Promotion Exam 3 (Module 6-8)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
primary
____ prevention is directed toward promoting health and prevention of disease, examples include immunization, diet and exercise education, seatbelt use, etc
secondary
____ prevention focuses on screening for early detection, examples include screenings and exams
tertiary
____ prevention begins after an illness is diagnosed and treated, examples include physical therapy and support groups
precontemplative
phase of transtheoretical model when the person is not thinking of making a change
contemplative
phase of transtheoretical model when the person is only thinking about change in the near future
decision making
phase of transtheoretical model when the person constructs a plan to change behavior
action
phase of transtheoretical model when the person takes steps to operationalize the plan of action
maintenance
phase of transtheoretical model when the person works to prevent relapse and sustain the gains made from actions taken
termination
phase of transtheoretical model when the person has the ability to resist relapse back to unhealthy behaviors
internal
____ stressors originate within a person
external
____ stressors originate outside of the person
developmental
____ stressors occur at predictable times through a person’s life
situational
____ stressors are unpredictable and may occur at any time during life
alarm
first phase of general adaptation syndrome (GAS), fight or flight response that lasts minutes to hours
resistance
second phase of general adaptation syndrome (GAS), adaptation occurs to stressor, cortisol activity still increased
exhaustion
third phase of general adaptation syndrome (GAS), endocrine activity increases having negative effects on body systems, body will fail if exposed to stress is prolonged
dialation
term for the cervix opening
effacement
term for the cervix stretching and thinning
bloody show
discharge of blood and mucus before labor
engagement
occurs when presenting part is at or beyond level of the maternal ischial spine
uterine contractions
what are the primary powers of labor?
abdominal muscles
what are the secondary powers of labor?
dilation
1st stage of labor?
expulsion
2nd stage of labor?
placental
3rd stage of labor?
restorative
4th stage of labor?
authoritarian
an ____ parent expects obedience from the child and discourages the child from questioning the family’s rules, provide low support and high control over the child
authoritative
an ____ parent shows respect for the child’s opinions and individuality, but still upholds ultimate authority
permissive
a ____ parent has little control over the behavior of their children and allow the children to set their own standards and rules
neglectful
a ____ parent is indifferent and low in responsiveness, often disconnected from child’s life
atraumatic
____ care is therapeutic care that minimizes or eliminates the psychological and physical distress experienced by children and their families in the healthcare system
lightening
occurs when the fetal presenting part begins to descend into the true pelvis
passageway, passenger, powers, position, psyche
what are the 5 P’s of labor?
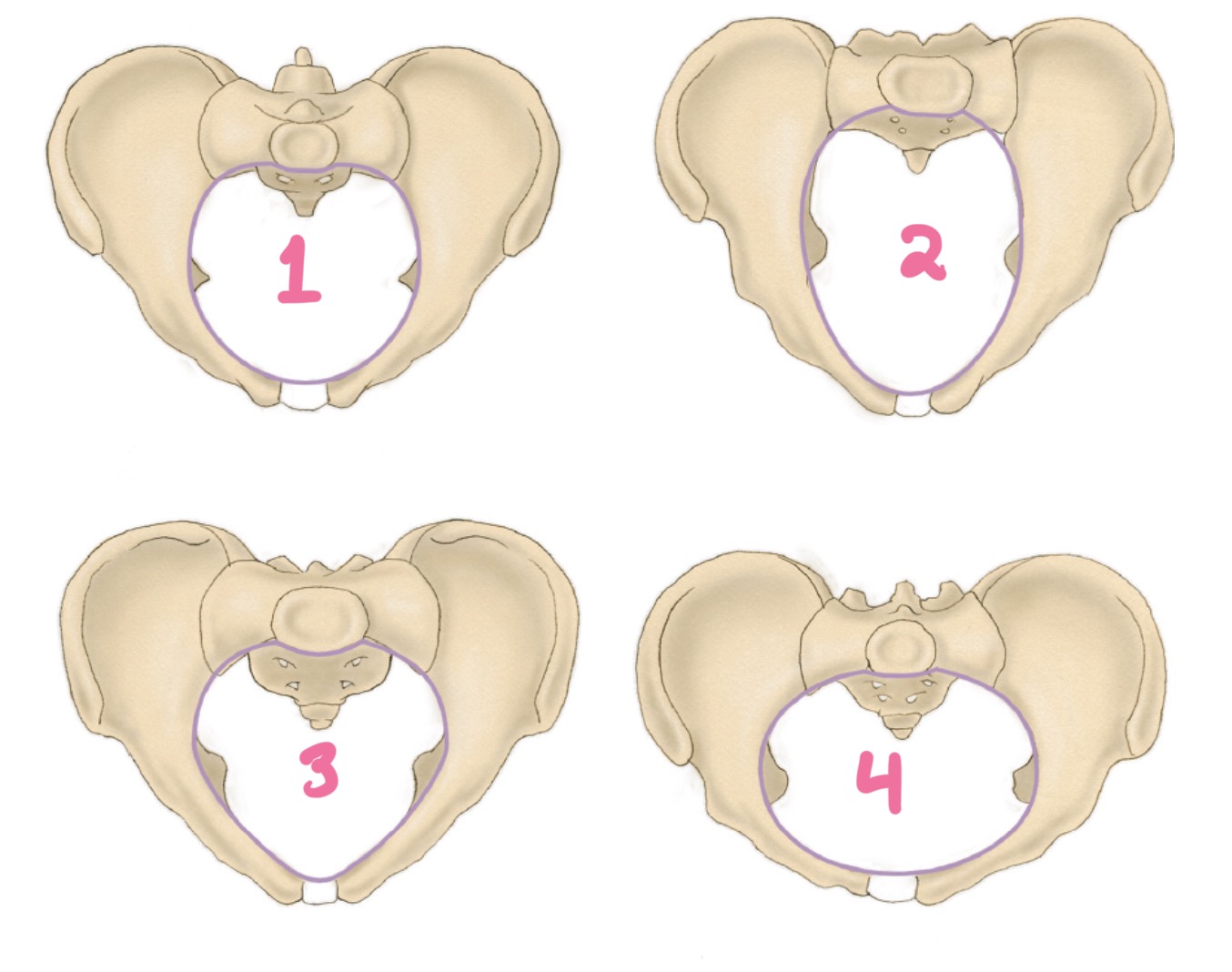
gynecoid
1?
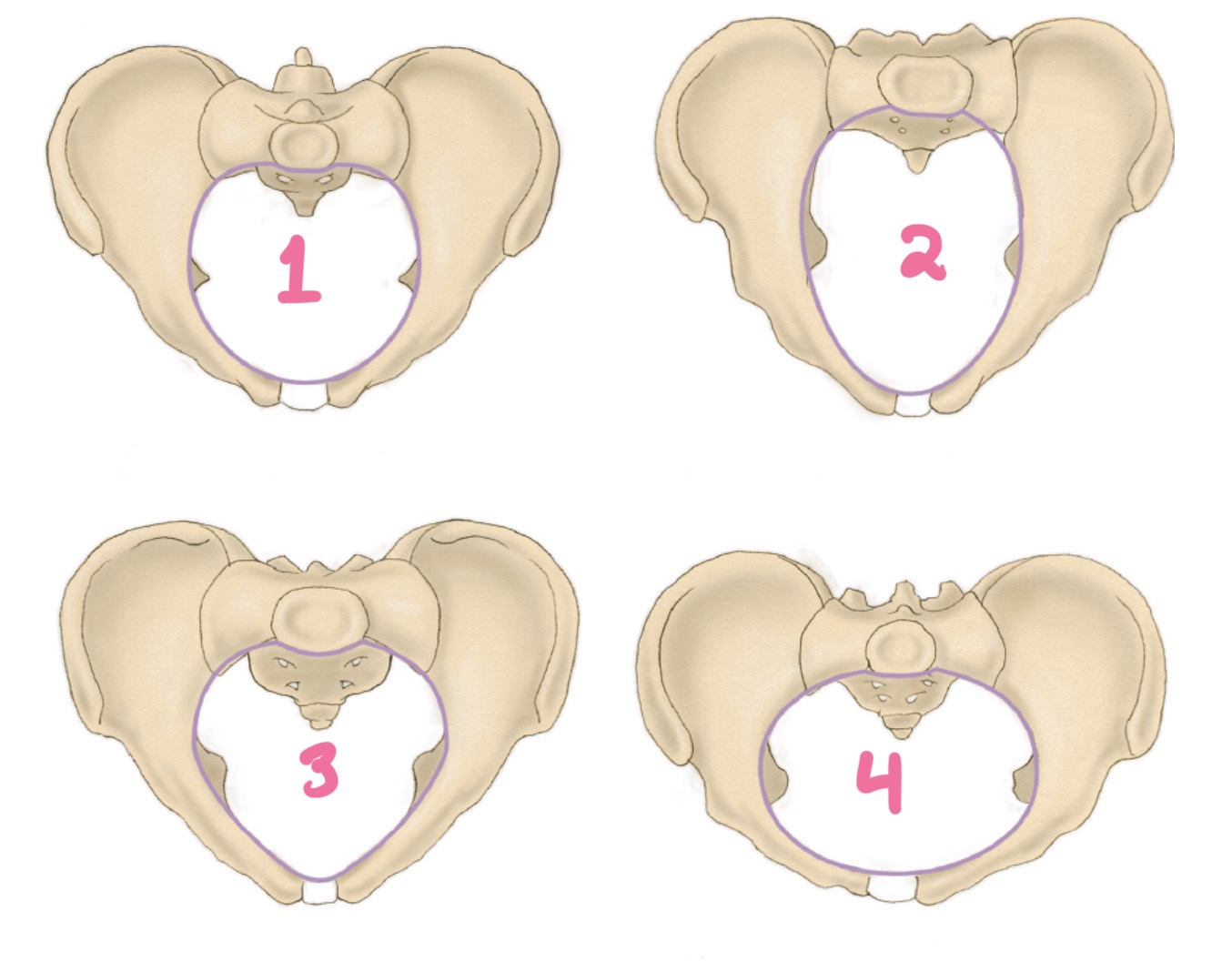
anthropoid
2?
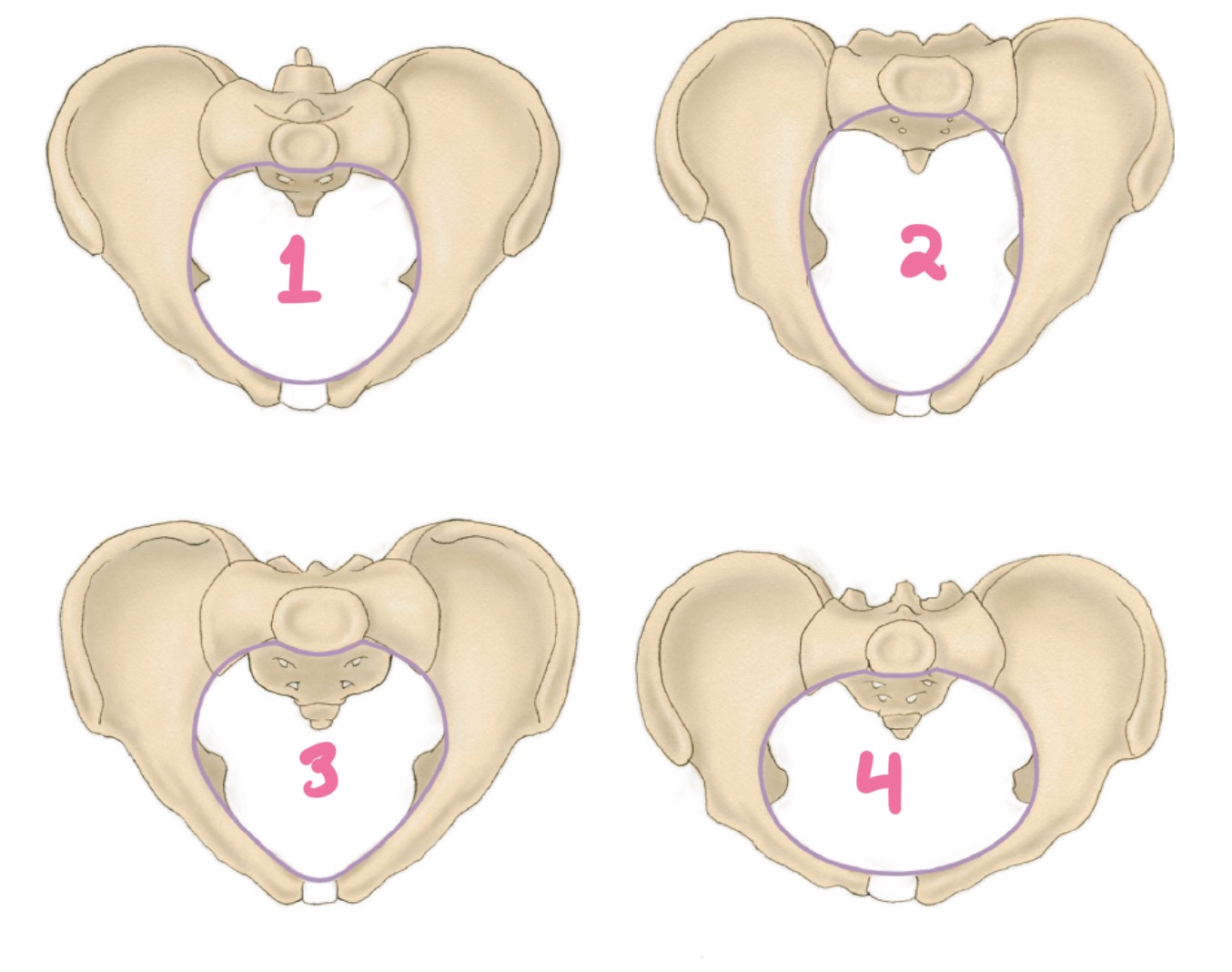
android
3?
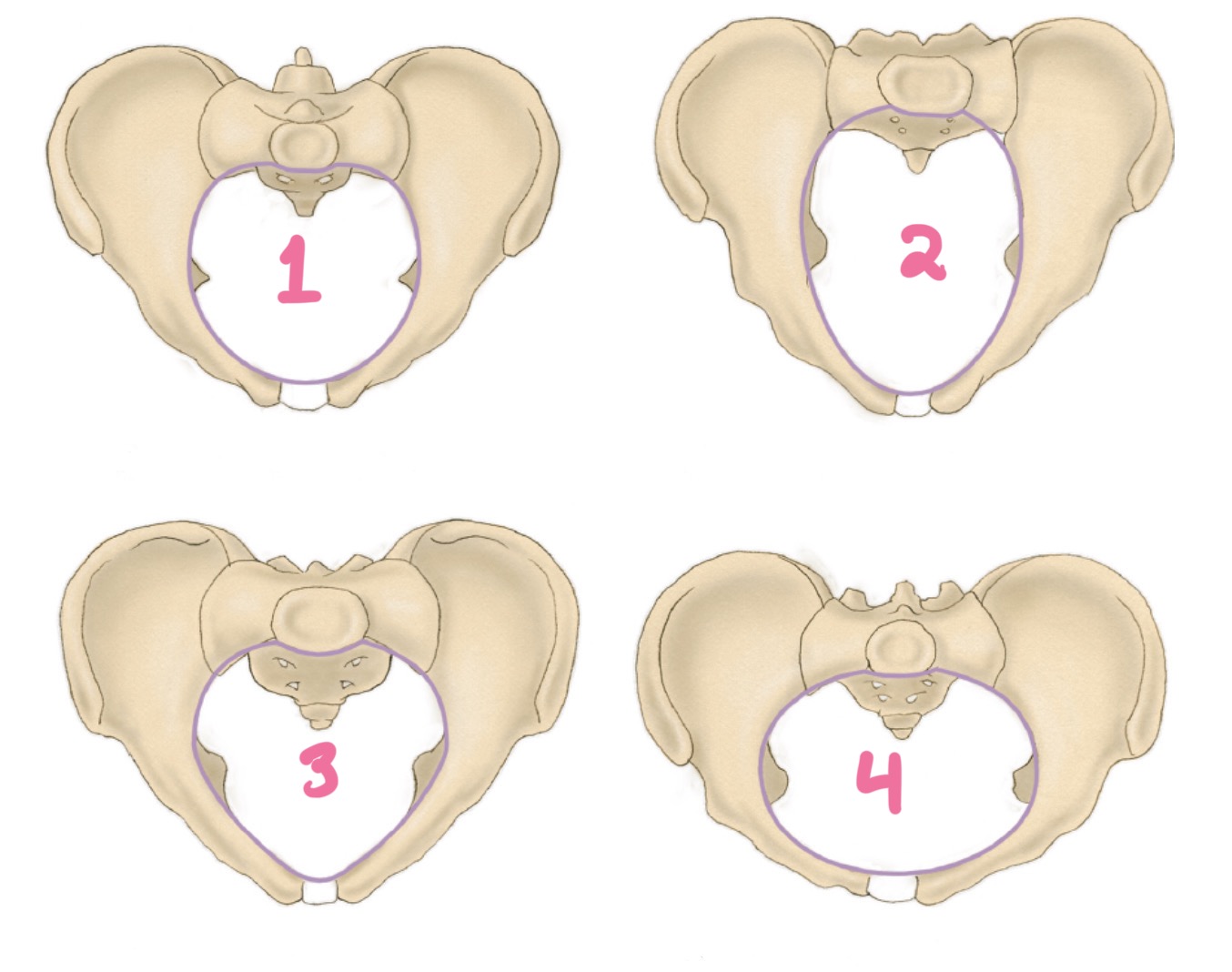
platypelloid
4?
vertex
teal presentation?
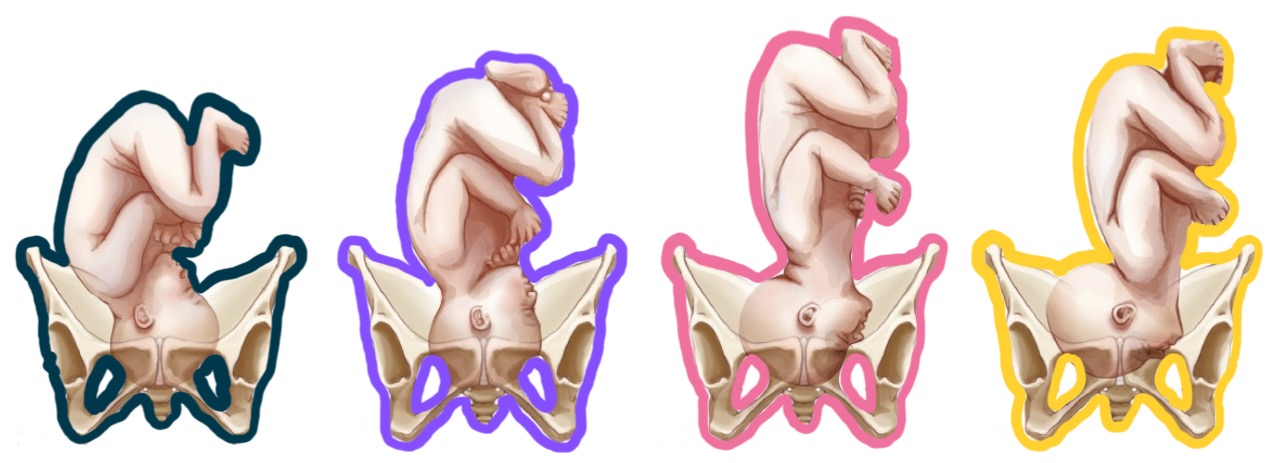
military
purple presentation?
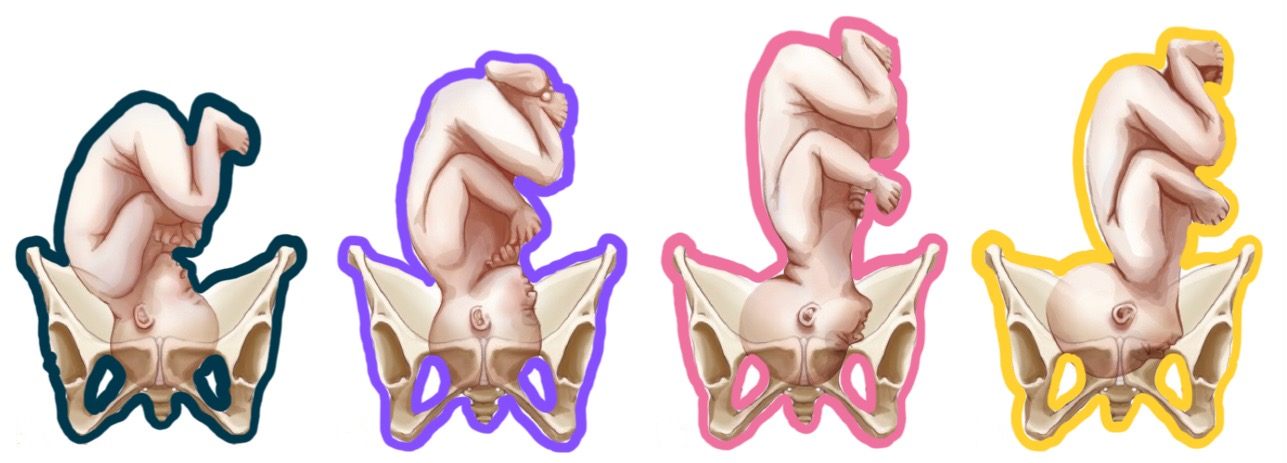
brow
pink presentation?
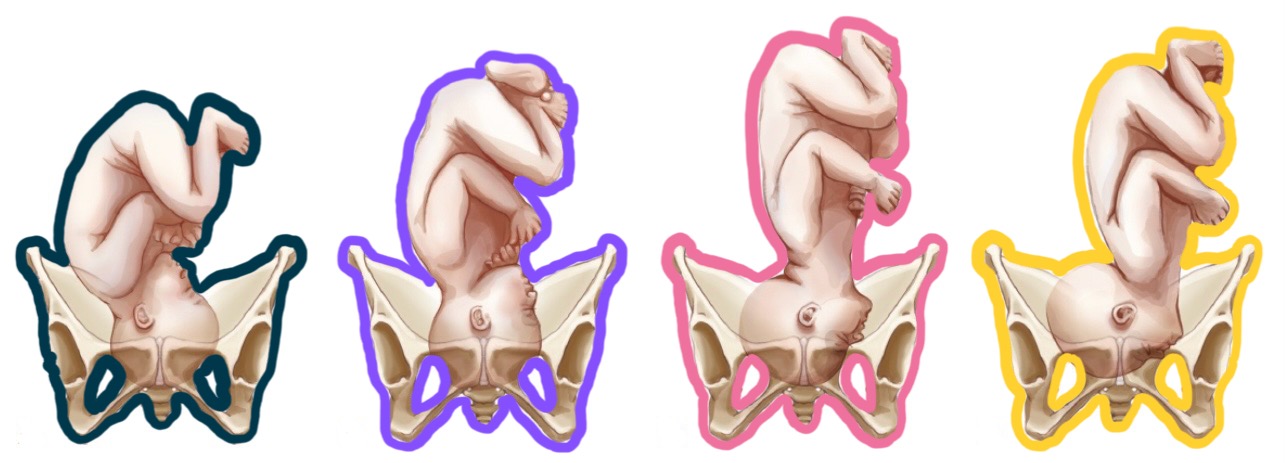
face
yellow presentation?
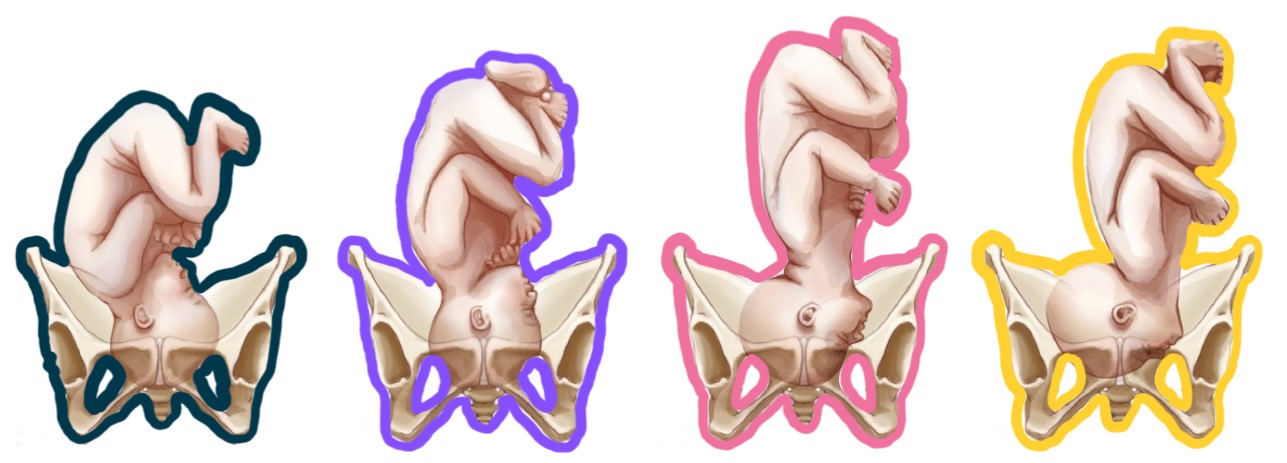
lie
fetal ____ refers to the relationship of the long axis (spine) of the fetus to the long axis (spine) of the mother
presentation
fetal ____ refers to the body part of the fetus that enters the pelvic inlet first
frank
green breech presentation?
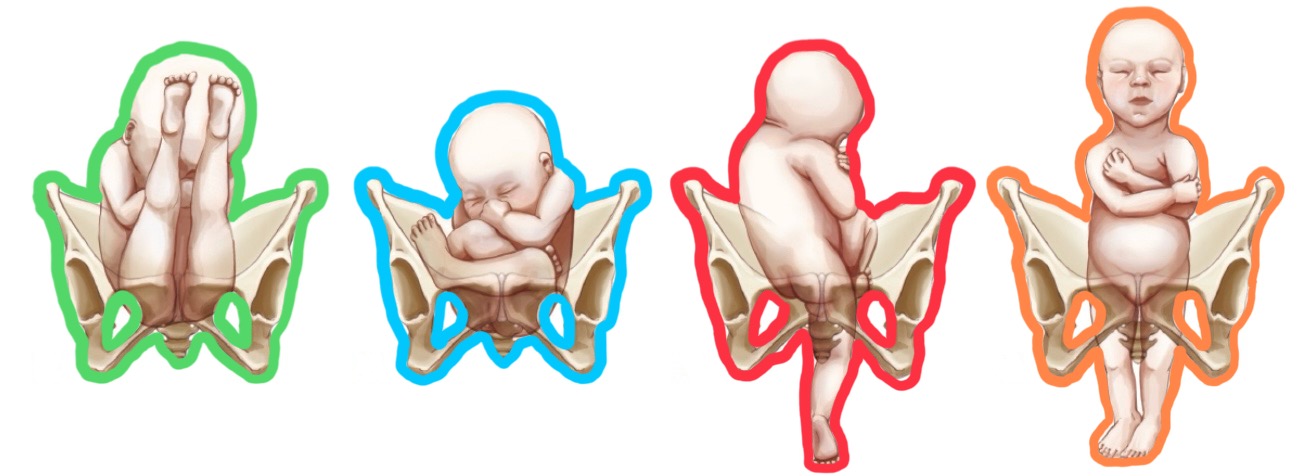
complete
blue breech presentation?
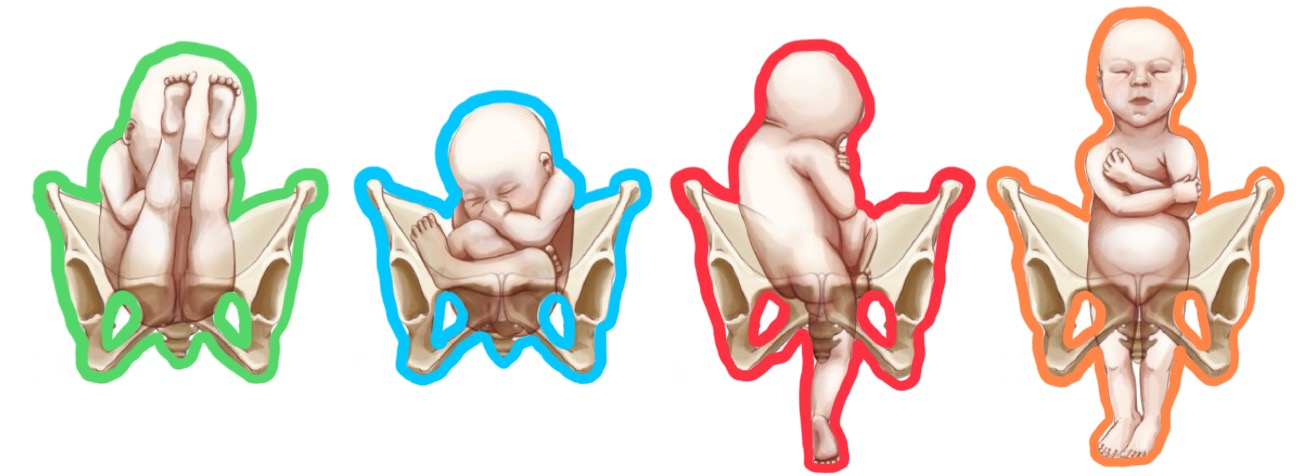
single footling
red breech presentation?
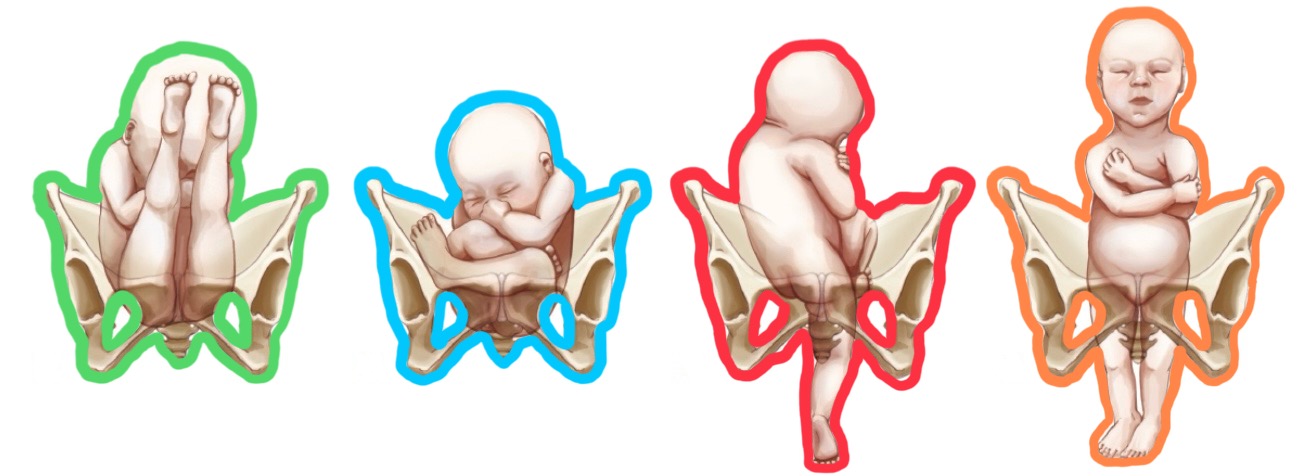
double footling
orange breech presentation?
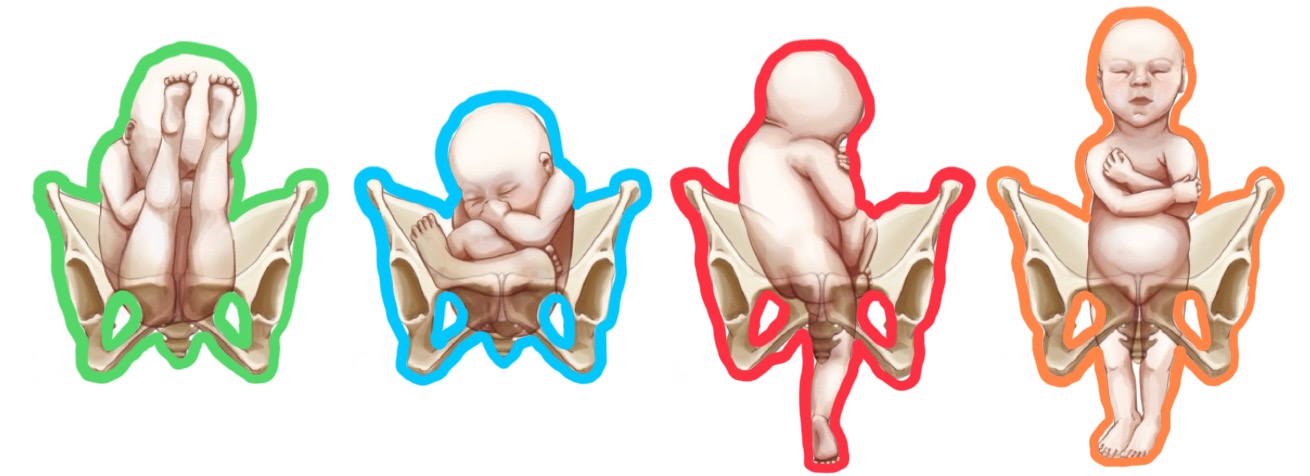
position
fetal ____ describes the relationship of a given point on the presenting part of the fetus to a designated point of the maternal pelvis
station
fetal ____ refers to the relationship of the presenting part to the level of the maternal pelvic ischial spines
marked variability
occurs when there are more than 25 beats of fluctuation in the FHR baseline, may be caused by cord prolapse or compression