ARDS and HMD - MedPath
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD)
Neonatal disease due to surfactant deficiency, leading to alveolar collapse
Adult respiratory distress syndrome
Acute onset, inflammatory lung injury with increased permeability
What affects gas exchange and lead to hypoxemia
ARDS and HMD
What does this refer to
Tendency of water molecules to contract to the smallest possible surface area (bead) with exposure to air
Increased ______ = increased work of breathing
Surface tension
What does this refer to
: The smaller a sphere’s radius (alveoli) the greater the surface tension and the more difficult (work) to expand the alveoli
Surfactant reduces fluid surface tension lining the alveoli and decreases tendency to collapse, preventing atelectasis
Laplace’s Law
What does this refer to
Fulminant form of respiratory failure characterized by acute lung inflammation and diffuse alveolocapillary injury
Injury to the pulmonary capillary endothelium
Inflammation
Surfactant inactivation
Atelectasis
Is a restrictive lung disorder
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
What does this refer to
Direct: pneumonia, aspiration, inhalation injury
Indirect: sepsis, trauma, pancreatitis, transfusions
Systemic inflammation is key
Causes of ARDS
What does this refer to
Initial injury increases capillary permeability
Fluid and proteins leak into alveoli, impairing gas exchange
Inflammatory mediators recruit neutrophils, worsening injury
Pathophysiology of ARDS
What phase of ARDS is the following
: damage and fluid leakage
Exudative
What phase of ARDS is the following
: repair and recovery
Proliferative
What phase of ARDS is the following
: scarring and chronic changes
Fibrotic
What phase of ARDS is the following
Occurs within 0–7 days post-injury
Alveolar edema with protein-rich fluid
Formation of hyaline membranes from fibrin and cell debris
Exudative Phase
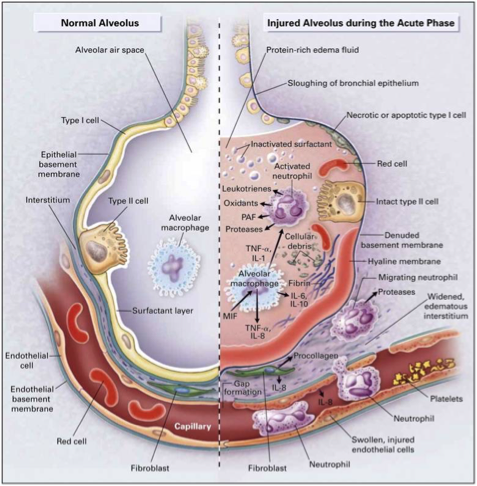
What phase of ARDS is the following
Occurs around day 7–21
Resolution of edema, proliferation of fibroblasts and type II pneumocytes
Beginning of tissue repair
Proliferative Phase
What phase of ARDS is the following
Occurs after 3 weeks
Fibrosis and remodeling of lung tissue
May result in permanent reduction in lung compliance
Fibrotic Phase
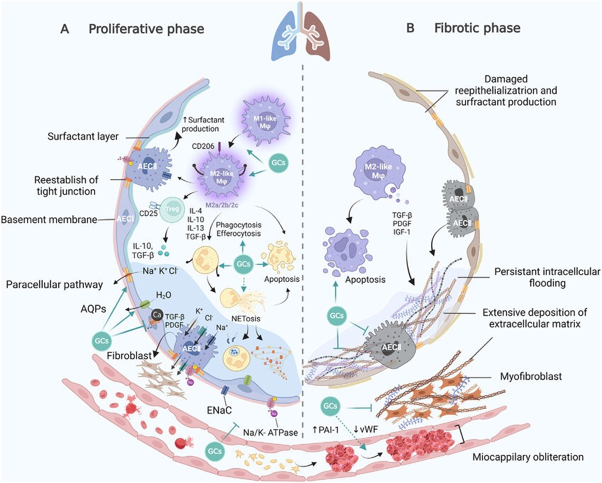
What does this refer to
Rapidly progressive dyspnea, tachypnea, hypoxemia
Inspiratory rales, cyanosis, accessory muscle use
24-48 hours- infiltrates on CXR
Become refractory to oxygen therapy —> increase PaCO2 —> organ dysfunction —> CO and BP decreases —> DEATH
Manifestations of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
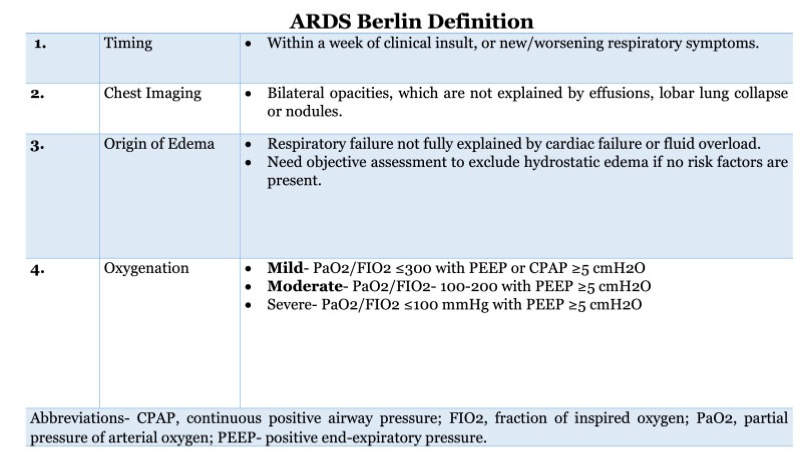
What does this refer to
Refractory hypoxemia, CXR with B infiltrates, and pulmonary edema (exclude cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
Based on Berlin Criteria:
Timing – 1 week
Origin of edema – noncardiac
Imaging – bilateral opacities
Oxygenation - PaO2/FIO2 with PEEP
Exclude cardiac failure with echocardiogram or BNP
Diagnosis of ARDS
What does this refer to
Chest X-ray: bilateral infiltrates, not explained by effusion/collapse
CT: more sensitive, shows ground-glass opacities and consolidation
Imaging in ARDS
What does this refer to
Early: hyaline (transparent or glassy) membranes lining alveoli
Later: type II pneumocyte hyperplasia, interstitial fibrosis
Neutrophil infiltration and alveolar damage
Histology in ARDS
What does this refer to
Treat underlying cause (e.g., antibiotics for sepsis)
Supportive care with oxygen and mechanical ventilation
Fluid management to avoid pulmonary edema
Management of ARDS
What does this refer to
Low tidal volume (6 mL/kg IBW) to prevent barotrauma
PEEP to prevent alveolar collapse
Prone positioning improves oxygenation
Ventilation Strategies
What does this refer to
Barotrauma from mechanical ventilation
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)
Long-term lung dysfunction and neuromuscular weakness
Complications of ARDS
What does this refer to
Mortality varies by severity: up to 40%
Many survivors have long-term physical and psychological effects
Better outcomes with early recognition and lung-protective ventilation
Prognosis of ARDS
What does this refer to
Occurs in premature infants due to immature lungs
Surfactant deficiency is central cause
Results in atelectasis, decreased lung compliance, hypoxemia
Hyaline Membrane Disease
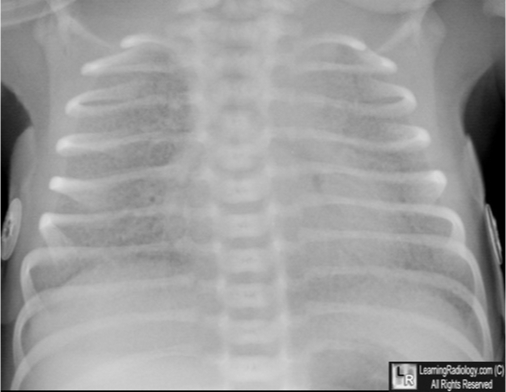
What does this refer to
Secreted by type II pneumocytes around 24–28 weeks gestation
Reduces surface tension, stabilizes alveoli
Deficiency causes alveolar collapse and impaired gas exchange
Surfactant Function
What does this refer to
Inadequate surfactant → alveolar collapse
Leads to hypoxemia, increased work of breathing
Proteinaceous exudate and necrotic cells form hyaline membranes
Pathogenesis of HMD
What does this refer to
Prematurity (<34 weeks), male sex
Maternal diabetes: delayed surfactant production
Cesarean delivery without labor: less stress-induced surfactant release
Risk Factors for HMD
What does this refer to
Tachypnea, nasal flaring, grunting, cyanosis within hours after birth
Progressive respiratory failure if untreated
Findings correlate with gestational age and severity
Clinical Features of HMD
What does this refer to
Chest X-ray: reticulogranular (ground-glass) pattern, air bronchograms
Blood gases: hypoxemia, respiratory acidosis
Confirmatory: lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio <2.0 in amniotic fluid
Diagnosis of HMD
What does this refer to
Collapsed alveoli with eosinophilic hyaline membranes
Similar histology to ARDS
Inflammatory infiltrates are minimal compared to ARDS
Histology in HMD
What does this refer to
Antenatal corticosteroids (betamethasone) accelerate surfactant production
Avoid elective delivery before 39 weeks unless indicated
Amniocentesis to assess fetal lung maturity if needed
Prevention of HMD
What does this refer to
Surfactant replacement via endotracheal tube
CPAP for mild-moderate disease
Mechanical ventilation for severe cases
Treatment of HMD
What does this refer to
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (chronic lung disease)
Air leak syndromes (pneumothorax)
Intraventricular hemorrhage in very premature infants
Complications of HMD
What does this refer to
Greatly improved with surfactant and modern neonatal care
Mild cases often recover completely
Severe or recurrent cases may have long-term respiratory issues
Prognosis of HMD
What does this refer to
: acute, inflammatory, adult disease
Impairs gas exchange and respiratory failure
ARDs
What does this refer to
: neonatal surfactant deficiency
Impairs gas exchange and respiratory
HMD