Joslyn Roberts - Parts of Speech: Gr. 9 Grammar
Get your Grammar
Game on…
Grammar & Sentence Fluency for Grade 9
Why do we study and practice grammar?
Being able to communicate clearly and effectively is an essential skill, and proper use of standard English conventions helps ensure that what you write can be clearly understood. This unit will review some of what you already know about sentence structure and grammar, and will provide new information and practice to make you even stronger writers. The topics in this unit relate directly to the following Massachusetts education standards.
Massachusetts ELA Standards: Conventions of Standard English Grades 9-10
1. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking; retain and further develop language skills learned in previous grades.
a. Manipulate and rearrange clauses and phrases in sentences, paying attention to agreements of pronouns and their antecedents, logical use of verb tenses, and variety in sentence patterns.
b. Use various types of phrases (noun, verb, adjectival, participial, prepositional) and clauses (independent, dependent, noun, relative, adverbial) to convey specific meanings and add variety and interest to writing or presentations.
c. Use parallel structure as a technique for creating coherence in sentences, paragraphs, and larger pieces of writing.
2. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing.
a. Use a semicolon (and perhaps a conjunctive adverb) to link two or more closely related independent clauses.
b. Use a colon to introduce a list or quotation.
c. Spell correctly, recognizing that some words have commonly accepted variations (e.g., catalog/catalogue).
By the end of this unit, students will
* understand the function of various types of words
* understand how words are joined to make phrases and clauses
* understand the differences between types of phrases and types of clauses
* be able to identify the elements in the 5 basic sentence patterns
* be able to identify types of phrases, clauses, and sentences
* know and apply grammar rules related to spelling, capitalization, and punctuation (mechanics)
* write using proper sentence structure and mechanics
Words and their functions…
parts of speech
The Eights Parts of Speech
| Words that identify objects, ideas, actions, or state of being | Words that modify or describe | Words that show connection, relation, or emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Nouns | Adjectives | Conjunctions |
| Pronouns | Prepositions | |
| Verbs | Adverbs | Interjections |
What do you remember about the parts of speech? Try this interactive activity at Grammar Bytes: Grammar Bytes: Parts of Speech 1
Now review some information about parts of speech.
Check out this video for a catchy review and this one for a good review of each part of speech with examples.
| Nouns Capitalize proper nouns | Definition: A noun is a word that names a person, place, a thing, or an ideacommon nouns: ordinary, everyday words (bell, whistle, chair)proper nouns: identify specific people, places or times. Proper nouns are capitalized. (Dedham, White House, Dedham High School, Charles River)concrete nouns: identify specific, perceptible objects (box, boat, tree)abstract nouns: identify ideas, concepts or emotions (love, liberty, happiness)singular nouns: one thingplural nouns: multiple things**to form a plural noun add s to singular noun not ending in s (1 book, 3 books)**add es to singular nouns ending in s (1 class, many classes)**change the y to an i and add es to words ending in y (1 pony, 6 ponies) |
|---|---|
| Pronouns take the place of a noun | Definition: words that take the place of a noun (boy - he, him, his)subject: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they (I run, he runs, they sing)object: me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them (to him, for her, with me)possessive: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, yours, theirs (they are mine, is that yours?)interrogative: who, which, what (Who is it? What is that?)relative: who, which, what, that (the teacher, who studied in England; the cat that ate my dinner)demonstrative: this, that, these, those (give me that, these are delicious) |
| adjectives | Definition: modify a noundescriptive: describe a noun (beautiful flowers, tall trees)demonstrative: this, that, these, those (this book, those students)possessive: my, our, your, his, her, its, their (my home, its engine, her friend) |
| Articles are a type of adjective:the, a, an | Definition: a type of adjective that identifies which onedefinite (a specific reference): the (the book, the car)indefinite ( a non-specific reference): a or an (for words beginning with a vowel) (an apple, a cookie) |
| verbs | Definition: show action or state of beingInfinitive form: “to” form of a verb (to laugh, to be, to need)action verbs: show action (to run, to sing, to study)linking verbs: used to show state of being – what something is or what something is like (to be – am, is, are, was were, will be) (Mrs. Rocha is a teacher. They will be graduates. Betty is talented.)auxiliary verbs: helping verbs which form different verb tenses (had been singing, will run, did eat)modals: slightly change the meaning of the verb so that the action is not necessarily being done, but is being contemplated or is a possibility (can, should, would, may, might, must) (I study, I can study, I should study, I might study) |
| Adverbs modify verbs | Definition: modifies a verb (runs quickly); modifies an adjective (she is very beautiful); modifies an adverb (they jumped quite excitedly)show time, frequency, manner |
| prepositions | Definition: shows the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word in the sentence; are part of a prepositional phrase that includes the preposition, a noun or pronoun that is the object of the preposition, and any adjectives that describe the object; prepositional phrases act as adjectives or adverbs in a sentence.A preposition shows direction, place, time, cause, manner, or amount.Parts of a Prepositional Phrasebeneath the hardened lava(preposition) (modifiers) (object of the preposition)toward a brighter future(preposition) (modifiers) (object of the preposition)Examples of prepositions: aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, as, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, by, concerning, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, onto, opposite, out, outside, over, past, pending, regarding, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, unto, up, upon, with, within, withoutSample prepositional phrases: behind the big, red barn; across the busy street; against the stockade fence, to my favorite actress |
| Conjunctions a joining word | Definition: connect words, phrases, or clausesCoordinating conjunctions connect equal ideas: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So (FANBOYS)Subordinating conjunctions connect ideas giving one more importance: examples- after, although, as (if), because, before, if, since, unless, until, when(ever), whereas, whilecorrelative pairs: conjunctions that are used together**I like both cake and ice cream**I like neither cake nor ice cream**I like either cake or ice cream**I like not only cake but also ice cream |
| interjections | Definition: word or phrase that expresses emotion or exclamation. An interjection has no grammatical connection to other words.ExamplesOh, I didn’t know he had three eyes.Whew, it’s hot in this classroom.Ouch! That hurt. |
| More Practice | Parts-of-speech test - Grammar MonsterOnline Writing Lab (OWL): Prepositions |
Creative practice…
**Look at the picture in each photo box.**Write at least two examples of each part of speech related for each photo
Example
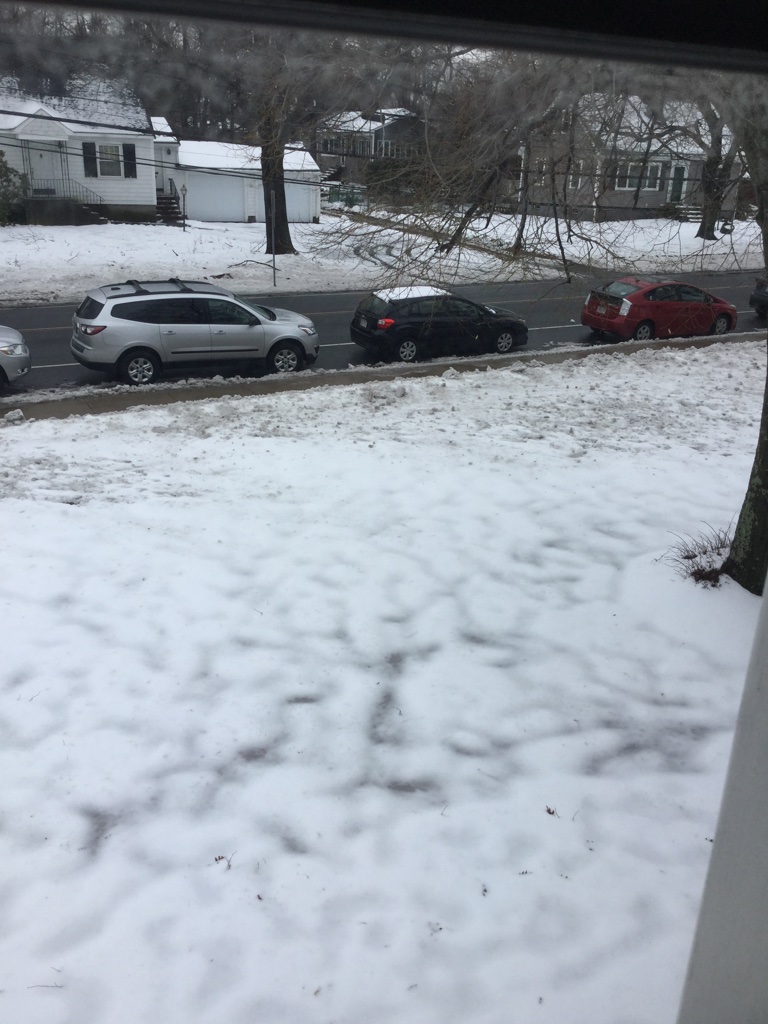 | noun: snow, cars, housepronoun: They are parked. It is cold.adjective: The cold, white snow.verb: The cars drove by. The snow covers the ground. The snow is wet.adverb: The cars drive slowly. The snow fell heavily.preposition: The cars are near the sidewalk. The house across the streetconjunction: The snow and the house are white. The street is bare since the town plowed.interjection: Wow! It is cold! Danger! The ice is slippery. |
|---|
| Photo | Examples related to the photo |
|---|---|
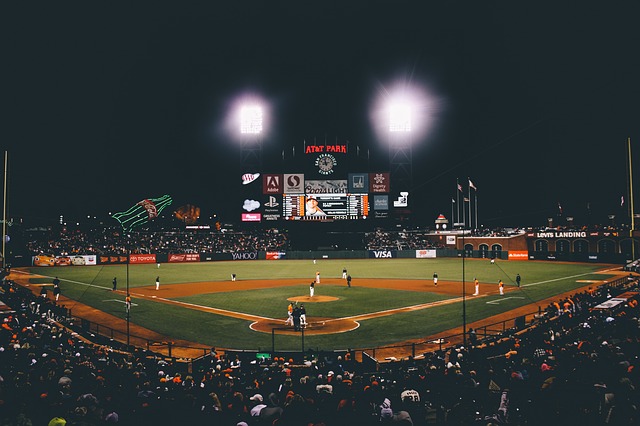 | nounpronounadjectiveverbadverbprepositionconjunctioninterjection |
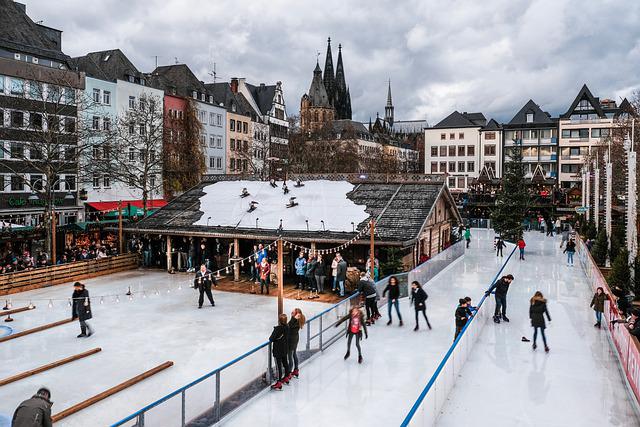 | noun pronoun adjective Adverbverbprepositionconjunctioninterjection |
Test yourself again.
Grammar Bytes: Parts of Speech 2
Grammar Bytes: Parts of Speech 3
Have you improved?