Chapter 8 - Monopoly, oligopoly & monopolistic competition
Imperfect competition
Price setter: firm with at least some latitude to set its own price.
Pure monopoly: the only supplier of a unique product with no close substitutes.
Monopolistic competition: industry structure in which a large number of firms produce slightly differentiated products that are reasonably close substitutes for one another.
Oligopoly: industry structure in which a small number of large firms produce products that are either close or perfect substitutes.
5 sources of market power
- Market power: firm's ability to raise the price of a good without losing all its sales.
- Exclusive control over important inputs
- Patents and copyrights
- Government licenses or franchises
- Economies of scale and natural monopolies
- Constant returns to scale: production process is said to have constant returns to scale if, when all inputs are changed by a given proportion, output changes by the same proportion.
- Increasing returns to scale = economies of scale: production process is said to have increasing returns to scale if, when all inputs are changed by a given proportion, output changes by more than that proportion.
- Natural monopoly: monopoly that results from economies of scale (increasing returns to scale).
- Network economies
Profit maximization for the monopolist
Marginal revenue: change in a firm's total revenue that results from a one-unit change in output.
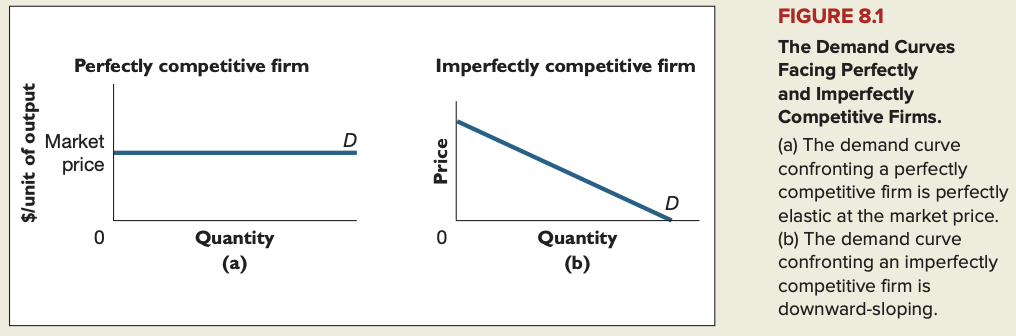
Both the perfectly competitive firm and the monopolist maximize profit by choosing the output level at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. But whereas marginal revenue equals the market price for the perfectly competitive firm, it is always less than the market price for the monopolist. A monopolist will earn an economic profit only if price exceeds average total cost at the profit-maximizing level of output.
Using discounts to expand the market
Price discrimination: practice of charging different buyers different prices for essentially the same good/service.
Perfectly discriminating monopolist: firm that charges each buyer exactly his/her reservation price.
Hurdle method of price discrimination: practice by which a seller offers a discount to all buyers who overcome some obstacle.
Perfect hurdle: threshold that completely segregates buyers whose reservation prices lie above it from others whose reservation prices lie below it, imposing no cost on those who jump the hurdle.