desires, feelings, and memories.
Information processing of which we are unaware of.
Subconscious (preconscious)
Thoughts, feelings, and impulses that are not presently in awareness, but can be readily called into consciousness.
Id
The unconscious source for all innate needs, emotional impulses, and desires.
Pleasure over pain and reality
Referred to as “the shoulder devil”
Ego
Mediates the demands of the Id, superego, and reality.
Focuses on reality
Superego
Criticizes and prohibits the expression of drives, fantasies, feelings, and actions.
Referred to as “the shoulder angel”
Critical self-conscious and judgement
Self-Actualizing Tendency
Realizing one’s full potential by pursuing personal growth and self-fulfillment; the ability to become the best version of yourself.
Unconditional Positive Regard
An attitude of total acceptance toward another person; accepting a person for who they are despite their flaws/faults.
Self Concept
All our thoughts and feelings or answers center around the question of “who am I?”; our perception of ourselves.
Reciprocal Determinism
Behavior + internal personal + environmental influence = our interaction.
Ex: Ms. Shughoury is social & caring (a personal factor). Because of this, she chooses to become a high school teacher (behavioral factor). Because of her choice to be a high school teacher, she is in an environment of teaching, mentoring, talking, learning, and acting professional (environmental factors). Because she is talkative and excited, her students tend to be talkative and excited which reinforces her social personality.
Self-Efficacy
An individual’s belief in their capacity to execute tasks; one’s belief in their ability to accomplish (succeed/achieve) a task or goal.
Self-Esteem
How we value and perceive ourselves; our self-worth.
Traits
Internal characteristics that make up our personality and influence how we behave.
Openness
Independent
Willing to try new things; adventurous
Variety = good
New experience
Conscientiousness
One of the big 5 personality traits
Organized
Careful; meticulous
Disciplined
Extraversion
Sociable
Prefers interactions and big group settings
“Peoples person” - outgoing and enjoys talking to others
Agreeableness
One of the big 5 personality traits
Mediator
Prioritizes peace and harmony
Cooperative
Neuroticism (Emotional Stability)
One’s ability to regulate their emotions.
Motivation
One of the driving forces behind human behavior; what drives people to act in certain ways.
Drive-Reduction Theory
The more one gets rewarded, the less interested a person becomes in a task.
Ex: You enjoy drawing → you get stickers and praises for every time you draw well → you’re expected to draw well → Perfectionism drains the joy out of drawing
Drive
Motivation to satisfy the need.
Homeostasis
The human body seeking stability and balance.
Arousal Theory
Motivated to maintain an optimal level of arousal.
Yerkes-Dodson Law
The higher the arousal → the more productive.
The lower the arousal → the less productive.
High-demanding stimulus increases attention and interest which can improve performance to an extent.
Too little arousal doesn't provide much in the way of motivation.
Too much arousal causes a stronger stress reaction that can hamper performance.
Ex: Listening to music while studying helps others.
Sensation-Seeking Theory
Crave new, intense, and complex experiences, even if they're dangerous to maintain, or achieve optimal levels of arousal.
Experience seeking - new sensation + experience.
Thrill Seeking - adrenaline rush.
Disinhibition - freedom from restrictive, conventional rules.
Boredom Susceptibility - restless when not stimulated.
Self-Determination Theory
Intrinsic Motivation: Internal factor.
- Relatedness: build connections.
- Competency: learning new things, awareness, new perspective.
- Autonomy: feel in control.
Extrinsic Motivation: External factor.
- Reward/money
- Social approval
- Grades
Social Trap
Pursuit short-term gains that negatively affects the group with long-term consequences that are harmful to the group → causes conflict.
When individuals act in their own self-interest, disregarding the group.
Lewin’s Types of Conflict
Approach-approach: when a person chooses between 2 equally desirable options, creating a positive dilemma where both options seem appealing.
Avoidance-avoidance: when a person chooses between 2 undesirable options, creating a difficult situation where none of the options are appealing.
Approach-avoidance: Options have both positive and negative aspects, making the decision complex because the person is both attracted and repelled by the same goal.
Ghrelin
Hormone that stimulates hunger and increases appetite.
"Hungry gremlin”
Leptin
Hormone that suppresses appetite and signals satiety (satisfied/feeling full) to regulate the body’s weight.
Pituitary Gland
Produces and releases hormones that regulate many bodily functions:
metabolism
reproduction
body growth
body temperature
blood pressure
etc.
Hypothalamus
Lateral: Controls feeding, energy, balance, and motivated behaviors.
Ventromedial: Responsible for appetite suppression and regulating body temperature.
Stomach Contractions Theory:
Our stomach contracts when we’re hungry.
Glucose Theory
Our appetite increases when our blood glucose increases and decreases when our blood glucose decreases.
Set Point Theory
The ventromedial and lateral hypothalamus interact to maintain a set point of body weight, feed intake, or related to metabolic signals.
Our body tries to maintain a specific default weight that our brain has predetermined by regulating our hunger and metabolism.
Sexual Hormones
Regulates arousal and desire.
Human Sexual Response Cycle
Desire
Arousal
Orgasm
Resolution
Sexual Dysfunctions
Difficulties with sexual arousal due to low desire on a physiological aspect.
Paraphilias
Intense sexual arousal from atypical situations, objects, fantasies, behaviors, individuals, or places.
freak
Emotions
Complex mental reactions that can be experienced as strong feelings → shown through facial expressions and body language.
Different elements of emotions:
Physiological arousal - bodily changes
Subjective feelings - personal experience
Cognitive appraisal - interpretation of the situation
Behavioral expression - observable actions
Universally recognized emotions:
Sadness
Joy
Fear
Disgust
Anger
Surprise
Display Rule
How people display their emotions based on their cultural norms, etiquette, and social expectations.
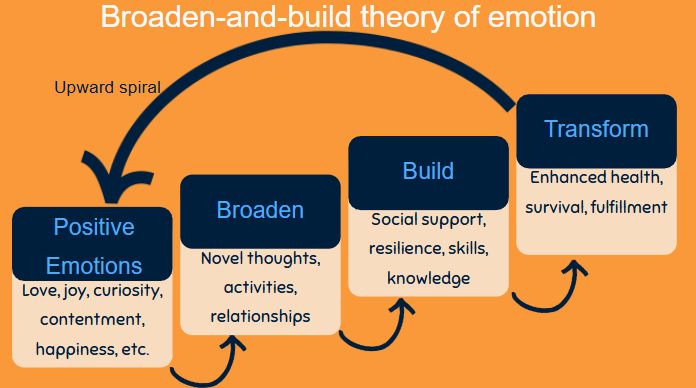
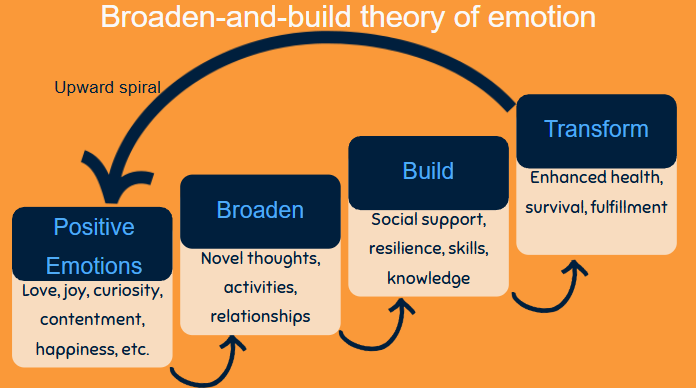
Broaden-and-Build Theory
Positive emotions broaden an individual’s momentary (thought-action supply).
- Makes the world seem more “open”
- Broadens cognition and awareness
- Negative emotions narrow down one’s focus
Facial Feedback Effect
The tendency of facial muscle states to trigger corresponding feelings.
- Experiments have also demonstrated that Botox injections, which paralyze facial muscles, can reduce the intensity of emotions.
- This suggests that facial expressions can play a role in shaping our emotional experiences.
Ex: Smiling can induce feelings of happiness, while frowning may lead to feelings of sadness or displeasure.
Behavior Feedback Effect
The tendency of behavior to influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Ex:
Standing tall with good posture can often make you feel more confident while slouching can make you feel less confident.
Speaking in a cheerful voice can positively influence your mood while speaking in a monotone can make you feel more down.
Talking to yourself with positive affirmations can enhance your motivation and self-esteem.
Projective Tests
Thematic Apperception Tests: Allows people to express their inner feelings and interests by describing/interpreting pictures.
Rorschach Inkblots: Interpreting blot pictures to analyze and identify people’s inner thoughts and feelings.
Locus of Control
How much individuals believe they control their lives.
Incentive Theory
Explains how people are motivated by external rewards and avoid negative outcomes. People are motivated to work harder when their accomplishments are tied to rewards.