6.2 The blood system
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
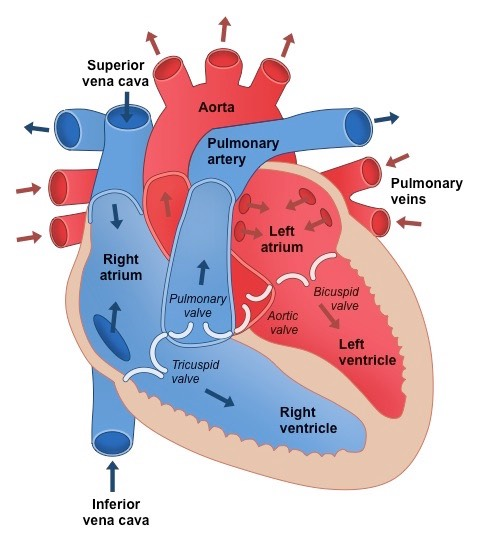
Aorta
The largest artery of the circulatory system. It carries blood from the left ventricle to smaller arteries in all organs, except the lungs.
Arteriole
The smallest branch of an artery.
It connects with a capillary.
Artery
A blood vessel which thick elastic walls that carries blood away from the heart.
Atrium
A chamber a the top of the heart that receives blood from veins.
Blood pressure
The force that blood exerts against the wall of a blood vessel. Consists of two numbers, systolic and diastolic.
Capillary
A small blood vessel made of a single layer of endothelial cells to allow exchange of gases, nutrients and waste.
Cardiac output
The volume of blood pumped per minute by each ventricle of the heart
Diastolic pressure
The pressure measured in the arteries while the ventricles are relaxed (during diastole).
Elastic fibres
Protein fibres (elastin) found in the walls of arteries and veins that can lengthen and then recoil.
Epinephrine
A hormone (also called adrenalin) produced by adrenal glands as a response to stress, increases heart rate.
Medulla
Part of the brain, at the base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing rates.
Myogenic contraction
Contraction of the heart on its own, without being stimulated by a nerve
Pacemaker
A region of cells in the right atrium (or an electronic device) that sets the rate of heart contraction.
Systolic pressure
The maximum blood pressure in the arteries at the peak of ventricular contraction (Systole)
Atrio-ventricular Valves
A valve in the heart that stops blood from moving from the ventricles at the atria during contraction of the ventricles (aka Bicuspid and Tricuspid valves)
Vasoconstriction
When circular muscles in an artery wall contract, narrowing the lumen, preventing blood flow (Increases blood pressure, occurs in the skin when cold)
Vasodilation
When circular muscles relax, increasing the lumen size and increasing blood flow. (Lowers blood pressure)
Vein
A blood vessel with valves, a large lumen and quite thin walls, that returns blood to the heart.
Ventricles
Lower chambers of the heart that receive blood from the atria and contract to force blood into the aorta or pulmonary artery.
The different sides of the heart
The right side
the deoxygenated blood from the body tssues
pumps it to the lungs (pulmonary circula5on).
The le\ side
oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to all the body ,ssues (systemic circula5on).
thicker muscular lining (myocardium) because it needs to pump blood greater distances.