Bio 201: Cell Cycle and Plant Reproduction Concepts
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Pollen Grain
Contains two cells: tube cell and generative cell.
Tube Cell
Develops into a pollen tube for sperm delivery.
Generative Cell
Divides to form two sperm cells during pollen development.
Cell Cycle
Series of phases for cell growth and division.
Interphase
Cell prepares for division; includes G1, S, G2 phases.
M Phase
Phase where mitosis and cytokinesis occur.
G1 Phase
Cell grows and performs normal functions.
G0 Phase
Inactive phase where cells do not divide.
Mitosis
Process of nuclear division resulting in two identical cells.
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and spindle apparatus forms.
Telophase
Nuclear envelopes reform around separated chromosomes.
Checkpoint Proteins
Regulate progression through the cell cycle.
Neurogenesis
Formation of new neurons under specific conditions.
DNA Damage Response
Neurons reactivate cell cycle due to DNA damage.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes with the same genes but possibly different alleles.
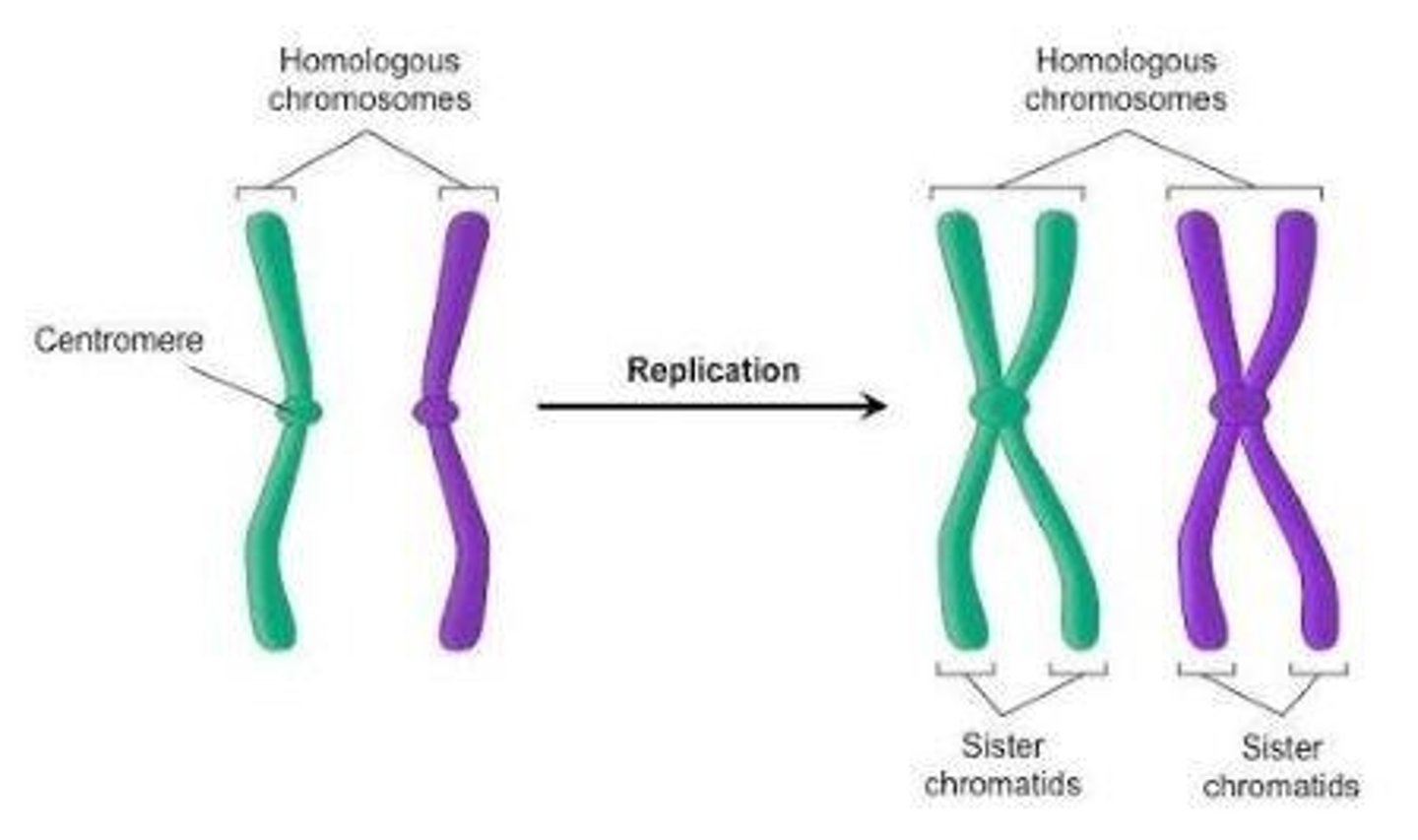
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome connected at the centromere.
Hexaploid
Organism with six homologous copies of each chromosome.
Diploid
Cell with two complete sets of chromosomes.
Meiosis I Product
Results in two haploid cells, not identical.
Independent Assortment
Random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
Sperm Cell Mutation
Percentage of mutated sperm cells depends on allele segregation.
Mitosis Location
Occurs in the generative cell during pollen development.
Meiosis Location
Occurs in the anthers of flowering plants.
Bulge in DNA
Caused by incorrect nucleotide incorporation during replication.
Cell Cycle Machinery
Components necessary for cell cycle activation and regulation.
Mitosis Steps
Include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Chromosome Identification
Chromosome pairs from different individuals may differ in genes.