Microbiology Chapter 2 (Nester)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Atoms
The basic units of all matter and are made up of three major components. (Neutrons, Protons, and Electrons)
Neutrons
Uncharged particles
Protons
Positively charged particles
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
Element
Consists of only one kind of atom and cannot be separated into simpler parts by chemical methods.
Ion
An atom that gains or loses an electron that is no longer neutral.
Cations
Positively charged ions.
Anions
Negatively charged ions.
Ionic Bonds
Form between cations and anions because of strong attractions between positive and negative charges. The resulting product is usually a salt.
Covalent Bond
When atoms share pairs of valence electrons. One pair of shared electrons is this. Very strong.
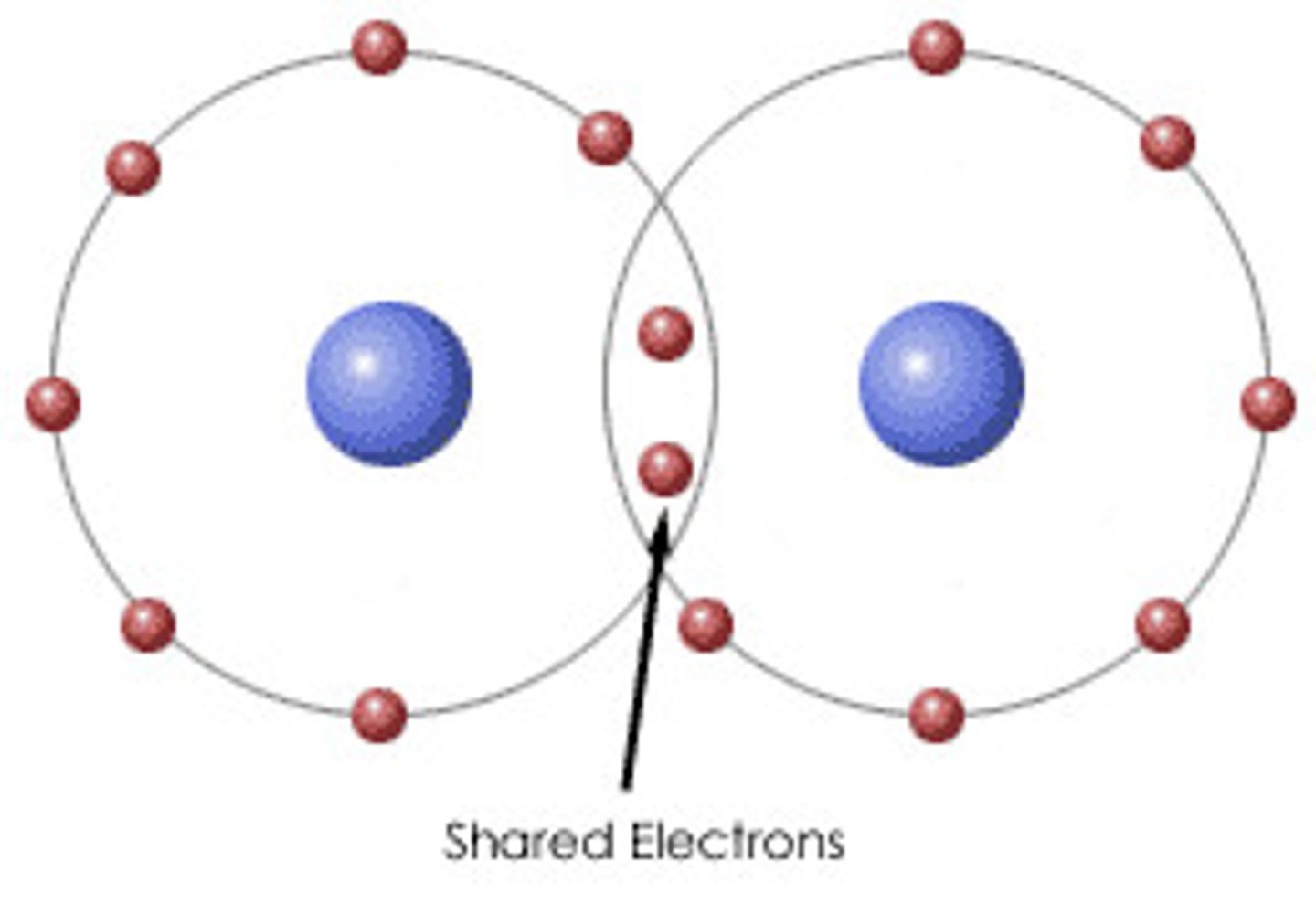
Molecule
Two or more atoms joined together by a covalent bond.
Compound
A molecule consisting of more than one element.
Organic Compound
Carbon atoms joined by covalent bonds to hydrogen atoms form this.
Inorganic Compound
All other compounds in life.
Non-polar covalent bond
When electrons are shared equally.
Polar Covalent Bond
When electrons are shared unequally.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds formed when a hydrogen atom in a polar molecule is attracted to an electronegative atom in the same or another polar molecule.
Hydrophilic
Water loving. (Salts and polar molecules)
Hydrophobic
Water fearing. They do not dissolve in water because they cannot form hydrogen bonds.
pH
A measure of somethings acidity.
Buffers
Compounds that stabilize the pH of solutions.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The energy currency of a cell.
Macromolecules
Large molecules. There are four major classes. Most are polymers.
Proteins, Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids, and Lipids
Four major classes of macromolecules.
Polymers
Subunits that are joined together
Dehydration Synthesis
A chemical reaction that removes h20.
Hydrolysis
The reverse reaction of breaking a macromolecule down to its subunits by adding h20.
Enzymes
Chemical reactions require specific __________.
Catalyzing Reactions, Transporting Molecules, and Motility
Name 3 most important roles of proteins.
Amino Acids
Subunits that make up proteins. There are about twenty major ones and can be arranged into a number of combinations in a protein.
Protein
One or more long polypeptides folded to create a functional molecule.
Peptide Bonds
Amino acids are held together in an unbranched chain.
Carbohydrates
A diverse group of compounds that include sugars and starches. They play several critical roles in biology.
Energy Source, Energy Storage, Source of Carbon, Structural Components
Name 4 critical roles that carbohydrates play in biology.
Monosaccharides
Simple Sugar.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides joined together by covalent bonds.
Polysaccharides
Are large molecules composed of long chains of monosaccharide subunits or their derivatives.
Nucleic Acids
Carry genetic information.
DNA
The master molecule of the cell. The nucleotides have 3 different parts which are a nucleobase, deoxyribose, and a phosphate group.
RNA
Involved in the process that decodes the information in DNA to create a sequence of amino acids in proteins.
Lipids
Critically important in the structure of membranes, which function as cells gatekeepers. Very diverse group and are highly soluble in water. Most common are fat.
Phospholipids
Contain a phosphate group linked to one of a variety of other polar molecules. Considered a compound lipid.
Steroids
Simple lipids that have a characteristic structure consisting of four connected rings.