6.1-6.4: Electrolysis
Electrolysis is the break down of an ionic compound when in molten or in aqueous form by the passage of electricity
- When an electric current is passed through a molten ionic compound the compound decomposes or breaks down
- The process also occurs for aqueous solutions of ionic compounds
- Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity hence they do not undergo electrolysis
- Ionic compounds in the solid state cannot conduct electricity either since they have no free ions or electrons that can move and carry charge
- this happens in molten or aqueous solutions or substances
- Ionic substances don’t conduct when solid but do conduct when melted or dissolved. They break down at the same time.
- Molecular substances are non conductors because they contain no free electrons or charger particles that can flow through them
Definitions
Electrode is a rod of metal or graphite through which an electric current flows into or out of an electrolyte
Electrolyte is the ionic compound in molten or dissolved solution that conducts the electricity
Anode is the positive electrode of an electrolysis cell
Anion is a negatively charged ion which is attracted to the anode
Cathode is the negative electrode of an electrolysis cell
Cation is a positively charged ion which is attracted to the cathode
The only solids that conduct are the metals and graphite
Any liquid that contains ions will conduct electricity - principal of electrolysis
remember: P A N I C
%%Positive is Anode Negative is Cathode%%
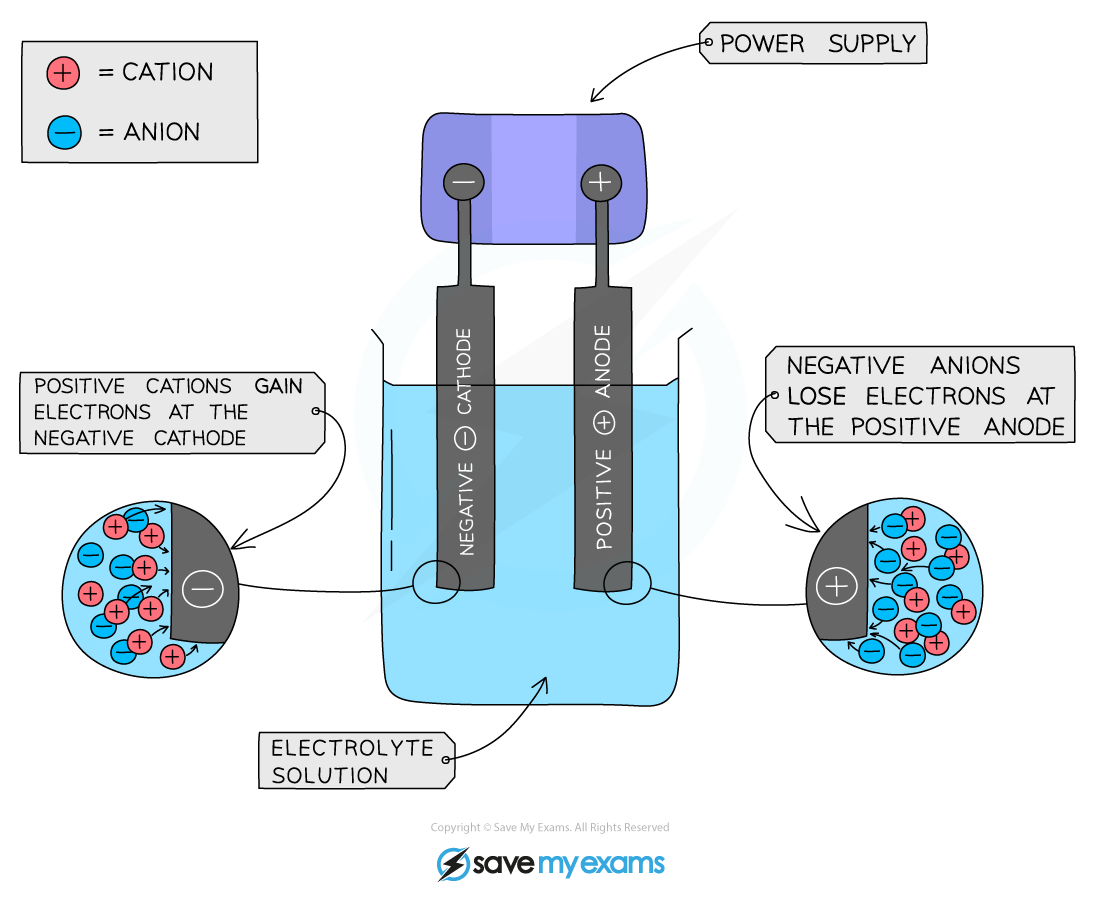
Positive electrode (anode)
- Non-metal ions (other than hydrogen) are attracted to the positive electrode
- Non-metal ions will lose electrons to form the non-metal
- The product formed depends on which ion loses electrons more readily, with the more reactive ion remaining in solution
Negative electrode (cathode)
- H+ and metal ions attracted to the negative electrode but only one will gain electrons
- Either hydrogen or metal will be produced
If the metal is above hydrogen in reactivity series, then hydrogen will be produced and bubbling will be seen at the cathode
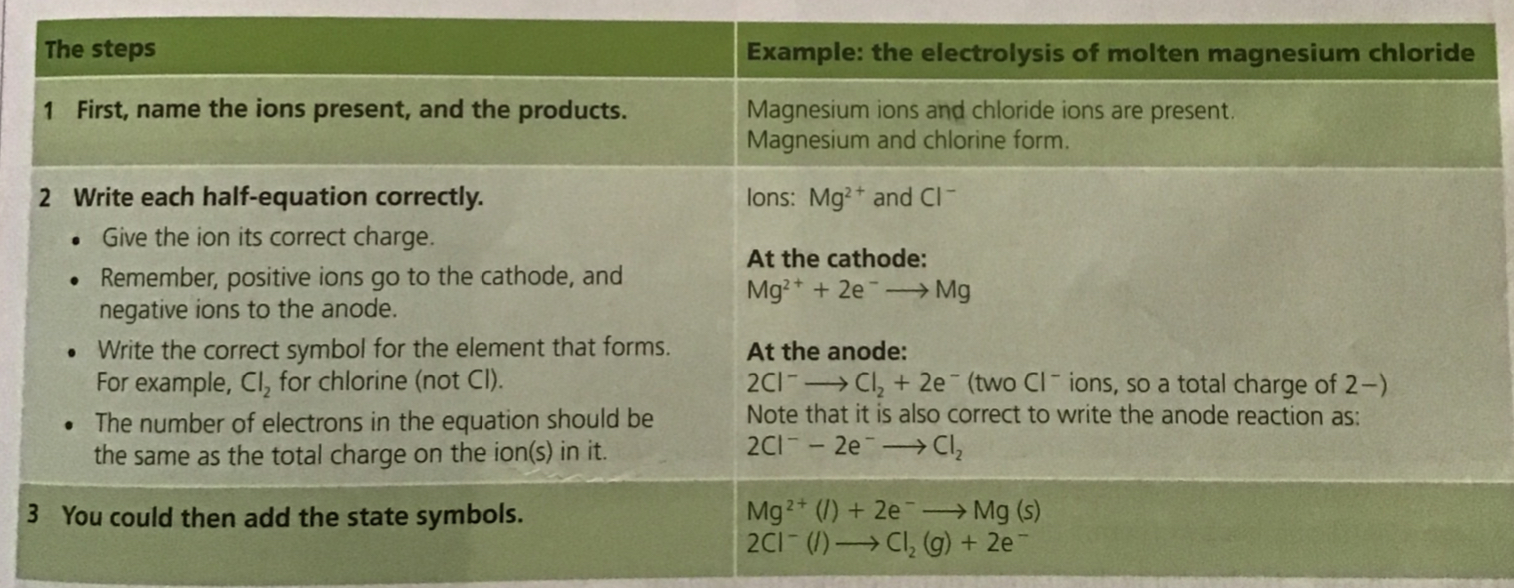
Example of lead (II) bromide
Method:
Add lead(II) bromide into a beaker and heat so it will turn molten, allowing ions to be free to move and conduct an electric charge
Add two graphite rods as the electrodes and connect this to a power pack or battery
Turn on power pack or battery and allow electrolysis to take place
Negative bromide ions move to the positive electrode (anode) and each loses one electron to form bromine molecules. There is bubbling at the anode as brown bromine gas is given off
Positive lead ions move to the negative electrode (cathode) and gain electrons to form a grey lead metal which deposits on the surface of the electrode


Determining what gas is formed:
- If the gas produced at the cathode burns with a 'pop' when a sample is lit with a lighted splint then the gas is hydrogen
- If the gas produced at the anode relights a glowing splint dipped into a sample of the gas then the gas is oxygen
The halogen gases all produce their own colours (bromine is red-brown, chlorine is yellow-green and fluorine is paleyellow)
Positive electrode
- Negatively charged OH– ions and non-metal ions are attracted to the positive electrode
- If halide ions (Cl-, Br-, I-) and OH- are present then the halide ion is discharged at the anode, gains electrons and forms a halogen (chlorine, bromine or iodine)
- If no halide ions are present, then OH- is discharged at the anode, gains electrons and forms oxygen gas
- In both cases the other negative ion remains in solution
- The concentration of the solution also affects which ion is discharged:
- If a concentrated halide solution is being electrolysed, the halogen forms at the anode
- If a dilute halide solution is being electrolysed, oxygen is formed
- For example:
- For a concentrated solution of barium chloride, the Cl-ions are discharged more readily than the OH- ions, so chlorine gas is produced at the anode
- If the solution is dilute however only the OH- ion is discharged and so oxygen would be formed
Negative Electrode
Positively charged H+ and metal ions are attracted to the negative electrode but only one will gain electrons
Either hydrogen gas or metal will be produced
If the metal is above hydrogen in the reactivity series, then hydrogen will be produced and bubbling will be seen at the cathode
This is because the more reactive ions will remain in the solution, causing the least reactive ion to be discharged
Therefore, at the cathode, hydrogen gas will be produced unless the positive ions from the ionic compound are less reactive than hydrogen, in which case the metal is produced


The reactions at the electrodes and electroplating
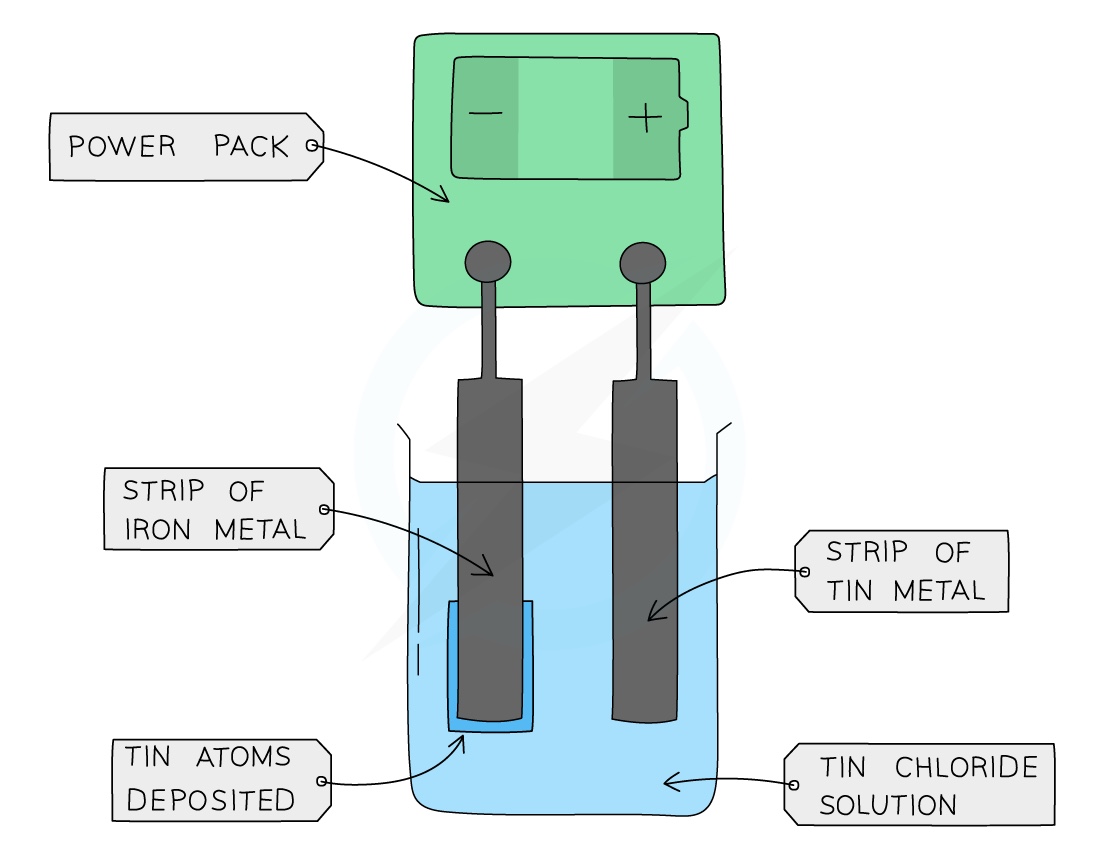
Electroplating
Electroplating is a process where the surface of one metal is coated with a layer of a different metal
The anode is made from the pure metal you want to coat your object with
The cathode is the object to be electroplated
The electrolyte is an aqueous solution of a soluble salt of the pure metal at the anode
Uses of Electroplating
- Electroplating is done to make metals more resistant to corrosion or damage
- e.g, chromium and nickel plating
It is also done to improve the appearance of metals,
- e.g. coating cutlery and jewellery with silver
Electroplating
Electroplating means using electricity to coat one metal with another, to make it look better, or to prevent corrosion. For example, steel car bumpers are coated with chromium, Steel cans are coated with tin to make tins for food, and cheap metal jewellery is often coated with silver.
The drawing on the right shows how to electroplate a steel jug with silver. The jug is used as the cathode. The anode is made of silver.
The electrolyte is a solution of a soluble silver compound, such as silver nitrate. At the anode The silver dissolves, forming silver ions in

Conductors and Insulators
Conductors of electricity allow electrical charge to pass through them easily
Conductors can be:
- Solids such as metals or graphite
- Liquids such as molten lead bromide or molten metals
- Solutions such as sodium chloride solution
Copper is used extensively in electrical wiring as it is an excellent conductor and is malleable and easy to work with
Aluminium is used in overhead cables which are reinforced with a steel core
The steel core provides extra strength and prevents the cable from breaking under its own weight
Although not as good a conductor as copper, aluminium is less dense and cheaper than copper
Insulators
- Insulators resist the flow of electricity and do not conduct
- Most insulators are solids of plastic, rubber or ceramic
- Plastics are used as insulators and are placed around electrical wiring and for some tool and machine handles
- Ceramics are used in very high voltage lines where contact between the power line and the metal of the pylon would be dangerous
Industrial Application of Electrolysis
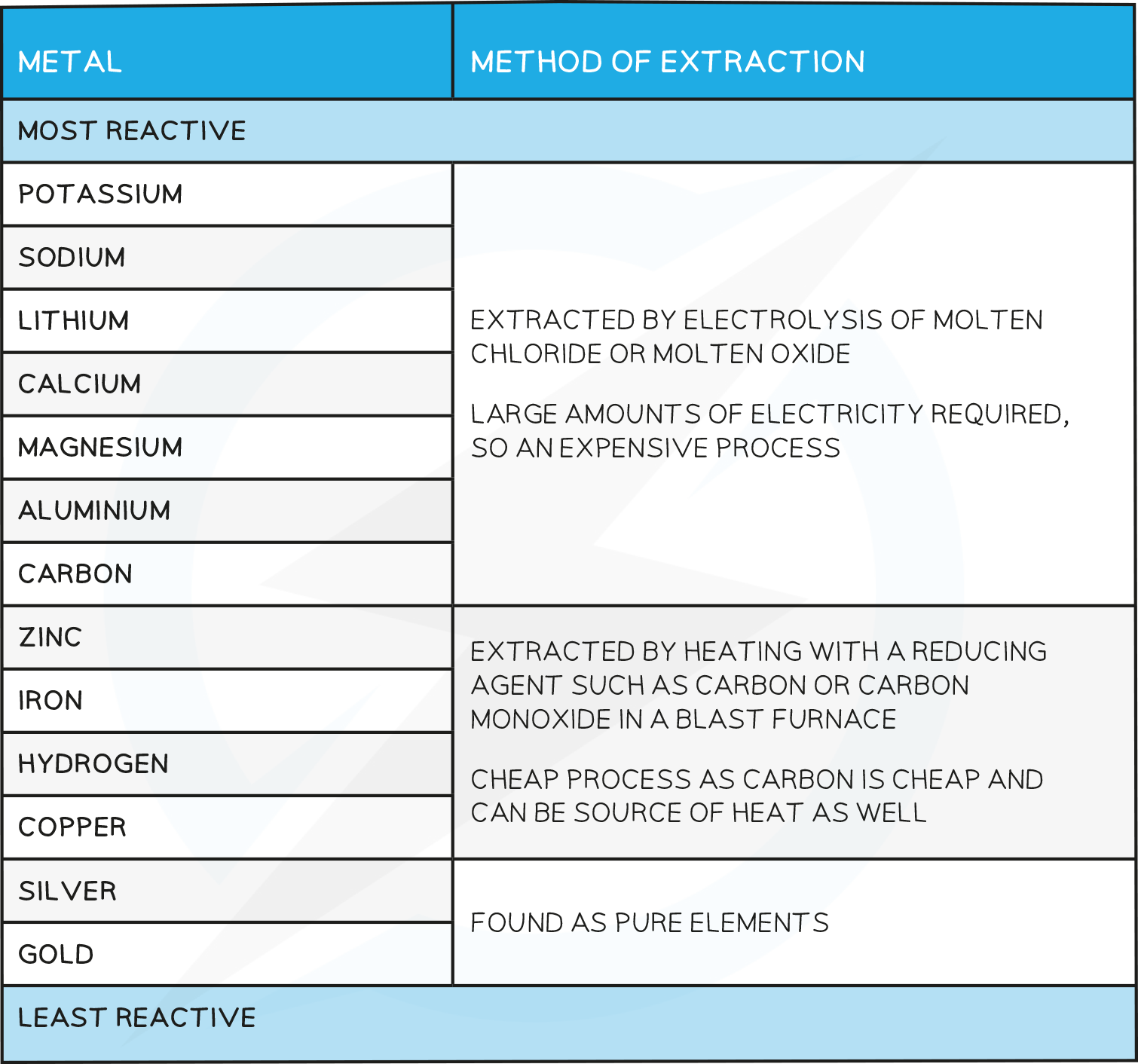
Extraction of Aluminum
The Earth’s Crust contains metals and metal compounds such as gold, iron oxide and aluminium oxide
To be useful, the more reactive metals have to be extractedfrom their ore through processes such as electrolysis, using a blast furnace or by reacting with more reactive material
Metals which lie above carbon have to be extracted by electrolysis as they are too reactive to economically be extracted by displacement
Material obtained is : Aluminum ore Bauxite
The bauxite is first purified to produce aluminium oxide Al2O3
%%Aluminium oxide has a very high melting point so it is first dissolved in molten cryolite producing an electrolyte with a lower melting point, as well as a better conductor of electricity than molten aluminium oxide. This also reduces expense considerably%%
@@The electrolyte is a mixture of aluminium oxide in molten cryolite at a temperature of about 1000 °C@@. The molten aluminium is siphoned off from time to time and fresh aluminium oxide is added to the cell. ^^The cell operates at 5-6 volts and with a current of 100,000 amps. The heat^^ generated by the huge current keeps the electrolyte molten
A lot of electricity is required for this process of ==extraction which is very expensive==

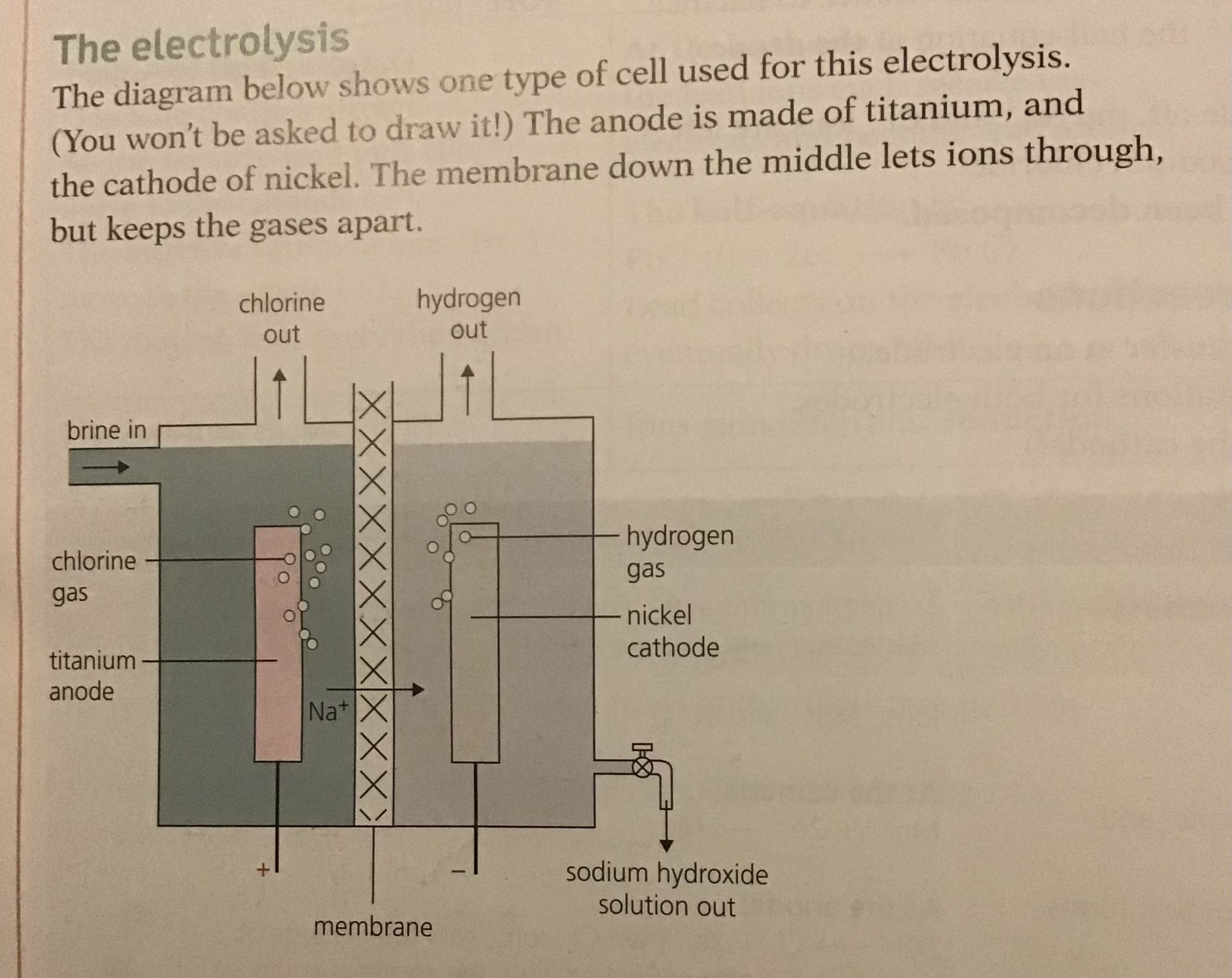
Manufacture of Hydrogen, Chlorine and Sodium hydroxide
Brine is a concentrated Solution of Sodium Chloride or common salt. It can be obtained by pumping water into salt mines to dissolve the salt, or by evaporating seawater.
May not sound exciting but from it we get chemicals needed for thousands of products we use every day. when it undergoes electrolysis the over all reaction is
2NaCl (aq) + 2H20 (l) ———> 2NaOH (aq) + Cl2 (g) + H2 (g) \n
When electrolysed it produces chlorine and hydrogen at the electrodes leaving behind sodium hydroxide solution
These substances all have important industrial uses:
- Chlorine is used to make bleach
- Hydrogen is used to make margarine
- Sodium hydroxide is used to make soap and detergents
The electrolyte is concentrated sodium chloride which contains the following ions: Na+, H+, Cl- and OH-

\n
\n
\n
\n
\n \n