chapter 1: a&p (introduction)
what is anatomy?
- scientific study of structures
Gross Anatomy: study of larger structures
(ex: brain)
- Regional Anatomy: study of interrelationships of structures in a specific region
- Systemic Anatomy: study of structures that create a body system
- Surface Anatomy: understanding internal structures based on their relationship to overlying skin
Microscopic Anatomy: study of structures not observable to the human eye
(ex: nervous tissue)
- Cytology: study of cells
- Histology: study of tissues
- Embryology: study of developmental changes BEFORE birth
what is physiology?
- chemistry & physics of body structures & how they function to SUPPORT life
(example:
Renal Physiology: Kidney Function
Cardiovascular Physiology: Heart & Blood Vessels
Neurophysiology: Brain Function
Exercise Physiology: Responses and adaptation to physical exercise)
Homeostasis: state of steady internal conditions
(ex: BPM, Temperature, BP)
* FORM FOLLOWS FUNCTION *
Organization of Life:
Chemical (Atoms: H) → Molecules (H20) → Cellular → Tissue → Organ Level → Organ System → Organismal
Cell: smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism
Tissue: group of similar or physically interacting cells that form a specific function
Organ: anatomical feature compose of multiple tissue types
Organ System: groups of organs that must work together to maintain homeostasis
Organism: an independent living being with cellular structure
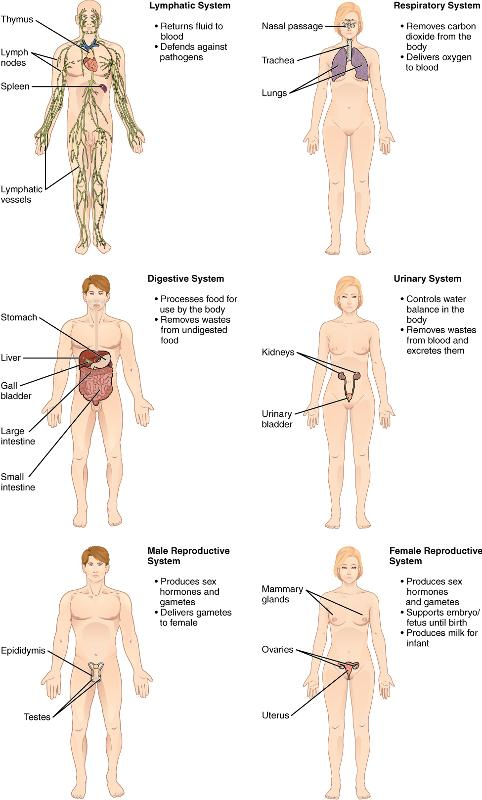
Integumentary System:
- encloses internal body structures
- site of many sensory receptors
Skeletal System:
- supports the body
- enables movement (with muscular system)
Muscular System:
- enables movement (with skeletal system)
- helps maintain body temperature
Nervous System:
- detects & processes sensory information
- activates bodily responses
Body Systems:
- Function & Label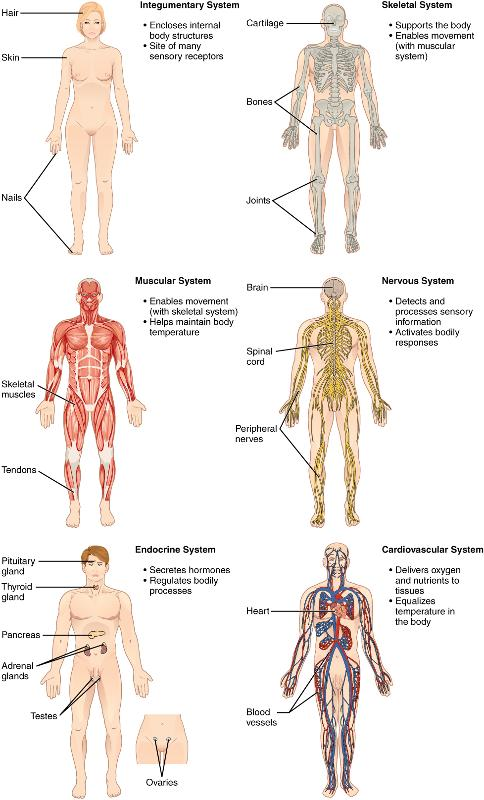
FUNCTIONS of Life: processes fueled by requirements
- Organization: separate compartments to promote function
- maintaining boundaries
- Metabolism: reactions to generate or use fuel
catabolism: breaks down molecules
anabolism: builds new molecules
cellular respiration: glucose & O2 → ATP
digestion: break down food & make it absorbable & absorb nutrient
excretion: remove waste
- Responsiveness: adjust to changes in the environment
withdrawal reflex & sense stimulus change in environment & react to them
- Movement: motion
digestive
heart pumping blood circulatory
+ (additionally)
- Reproduction →
- Development → Zygote (Sperm Cells)
- Growth →
REQUIREMENTS for Life: necessary to live
- Oxygen: key component of metabolic reactions to create ATP
- Nutrients: substances consumed that are essential to survival
Macronutrients: (large amt.) protein, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids
Micronutrients: (small amt.) vitamins (organic molecules), (carbon base)
Minerals: (inorganic)
H2O
- Temperature: narrow range supports homeostasis
⬇ temp ⬆ reaction time
⬆ temp ⬇ reaction time
- Atmospheric Pressure: force exerted by gases around Earth
any pressure applied onto another substance through force
ratio of gas
scuba diving (nitrogen in tissue & expand)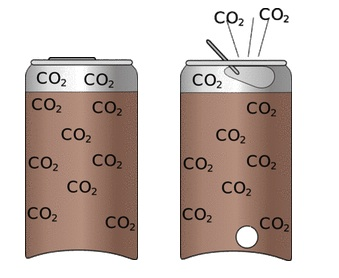
Homeostasis
- Set Point: physiological value that normal range fluctuates around
- Normal Range: restricted values around set point that is healthy and stable
Negative Feedback Loop
➡ achieve homeostasis
1. Input: stimulus senses by body, internal (ex: bright light)
2. Receptor: sensing (senses change) (ex: light) = sensor
⬇ afferent pathway
3. Control Center: integrates stimuli & takes in all stimuli / context of what you know (brain) (ex: snow = cold)
⬇ efferent pathway
4. Output: command
5. Response: any action by an effector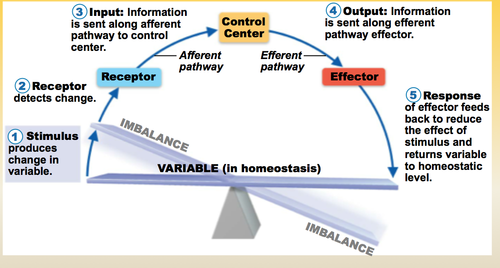
Positive Feedback Loop
➡ in direction & make input stronger to elicit stronger response
➡ for an extreme response
1. Blood Loss
2. Recruit Platelets
3. Make Clot
4. Bring More Platelets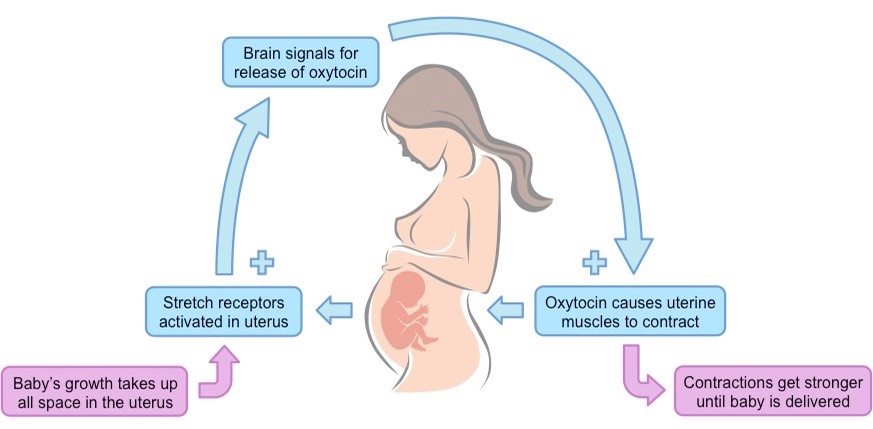
Body Regions
- axial: (body, head, neck, trunk) (superior/inferior)
- appendicular (limbs, arms, legs) (proximal/distal) 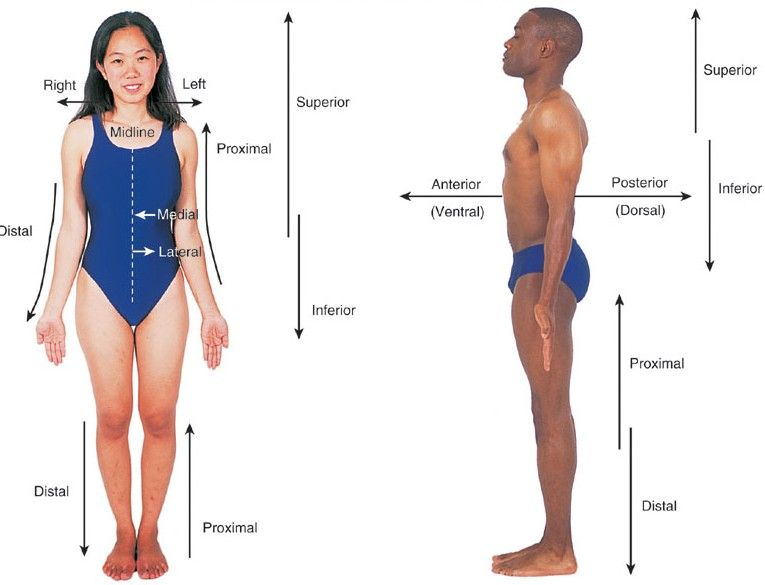
Anatomical Position & Regional Terms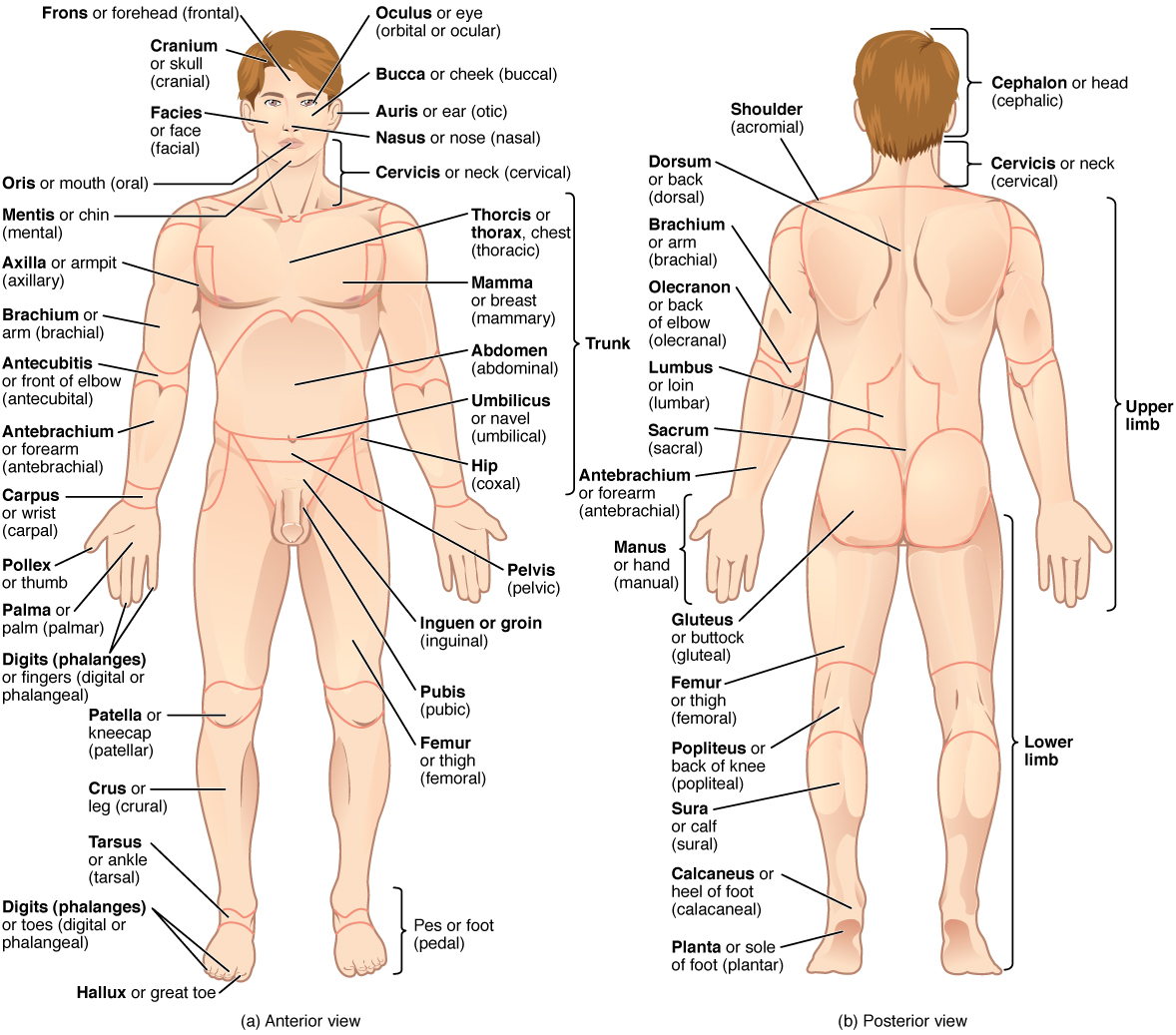
Body Planes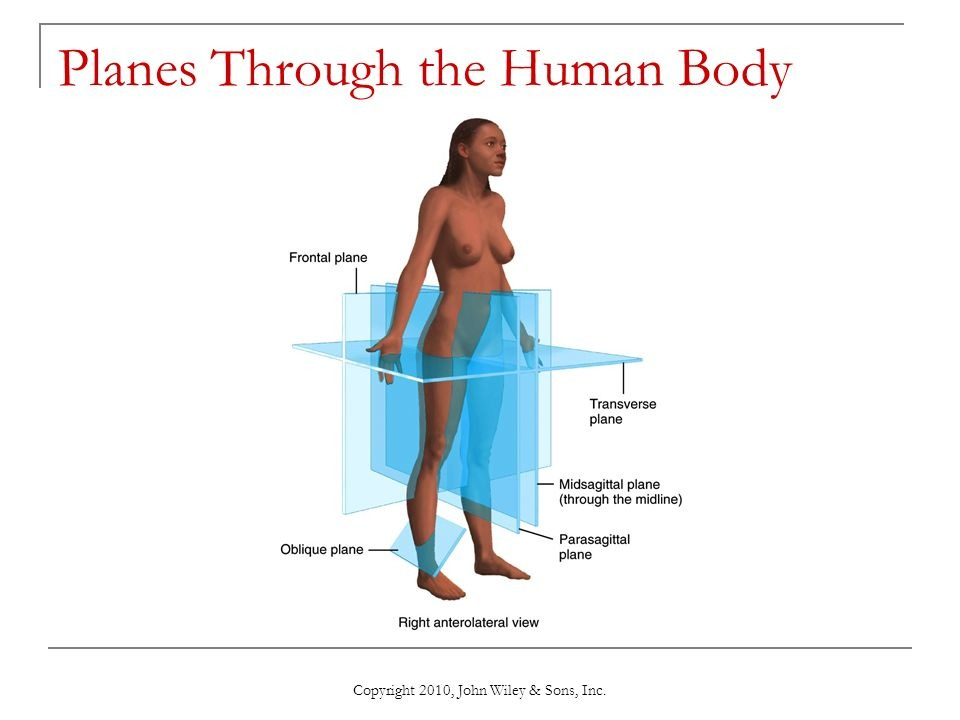
Body Cavities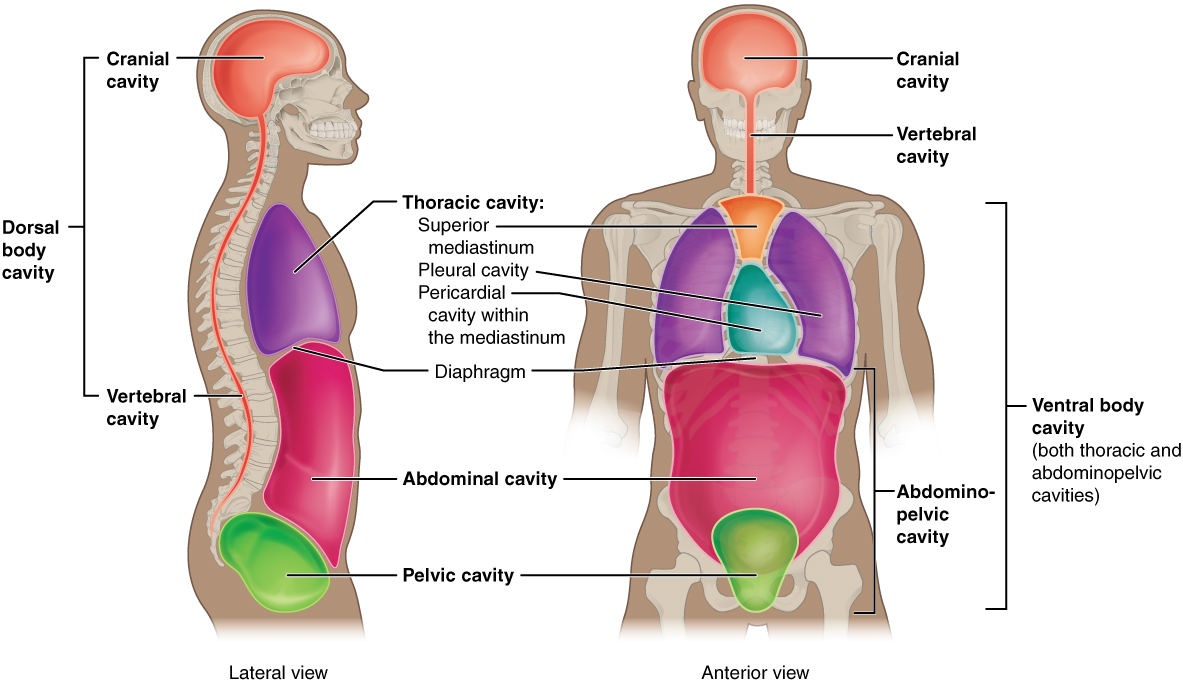
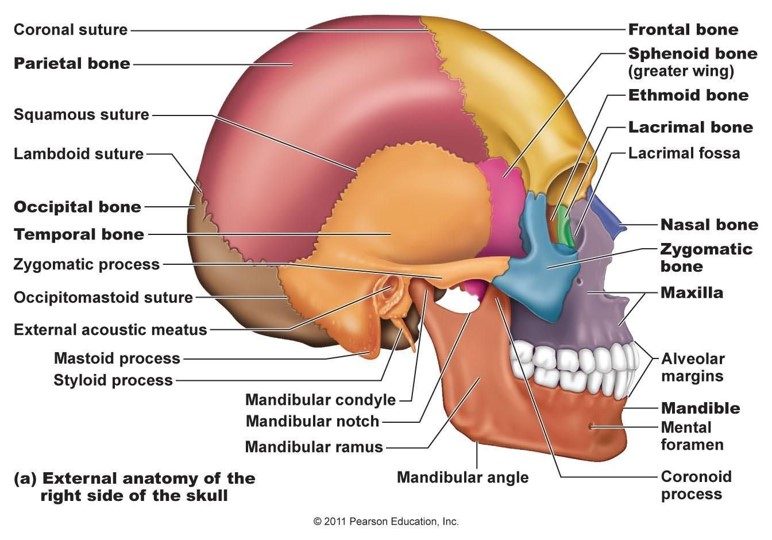
Bones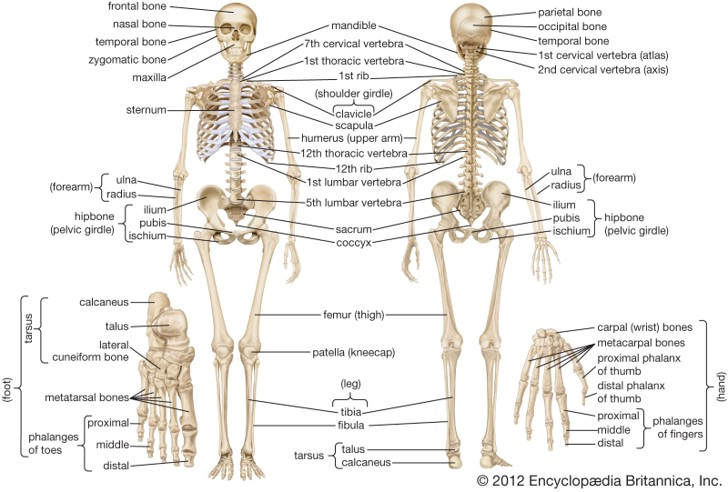
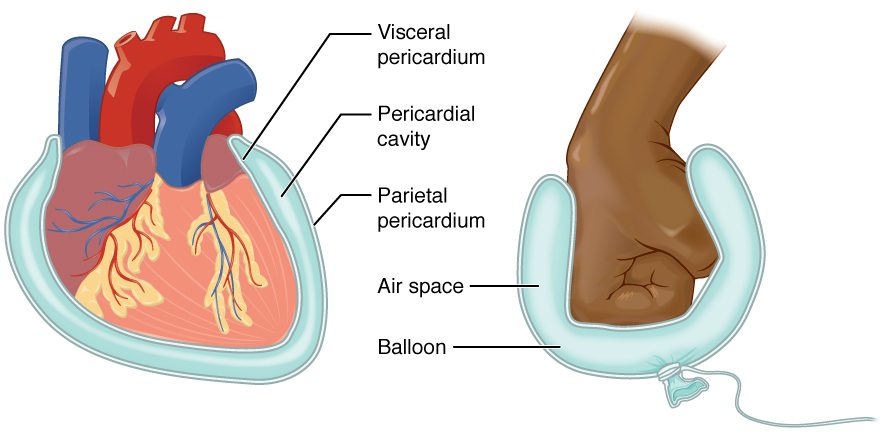
Serous Membranes
- Thin double membranes that protect organs in thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
- Visceral (attached to organs) and parietal (attach to bone/connective tissue/parietal) layers
- Filled with fluid
Abdominopelvic Quadrants 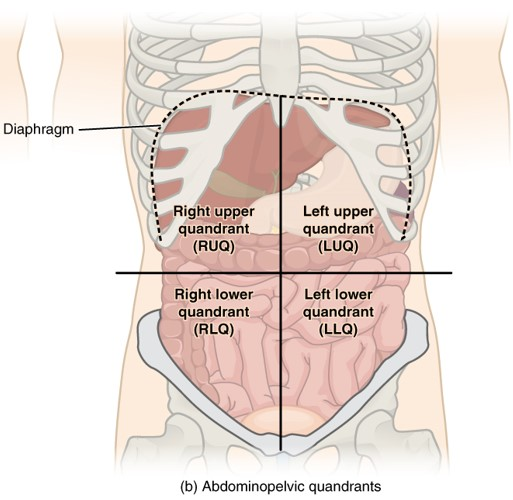
Medical Imaging
- X-ray: electromagnetic radiation that penetrates solids; less easily penetrated substances turn up brighter (short wavelength to penetrate tissue)
- Computed tomography (CT): computers analyze cross-sectional X-rays
➡ Computerized axial tomography = CAT scanner
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): tracking radio signals emitted by tissue
exposed to radio waves or magnetic fields
➡ Malignancies give off different signals than normal body tissues
- Positron emission tomography (PET): “radiopharmaceuticals” emit short-lived (safe) radiation to trace a substance over time
- Ultrasonography: sound waves to cause echoes that are converted into an image by computer