Theories of evolution test
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Charles Darwin’s idea of how species change over time is called what?
Natural Selection (change due to differential survival and reproduction).
Explain the 4 conditions necessary for natural selection.
Populations show variations in genes and traits
Not all will survive: environmental pressures like predators and competition for food, select some individuals and reject others
Heredity survivors live longer, reproduce more, and pass on those favorable genes
overtime, the more favorable a trait becomes more common in the population, causing a population to change
Where did Darwin collect much of his data about Finches?
Mainly in South America and the Galapagos Islands
Did Darwin include information about Genetics in his theory of Natural Selection? Why or why not?
No, Darwin did not include information about genetics in his theory as it had been against religion and the belief that God had created each species as it had already been.
Darwin concluded that the finches he studied were all related to a __________ on the mainland of South America.
Common ancestor
State Darwin’s Descent with Modification theory.
Species descend, with changes, from other species (common ancestors) over time.
7) Compare and contrast natural selection with artificial selection
Natural selection is change due to differential survival and reproduction.
Artificial selection is where humans select who reproduces and how many times (breeding).
Both natural and artificial selection may cause a change in allele frequency in a population over time (evolution).
What is meant by the “fitness” of an organism? What is an organism with greater “fitness” more likely to do?
Fitness refers to the ability to pass on your genes to the next generation. An organism with greater fitness is more likely to pass down beneficial traits to their offspring.
Do individuals evolve? Do populations evolve?
Individuals do not evolve, rather, populations evolve due to various reasons such as natural selection, mutations, genetic drift, non-random mating, and more.
Name the 3 ways variations in genotypes arise.
Mutations produce new alleles for a trait, migration (gene flow) where individuals enter or exit causes genes to move, and genetic drift (change due to chance/random events) may all cause variations in genotypes to arise.
What is meant by the gene pool?
The gene pool refers to all genes, including all the different alleles that are present in a population.
What is an allele frequency?
Allele frequency is how common or frequent certain alleles are in a population’s gene pool.
Calculate the allele frequency of F and f: There are 75 bunnies in a population that contains 2 alleles for fur color (B - brown and b - white). 28 of them are white. The rest are brown. Of the brown, 17 are heterozygous and 30 are homozygous.
28: bb
30: BB
17: Bb
b) 73/150 = .48666667 = 48.7% b
B) 77/150 = .51333333 = 51.3% B
14) What does it mean if allele frequencies change over time?
If the allele frequency changes over time that means evolution has occurred in the population.
15) List the 5 conditions that can cause evolution to occur:
Small population
Non- random mating
Mutations
Gene flow
Adaptation
16) If none of these 5 conditions occur, what can we say about that population?
If none of these 5 conditions occur then the population has maintained genetic equilibrium, meaning that the frequency of the alleles in the population does not change.
17) What is gene flow & give an example?
“The exchange of genes between two populations”
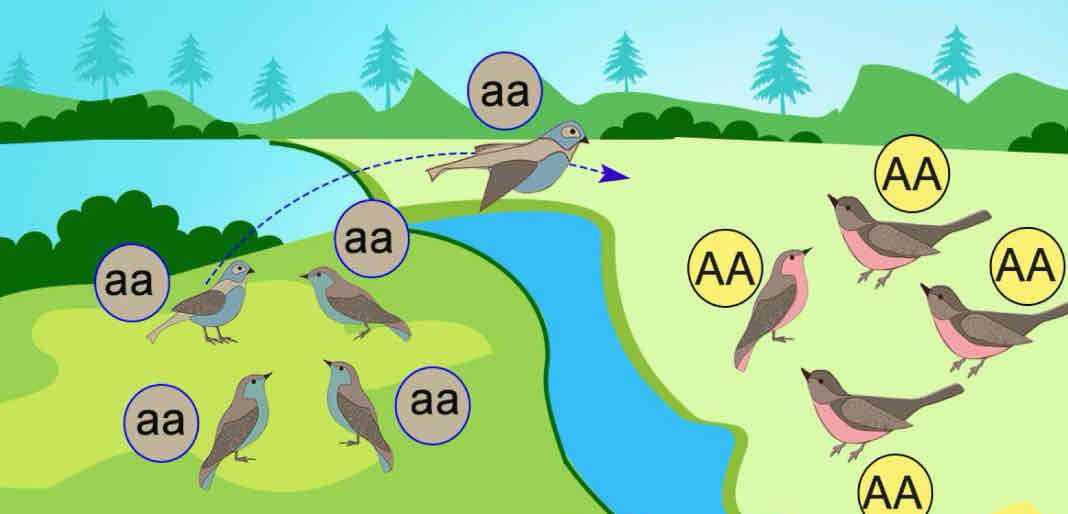
What is genetic drift?
Change due to chance or random events; affects small populations more.”
In what size populations does genetic drift apply & explain why?
It affects small populations the most because since they are so small in numbers there is likely less variation and less ability to respond well to something that would stimulate evolution.
20) Do all populations mate randomly? Explain.
No, not all populations mate randomly, some may mate by looking for specific traits in their partner. This is called non random mating.
21) Name the 3 ways that natural selection can act on a polygenic trait & explain each. (Include a sketch of the graph before and after natural selection takes place.
Stabilizing: individuals with the average form of a trait have the highest fitness
Disruptive: individuals with either extreme variations of a trait have greater fitness
Directions: individuals that display a more extreme form of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with an average form of the trait
Evidence of Evolution
22) What are homologous structures and give an example.
Similar structures in different but related species that have been inherited from a common ancestor
What are vestigial structures & give an example.
Organs or structures that lose their function in the organism but had a function in an ancestor and become reduced in size due to efficiency. Some examples in humans are the appendix, wisdom teeth, and tailbone.
Vestigial structures show ___________ ancestry.
Common
In the early stages, how do all vertebrate embryos compare with each other? What does this indicate?
All vertebrate embryos look similar to each other and it’s difficult to tell the difference between them. This would indicate that all species have come from a common ancestor.
Organisms with homologous (similar) _______ & ______ are probably more closely related.
structures & amino acids
What is a fossil?
“traces” of dead organisms found in layers of rock, formed at different times in the Earth’s history
Define speciation.
It’s the formation of new species, two groups must become isolated from each other so gene flow stops.
Members of a species can _______ to produce ______and offspring.
Interbreed
Healthy and fertile
Give two examples of how geographic isolation could occur.
Large body of water forming and continental drift could separate populations.
What happens to the 2 subgroups after being geographically isolated from each other?
They are unable to mate and therefore the gene flow stops and the subgroups change over time and they can become so different from one another that they could no longer be able to interbreed if given the chance.
Name and describe 4 types of reproductive isolation.
a. Behavioral isolation - different courtship ritual or reproductive strategies
b. Temporal (seasonal) isolation - different mating times
c. Mechanical isolation - reproductive organs are not compatiable
d. Post zygotic isolation - mating occurs but the offspring dies early or it is infertile
Not recognizing mating calls is an example of what type of isolation?
This is behavroial isolation, they have different reproductive strategies.
Having different breeding times is an example of what type of isolation?
Temporal isolation.
What is a cladogram and what does it show?
It’s a method of visulaizing speciation and degree of relatedness, it shows relatedness based on shared derived characteristics and branches show common ancestors. Groups that share a more recent common ancestor are more closely related.
What do the branch points on a cladogram represent?
They represent when the common ancestor species split up into different categories based on characteristics.
What is a derived character? Give an example using the diagram below.
Derived characteristics are those that have evolved in a particular lineage and are not present in the common ancestor. AN example would be hair and amniotic egg.
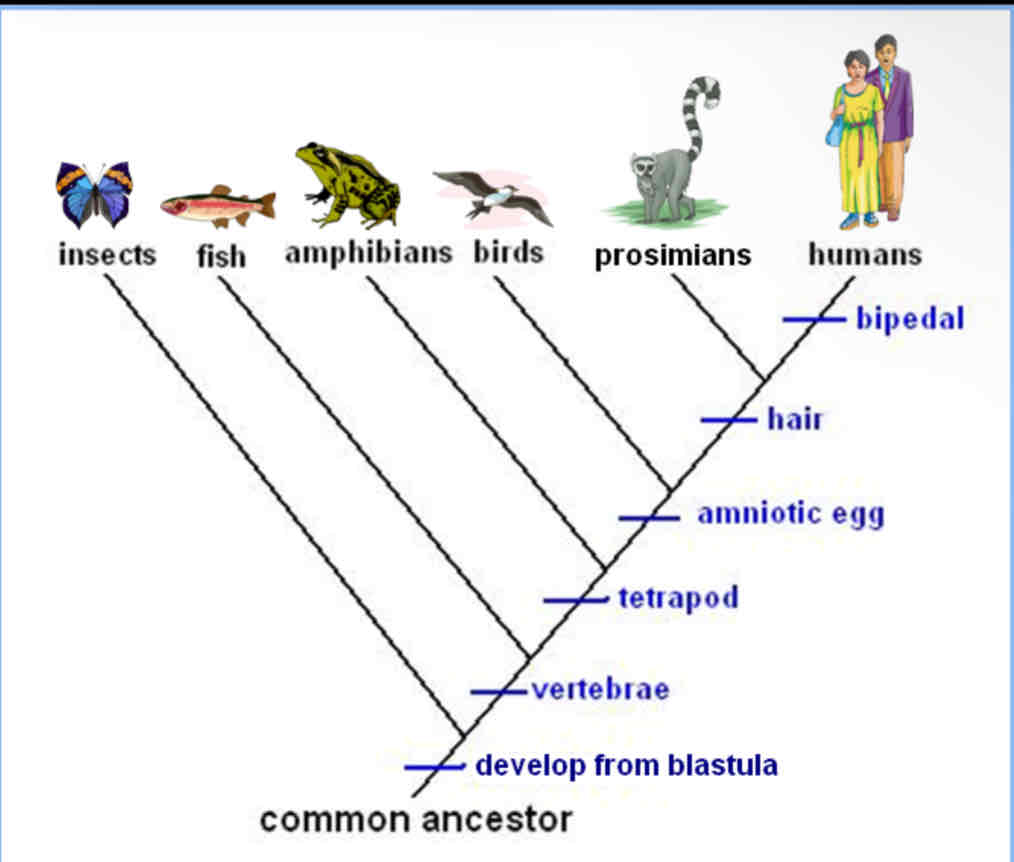
Use the cladogram to answer the following questions:
A. What traits do all of the organisms have in common?
B. What trait do only humans and prosimians share?
C. Which organisms have an amniotic egg?
D. Who is more closely related to the fish: The insects or amphibians?
E. Who is more closely related to the birds: prosimians or humans?
F. Which trait is unique to humans?
A. They all develop from blastula.
B. They only share the hair trait.
C. Birds, prosimians, and humans.
D. The amphibians because they both share the trait of a tetrapad.
E. They are both equally closely related.
F. Bipedal