Endocrine System: Hormones
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:40 AM on 12/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
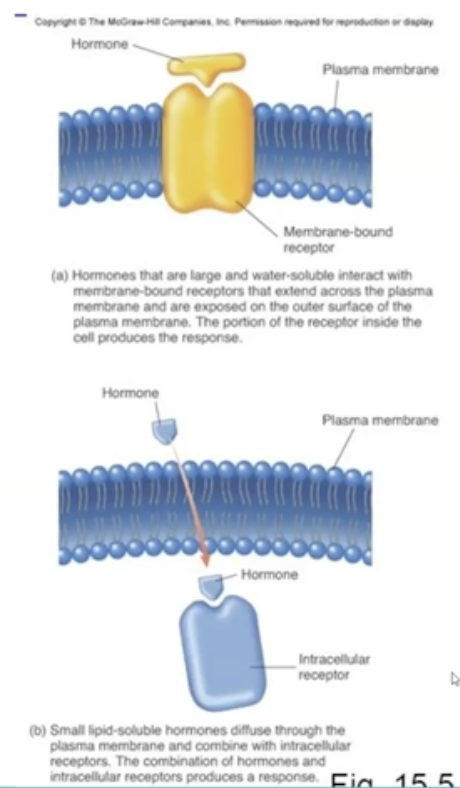
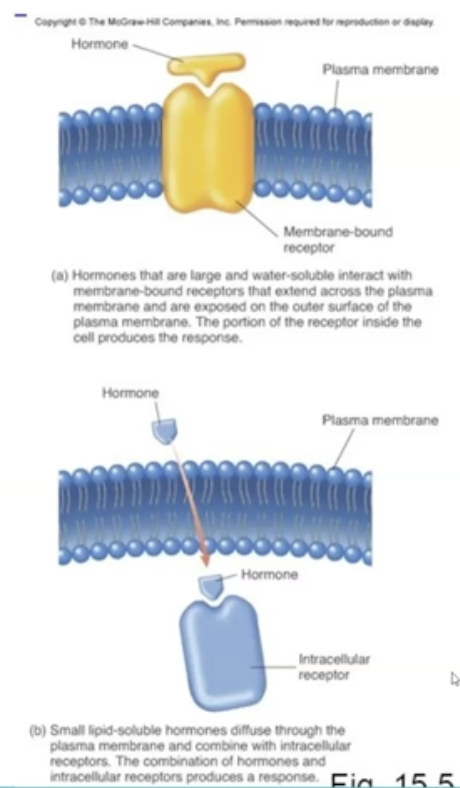
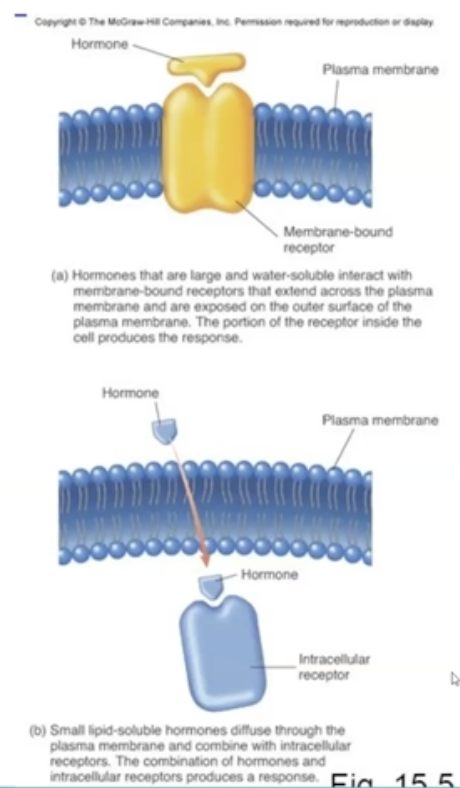
What are the two major types of hormones?
1. membrane-bound receptor hormones
2. intracellular receptor hormones
2. intracellular receptor hormones
2
New cards
What is membrane-bound hormone?
The hormone cannot pass through the cells and needs a gated channel (non-steriods)
3
New cards
What is an intracellular receptor hormone?
The hormone that can pass easily through cells. (Steroids)
4
New cards
in _____ change occurs rapidly
membrane bound receptors (reheating a frozen meal analogy)
5
New cards
What are the 2 mechanisms of membrane-bound receptors?
G proteins and other membrane-bound receptors
6
New cards
What does G proteins do?
Trigger response from intracellular mediators which will cause cellular change
7
New cards
What does Other Membrane Bound Receptors do?
Trigger a direct change to the cell
8
New cards
What are the first 3 steps of G protein function?
1. Hormone binds to receptor causing receptor to change shape
2. Receptor binds to a subunit of the G protein inside the cell
3. Subunit releases GDP then binds with and it is actived by GTP
(check image)
2. Receptor binds to a subunit of the G protein inside the cell
3. Subunit releases GDP then binds with and it is actived by GTP
(check image)
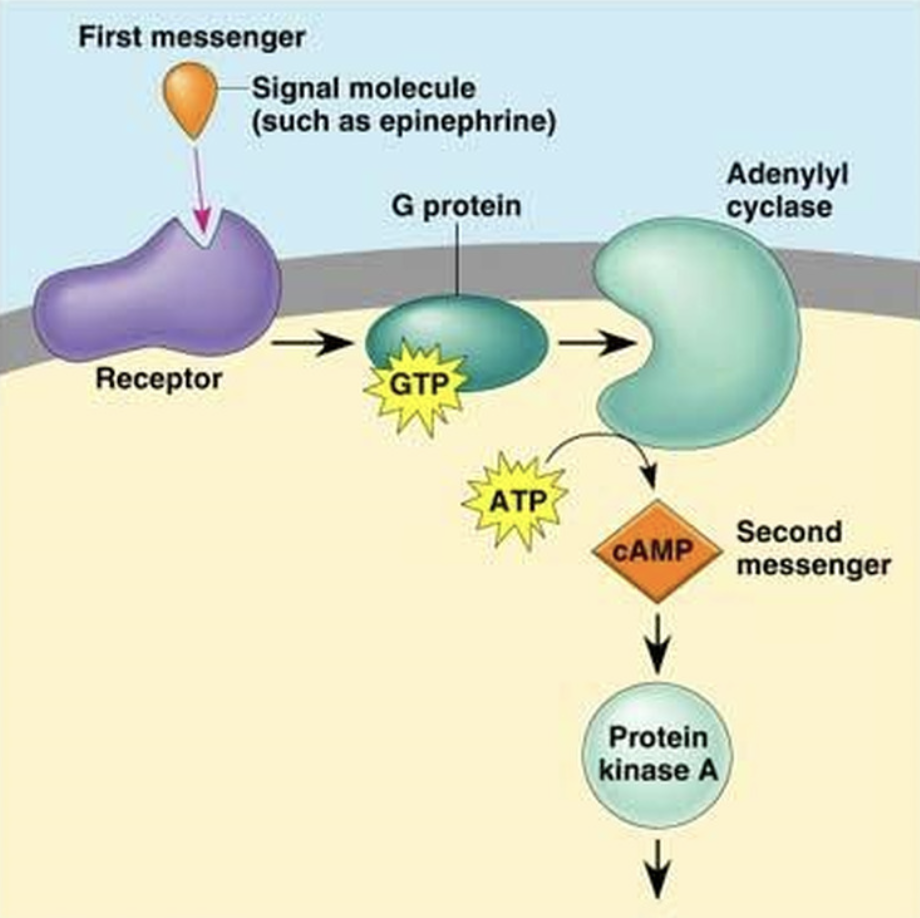
9
New cards
What is the 4th and last step of G protein function?
4. Subunit combines with other proteins to either:
1. Open ion channels when Ca2+ acts as an intracellular mediator
Example: in smooth muscle
OR
2. Activate cAMP (adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP) whcih activates enzymes through phosphorylation (attachment of phosphates) to increase or decrease their activity
Example: Glucagon increases release of glucose in liver
1. Open ion channels when Ca2+ acts as an intracellular mediator
Example: in smooth muscle
OR
2. Activate cAMP (adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP) whcih activates enzymes through phosphorylation (attachment of phosphates) to increase or decrease their activity
Example: Glucagon increases release of glucose in liver
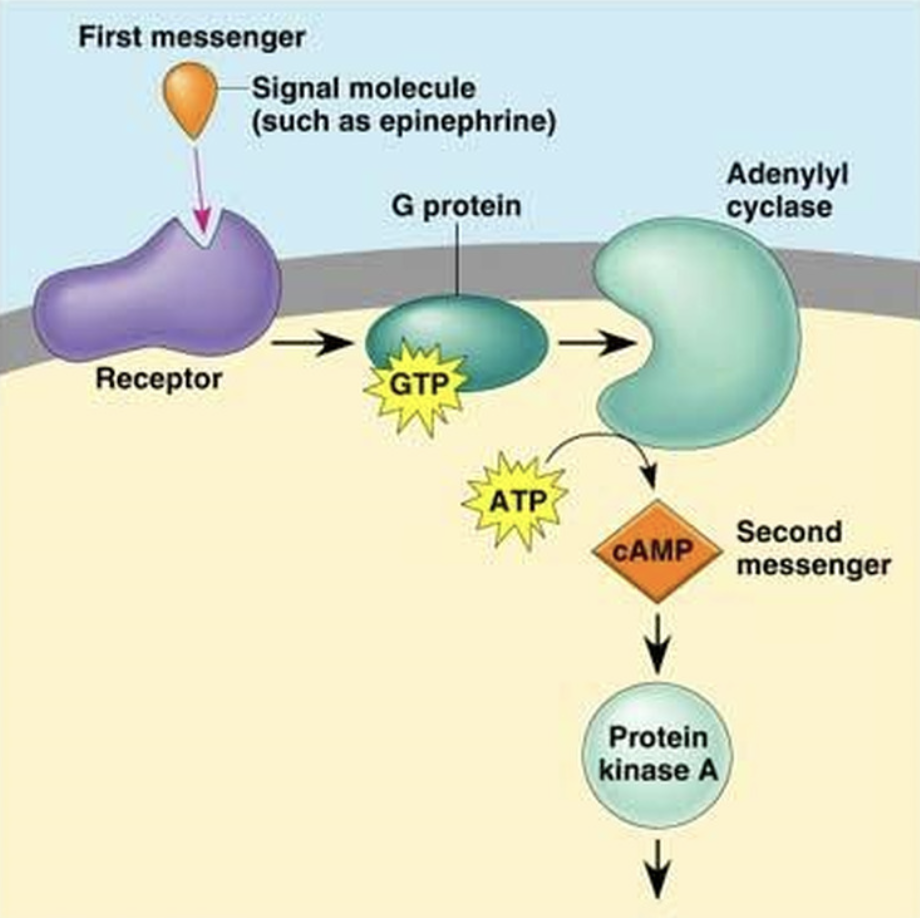
10
New cards
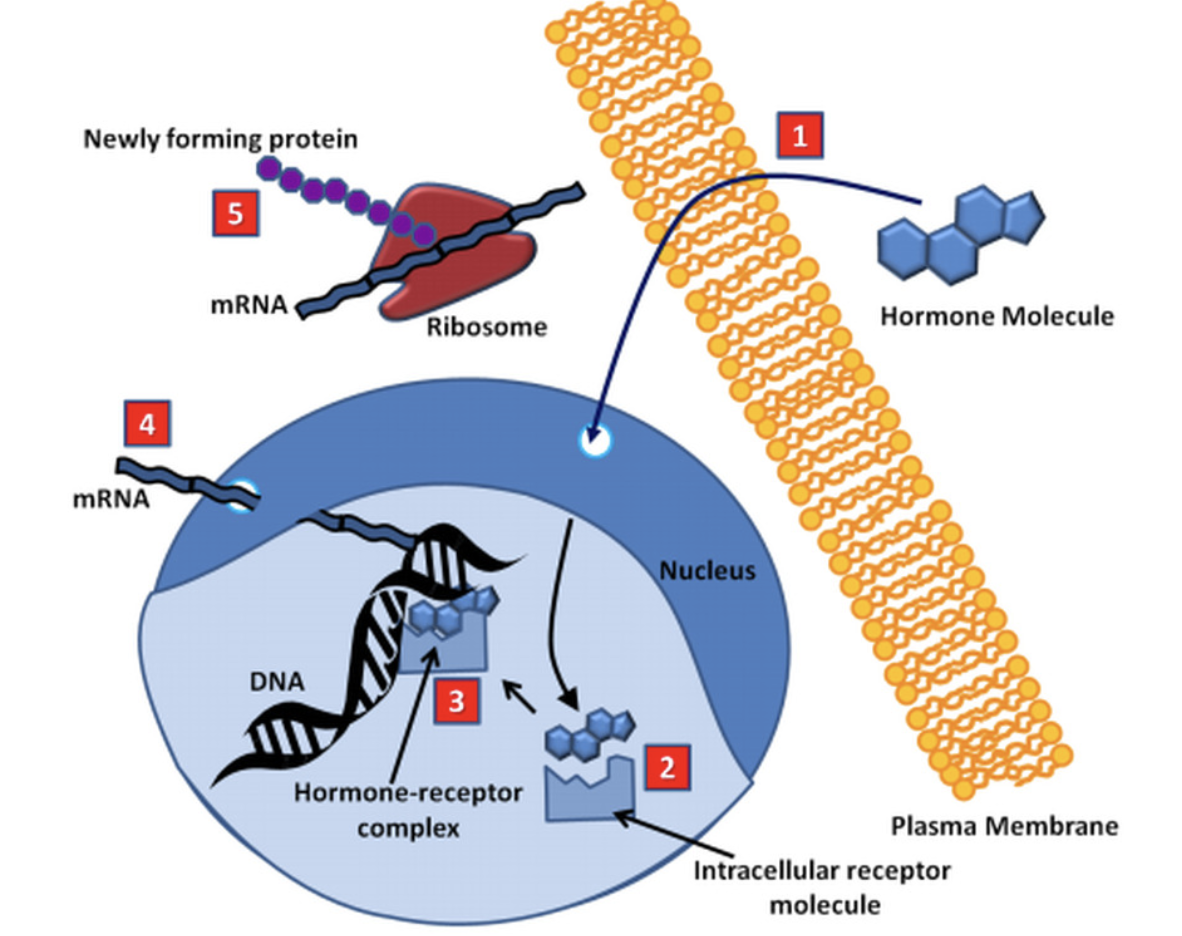
What is Intracellular Receptors?
They can pass through cells but interact with DNA to produce a new one. Takes several hours as they are creating a new one. (Ex:Steroid hormone)
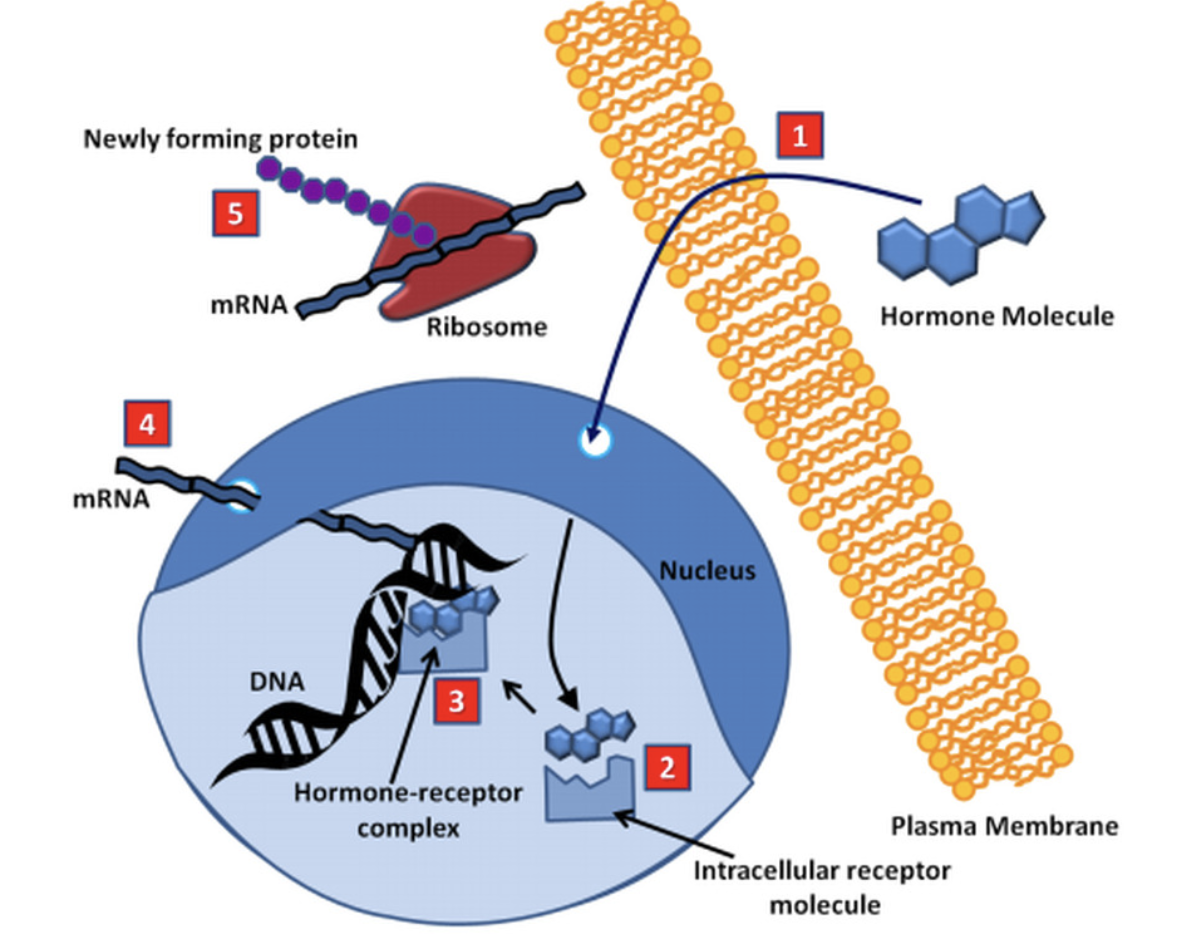
11
New cards
What are the two types of modulated systems in our body? (modulated system = hormones that determine strength of signals)
Amplitude Modulated and Frequency Modulated
12
New cards
What does Amplitude modulated mean?
The concentration of the hormone determines the strength of the signal.
Lower hormone = weaker strength.
Example: Endocrine System
Lower hormone = weaker strength.
Example: Endocrine System
13
New cards
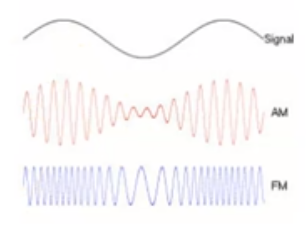
What is frequency modulated system?
How often the signal is sent determines the strength of singal.
Low amount of hits per second = less strength
Example: Nervous system
Low amount of hits per second = less strength
Example: Nervous system
14
New cards
What are the 3 types of Control Secretion Rates (aka how much hormone Brain need to release)
Extracellular concentration Control, Neural control and Hormonal concentration
15
New cards
What does Extracellular concentration Control mean?
Produces Hormones based on the concentration of non hormonal substances.
Example: concentration of glucose determines how much insulin is released
Example: concentration of glucose determines how much insulin is released
16
New cards
What is Neural Control?
Endocrine glands produce Neurotransmitters as hormones to affect the brain.
Example: Epinephrine from the adrenal glands makes your heart beat fast.
Example: Epinephrine from the adrenal glands makes your heart beat fast.
17
New cards
What is Hormonal Control?
Release of hormone to target a particular tissue
Example: Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland causes hormone release from the thyroid.
Example: Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland causes hormone release from the thyroid.
18
New cards
What are the two types of feedback loops?
Positive Feedback and Negative Feedback loops
19
New cards
What is positive feedback loop?
Signal continues to increase and stimulate the secretion of more of the hormone
Example: Baby's birth releases oxytocin for uterine contraction
Example: Baby's birth releases oxytocin for uterine contraction
20
New cards
What is a negative feedback loop?
Signal decreases the secretion of hormones
Example: Blood sugar regulation
Example: Blood sugar regulation
21
New cards
What are the 3 types of hormone regulations (aka how stable are hormones)?
Chronic Hormone, Acute Hormone, and Cyclic Hormone.
22
New cards
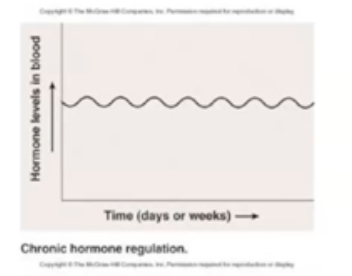
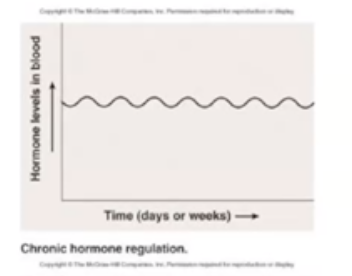
What is Chronic Hormone Regulation?
Relatively constant concentrations are maintained for long periods of time, Ex: GH or Thyroid
23
New cards
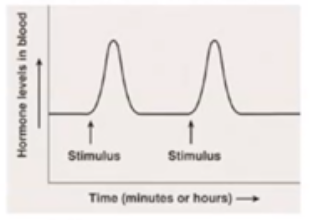
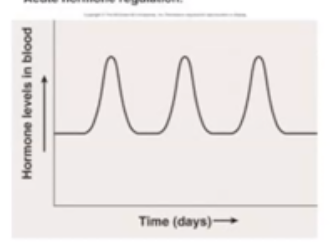
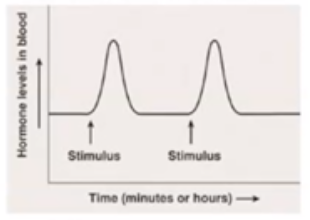
What is Acute Hormone Regulation?
Hormone rapidly increases in response to stimulus. Example: Epinephrine
24
New cards
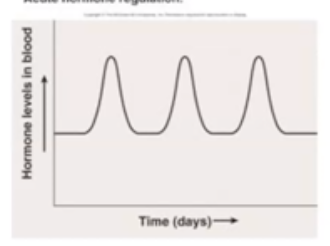
Cyclic Hormone Regulation
Increases and decreases in the concentration occur at roughly the same time and in the same amount. Example: Estrogen and Progesterone (period cycles)