LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Lymph
Tissue fluid (interstitial fluid) that enters the lymphatic vessels
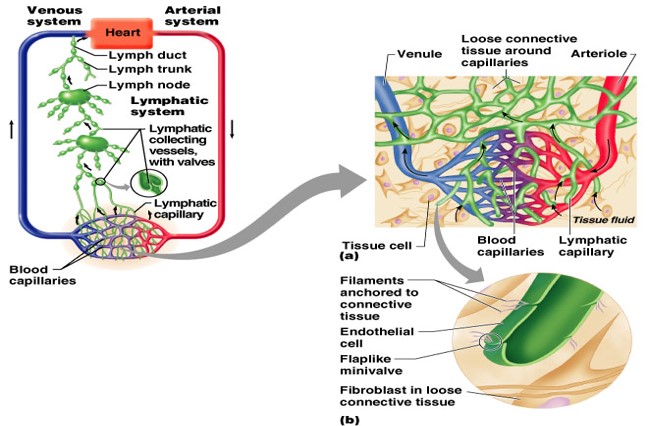
- Essentially a drainage system accessory to venous system
- Larger particles that escape into tissue fluid can only be removed via lymphatic system
Functions
- Network that filters antigens from the interstitial fluid
- Primary site of immune response from tissue antigens
- Lymphatic drainage in all organs of the body except brain, eyes, marrow and cartilage
- Flaccid thin walled channels → progressive caliber
- 600 lymph nodes in body
- Slow flow, low pressure system returns interstitial fluid to the blood system
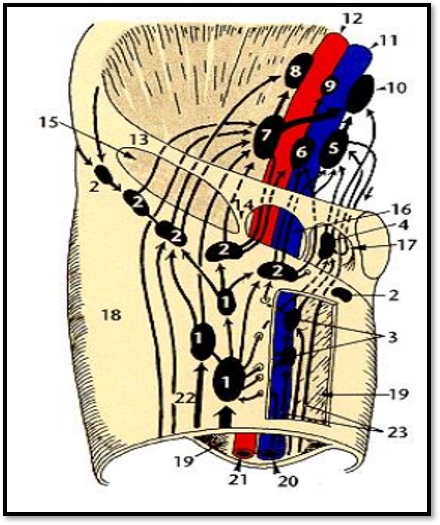
Components of lymphatics
Lymph
Lymphatic Vessels
Lymphatic Organs
Lymphatic cells
 Lymphatic Capillaries
Lymphatic Capillaries
Features of structure:
Blind end
Single layer of overlapping endothelial cells
More permeable than that of blood capillary
Absent from avascular structures, brain, spinal cord splenic pulp and bone marrow

Lymphatic Vessels
- Three layered wall but thinner than vein
- More numerous valves than in vein
- Interposed by lymph nodes at intervals
- Arranged in superficial and deep sets
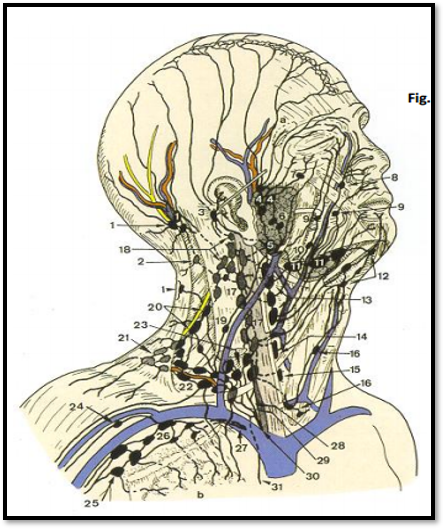
Lymph Trunks
- Right and left jugular trunks
- Right and left subclavian trunks
- Right and left broncho mediastinal trunk
- Right and left lumbar trunks
- Intestinal trunk
Lymphatic Ducts
Right lymphatic duct
Thoracic duct

Lymphatic Cells
- Also called lymphoid cells
- Located in both the lymphatic system and the cardiovascular system.
- Work together to elicit an immune response.
Types of lymphatic cells are:
- Macrophages
- Epithelial cells
- Dendritic cells
- Lymphocytes
Lymphatic Organs
- Primary organs
- Red bone marrow
- Thymus gland
- Secondary organs
- Lymph nodes
- Lymph nodules
- Spleen
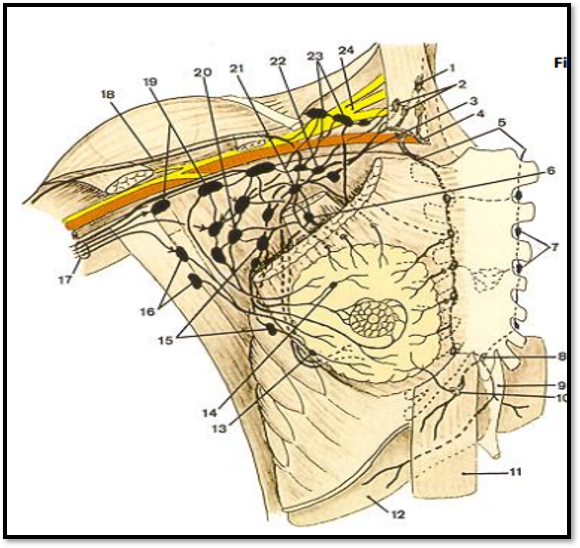
Lymph nodes:
Capsular shell
Fibroblasts and reticulin fibers
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
T cells
B cells

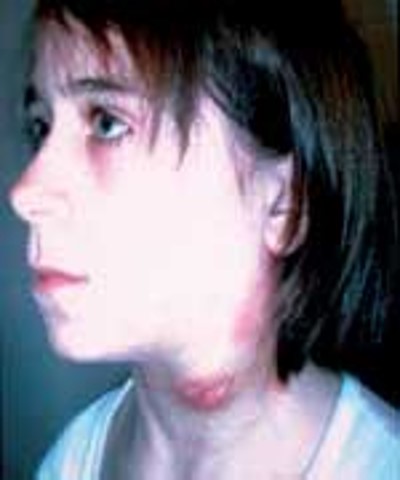
Lymphangitis
Inflammation of the lymph vessels
Commonest cause bacteria called streptococcus pyogenes(most common).
Lymph vessels appear as red streaks through the skin
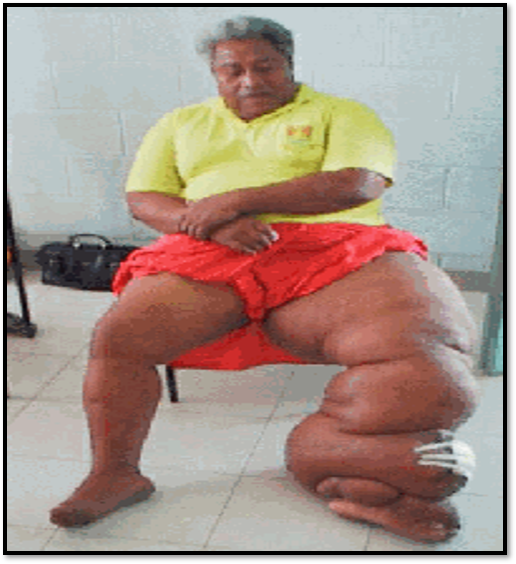

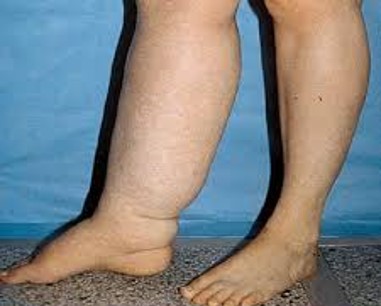
Lymphedema
Occurs due to accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the interstitial tissue
Sometimes can be appreciated after wearing tight clothing or jewelry on affected limb
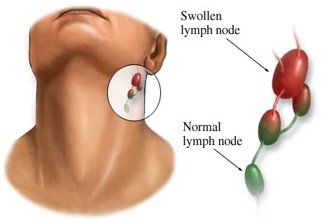
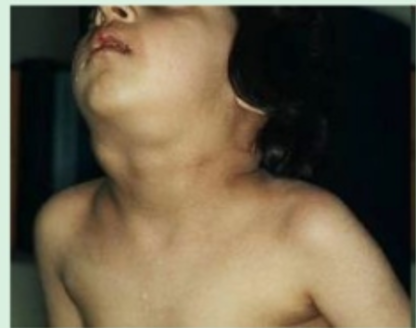
Lymphadenopathy
Means a disease of the lymph nodes
Lymph nodes become swollen/ enlarged and may be painful to touch
Lymphomas
Cancers originating either from the lymphocytes in the lymph nodes or the lymphatic tissue in organs
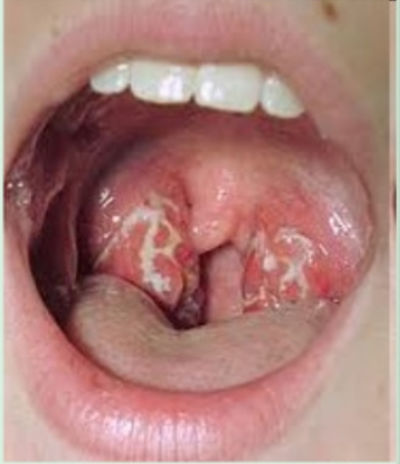
Tonsillitis
Infection of the pharyngeal tonsils
Tonsils are swollen, Fever and pain during swallowing usually present