Behavioral Neuron Exam #1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are anterograde and retrograde tracing used for? What are the differences between the two?
Anterograde transport- inject tracer into brain area A to see what areas brain area A projects to
Retrograde transport- inject tracer into brain area A to see all areas that connect to brain area A
Why? to help identify different parts of the nervous system and how different parts are connected
What protein allows anterograde transport to take place? What protein allows retrograde transport to take place?
Anterograde Transport uses kinesin. Retrograde transport uses dynein.
Give descriptions of the principles behind CAT scan, PET scan, EEG, angiograms, MRI
CAT scan: takes series of 2-D x-rays and combines them to make a 3-D view of the brain
PET scan: measures changes in blood flow to various parts of brain
EEG: records cells and averages traces of brain activity to form a varying line
Angiograms: provides image of the arteries in brain by injecting dye into arteries
MRI: uses magnetic and radio waves to see brain
True or False? Anterograde tracers make use of the protein kinesin to allow a researcher to inject the tracer into a brain area (Brain Area A) to see all the structures that Brain Area A projects to
True
Which of the following devices is used to freeze brain tissue for histological purposes?
a. operant chamber
b. stereotaxic apparatus
c. microtome
d. Cryostat
d. Cryostat
List the four steps (in order) given in lecture on how perfusions are performed. List the two reasons given in lecture for why perfusions are performed.
Perfusion: 1.) put syringe into left ventricle of heart 2.) turn on saline 3.) cut right atrium in heart 4.) replace saline with formalin (to preserve brain)
Perfusion is done to remove blood from brain and in order to preserve it
A(n) ________________________ is a brain imaging technique in which a dye is injected into either the carotid or vertebral arteries in order to view the arteries of the brain.
Angiogram
Briefly describe the research conducted by Roberts Bartholow that was discussed in class. Describe one contribution and one negative aspect of this study
Roberts Bartholow operated on Mary Rafferty and put electrodes into the cancerous tumor in the back of her head that dissolved her skull, he repeatedly experimented using these probes but once he turned the power up too high she ended up passing due to this.
One contribution is that Bartholow found the cerebral cortex and how it effects motor movements, the negative aspects of the study are many and range from lack of consent to not fully treating her ailments first and experimenting later
Which of the following statements regarding magnetoencephalography (MEG) is FALSE?
a. MEG has better spatial resolution than EEG
b. MEG is less expensive than EEG
c. MEG traces can be averaged over many trials to produce an event related field (ERF)
d. MEG can only look at neurons in the sulci
b. MEG is less expensive than EEG
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. MRI images provide greater spatial resolution than CAT scan images.
b. In CAT scans, light areas represent ventricles, gray areas = brain matter and dark areas = bone.
c. EEG recordings provide better spatial resolution than MEG recordings.
d. fMRI’s have poorer temporal resolution than MRI’s.
a. MRI images provide greater spatial resolution than CAT scan images
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. MEG has better temporal resolution than PET
b. PET scans have recently replaced CAT scans as the preferred method of detecting tumors.
c. PET scans have better temporal resolution than CAT scans.
d. Single unit recordings have better temporal resolution than PET scans.
e. MEG has better spatial resolution than human EEG
b. PET scans have recently replaced CAT scans as the preferred method of detecting tumors
Which of the following techniques focuses on the magnetic properties of hemoglobin (which carries oxygen in the bloodstream) by comparing the ratio of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin?
a. fMRI
b. MEG
c. CAT
d. MRI
e. TMS
a. fMRI
Describe how a CAT scan works to produce the picture to the right (you should include why different areas of the picture are different colors). How do the images obtained in a CAT scan compare to the spatial resolution of an MRI (i.e. better or worse)? What can a CAT scan be used for?
CAT scans take a bunch of 2-D pictures of the brain and turn it into a 3-D image of the brain with varying colors due to how different things absorb various amounts of x-ray radiation (Bone absorbs a lot, blood/air less, neural tissues in between), colors are flipped so bone is the lightest color. CAT scans are good for locating tumors, vascular diseases and lesions. Spatial resolution is better in CAT scans than MRI.
True or False? According to lecture, the resolution of MRI images generally surpasses the resolution of CAT scan images.
True, BUT, spatial resolution is better in CAT scans
Dr. Olton is developing a study on how the brain changes while looking at happy and sad images. Dr. Olton is especially interested in using a task that presents the happy and sad images for 30 seconds at a time. Dr. Olton is on a tight budget and wants to find a method that will allow him to conduct this study as cheaply as possible. Of the following methods that Dr. Olton is looking at, which is the best recommendation?
a. fMRI
b. PET
c. CAT
d. MRI
e. Angiogram
a. fMRI
Describe how a PET scan works
PET scans measure changes in blood flow in brain, it injects radioactive substances into the body and sees where that blood flow hits the brain
True or False? One advantage of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) over positron emission tomography (PET) scan imaging is that TMS is less invasive than the PET scan
True
True or False? One negative of MEG is that the technique can only be used to look at neurons in the sulci.
True
True or False? According to lecture, the spatial resolution of MRI scans images generally surpasses the spatial resolution of CAT scan images.
False
True or False? In general, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) is a cheaper procedure than positron emission tomography (PET)
True
True or False? Anterograde tracing techniques involve injecting a tracer into Brain area “A” to determine all the brain areas that Brain Area A projects to.
True
True or False? In a typical CAT scan image, bone will show up as white, while air and cerebral spinal fluid will show up as black
True
True or False? One advantage of an electrolytic lesion is that the effects are generally reversible.
False
True or False? A CAT scan is generally used to take a static picture of the brain making it useful for looking at tumors and damage from a stroke, while an MRI is generally used to record brain activity while a person is actively performing a behavioral task.
False
The BOLD effect (blood oxygen level dependent effect) is most often associated with which of the following techniques?
a. electroencephalography
b. magnetoencephalography
c. positron emission tomography
d. computer assisted tomography
e. functional magnetic resonance imaging
e. functional magnetic resonance imaging
Which of the following brain imaging techniques could a researcher use to examine the brain changes following the presentation of a stimulus in a learning and memory task?
a. fMRI
b. EEG
c. PET Scan
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
a. fMRI
b. EEG
Which of the following techniques has the best temporal resolution?
a. electroencephalography (EEG)
b. computer-assisted tomography (CAT)
c. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
d. positron emission tomography (PET)
e. both b and c
b. computer-assisted tomography
Which of the following techniques is generally considered the least expensive?
a. electroencephalography
b. magnetoencephalography
c. positron emission tomography
d. computer assisted tomography
e. magnetic resonance imaging
a. electroencephalography
Which of the following techniques usually involves the injection of radioactive oxygen or glucose to measure changes in blood flow?
a. electroencephalography
b. magnetoencephalography
c. positron emission tomography
d. computer assisted tomography
e. magnetic resonance imaging
c. positron emission tomography
A(n) ______________________________________ is a tiny signal embedded in an ongoing EEG signal which is found by averaging multiple traces of multiple trials.
ERP or event-related potential
A __________________________________________ is the device which keeps the head in place during a surgery and is used to make measurements during a surgery.
Stereotaxic
A(n) ______________________________________________ provides an image of the arteries of the brain by injecting a dye into the carotid or vertebral arteries to
Angiogram
The _______________________________ is the protein that is used to transport RETROGRADE tracers back to the cell body while _______________________________ is the protein used to transport ANTEROGRADE tracers to the axon terminals.
Dynein, Kinesin
The _________________________________ and _______________________________ are the two main reasons why a perfusion is done.
removal of blood from brain, preservation of the brain
A ______________________________ is a machine that is used to freeze and section the brain.
cryostat
Which of the following researchers was most instrumental in developing a topographical map (Homonculus) of the primary motor cortex?
a. Charles Sherrington
b. Pierre Flourens
c. Karl Wernicke
d. John Hughlings Jackson
e. Korbinidian Brodmann
d. John Hughlings Jackson
Explain the technology behind magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), going over all the steps presented in class.
MRI’s use both magnets and radio waves
-first we see atoms in a normal orientation, then in the magnetic field they become aligned
-then a radio wave is passed to make atoms rotate, next turn off radio wave and measure how atoms rebound themselves back to the magnetic field position
What is temporal resolution, spatial resolution, and contrast resolution?
Temporal Resolution: how a scan can show second by second changes in the brain
Spatial Resolution: how well you can tell different brain areas apart
Contrast Resolution: how clear the scan is
Fear Conditioning
Putting a rat in a grid based container, playing a tone and then lightly shocking the rat, the rat will then show freezing behavior like raised fur, crouched posture, may leap to escape shocks
What does the Amygdala do? What happens if its lesioned?
takes input from all senses and reads the emotional significance of other people/things, which then outputs as fluctuations in heart rate, adrenaline. When lesioned it leads to lack of aggression and lowered emotional response, decrease in fear conditioning. When stimulated it ca elicit fear, rage, fight/flight, or even pleasure responses.
What is a spatial task?
Think of the example in class where a student had to outline a star using only a mirror to see with, to solve this you can use visual cues in the environment to then map the star shape
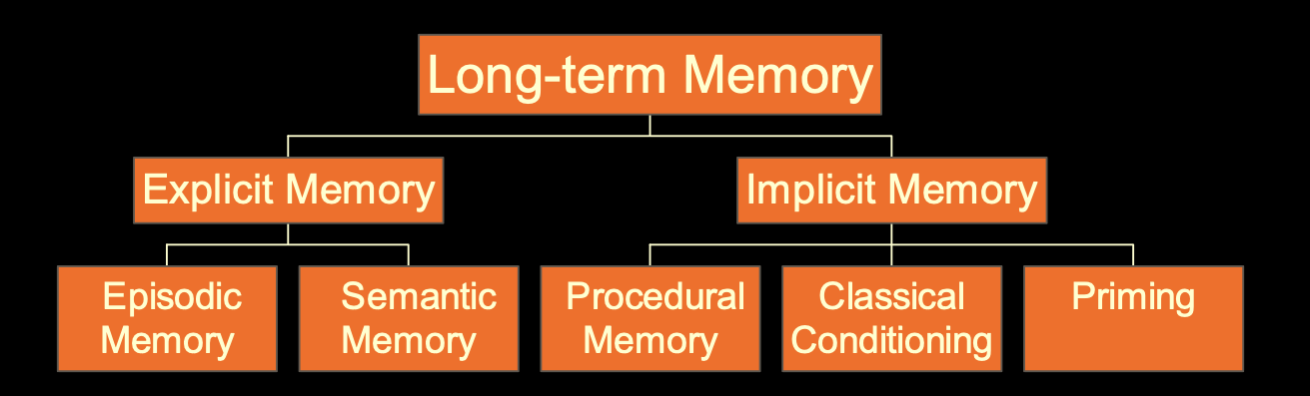
What is episodic and semantic memory?
Episodic Memory: memory tied to your own personal experiences ex. what did you have for dinner?
Semantic Memory: memory of general facts/ definitions about the world
What is implicit memory, procedural memory, priming?
Implicit memory: nondeclarative memory, influences thoughts/behaviors but does NOT enter consciousness
Procedural memory: memory that lets you perform specific learned skills/habitual responses
Priming: influence of one memory on another, activates one or more existing memories by a stimulus, can effect subsequent thoughts/actions
Patient HM and implicit/explicit memory
HM had parts of his temporal lobe removed for his seizures, afterwards he could remember explicit memories acquired before surgery but could not form new ones. BUT could perform normally on procedural/implicit memory tasks. In the end this shows that explicit memory is in temporal lobes but implicit is not.
What is allocentric spatial cues and egocentric response cues?
Allocentric Spatial Cues: find spatial location by using cues in the environment (posters, clocks, etc..)
Egocentric Response Cues: based on where your body is, based on left and right turns
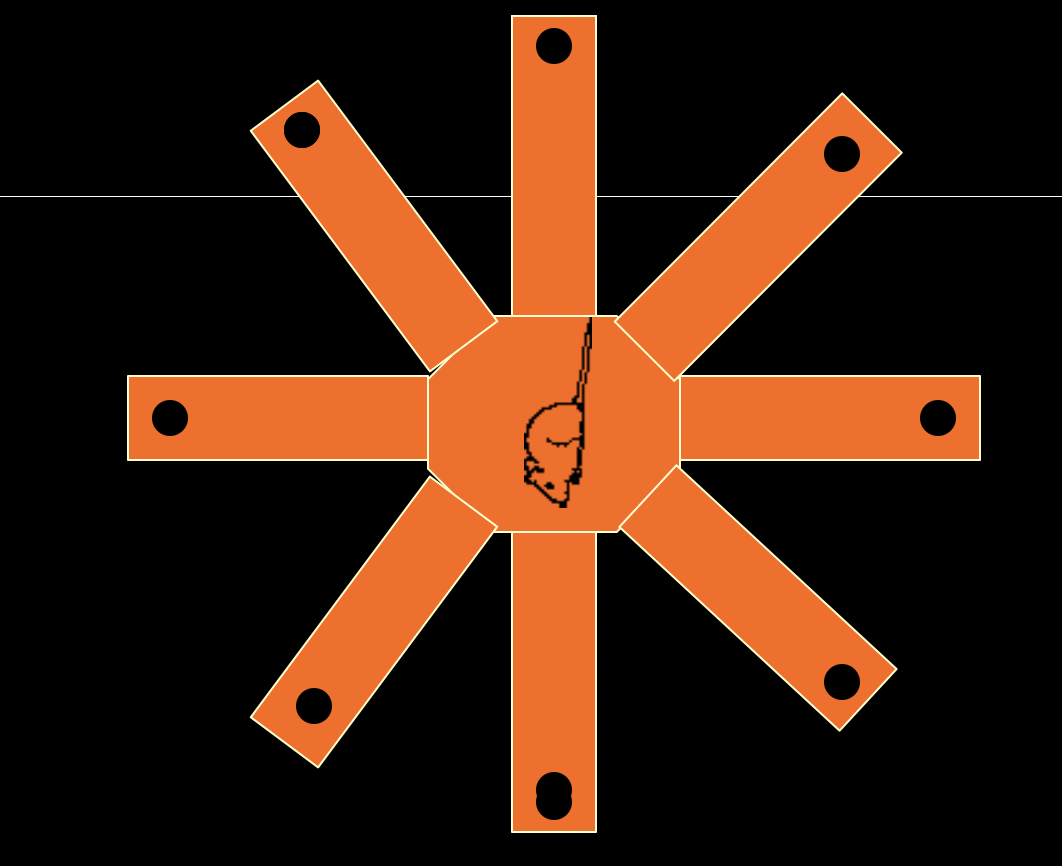
What types of experiments use affective memory?
Since affective memory is just recalling previous experiences, experiments involving rats in the water maze, in the chamber that shocks them with a tone, and 8-arm food placement
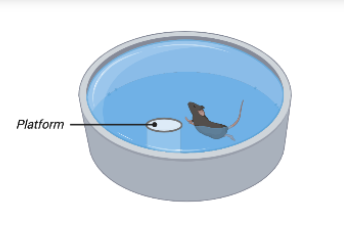
How can you test allocentric spatial, egocentric response, affect, and visual cues?
Affect- fear conditioning (think of rat with tone and a shock that shows freezing behavior)
Visual- using water basin and moving platform where platform is NOT invisible, moved to different locations, mouse has to SEE where the platform has been moved
Egocentric response-using water basin where platform is invisible, put mouse in same place so they have to remember where to turn their body
Allocentric spatial- using water basin where platform is invisible but always stays the same, mouse starts in different areas and has to use background cues like (posters/clock) to see where to move to the platform)