Stem cells, tissues, tissue injury
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
what is a stem cell
vital foundation to life; starts as a single cell; A SINGLE CELL THAT CAN REPLICATE ITSELF OR DIFFERENTIATE INTO MANY CELL TYPES
What can a stem cell do
replicate itself and differentiate into many cell types
stem cells are
undifferentiated/immature
how are stem cells distinguishable from other cells of the body
-undifferentiated/not specified
-able to self renew
-have the potential to differentiate
what can stem cells turn into
- daughter cells that remain stem cells
- differentiated cells
what is prodominate stem cell division type
asymmetric - maintains the stem cell pool that won’t differentiate and mature
what happens in asymmetric stem cell division
- stem cell
- progenitor cells
What is a progenitor cell?
daughter stem cell that goes off to differentiate
when does symmetric stem cell division occur
under times of stress when we need one specific type of stem cell
what happens in symmetric stem cell division
- two progenitor cells are made
- two stem cells are made
---> TWO IDENTICAL CELLS ARE MADE
when would you see symmetric stem cell replication
- when you have lost a lot of blood
What is stem cell differentiation
Process by which unspecialized stem cells give rise to specialized mature cells
what is the stem cell niche environment.
- provides nourishment, structural support, and protection
what encompases the stem cell niche
cellular components, secreted factors, ECM, and hypoxia/metabolism
Why are stem cells normally dormant
reduces mutation possiblity. it is a protective state supported by the niche factors.
what promotes stem cells to wake every few months
- THEIR NICHE
--> decrease or increase in growth factors/chemicals
--> theory about vacant niche spot exists, signaling cells to divide
what happens to the area where stem cell division is normally occuriing under stress
- extramedullary niches may form (in the LIVER, SPLEEN, LYMPH NODES)
Under extreme stress, where can we get more blood
extremedullary niche areas can form hematopoiesis
where does stem cell division normally take place
bone marrow
what are the stem cell types
- embryonic - blastocyst, puripotenet capability
adult stem cells - anything after the blastocyst
- pluripotent
- totipotent
how do we work around getting embryonic stem cells from blastocytes
induced pluripotent stem cells - genetically modified mature adult stem cells brought back to pluripotent state.
totipotent stem cells, where are they found?
cell with greatest differentiation potential; they give rise to every type of cell. during early embryonic development; have the potential to give rise to ALL cells including placents
outer cell mass of blastocyte
what stem cells can make the placenta
totipotent
What do totipotent cells differentiate into?
into the blastocyte
what does the outer layer of the blastocyte form
- placenta and other structures supporting fetal development
what does the inner cell mass make
- has pluripotent cells which form the germ layer
what can the pluripotent stem cell differentiate into
-essentially any type of cell other than the placenta
ectoderm develops into?
think outer stuff.
skin and nervous system, sensory organs (mouth, sinus, teeth)
what does the trophoblast form
placenta
What does the endoderm give rise to?
think insides.
digestive tract, lungs and respiratory tract, bladder
what does the mesoderm give rise to
“middle” between outer most ectoderm and most middle endoderm.
muscles, bones, blood/blood vessels, lymph tissue, cartilage
multipotent stem cells
stem cells that can become a limited number of types of tissues and cells in the body; still can become a lot of things but less differentiation potential than pluripotent
adult stem cells are
multipotent
what is the function of adult stem cells
stored in the body to maintain and repair/replace dead or damaged cells; make all cell types from the tissue they live in; can self-renew
mesenchymal stem cells create what?
BONE
bone marrow and skeletal stem cells that give rise to:
- osteoblasts/osteocytes
- chondrocytes
- adipocytes
- stromal cells
neural stem cells create what?
NERVOUS TISSUE
special cells in the nervous system that are capable of dividing to form new tissue, including new neurons
Where does hematopoiesis take place?
depends on where we are in life
after birth, in bone marrow. into adult hood, main sites are in vertebra, sternum, and ribs.
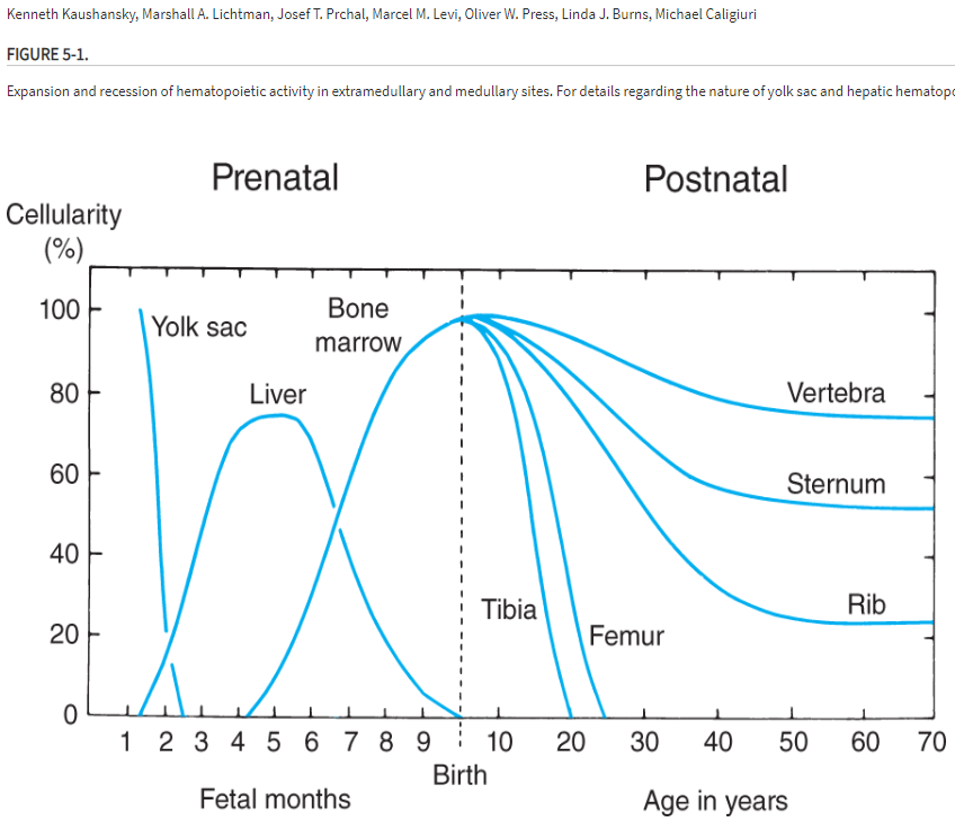
Where is bone marrow found in the bones specifically?
medullary cavity
describe the structure of bone marrow
- stroma: network of sinuses
- vasculature: arteries and capillaries
- innervation: myelinated and unmyelinated to amintain vessel tone
What is yellow marrow?
fat cells that replace the hematopoetic cells with age. found in bones that once made blood cells.
hands, feet, arms, legs
what cells function as the regulators of hematopoesis
endothelial cells
what cell is responsible for the network that cells rest upon?
adventitial reticular
what is the pre curosor to a RBC
reticulocyte
what is the pre cursor to a platelet
megakaryocyte
what does the lymphoid progenitor stem cell give rise to
lymphocyte
do we have more granulocytes or agranulocytes
granulocytes
what are the granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What are the agranulocytes?
lymphocytes and monocytes
what is the growth hormone for leukopoeisis
CSF
What do stem cell recipients undergo before a transplant?
chemo to kill their immune system and make room for the donor cells
what is EPO used to treat
anemias, associated with low epo levels
what reactions do granulocytes produce?
their inflammatory and allergic reactions
neutrophils
ACUTE INFECTION
- most common granulocyte
- enter tissues; triggered by infection or cytokines
- short half life; 6 hrs
- cause inflammation
- bind to integrin; attracted by selectins
- pass through capillary walls via diapedesis
- leave circulation via GI
eosinophils
- short half life
- PARASITIC INFECTIONS AND ALLERGY
- attracted by selectins, bind to integrins, and enter through diapedesis
- most abundant in GI, respiratory and urinary tracts
basophils
release histamine, involved in immediate hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
when would you give supplemental EPO
renal failure, chronic inflammation, myelodysplastic syndromes
when would you give TPO (thrombopoietin)
in immune thrombocytopenia
when would you give G-CSF
- drug induced neutropenia
- congenital disorders with low nuetrophil count
- to pt after chemotherapy
Thrombopoietin stimulates what
production of platelets
thrombocyte life span
10 days
where is thrombopoietin secreted
liver
what does TPO stimulate
megakaryocytes to fragment and release enucleated cells
what is the average half life for neutrophils
6 hrs
what are the key cells for acquired immunity
Lymphocytes
where do T cells form
Thymus
B cells form where
bone marrow
Where are the majority of t-cells and b-cells found
in lymph nodes and spleen
what is the life span of a monocyte
3 months
T cell life span as compared to B cells
B cells have shorter life
what are monocytes stimulated by
cytokines released from T lymphocytes
what are examples of tissue macrophages
- kupffer cells in liver
- pulmonary alveolar macrophages
- microglia in brain
characteristics/functions of neutrophils
- multilobed nucleus
- granules
- ingest and destroy microorganisms
- coordinate early inflammation
Basophil characteristics and function.
- become mast cells in tissue and release histamine
lymphocyte feature and function
- small cell with different morphology
- generate specific immune respone
- B lymphocyte become plasma cell
- T cells provide cell mediated immunity
erythrocyte life span
120 days
function of erythrocyte
transport oxygen
when is EPO released from the kidneys
when O2 is decreased
maturation of RBC in bone marrow depends on what
- iron
- vitamin B12
- folic acid
features of RBC
- decreased in size
- make hemoglobin
- no organelles
- no nucleus
what are the 4 main tissue types
muscle, epithelial, connective, nervous
epithelial characteristics
- avascular, rely on diffusion through basal layer.
regenerate quickly
- apical, basal surfaces.
closely attached to one another
epithelial functions
barrier, protection of underlying structures, absorption & secretion.
what is epithelial tissue derived from (ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm?)
all 3 germ layers
Connective tissue components
collagen for tensile strength reticular, elastin
mechanism of cell atrophy
decreased protein synthesis and increased protein degredation in cells
physiologic and pathologic cell atrophy
physiologic: due to normal stressor (e.g. the size of the uterus after pregnancy)
pathologic: loss of blood/innervation, aging, decreased workload
hypoplasia
SMALLER AMOUNT OF CELLS
tissue that did not develop normally and is smaller than it should be
mechanism of atrophy
decrease in protein synthesis and increase in protein degradation
hyperplasia mechanism
MORE CELLS = MORE DIVISION HAPPENING
physiologic hyperplasia examples
breasts during pregnancy
endometrium thickening during menstrual cycle
liver growth post resection
pathologic hyperplasia examples
growth of adrenal gland due to ACTH (makes them bigger),
proliferation of endometrium due to prolonged estrogen stimulus
what cells dont undergo hyperplasia
myocytes of the heart or neurons
hypertrophy
increase of cell size due to increase in protein
physiologic hypertrophy
enlarged skeletal muscle with exercise (size of cells get bigger, number of cells don’t increase)
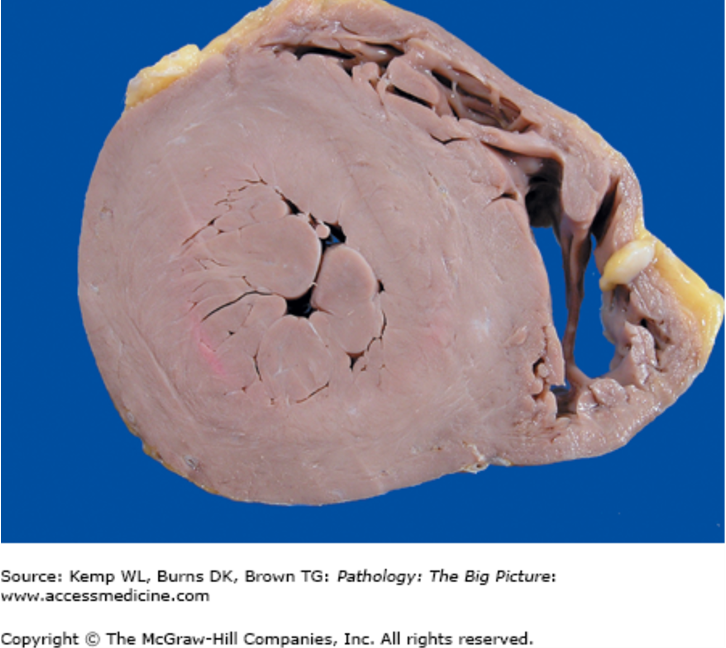
pathologic hypertrophy example
increase in heart size due to aortic stenosis
metaplasia
ONE CELL TYPE TO ANOTHER
change from one cell type to another cell type in abnormal location
metaplasia mechanism
cell at site cant handle new environmental thing so it converts to a different type
metaplasia example
barrett esophagus - stomach acid is irritating the esophageal epithelial cells so it transforms to a cell type that handles it better.
what is metaplasia caused by
chronic chemical or mechanical irritation
is metaplasia reversible
yes, if the stressor goes away.
if it persists: may cause neoplasm