quizzes- cannulation
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
veins
thin walled
fibrolus
have a large diameter and low pressure
veins __ to propel blood through the vein towards the _
contract, heart
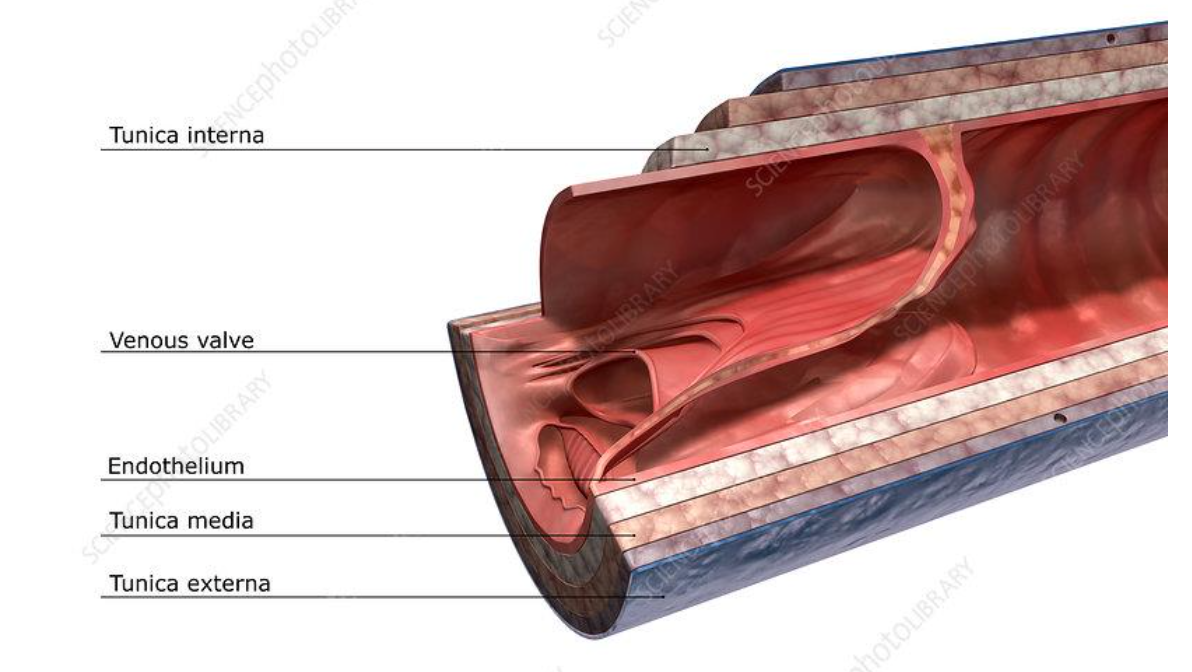
veins consist of the following three layers:
tunica externa - outer layer
tunica media- elastic smooth muscle fibres and nerve supply
tunica intima- innermost, epithelial lining
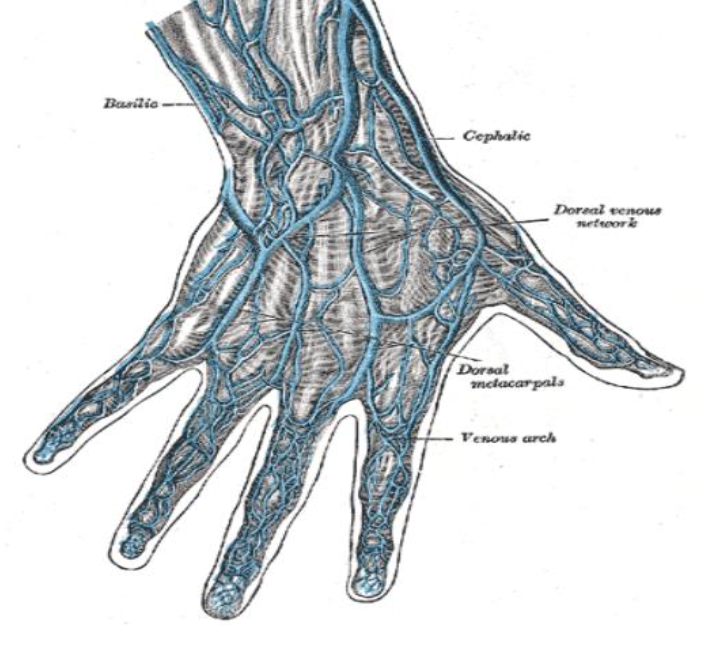
veins in arm and hand
veins of upper limb are divided into 2 groups:
1.superficial v- located just under the skin and often are visible
2- deep v- run closely to arteries and have more valves than superficial veins
veins of the hand
• The ___ ____ veins run along side of the fingers and join to form the 3 dorsal metacarpal veins
dorsal Digital
Veins of the hand should be avoided as the vessels have
thinner walls and so they can easily collapse.
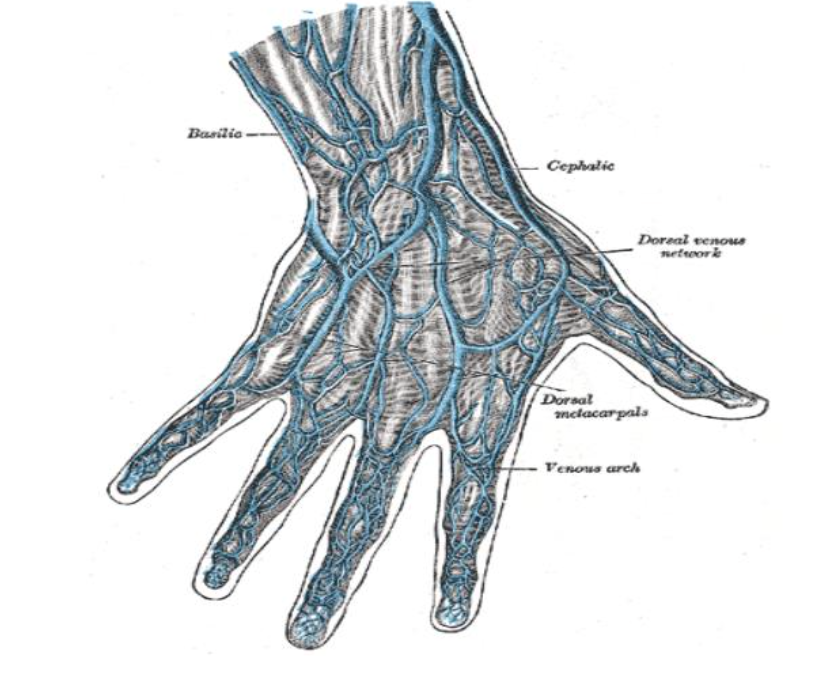
Major Superficial Veins of the Arm are as follows:
Dorsal
Cephalic
Basilic
Medial Cubital Fossa
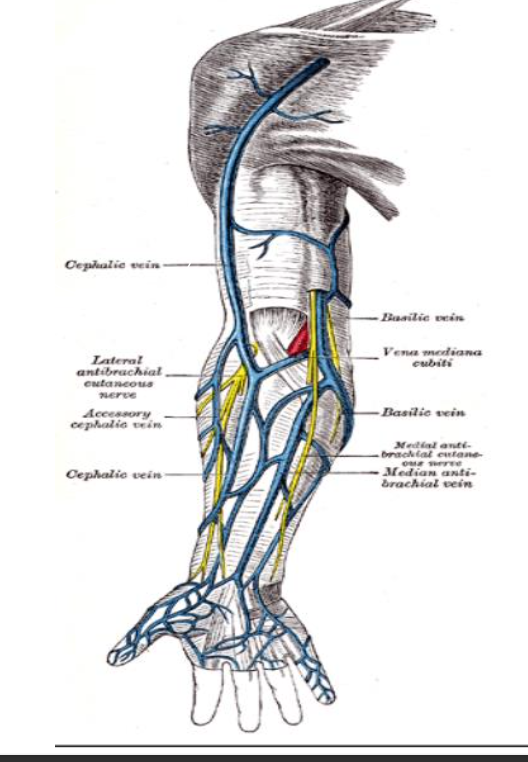
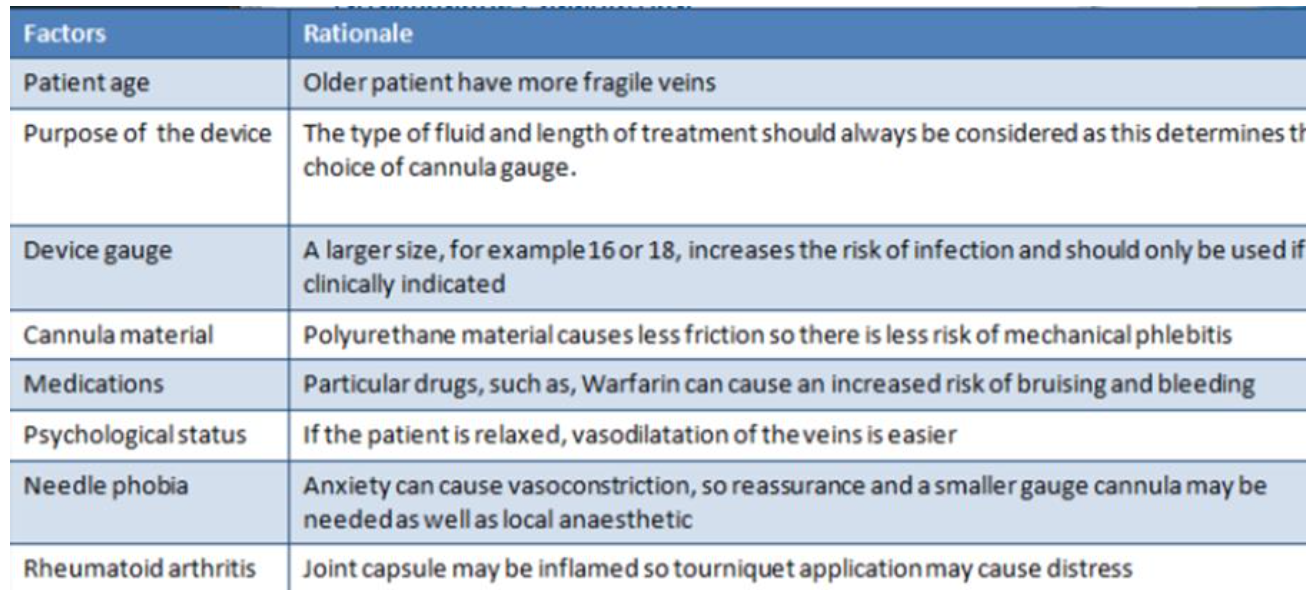
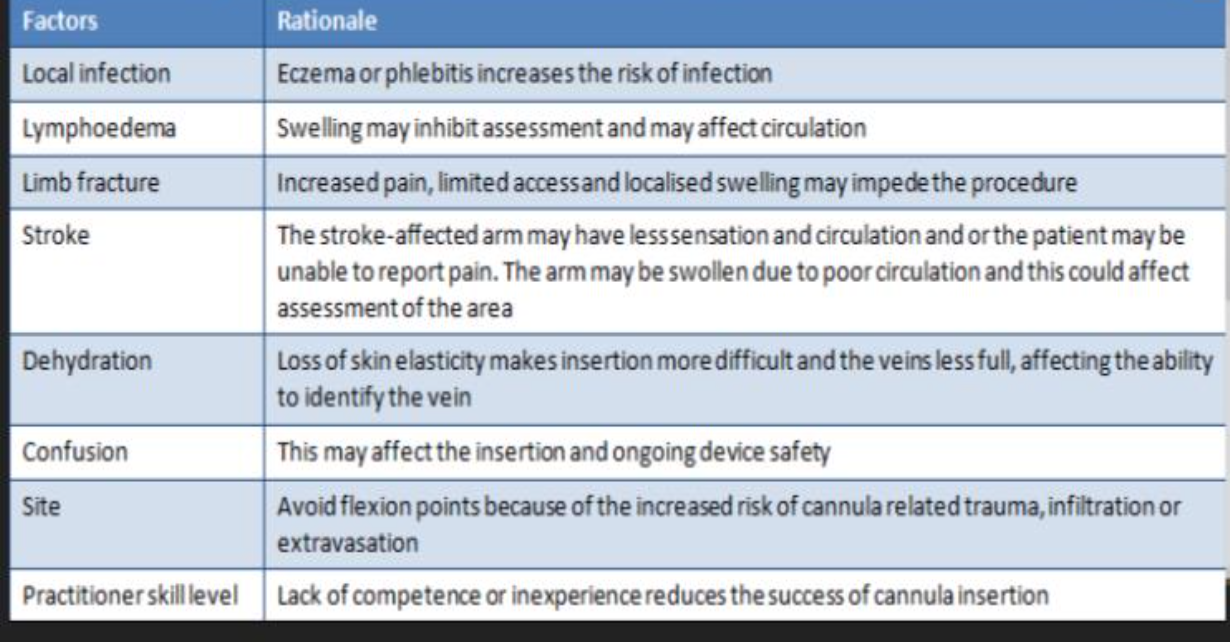
Sites for Peripheral IV Cannulation
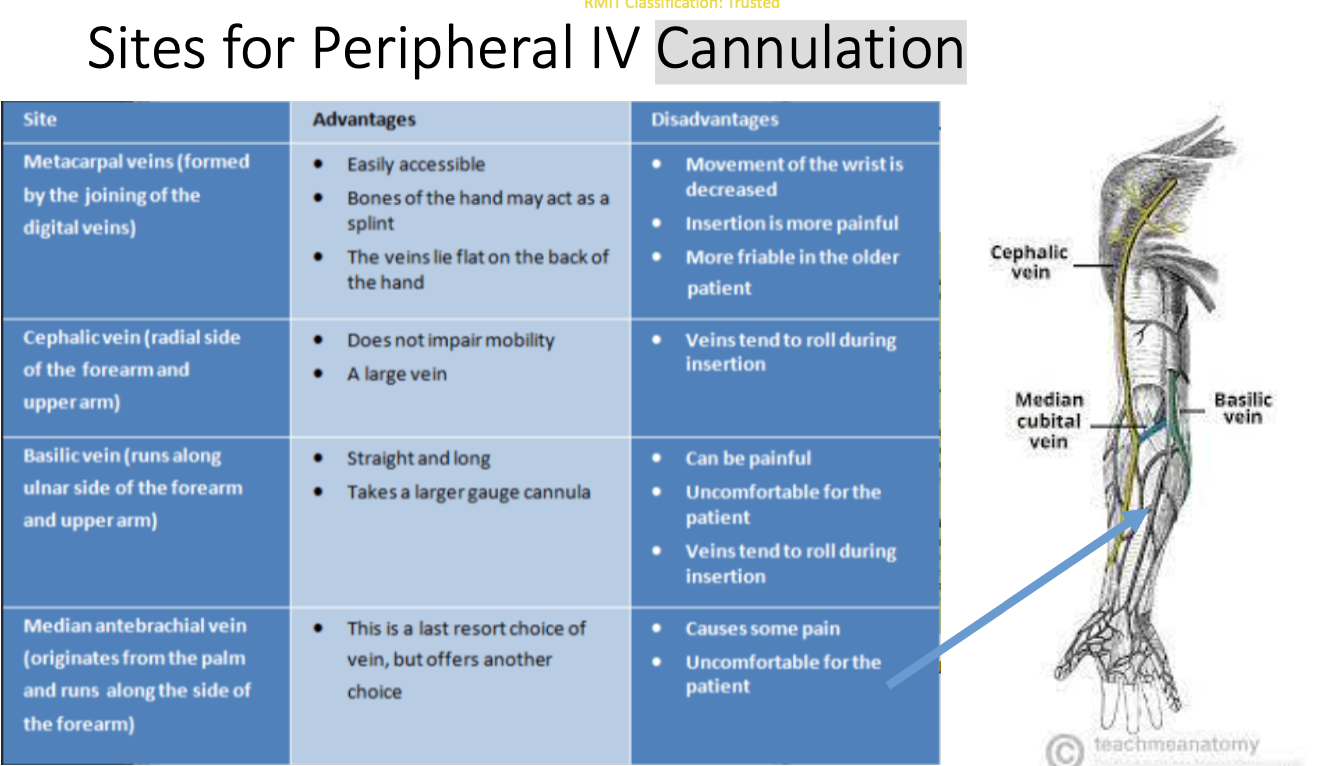
General Principals when choosing a vein for
peripheral IV Cannulation
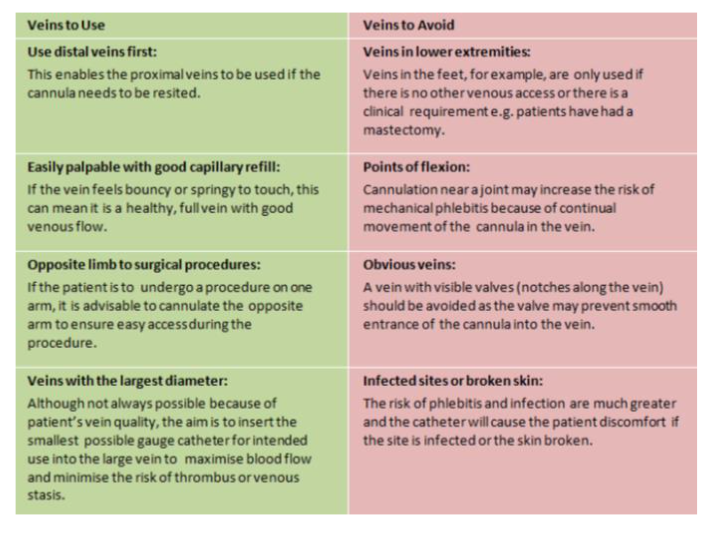
Assessment factors for IV cannulation
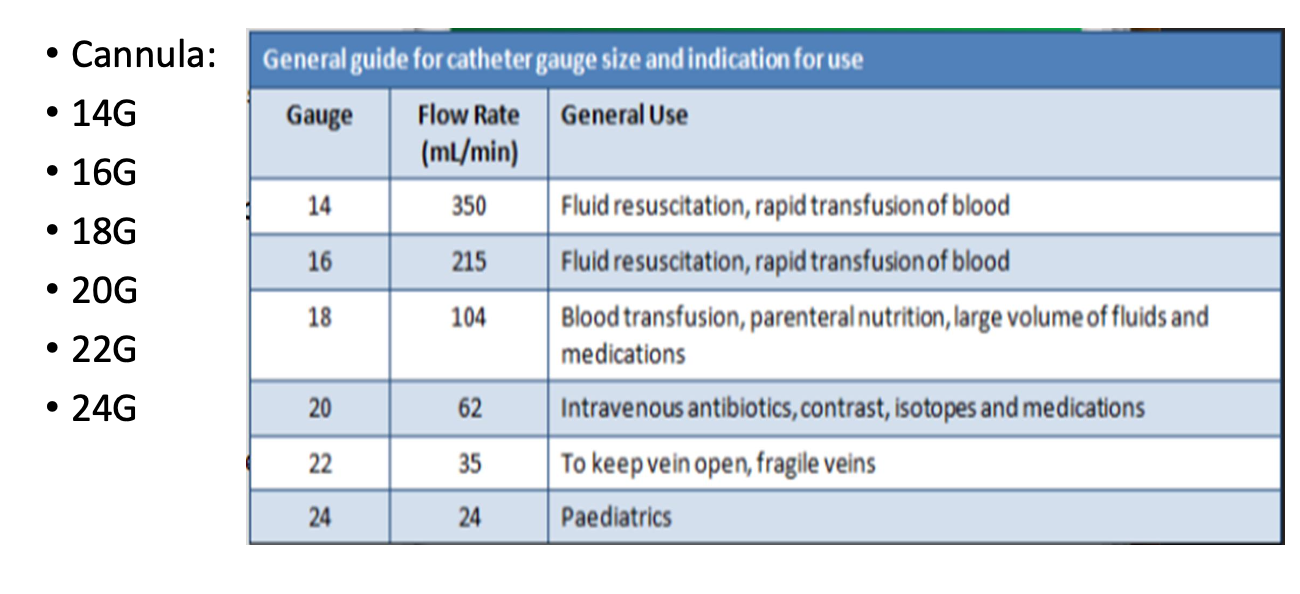
Other Factors to be aware of:
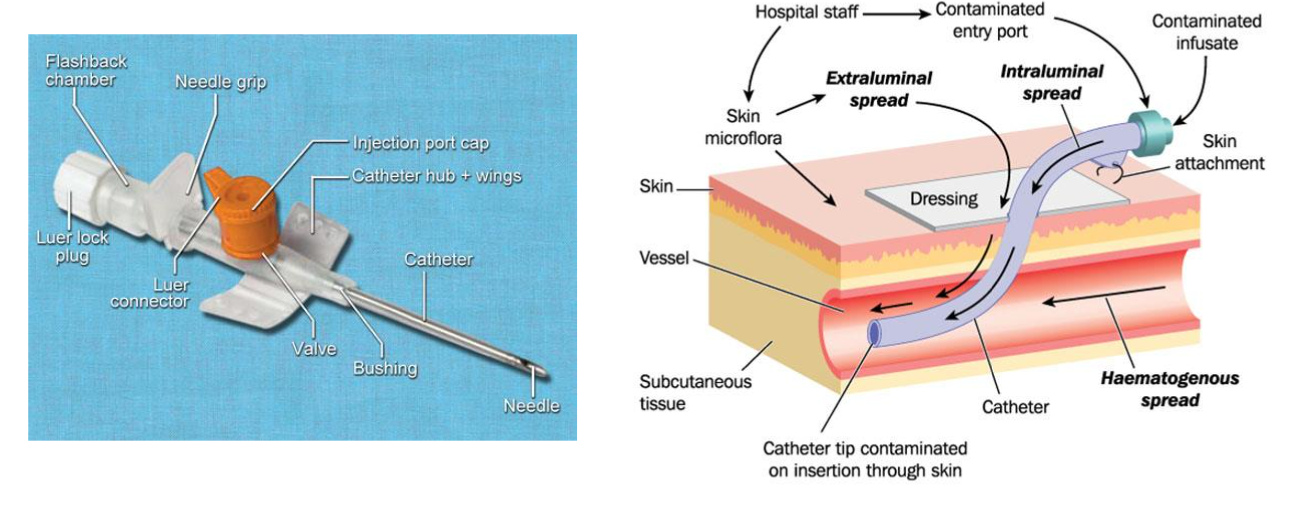
Equipment
Dressing/IV trolley with sharps container and waste bag
• Dressing pack
• Gloves (sterile)
• Alcoholic chlorhexidine
• Transparent semi permeable dressing
• Cannula (size depending on need)
• Giving and Extension set (and prescribed IV fluids)
• Syringe 10ml with 0.9% Normal saline
• Tourniquet
Assessing and Preparing the patient
1 Check patient for baseline vital signs, diagnosis and allergies to
medications, cleansing fluids & dressings
2 Provide a clear explanation of the procedure including potential
adverse and side effects
3 A relaxed patient is generally easier to cannulate
4 Assess the dominant/non-dominant side and check the veins for
status and suitability
Preparing equipment
1 Equipment should be gathered on trolley in treatment room with
sharps container
2 IV fluids should be prepared by priming the giving set
3The equipment should not be opened until in the patient’s room and patient education, assessment of vein and appropriate positioning has been attended
Positioning the patient
If possible use the non dominant arm
• Raise bed prior to procedure
• Place the arm in a supported comfortable position
• Use a tourniquet to find vein but release it while you are getting
equipment ready
• Position patient with pillows or towels
• Have IV trolley close by
Preparing vein
Warm veins by
• Rubbing
• Washing client’s hands under warm water
• Apply warmed towel
• If limb is warm ask the patient to gently clench and unclench their
hand
• Or gently rub up and down the vein
Before inserting cannula
The tourniquet is applied above the IV insertion site and should not
be left on for more than 2-3 minutes
• Don gloves and clean site with appropriate solution using a circular
outward movement
• Allow site to air dry or dry with sterile swab
Inserting the cannula
• Hold cannula and rotate the barrel 360 degrees
• Apply skin traction to immobilize the vein
• Ensure cannula has bevel side UP and insert at approximately 30 degree angle
• You will see a flashback of blood in the chamber once you have pierced the vein
• Then advance the cannula a few more millimetres and then flatten the cannula, stabilise
the device and advance the cannula until at skin level
• Remove the stylet and apply pressure just beyond the catheter tip
• Gently stabilise the cannula hub
• Release the tourniquet
• Attach the extension line
• Apply dressing and secure cannula
• Flush cannula with 5-10ml 0.9% sodium chloride to ensure patency
• Connect to IV fluid
• Dispose of sharps and waste
• Document in patient notes
Documentation
Site of insertion-vein and arm/hand
• Type and gauge of cannula
• Date and time of insertion
• Type and amount of IV solution
• Reason for IV therapy
Things to know before inserting a Cannula
Sites to Avoid:
Previous IV Sites
• Bruised Areas
• Patients Dominate arm- if possible
• Flexion or Joint areas due to increased risk of mechanical damage
• Veins below a previous IV site
• Median Cubital vein should be reserved for venous blood sampling
and emergency fluid resuscitation
Veins of the hand should be avoided as they have thinner walls and
may collapse more easily
• The skin of the hand is also more sensitive than the arm, so IV
cannulation may be painful
• Skin at the back of the hand can be very loose or very tough, this may
make it difficult to cannulate
• Cannulas in the back of the hand should only be used for short term
and reserved for small gauge cannulas only
Sites NOT to be used
Avoid using AV fistula site for venepuncture.
Avoid scarred, burned, sutured, or fractured areas.
Avoid damaged veins or sites with phlebitis.
Avoid infected areas.
Avoid sites with skin conditions.
Avoid hard, sclerotic, or thrombosed veins.
Avoid arm on side of mastectomy or axillary surgery.
Avoid areas with reduced sensation.
Avoid veins close to arteries.
Always palpate for arterial pulse before venepuncture.
Why is it NOT ok to cannulate the side of a
mastectomy?
Why is it NOT okay to cannulate the side of a mastectomy?
Lymph nodes are often removed during mastectomy.
This can cause lymphostasis (blocked lymph flow).
Reduced drainage increases infection risk.
Tourniquet pressure may cause injury.
Why is it NOT ok to cannulate an artery
too large cannula- Risk of occlusion, pseudoaneurysm, or haematoma.
Accidental arterial injection of medications can cause ischaemia, necrosis, gangrene, or limb loss.
Signs of arterial cannulation:
Bright red, pulsatile blood flowing backward into the cannula.
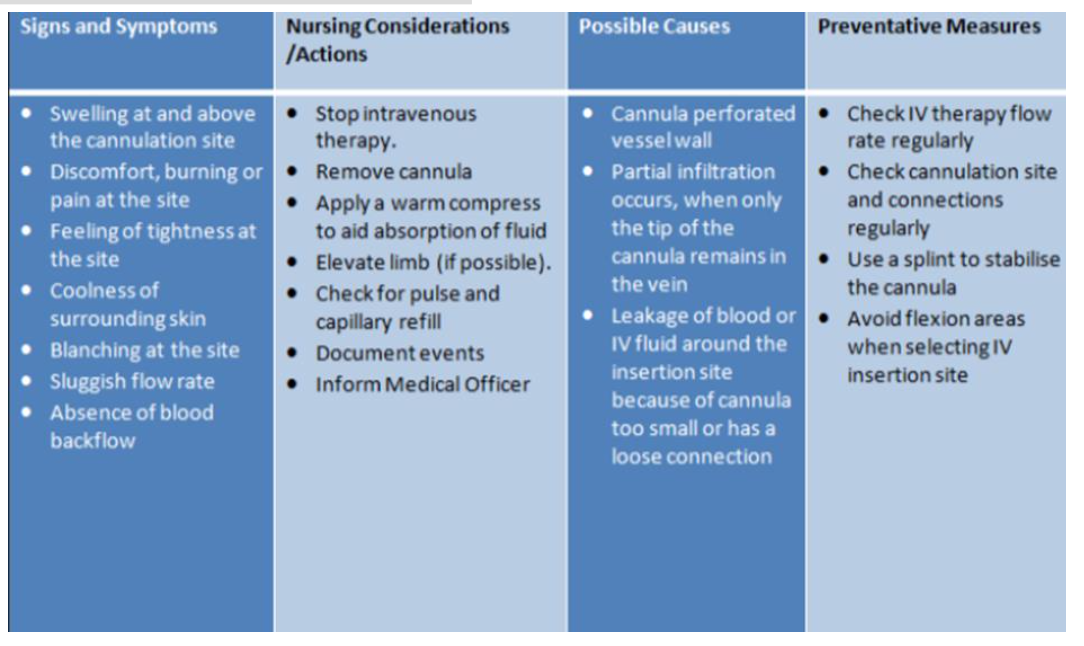
Complications of IV Cannulation
Extravasation
• Haematoma
• Phlebitis
• Venous Spasm
• Occlusion
• Thrombophlebitis
• Infection
Extravasation
The infiltration of a drug from an I.V. line into surrounding tissue.
Causes
• Catheter erodes through the vessel wall at a second point,
• Increased venous pressure causes leakage around the venepuncture
site
• When a needle pulls out of the vein.
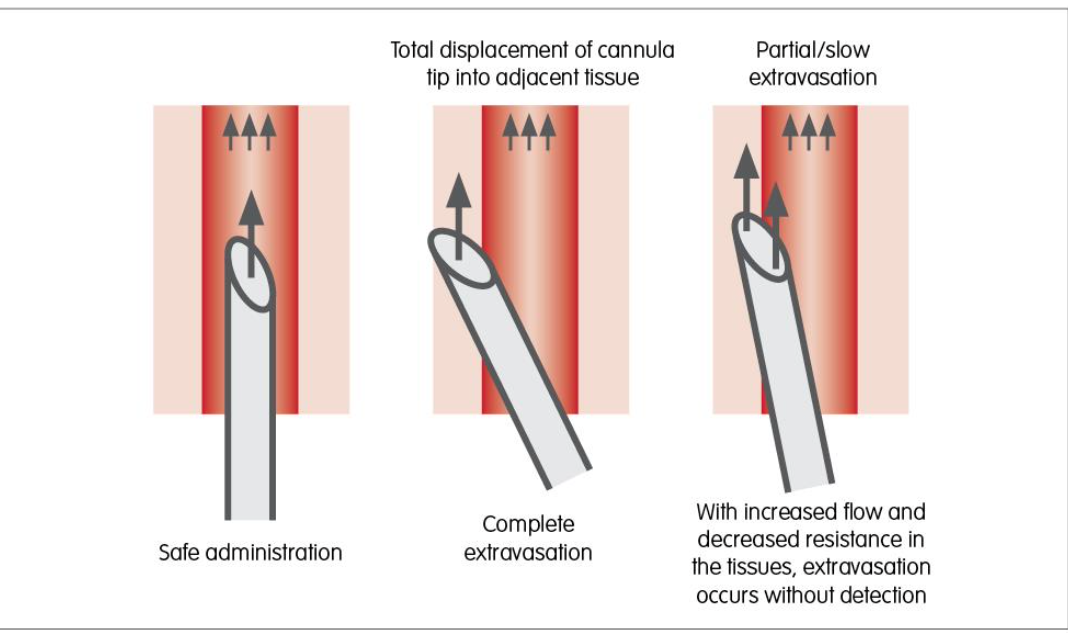
Signs & Symptoms of Extravasation
• Oedema and changes in the site's appearance
• Coolness of the skin.
• Slowing of infusion
• Pain or a feeling of tightness around the site.
• Possible consequences include necrotic ulcers, infection,
disfigurement, and loss of function
Intervention Extravasation
Remove cannula
• Elevate affected arm
• Apply ice pack (early) or warm compress (late)
haematoma
Localised collection of extravasated blood, usually clotted, in an organ or tissue.
haematoma cause
Cause
• Blood leaking out of the vein into the tissue due to puncture or trauma
haematoma signs and symptoms
Signs & Symptoms
• Swelling, tenderness and discolouration
haematoma prevention
Prevention
• Proper device insertion
• Pressure over site on removal of cannula Intervention
• Apply appropriate pressure bandage, monitor the site
Phlebitis
Inflammation of the vein
Phlebitis cause
Poor aseptic technique
• High osmolarity I.V. infusions or drugs
• Trauma to the vein during insertion/incorrect
cannula gauge
• Prolonged use of the same site
Phlebitis signs and symptoms
• Tenderness, redness, heat and oedema
Phlebitis intervention

Occlusion
Slowing or cessation of fluid infusion due to:
Fibrin formation in or around the tip of the cannula
• Mechanical occlusion (kink) of the cannula Cause
• Cannula not flushed
• Kinking of the cannula
• Back flow or interrupted flow
occlusion signs and symptoms
I.V. not running
• Blood in the line
• Discomfort
occlusion intervention

Infection
Pathogen in the surrounding tissue of the I.V. site.
pathogen cause
• Lack of asepsis
• Prolonged use of the same site
infection signs and symptoms
Tenderness and swelling
• Erythema/purulent drainage
infection intervention

Other Complications