Super Mega Uber Cool Awesome DDS Study Set: IE 4
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
In the context of the Biopharmaceutical Classification System, what is the solubility and permeability for each class?
Class 1: High solubility & high permeability
Class 2: Low solubility & high permeability
Class 3: High solubility & low permeability
Class 4: Low solubility & low permeability
What is an advantage of capsules over liquid oral dosage forms, in terms of stability?
Higher chemical stability
Why are _________ usually the dosage form of choice for clinical trials performed using the oral administration route?
Capsules because they are easier to make & they completely hide the active ingredient which helps the study stay double blind
What kind of drugs are not suitable to be filled in capsules?
Drugs that are:
Susceptible to moisture
Interact with gelatin
Hygroscopic or deliquescent (solubilized by environmental moisture)
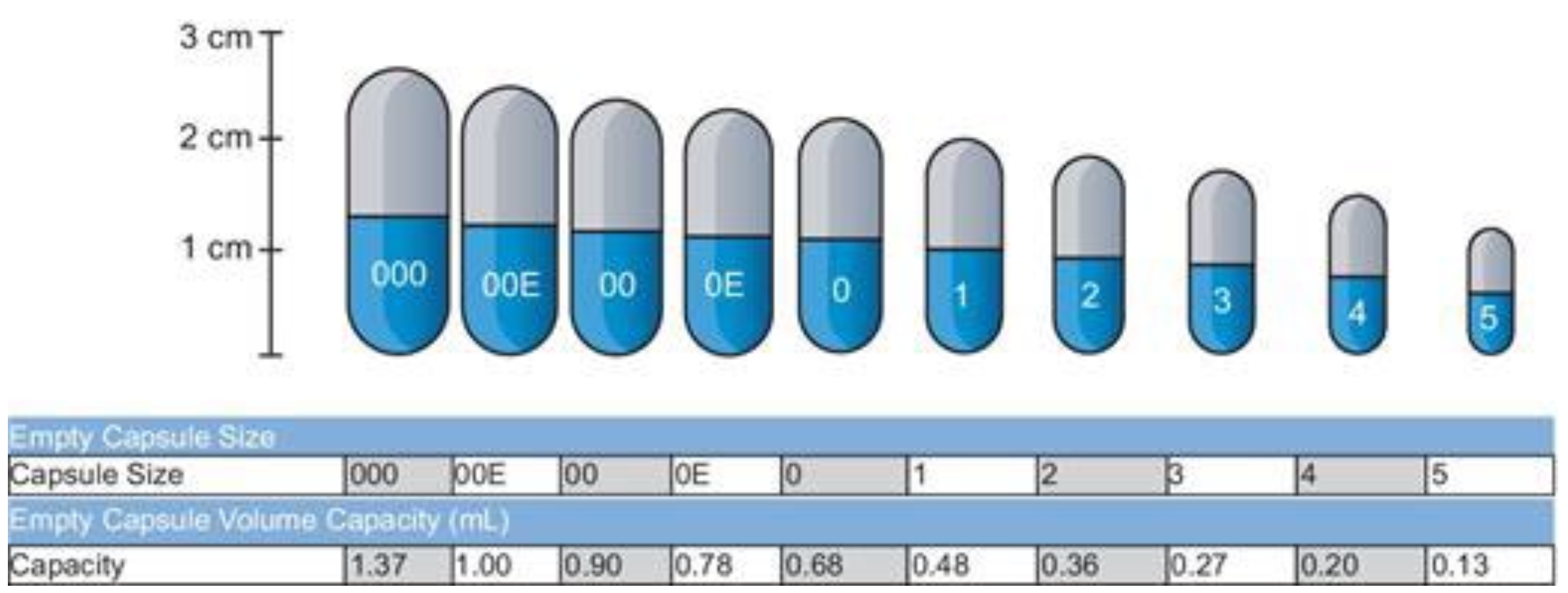
For hard gelatin capsules, what is the smallest and the largest size?
000 is the largest & 5 is the smallest
*see image
What is the disintegration test?
Capsule shell should disintegrate with no core remaining in less than 15 to 30 minutes
What are the Compendial Requirements for capsules?
Disintegration test
Dissolution test
Weight variation
Content Uniformity
Content Labeling Requirement
Stability Testing
Moisture Permeation Test
What is being tested in the moisture permeation test?
The container, not the drug
Are lozenges/troches used for local or systemic effects?
Both
What kind of medications are used when making chewable tablets?
They’re useful for larger doses
Who usually benefits from chewable tablets?
Pediatric
Veterinary

An effervescent tablet begins as a tablet and is intended to turn into a ___________ after broken up.
Solution
Do effervescent tablets require a disintegrant?
Naur
What is the rationale for extended-release dosage forms?
To maintain a steady therapeutic blood concentration, focus on the formulation rather than the drug's physical or pharmacokinetic properties.
Why is there an increase in patient compliance with extended-release dosage forms?
There is a reduction of frequency in dosing
What are some disadvantages with extended-release dosage meds?
Hard to adjust the dose
Takes longer to kick in
Risk of dose dumping (sudden release of the drug)
What kind of lipophilic character is required for passive transdermal drug delivery?
High lipophilicity
What melting point is required for passive transdermal drug delivery?
<250°C
What molecular weight is required for passive transdermal drug delivery?
<500 Da
What Log K is required for passive transdermal drug delivery?
1-5
What kind of water solubility is required for passive transdermal drug delivery?
≈0.05 to 1 mg/mL
What are some disadvantages for transdermal drug delivery?
Possible contact dermatitis
It takes a while for it to kick in
It is only suitable for potent drugs
Sterile products largely constitute products administered via the __________ route.
parenteral
What is the difference between a bactericide and bacteriostatic?
A bactericide will KILL bacteria whereas a bacteriostatic PREVENTS growth go bacteria
What is an antiseptic?
A microorganism inhibitor that halts growth and activity without killing them
Disinfection doesn't completely destroy everything. What does it leave behind?
Usually the spores are not destroyed
What must be absent for something to be sterile?
There must be a complete destruction of microorganisms AND their spore forms
What does USP Chapter 800 cover?
Hazardous drugs
What does USP chapter 795 cover?
Non-sterile preparations
What does USP chapter 797 cover?
Sterile preparations
What is the difference between [Drug] Injection and [Drug] for injection?
[Drug] Injection: Liquid preparations that are drug substances or solutions
thereof
[Drug] for injection: dry solids that, upon the addition of suitable vehicles,
produce a solution for injection
What is considered Low-risk CSP?
Manufactured under ISO5 conditions
Aseptic transfer of sterile products by the manufacturer using sterile equipment for compounding IV admixtures
Does not involve open systems
No more than 3 components
What is considered medium risk CSP?
Similar to Low-risk CSP but with additional criteria:
IV admixture contains more than three components
Lacks antimicrobial preservatives and is administered over more than 2 days
Involves complex preparation
What is considered high risk CSP?
Similar to Low-risk CSP but with additional conditions:
Compounding non-sterile manufactured ingredients followed by terminal sterilization
Compounding conducted in conditions outside ISO5
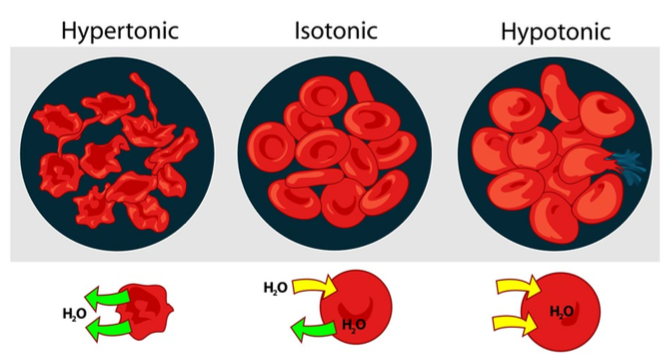
What are the two isotonic solution examples we should know?
Sodium chloride (0.9%), dextrose (5%)
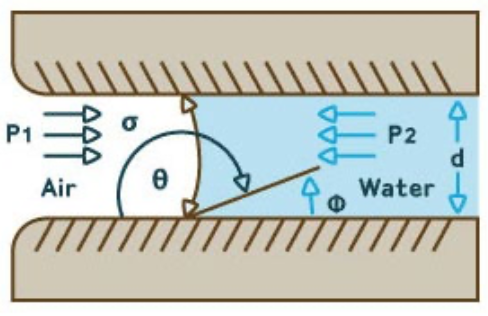
What is the bubble test?
It tests the pore size of microporous filters to check the filter integrity
In the context of secondary engineering controls (SEC), what are the ISO classes needed in their areas?
Direct compounding area (DCA) represents ISO classes 3 or 4
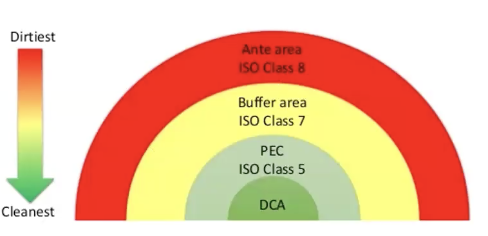
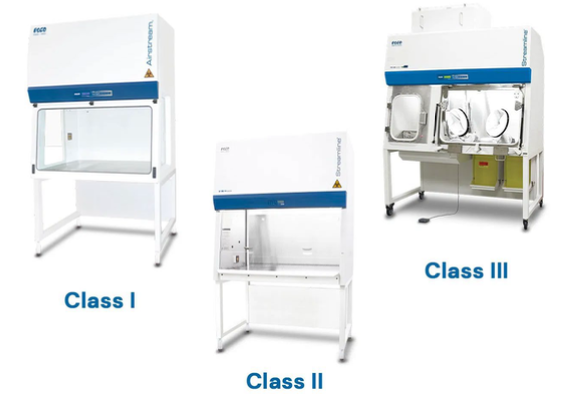
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical laminar flow hoods?
Horizontal: Increased turbulence with large items raises the risk of contaminants blowing into the operator's face
Vertical: Less cross-contamination among items placed in the workspace
Do laminar air flows protect the operator?
Naur, they’re intended to be used to protect the product but the higher classes of biosafety cabinets offer some protection to the operator

What is the relationship between gauge number and the thickness of the needle tip?
The larger the gauge number the thinner the needle
Example: 27 gauge needle finer than 13 gauge needle
What are the charges associated with α and β particles?
α particles: Positive
β particles: Negative
Which charge is more penetrating, α or β particles?
β particles
Which charge is more ionizing, α or β particles?
α particles
Are α particles dangerous to humans?
They are extremely harmful and can cause damage to the DNA BUT they cannot penetrate the outer layer of the skin so if the particle is outside the skin you’re fine
Which scan results in better contrast and spatial resolution, PET or SPECT scans?
PET
What is the most common route of administration for radioimmunotherapy?
Intravenous but sometimes oral is done too
Can we use γ rays for targeted radiotherapy?
FUCK NO, they’re used for imaging ❤
Is the EPR mechanism applicable to small molecules?
Naur, only large ones
Does endocytosis require energy?
Yeth
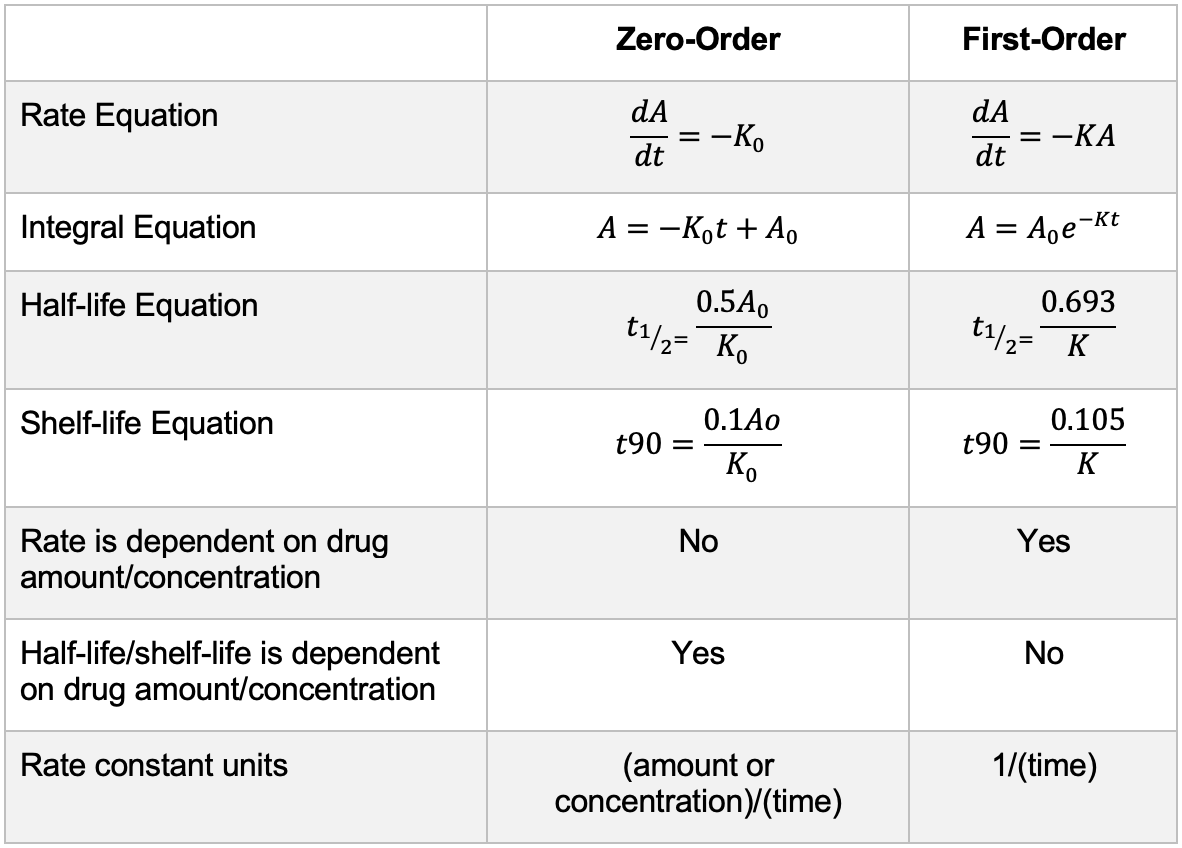
For a zero-order reaction: a ________ line is obtained when amount of drug versus time is plotted on a linear graph
Straight
*not graphing the log concentration
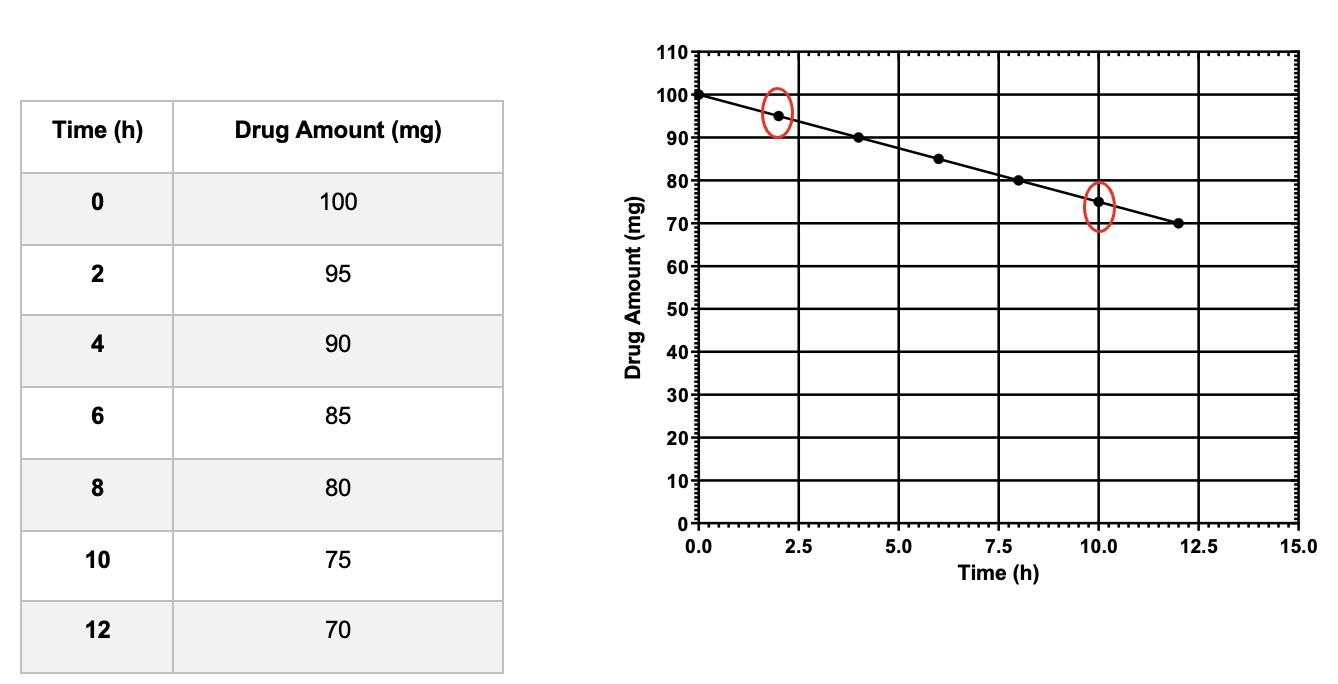
Describe the relationship with concentration for the zero order and the first order reactions.
Zero Order: Rate of a reaction is independent of the concentration or the amount of the drug
First Order: Rate of a reaction is proportional to the amount or concentration of the drug
For a first-order reaction: when the _____________________of a drug versus time is plotted on a linear graph, a straight downwards line is obtained.
Log of amount or concentration
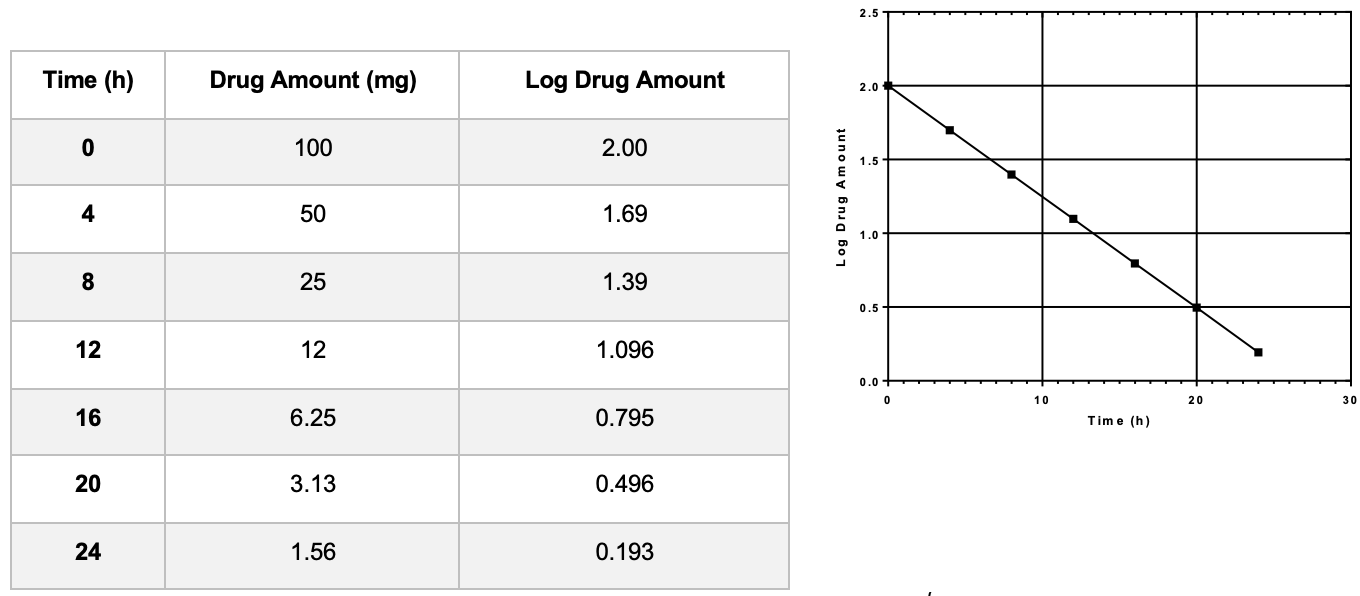
What are the differences in equations for zero order and first order?
See image