Ch 14 - Money and Banking
(Macroeconomics)
What is money?
- ^^Money^^ is anything which society deems as an acceptable method of payment in exchange for a good or service. Previously, societies used to accept silver, copper, and gold as methods of payment. Currently, our currency is paper money and coins, which is accepted all over the world. This makes it easier to export and import goods and services, regardless of the value of money.
- Checking accounts are called demand deposits, while savings, loans, credit unions, and such are called other checkable deposits. Demand deposits and other checkable accounts can be referred to as transaction accounts.
@@Credit Cards@@
- ^^Credit cards^^ are cards which are issued by a bank and allow its holder to purchase goods and services using credit. For example, any goods purchased on credit will be paid by the bank, however, they expect you to return the money (sometimes with interest). Repaying the amount in a short period of time gives you a good credit score, and tells the bank that you could be trusted with a loan of any size.
- Credit cards are a convenient way to take a miniscule loan form a bank. They use their depositors’ money to pay for the goods you purchase.
- ==NOTE==: credit cards are NOT part of the money supply
@@Savings Accounts@@
- ^^Savings accounts^^ are not generally accepted to pay for goods, by they are liquid and should be accepted and counted as money. M2 includes everything in M1 plus money deposited in savings and other miscellaneous items.
- ^^Liquidity^^: ability to turn an asset into cash rapidly and without loss
@@Fiat Money@@
- ^^Fiat money^^ refers to the coins and paper money which have no standing behind them except the act that they are legal tender.
- Legal tender is the coin or paper currency which must be accepted in exchange for goods or services by the decree of the government.
- Previously, the US used to run on a gold standard, meaning that the money supply was backed by gold or a combination of gold or silver, and it would be their main method of money exchange. The supply of money must be limited since the supply of gold is limited.
- A fiat monetary system is more flexible in the sense that gold holdings of the government need not increase in order to expand the nation’s supply of money. Similarly, nations do not keep the supply of their fiat currency limited will see it imish in value, even to the point of becoming worthless.
@@The Functions of Money@@
- Money is the most efficient method of exchanging goods and services compared to bartering. It is referred to as the medium of exchange. A barter economy requires the exchange of goods of similar or equal value, which makes it tricky to assign value to goods.
- Medium of exchange - Money used to buy goods and services
- Unit of Account - Money is used to measure and compare
- Store of Value - Money is used to accumulate wealth
@@The Federal Reserve System@@
- The ^^Fed^^ is the central bank of the united states. Meaning that it controls the money supply and supervises all depository institutions within the country. All banks (of all kinds) report to the Fed regarding their actions, and they have the authority to audit any institution to monitor and approve the ongoings of the bank. Banks plead to the Fed to get a loan.
@@Fractional Reserve Banking@@
- Banks and depository institutions keep a fraction of the money deposited with them on hand. Most of any given deposit is used to make loans ot other investments.
- The Fed keeps a fraction (10%) of the funds deposited in transaction accounts as reserves. This regulation helps the Fed control the money supply. ^^Transaction accounts^^ are checking accounts and other accounts that function as checking accounts.
@@T-Accounts@@
- ^^T-Account^^ is the balance sheet of a hypothetical bank. T-Account is an accounting tool that may be used for recording transactions. The left side of the T-account is used to record transactions involving the bank's assets, while the right side of the ledger stores the changes in the bank’s liabilities.
- NOTE: a balance sheet must always stay balanced. If the amount is deducted from one side, an equal amount must be added to the same side, or deducted from the other side.
- Banks use about all their excess reserves for loans or investments because that is how profits are maximised.
@@The Money Expansion Process@@
- The transaction accounts are part of the money supply as measured by M1 and M2, meaning that the money supply is increased when banks make loans with their excess reserves.
- The money expansion process leads to banks creating transaction account money by using their reserves to make loans or buy investments. The money deposited into transaction accounts is part of the money supply.
- Money Multiplier = 1.Reserve Requirement
- If the money multiplier is 10%, Money multiplier = 1/0.10 = 10
- Change in money supply = Money Multiplier * change in bank reserves
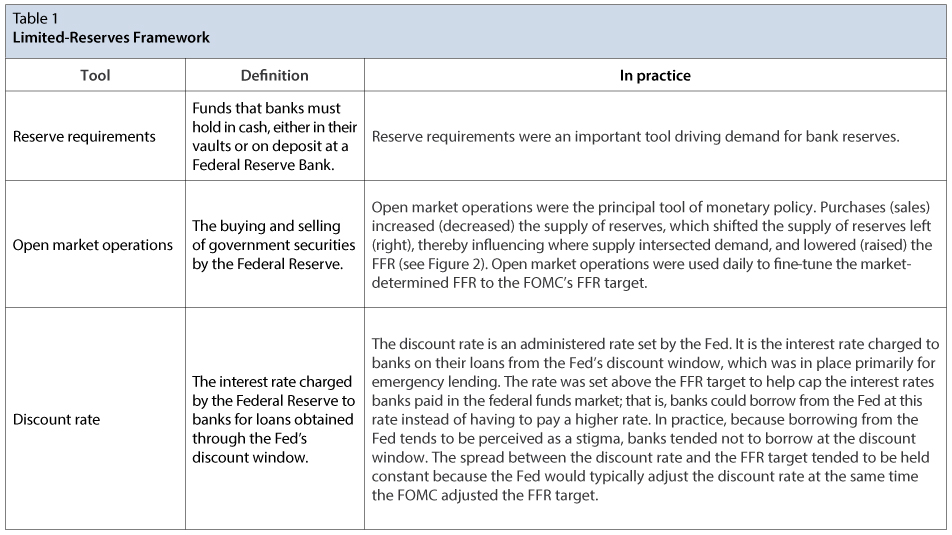
@@Policy Tools of the Federal Reserve@@
A counterfeit amount of money is able to lead to significant change in the money supply because of the monetary expansion process.
With more reserves in the banking system, loans and investment increase and the money supply expands. With fewer reserves, loans and investments contract and the money supply decreases by a multiple of the initial change in reserves.
Monetary base: is bank reserves plus currency in circulation. To change the money supply, the Fed changes the monetary base by altering bank reserves and then the money supply changes by a multiple of the change in the monetary base.
Policy tools of the Fed:
Fed could raise or lower the reserve requirements for depository institutions. If reserve requirement was lowered, banks would have excess reserves and could make more loans and investments. This would increase the money supply. To decrease money supply, the Fed would raise reserve requirements.
Another policy tools involves discount rate. Discount rate is the rate of interest the Fed charges when it makes loans to depository institutions. Fed charges banks a low rate of interest on the loans it makes.
- More banks are encouraged to borrow with the Fed discount rate.
- Money multiplier = 1/Reserve Requirement
- Change in money supply = Money Multiplier * change in bank reserves
- The Fed being able to initiate changes in the money supply is open market operations. @@Open market operations@@ is when the Fed buys and sells government securities in the secondary market. These often go by the name treasury notes, bonds, or notes.
@@Secondary Market@@
When the government issues security to the lender that states the amount of the loan, the rate of interest and the length of the loan.
^^Secondary market:^^ the lender need not hold the government security until it matures, at the time the kender may sell the government security to another investor.
Lenders aiming to sell government securities that have a relatively high rate of interest attached to them will experience a profit in the secondary market. However, those with low rates will experience a loss.
The Fed participates in the secondary market for government securities in order to change the money supply.
- Money multiplier = 1/Reserve Requirement
- Change in the Money Supply = Money multiplier * Change in bank reserves
If the Fed wanted to decrease the money supply, it would sell securities in the secondary market.