Coagulation 1 - Hemostasis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
liquid, thrombus, blood flow
Hemostasis
Cellular and biochemical events that collaborate to:
Keep blood ______ within the vein and arteries
Prevent hemorrhage by forming a ________
Re-establish _____ ____ during the healing process
Vascular, coagulation, fibrinolytic
Hemostasis Maintenance
_______ system
Platelets
Plasma _________ factors
_____________ system
constriction, von Willebrand, platelets
Vascular System
Vaso__________
Endothelial cells release ___ __________ factor during vascular injury and activate ________
inactivated, constriction, platelet plug, coagulation cascade, fibrinolysis
Platelets
Platelets normally circulate freely in plasma, in an __________ state
Help induce vaso_________ (vasospasm)
Form a ________ _____ to stop further bleeding
Activate the ___________ ________ to stabilize the platelet plug
Initiate repair processes including clot retraction and clot dissolution (____________)
adhesion, activation, degranulation, aggregation, activation, fibrin
Platelets in Action
Damage to blood a vessel initiates platelet activation:
________ of platelets to the damaged vascular wall
_________ leading to platelet ___________, which stimulates changes in platelet shape and biochemistry
___________ as platelet-vascular wall and platelet-platelet adherence increases
________ of the clotting system and development of an immobilizing meshwork of platelets and ______
endothelial, thromboxane, prostacyclin, calcium
Subendothelial Exposure
Platelets rush to close the __________ opening after injury
Occurs after endothelial sloughing
Platelets begin to fill endothelial gaps
Promoted by ___________ A2 (TXA2)
Inhibited by ____________ I2 (PGI2)
Platelet function depends on many factors, especially ________
GP1b, endothelial, collagen, vWF, receptors, glycoproteins
Adhesion
Platelets Glycoprotein 1b (____) attaches to vWF (subendothelial matrix)
Adhesion is initiated by loss of ____________ cells, which exposes adhesive glycoproteins such as _______ and ___ in the subendothelium
vWF and other adhesive glycoproteins in the plasma deposit to the damage area
Platelets adhere to the subendothelium through ________ that bind to adhesive ______________ (GPIb, GPIa/IIa, GPIIb/IIIa)
stickiness, TXA2, constriction, degranulation, IIb/IIIa, shape
Activation
Platelet shape change and increase __________
Platelets initiate production of thromboxane A2 (____)
Vaso__________
____________ (ADP recruits and activated other platelets)
Aggregation
After platelets adhere they undergo an activation process that leads to a confirmational change in GP___/____ receptors, resulting in their ability to bind adhesive proteins, including fibrinogen and vWF
Changes in platelet _____
Formation of pseudopods
Activation of arachidonic pathway
COX-1, aspirin, decreased, decreased
Cyclooxygenase (___-_) converts arachidonic acid to TXA2 in platelets
_______ irreversibly inactivates COX-1
_______ production of TXA2
_______ platelet activation and aggregation
TXA2, GPIIb/IIIa, blood clot, coagulation
Aggregation
Induced by release of ____
Adhesive glycoproteins bind simultaneously to ______/____ on two different platelets (platelet-platelet binding)
Stabilization of the platelet plug (____ ____) occurs by activation of __________ factors, thrombin, and fibrin
RBCs, platelets, fibrin
Platelet plug formation
____ and _________ enmeshed in ______
The actual bandaid
platelets, thrombin, plasminogen
Clot retraction and clot dissolution
Clot retraction, using large number of ________, joins the edges of the injured vessels
Clot dissolution is regulated by _______ and __________ activators
Fibronolytic system
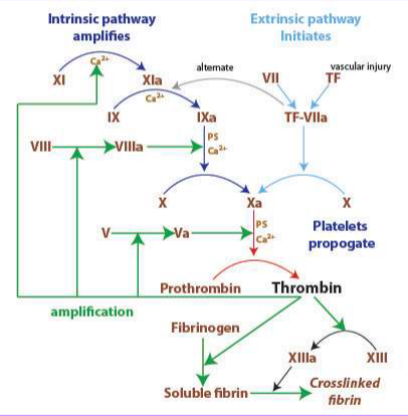
Coagulation Cascade
What do platelets activate?
aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time)
a blood test that measures how long it takes for your blood to clot. It's used to evaluate the intrinsic and common pathways of the coagulation cascade, helping assess the function of various clotting factors
PT (prothrombin time)
measures how long it takes blood to clot, specifically focusing on the extrinsic and common pathways of the blood clotting cascade. It's used to assess blood clotting ability, monitor the effects of blood thinners like warfarin, and check for potential bleeding disorders or liver problems.
Primary Hemostasis
What does this picture depict?

Secondary Hemostasis
What does this picture depict?
vascular, platelets, platelet plug, temporarily
Hemostasis Stages: Primary Hemostasis
Dependent on ________ intima and _________
Formation of “primary ________ ____”
____________ stops bleeding
coagulation, fibrinolysis, thrombin, platelet plug
Hemostasis Stages: Secondary Hemostasis
Dependent on __________ and ____________
Coagulation cascade creates ________ (→ fibrin) that “strengthens the ________ ____”
petechiae, purpura, epistaxis, hematemesis, telangiectasia, mucosal
Symptoms of a Primary Hemostasis Problem
________ (pinpoint)
_______ - purple discoloration of skin
__________ - nose bleed
___________
Menorrhagia
_____________ - spider-like vessels
_______ bleeding
ecchymosis, hemarthrosis, delayed, oozing
Symptoms of a Secondary Hemostasis Problem
__________ - deep tissue bleed
___________ - joint bleed
________ bleeding and ______ from wounds
Platelet tests
What kind of tests do you run if you think its a problem with primary hemostasis?
platelet count, time, function, aggregation
Primary Hemostasis: Platelet tests
CBC ______ _____/slide
Platelet function tests:
Bleeding ____
Platelet _______ analyzer (PF 100 or PFA)
Platelet __________
Coagulation Tests
What kind of tests do you run if you think its a problem with secondary hemostasis?
prothrombin, thromboplastin
Secondary Hemostasis: Coagulation Tests
__________ time (PT/INR)
Activated Partial ____________ time (aPTT)