psychopathology
1/112
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
typical mood symptoms in response to events (functional)
feeling blue or down but able to function normally; feeling happy and exuberant because something good happened
hypomania (between functional and dysfunctional)
moderate and frequent elation, inflated self-esteem, some impulsiveness, high energy
depression (between functional and dysfunctional)
moderate and frequent symptoms of sadness, apathy, fatigue, etc., that somewhat interfere with functioning
manic episode (dysfunctional
expansive mood including irritability, grandiosity, racing thoughts, and decreased need for sleep that significantly interferes with functioning
major depressive episode (dysfunctional)
severe symptoms of sadness, apathy, hopelessness, low energy, etc., that significantly interfere with functioning
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
episodic — typically 2-9 months if untreated
can be recurrent
recurrent
onset of a new episode of depression
probability of recurrence increases with # of past episodes, presence of comorbidities
relapse
return of symptoms within a fairly short period of time
Depression demographics
common illness
twice as common in women as in men
3x as common among people in poverty
prevalence varies among cultures
most common age of onset: early 20s
comorbidity rates for depression
high for other illnesses like anxiety
bipolar 1
requires only 1 instance of a manic episode occurring and no instance of a depressive episode
episodic and recurrent
high rates of suicide
bipolar 2
requires 1 instance of a hypomanic episode and 1 depressive episode (no manic episodes)
episodic and recurrent
high rates of suicide
demographics for bipolar disorder
~1 in 100 people in the US
average age of onset is 20s
heritability estimates
Depression: ~35%
Bipolar: ~60-85%
GWAS
Genome Wide Association Studies
new school molecular genetics
polygenic
no singular biomarker gene
5-HTT
serotonin transporter gene
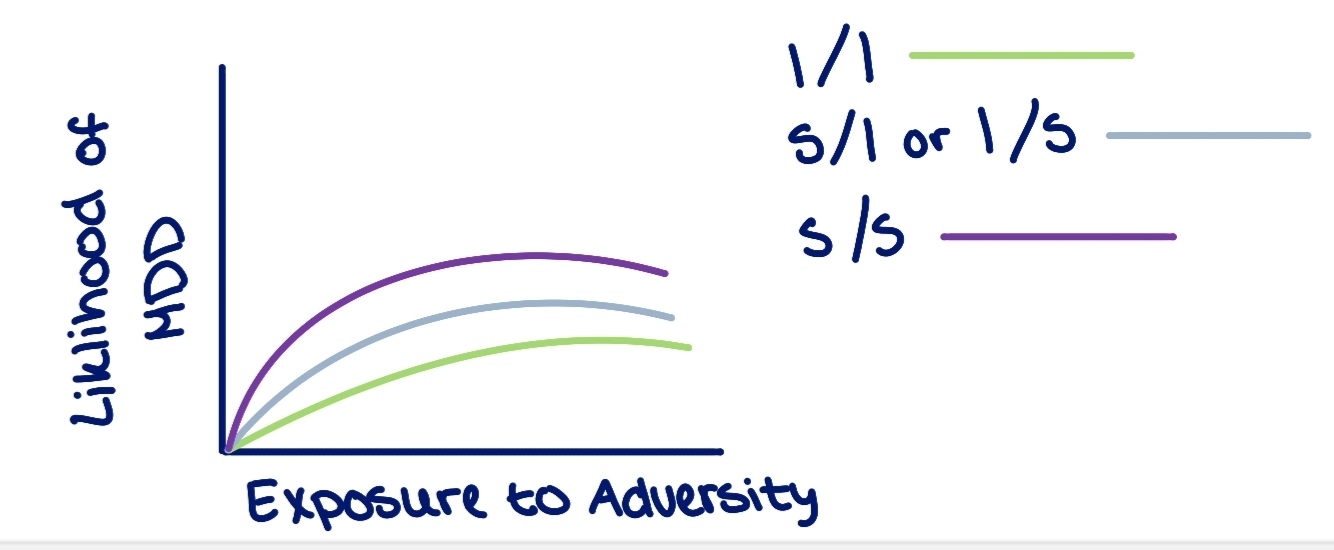
Dunedin Cohort
measured correlation between likelihood of developing MDD and the exposure to adversity
study could not / would not consistently replicate
Monoamine
family of neurotransmitters formed by singular amino-acid groups
monoamine hypothesis
early focus on serotonin (and norepinephrine), especially low absolute levels of serotonin
empirical system does not support this
SSRI
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
SNRI
selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
CAUSE: injury to left anterior prefrontal cortex
EFFECT: depression
comorbidity with depression
hypothyroidism and/or higher levels of some pro-inflammatory cytokines — overactivity of stress response system (cortisol)
Adveristy
umbrella term for hardship or circumstances in life that causes stress
stress of life + environment
early adversity — especially events related to loss and chronic stress
associated with long-term vulnerability
perinatal depression
depression associated with the time around birth — both parties in relationship can feel this, not just the individual giving birth
better term than post-partum depression
baby blues
sudden onset in days after giving birth where the person who gives birth has feeling of sadness, fatigue, etc., and end by itself w/ no functional consequences
negative affectivity (neuroticism)
trait that reflects person’s level of emotional stability
Lewinsohn - behavioral activation
absence of response-contingent positive reinforcement and/or high rate of negative experiences, low levels of activity/behavioral engagement
Seligman - “learned helplessness”
if you get punished regardless of what you do, you just “lie down and take it” aka no point in trying — this is operationally conditioned
cognitive theories of depression
negative thought patterns, beliefs cause depression
depressogenic
leading to depression
depressogenic schemas
negative views, beliefs about self, world, future
automatic cognitive biases
tendency to process information in negative ways
filters how we see/perceive the world → negative filter
Beck’s Theory — descriptive
depressed people are more likely to fall into negative cognitive triad
Beck’s Theory — causal
temporal precedence - does depressogenic schemas precede depression or come after
Beck’s negative cognitive triad
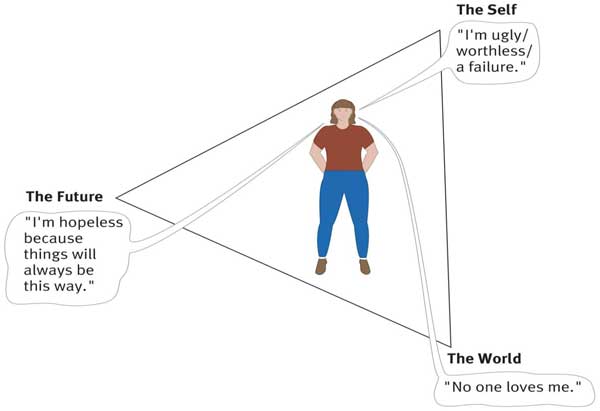
pessimistic attributional style
negative life events attributed to internal, stable, and global causes
“hi, i’m the problem, it’s me”
Helplessness/Hopelessness Theory (Abramson)
pessimistic attributional style
person perceives themselves as having no control over the situation AND certain that bad outcomes will occur or continue to occur → hopelessness
unipolar depression
negative life events, negative affectivity, negative cognitions, expressed emotion, and lack of social support
“downward spiral”
reward sensitivity
high responsivity to rewards, strong attachment to and pursuit of goals, life events that involve attaining goals
upward spiral — predictor of mania
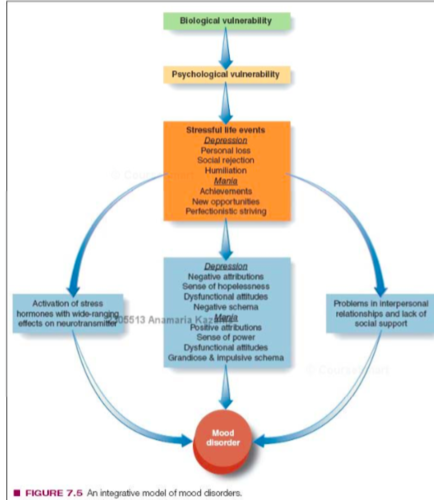
Integrative Model of Mood Disorders
bio (vulnerability)→ psycho (vulnerability) → social (stressful life events)
social — depression: personal loss, social rejection, humiliation
social — mania: achievements, new opportunities, perfectionistic striving
→ leads to activation of stress / depression or mania / problems with interpersonal relationships
→ calls towards mood disorder
File Drawer Probllem
Researchers can choose to not publish some results — negative or null — selection and publication bias
lithium
common medication used to treat bipolar disorder and also as a maintenance treatment
mood stabilizers
seroquil, quetiapine
used in combination and in replacement of lithium
self harm
umbrella term for self injurious behavior
suicidal ideation
thoughts or wishes to die, ranging from comparatively passive ideation to images of ending one’s life to concrete planning
suicide attempt
deliberate, self inflicted hard at least party intended to end one’s life (regardless of actual suicide completion)
suicide
death resulting from a suicide attempt
non-suicidal self injury (NSSI)
deliberate, direct destruction of body tissue without any intent to die — some people will completely deny the intent
ambivalent
having mixed feelings / contradictory ideas about something / someone
gender expectations
reinforces the gender gap when looking at rates of suicide
“psychache”
psychological / emotional pain — viewing life as painful
substitution of planning with ideation
most people who ideate about suicide will not go on to attempt suicide
Theoretical model flow chart
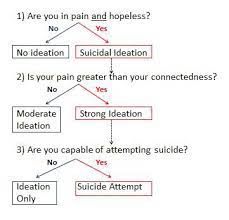
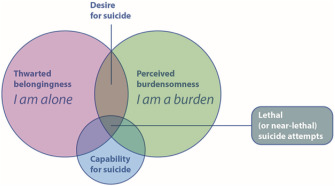
interpersonal theory of suicide (Joiner)
simultaneous presence of “thwarted belongingness” and “perceived burdensomeness” produce the desire for suicide, but the capability is required for an actual attempt to come to fruition
Direct Treatment for suicidality
Cognitive Therapy for Suicidal Patients
Indirect Treatment for suicidality
Targeting Depression via therapy or medication
barrier for suicidality treatment
most people do not receive mental health care for suicidality when they seek out help from their doctors and confidants
Stepped Care Model
in-patient hospitalization
partial hospitalization or intensive outpatient programs
outpatient care
brief intervention + follow-up
crisis support + follow-up
gatekeeper
someone who facilitates getting you connected to care
means restriction
reducing access to firearms, suicide deterrent nets on bridges, etc
Specific Phobia
Marked fear or anxiety about a specific object/situation — fear is disproportionate to actual danger posed — 6+ months
social anxiety disorder
fear of unfamiliar people or social scrutiny
panic disorder
anxiety about recurrent panic attacks
agoraphobia
anxiety about being in places where escaping or getting help would be difficult if anxiety symptoms occurred
generalized anxiety disorder
uncontrollable worry
panic attack
abrupt surge of intense fear or intense discomfort that reaches a peak within minutes
should not be a reaction to an event — should not be expected
“fear of fear” hypothesis
expectations of catastrophic consequences of having a panic attack in a crowded public space
key shared features of anxiety disorders
“excessiveness” — disproportionate
clinically significant distress or impairment
avoidance
no universal, objective demarcating line — no binary
Conditioned Learning of Fears (Mowrer)
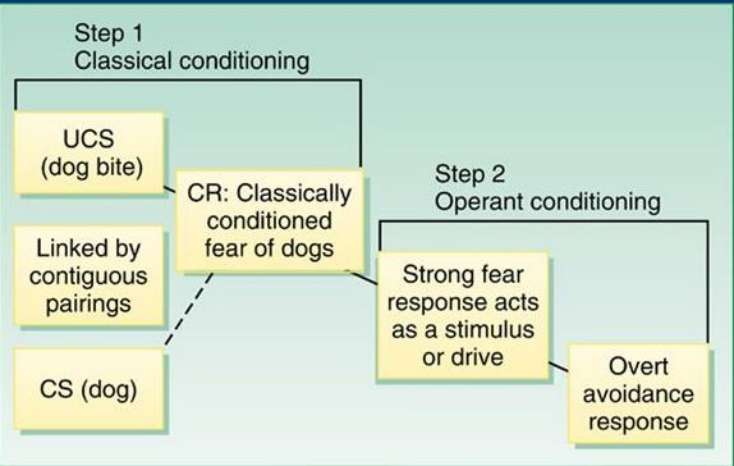
Associative learning
the process through which organisms acquire information about relationships between events or entities in their environment
prior learning
all the knowledge one has before learning about a particular topic
social and vicarious learning
a way of learning that allows individuals to learn from the experience of others
“The fear circuit”
amygdala → hippocampus → prefrontal cortex
Corticotropin releasing factor
neuropeptide that regulates the HPA axis
Cognitive biases
information processing, preferential attention to and recall of fear-relevant stimuli, overestimation of likelihood of danger
rumination
dwelling
locus coeruleus
major source of norepinephrine
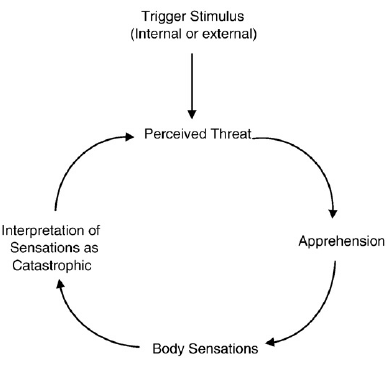
anxiety sensitivity
tendency to focus on bodily sensations, have difficulty interpreting bodily sensations, and interpret of bodily sensations as potentially harmful
panic circle
“problem orientation”
tendency to view challenges as threats
contrast avoidance model
worry produces sustained, modest negative affect and so protects from dramatic shifts in emotion
functional anxiety model
simultaneously believing that worrying is useful AND that worrying is harmful + uncontrollable → “meta-worries”
worrying suppresses physiological arousal
worrying distracts from/avoids more unpleasant emotions and thoughts
Exposure therapy - habitual model
do it until you become bored and unbothered
Exposure therapy - inhibitory learning model
learning to feel safe
close replications and multiple settings for generalizability
“Unified Protocol”
you may be able to come up with a singular modular treatment for a range of anxiety disorders
Benzodiazepines
targets GABA
ex. xanax, alprazolam
Obsessions
cognition
persistent and recurrent intrusive thoughts, images or impulses experienced as disturbing, inappropriate, or uncontrollable
usually persistent and recurrent
Compulsions
behavioral
repetitive behaviors or rituals that a person feels driven to perform, often according to very specific or rigid rules
unable to deviate from rules
can be excessive — logically and intellectually understood by the individual as unnecessary, but still compelled to follow through
impulsivity
the tendency to act without thinking
tichotillomania
compulsive hair pulling
excoriation
compulsive skin picking
body dysmorphia disorder
preoccupation with one or more perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable or appear slight to others
clinically significant distress or impairment
hoarding disorder
persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of actual value
perceived need to save items and distress associated with discarding them
congests and clutters active living areas and compromises living spaces
pre-potent actions
the thing you are most inclined to do and you would need to inhibit that initial impulse/inclination
trouble and failure to inhibit the impulse/inclination
glutamate
primary excitatory neurotransmitter
GABA
primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Thought-Action Fusion (Rachman)
thoughts are morally equivalent to actions → guilt, self blame, self recrimination, shame, as well as efforts to neutralize the thoughts and to seek reassurance