andrology and embryology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
smen parameters for seminogram - lower references
§Semen Volume - 1.5 ml
Sperm Concentration - 15 × 10^6 / ml
Total Sperm count - 39 × 10^6
Motility (Progressive Motility) - 32%
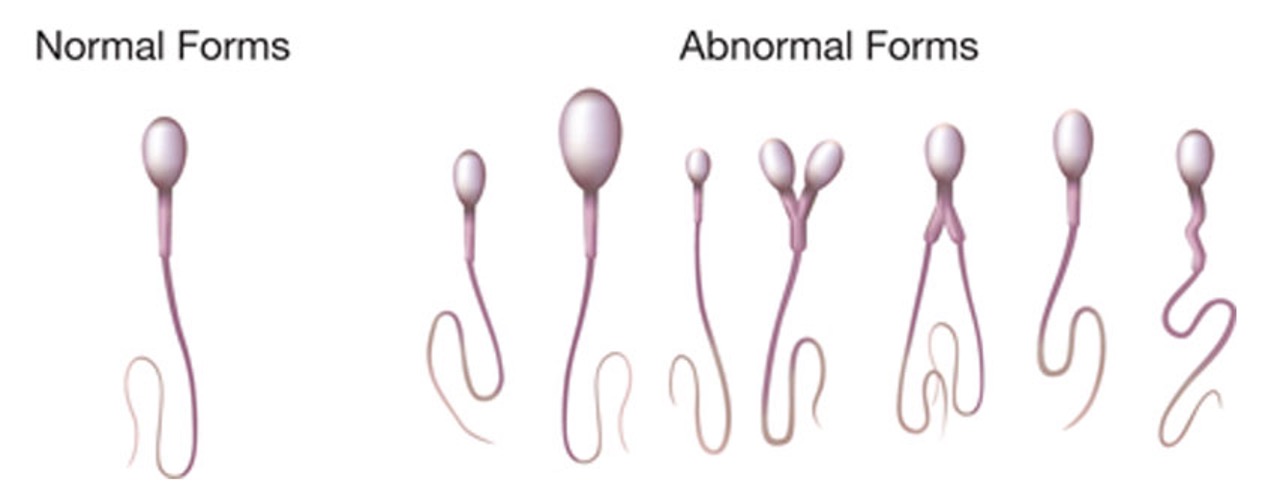
Sperm Morphology - 4%
Sperm vitality - 58%
all parameters greater lower references arw
normozoospermic - normal sperm
semen volume
beloq 1.5 ml - hypospermia
above 5.5 ml - hyperspermia
Measure of prostate and other glands secretions
Semen is essential for sperm protection, nutrition and survival
wet prep
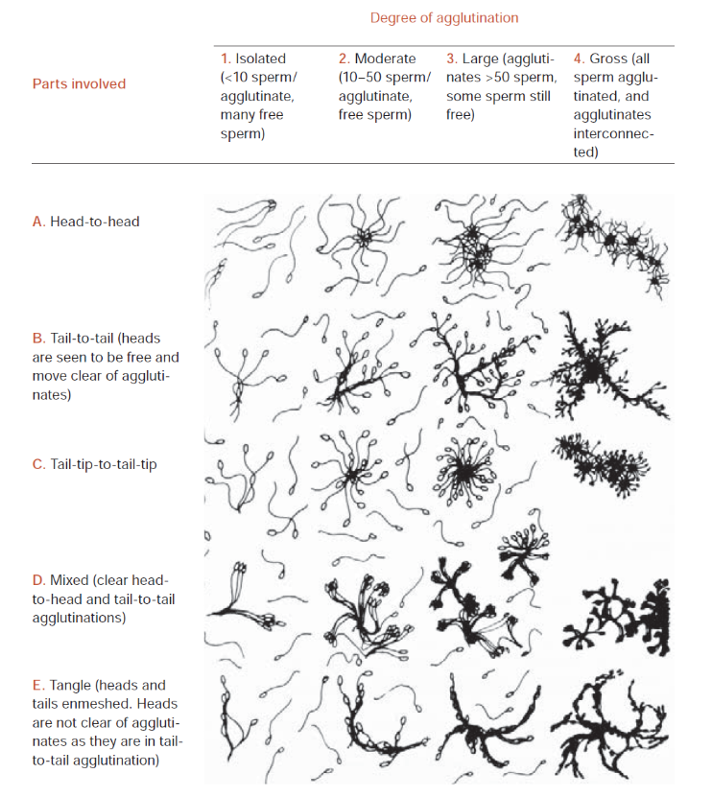
looks at agglutination, debris and round cells
severe agglutinination suggests prescence of anti sperm antibidoes
10 micro litre sample
when doing a wep prep why should you wait 1 minute after putting on the coverslip
to stop drifiting
progressive motility
assess around 200 sperms
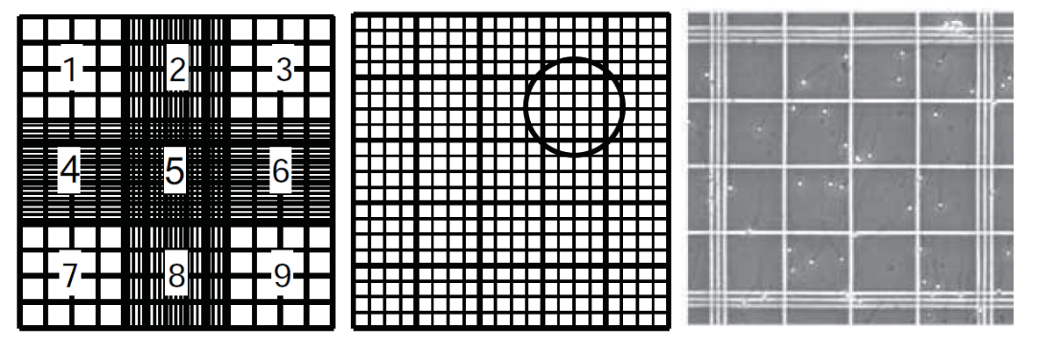
sperm concentration
Using improved Neubauer haemocytometer
Counting at least 400 sperms
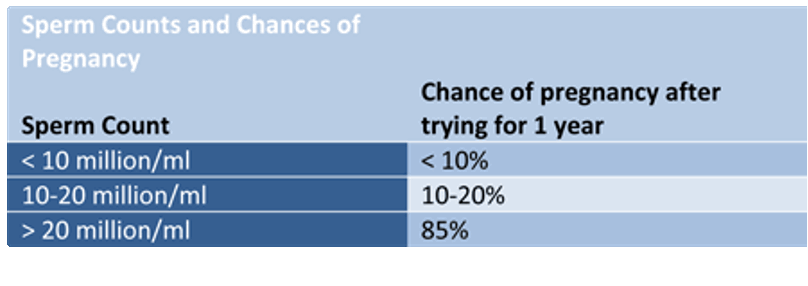
< 15 x 106 / mL Oligospermia - fewer cells than normal
total sperm count + formula
conc x volume
LOWER REFERENCES
≥ 39 x 106
< 39 x 106 Low sperm count
< 1-2 x 106 Azoospermia
Centrifugation of semen sample, < 1-2 x 106 Azoospermia
morphology
abormal forms - globozoospermia
vitality - active
§Eosin-Nigrosin Stain
10ul Stain solution + 10ul Semen
ÞFeathering technique
Þ1000X
§
Dead sperm = permeabilised membrane
= Pink
Percentage of live sperm
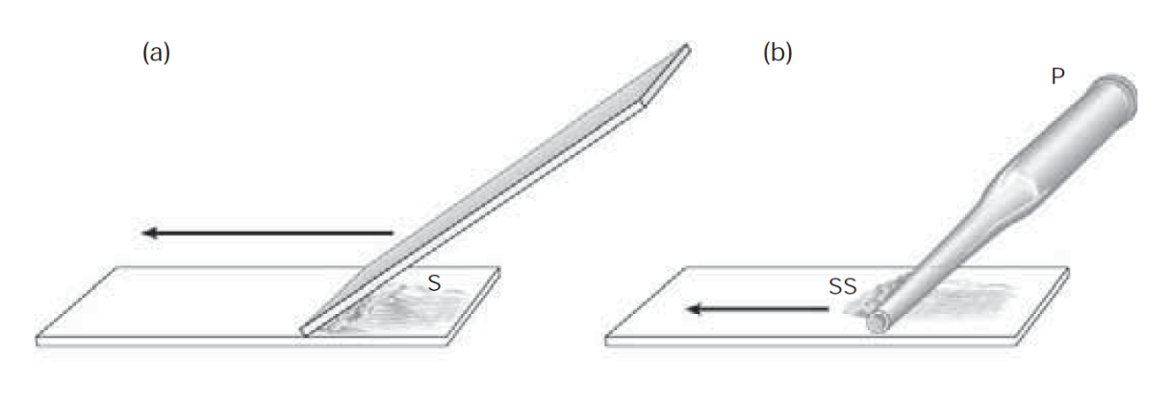
semen smearing method
§Feathering method (a) & Pipette method (b)
Ethanol fixed and air-dried
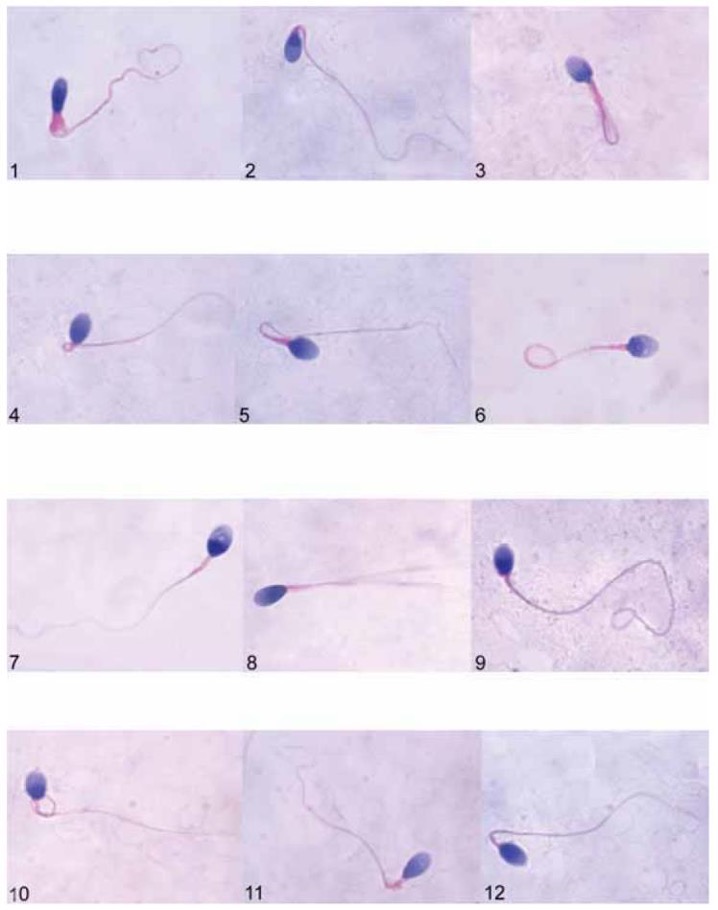
sperm morphology staining
§Papanicolaou Stain
§
Head : Pale blue
Mid-Piece: Red staining
Tail: Blue
Excess cytoplasm: Pink
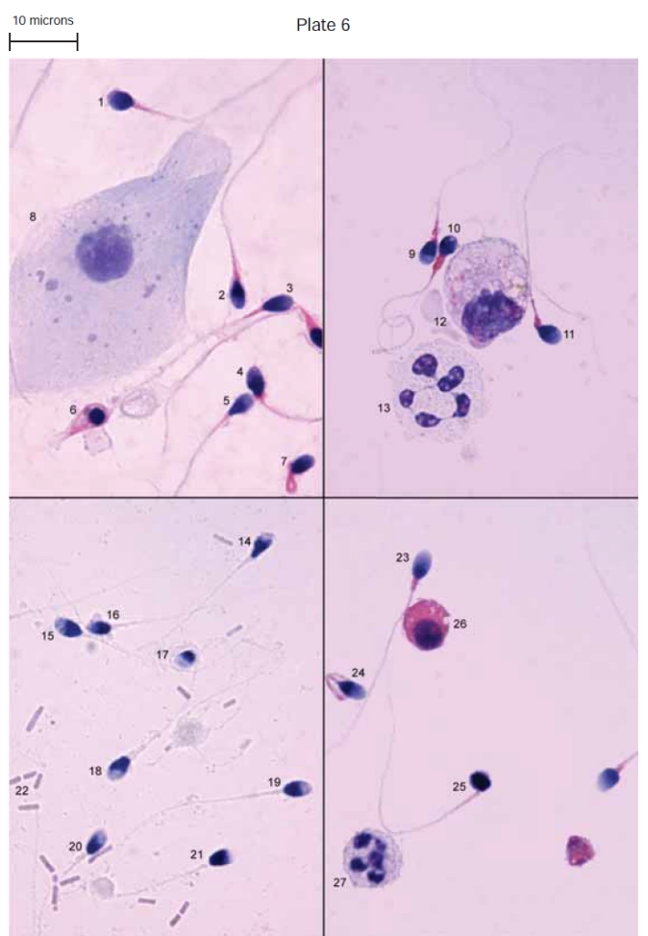
round cells
§Papanicolaou Stain
§
8: Epithelial cells
12: Macrophage
13 / 27 : Leukocyte (WBC)
22: Bacilli
26: Spermatid (95% of round cells)
Giemsa Stain for Leukocyte determination
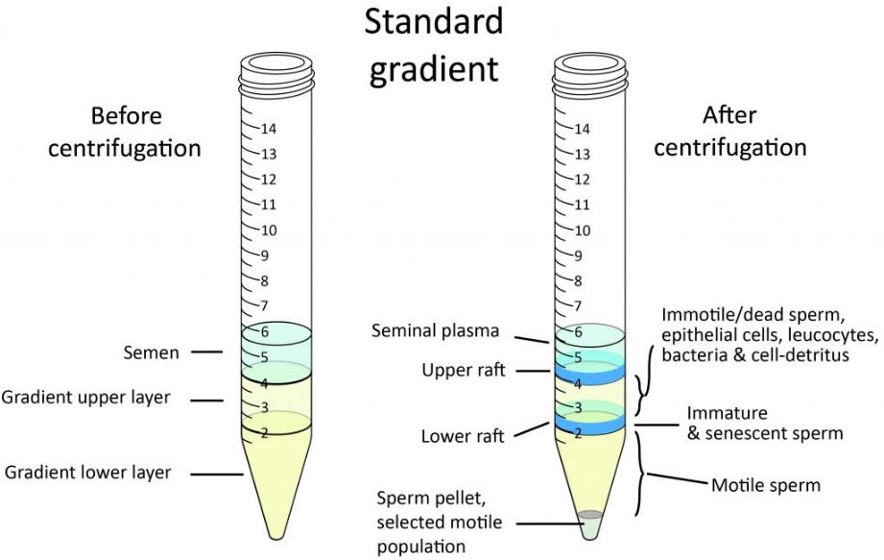
sperm prep techniques §
§Removing abnormal sperm, debris and rounds cells
§Techniques:
ÞSwim-up
ÞDensity gradient (40% Upper / 80% Lower)
conc and mobility assessed
HIV Infected semen sample
§If HIV, viral RNA and proviral DNA are detected in sample: semen and non-sperm cells
§
§CD4, CCR5, CXCR4 are expressed only by non-sperm cells.
§
§Density gradient followed by swim-up as a way of preventing infection of uninfected female partners.
§
§Prepared samples should be tested via RT-PCR before use.
§
§Procedure should be carried out in secure facilities to minimise cross-contamination of HIV-free samples
early cleavage grading
x,x,x,
Number of cells, Blastomere size, fragmentation
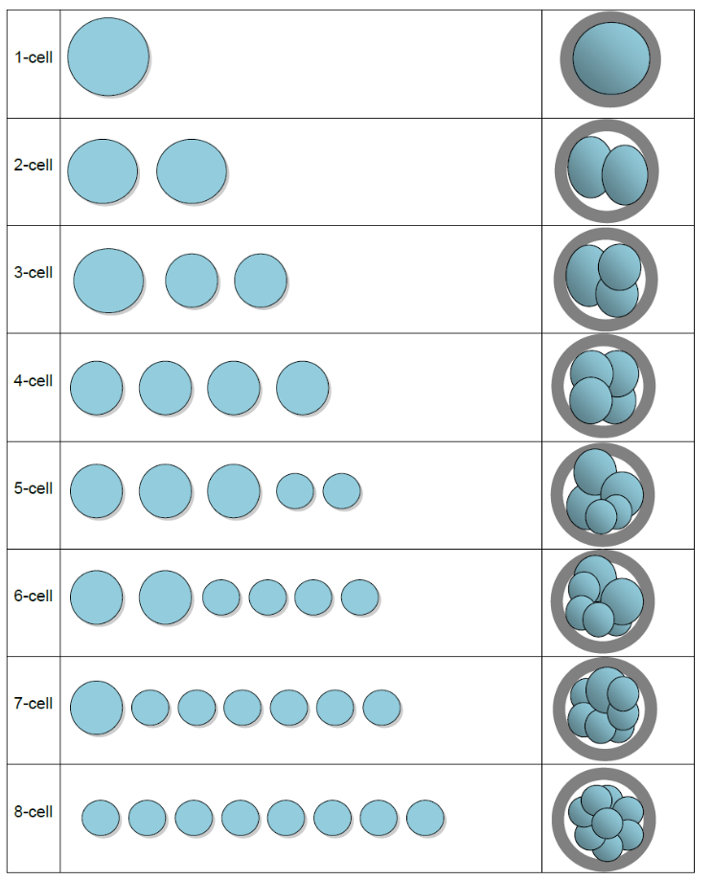

blastomere size
fragmentation
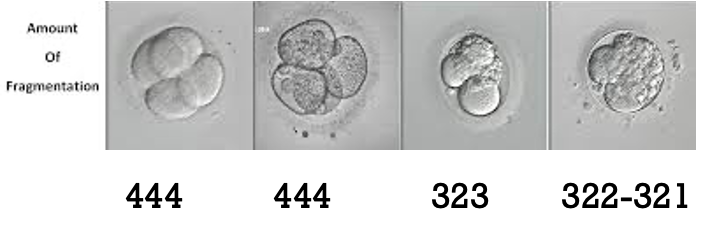
Fragmentation
Due to uneven division of the cells
Cytoplasmic debris
Higher fragmentation = lower likely hood of pregnancy
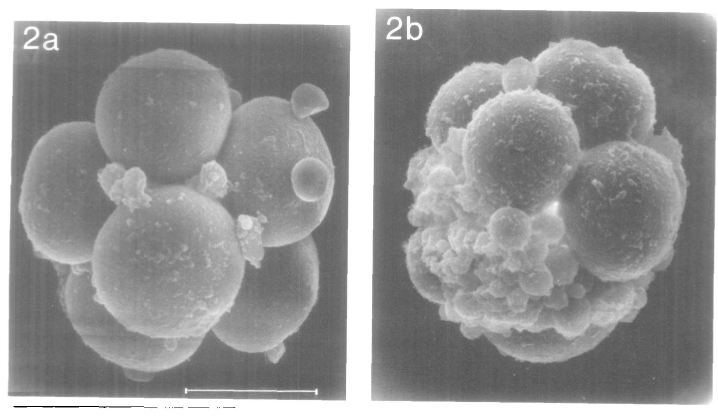

blastocyst grading
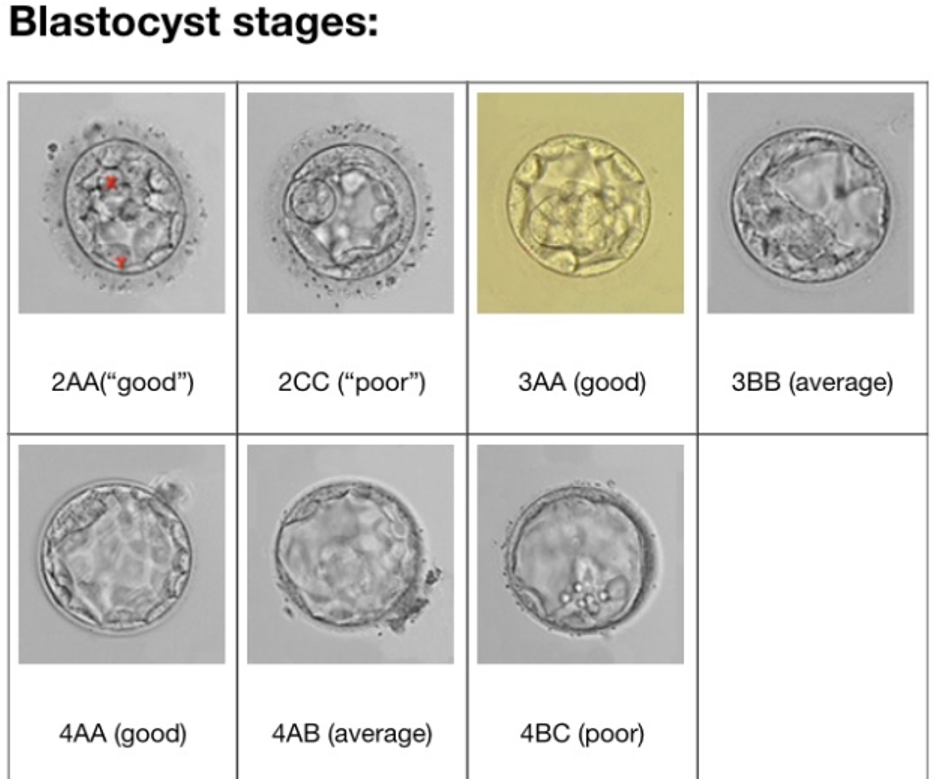
blastocyst grading - 3BB minimal
Discards grade ‘C’ blastocysts = potential?
Single embryo transfer of expanded blastocysts with grade ‘C’ ICM or grade ‘C’ TE resulted in live births at rates that, while lower than top quality blastocysts (34.1 versus 46.8%), resulted in 109 live births that had similar obstetric and perinatal outcomes compared to grade ‘A’ or ‘B’ blastocysts
embryo transfer , what jhappens to other good quality embryos
1 or 2 good quality embryo transferred
Freezing
Other lower quality embryos: either discarded or if consented by parents, given to research project (NHS and HFEA ethical approval)
frozen embryo transfer
Thawed (+ in vitro developed)
Re-freezing = Twice-frozen-thawed embryos have a lower post-thaw survival rate
But similar pregnancy and live birth rates to once-thawed embryos