Lecture 13- cytoskeleton 2 microtubules, cilia and flagella
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
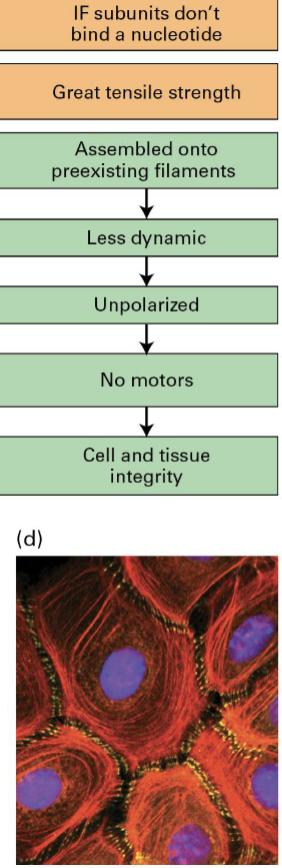
Intermediate filaments
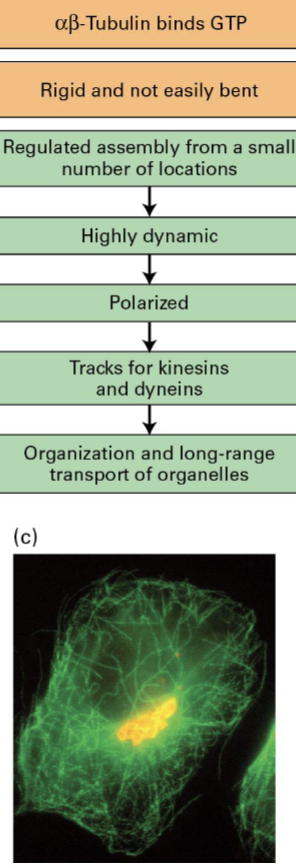
Microtubules
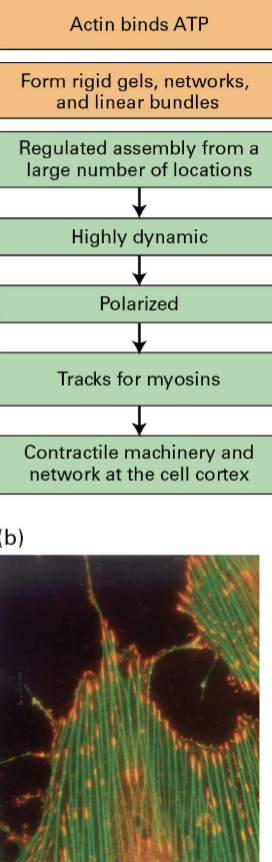
Microfilaments
what proteins use energy to move directionally
along cytoskeletal polymers
motor
moves along Tub to neg end
Dynein
moves along Tub to pos end
Kinesin
moves along Actin
Myosin
what contribute to structural support, organization, motility within the cell
microtubules
microtubules are what
polymers
microtubules made up of α and β subunits that can be added and released
heterodimers
# protofilaments
13
what is stabilized by associated proteins
microtubules
subunits are rapidly incorporated as dimers with what-bound
to the β-subunit, then what is hydrolyzed
GTP
what on β is exchanged in the cytosol for what
GDP, GTP
microtubule-organizing centers (MTOC) govern microtubule what
assembly
microtubule- organizing centers control centrosome and basal
body in what cells
animal
microtubule- organizing centers control nucleus in what cells
plant
centrosome is made up of # centrioles and PCM
(pericentriolar material)
2
microtubule assembly: dimers are added to (and lost from) which end
pos
𝛾-Tubulin sits in a ring in PCM and what bind to it to form microtubule
dimers
minus end is associated with what
centrosome
if all GTP is hydrolyzed, the microtubule can rapidly what
depolymerize
microtubule assembly & disassembly: requires energy from
GTP hydrolysis (beta) to what (expensive)
lengthen
some treatments change microtubule dynamics: binds dimer, adds to tubule, blocks further addition
colchicine
some treatments change microtubule dynamics: suppress addition
to tubule, may detach from MTOC
nocodazole,vinblastine
some treatments change microtubule dynamics: inhibits disassembly and thereby assembly
taxol
taxol, nocodazole,vinblastine, colchicine are ANTI CANCER or CANCER agents because they interfere with cell division
anti cancer
dynamic microtubule structures are regulated in cells
by
Microtubule Associated Proteins (MAPs)
EB1 binds near the what of microtubules
end
you attempt to make tubulin polymers in vitro
you add cell extracts to large amounts of 𝛼- and 𝛽-Tubulin,
ATP, GTP, GDP, and adjust the temperature to 37
after you get polymers, which of the following will be depleted
from the test tube?
GTP
you attempt to make tubulin polymers in vitro
you add cell extracts to large amounts of 𝛼- and 𝛽-Tubulin,
ATP, GTP, GDP, and adjust the temperature to 37
you have made tubulin polymers in vitro, but they are transient, which is not great for taking pictures.
which drug might help you maintain the microtubules
taxol
About your in vitro microtubules…
after much work (EM), you realize your polymers are
funny-looking because the tubes are too small in
diameter
which of these additions would help?
centrosomes = 𝛾-Tubulin ring complex
Taxol-treated cells have more or less dynamic microtubules
less
two motor protein families
use energy to move in opposite directions along microtubules
Dynein & Kinesin
•first implicated in cilia and flagella movement; later found in all animal cells (cytoplasmic)
•stalk binds MTs; head generates force; requires ATP
•binds cargo via dynactin protein
•moves organelles, vesicles, particles; positions Golgi,
centrosomes, mitotic spindle (required for cell division)
Dynein
~ 45 different blank-like proteins (KLPs) in mammals
• heads “step” along protofilament, 1 tubulin subunit at a time towards + end
•[ATP] dependent
•processive
• tend to move organelles (mitochondria, peroxisomes) and vesicles outward
Kinesin
Can Kinesin work upside down?
Yes
how fast (and expensive) is Kinesin movement?
one step is about 8nm
let’s say the distance from Golgi to the plasma membrane of an epithelial cell is 16 micro meters, and that kinesin can carry cargo there in 16 seconds. Each step expends 1 ATP
How many ATPs does this trip use?
2x103
in cultured neurons, your GFP fusion motor protein tends to move toward the cell body. is your motor protein a plus-end or minus-end directed motor?
minus
In cultured neurons, your GFP fusion motor protein
tends to move toward the cell body.

what known kind of motor protein does this resemble?
Dynein
what are microtubule-rich structures that beat or wave
flagella
protozoans, algae, sperm use flagella for what
movement
what are microtubule rich structures that can wave or be stationary
cilia
The axoneme of cilia/flagella is made up of microtubules and what
dynein
what proteins are also needed to build/maintain
the axoneme of cilia/flagella
motor
Kinesin 2 and what dynein transport cargo in and out
cytoplasmic
cilia move by microtubule sliding via ciliary what
Dynein
a mutation that disrupts which of the following proteins is the most likely to result in this outcome: Kartagener Syndrome
cilia exist but have defective or no movement
ciliary dynein
Kartagener Syndrome: cilia exist but have defective or no movement
you want a mouse model of the disease, so you want to make a genetic mutant. you know that the human patients have only small changes in the coding region of the dynein protein, not entire loss, and you know that cilia from these patients hydrolyze ATP at a similar rate to normal cilia.
so, which region of the protein(s) might be the best place to make a small deletion to mimic the disease?
heavy chain stem domain