Module 3 - Lumbar Normal Anatomy and Lines
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
AP lumbar
ID view
Lateral lumbar
ID view
To find instability
Why do we take lumbar flexion-extension projections?
Pars interarticularis
Why do we take oblique lumbar projections?
Shield
A _____ is used to decrease the dose to the reproductive system. Physicists are going away from them because they are not very effective
Recumbent (lying down)
What position is the patient in?
Weight bearing (standing)
What position is the patient in?
Lateral lumbar
What view do we see lumbar IVFs?
L4 lamina
ID 1
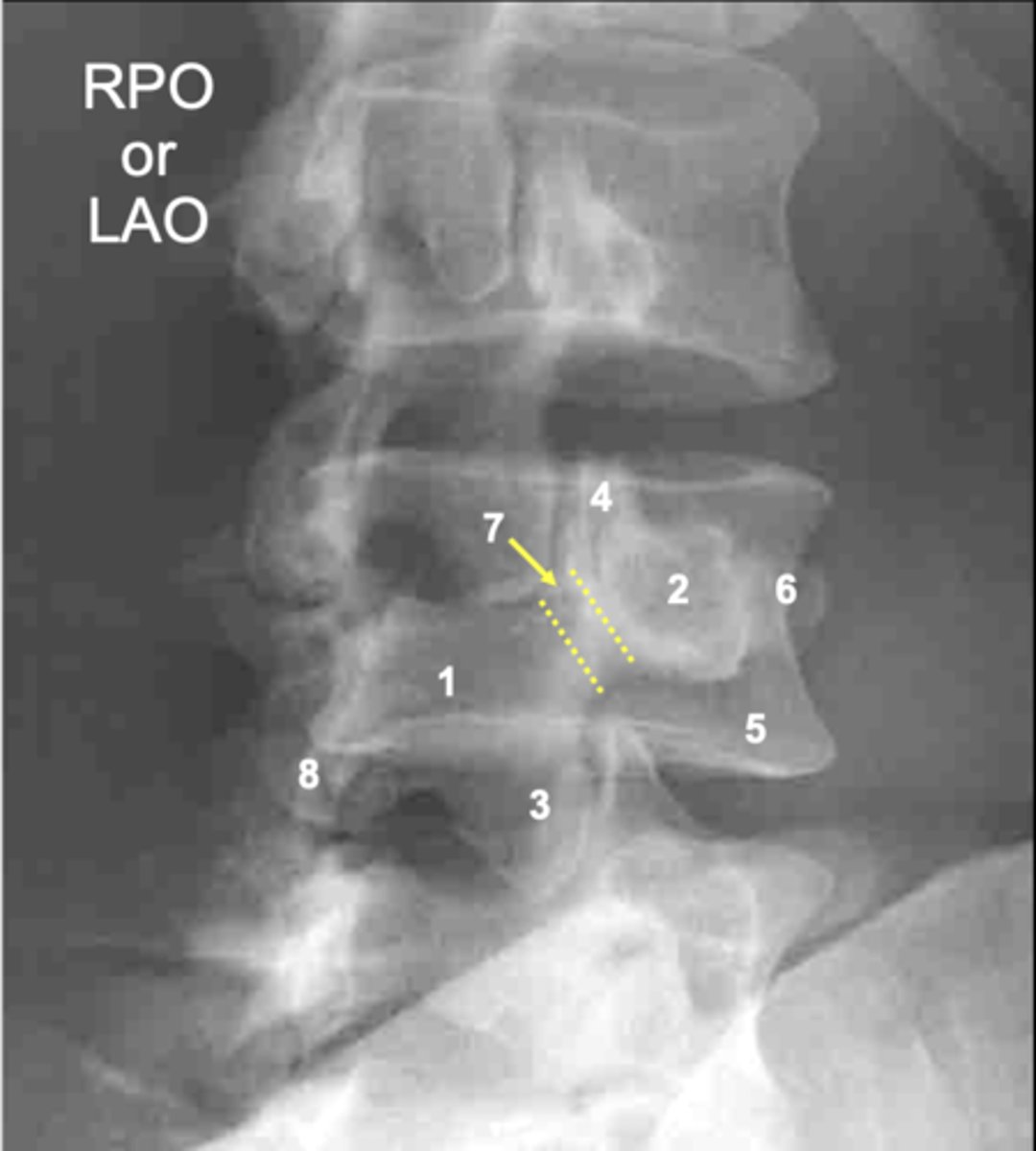
L4 pedicle
ID 2
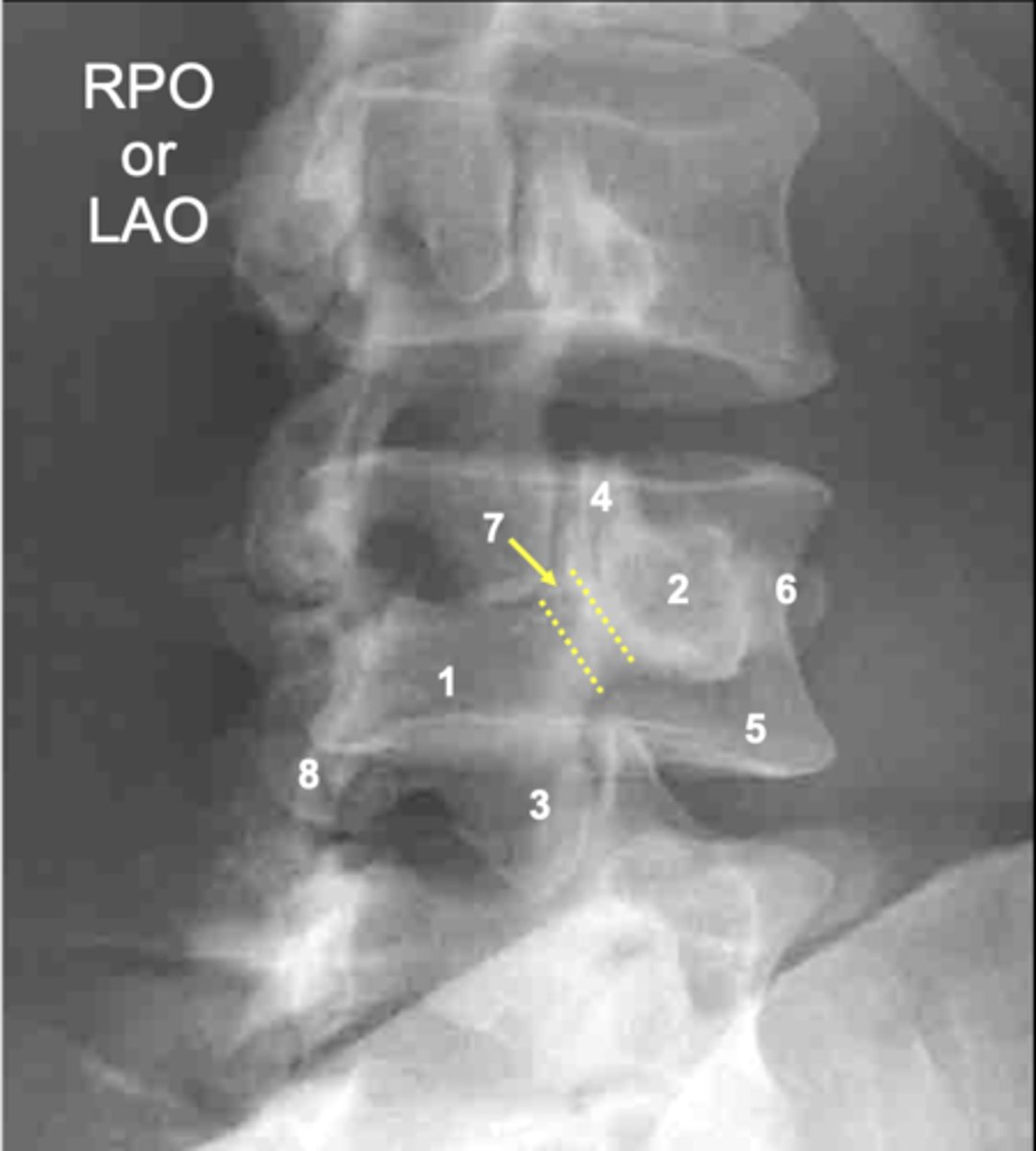
L4 inferior articular process
ID 3
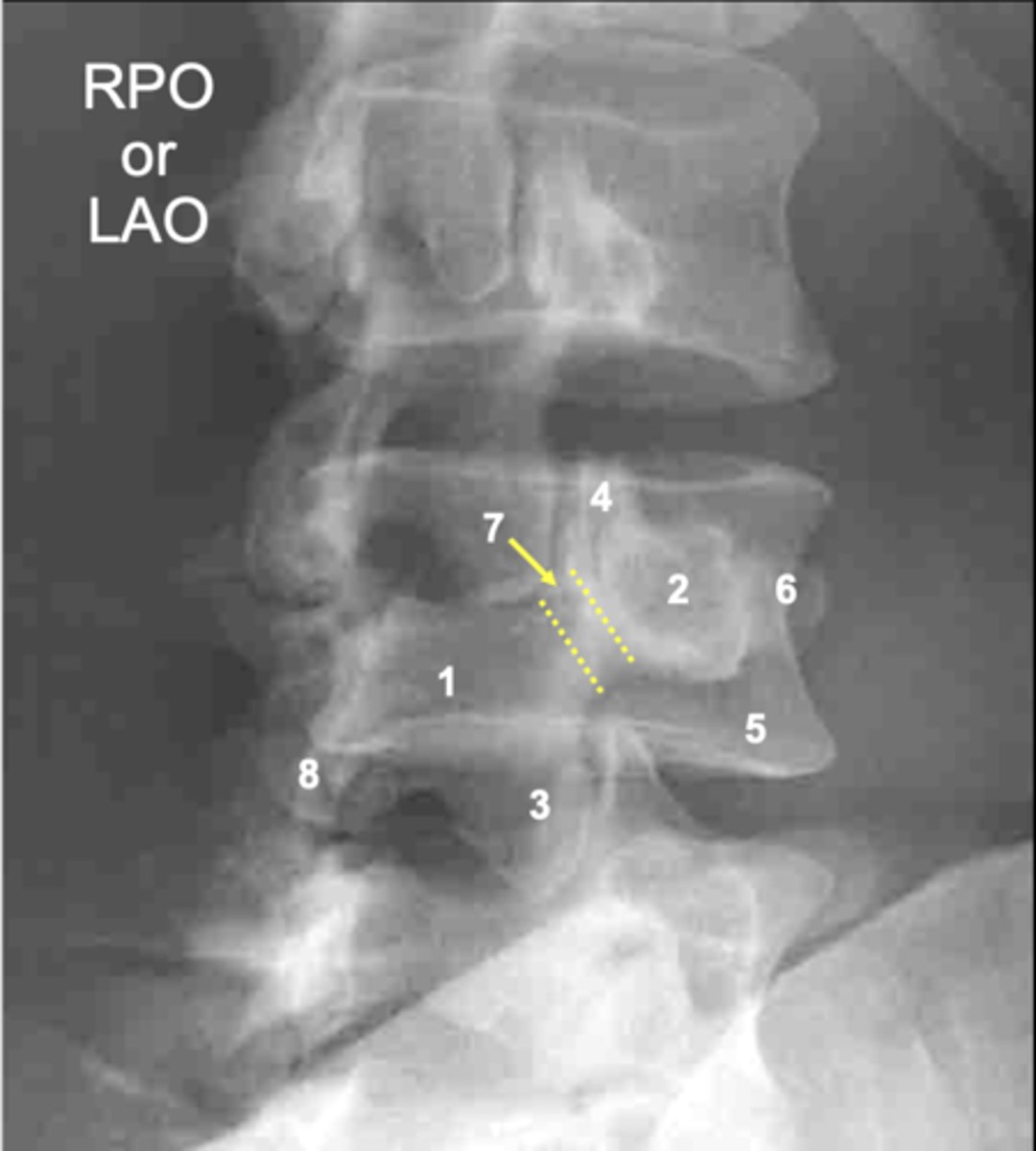
L4 superior articular process
ID 4
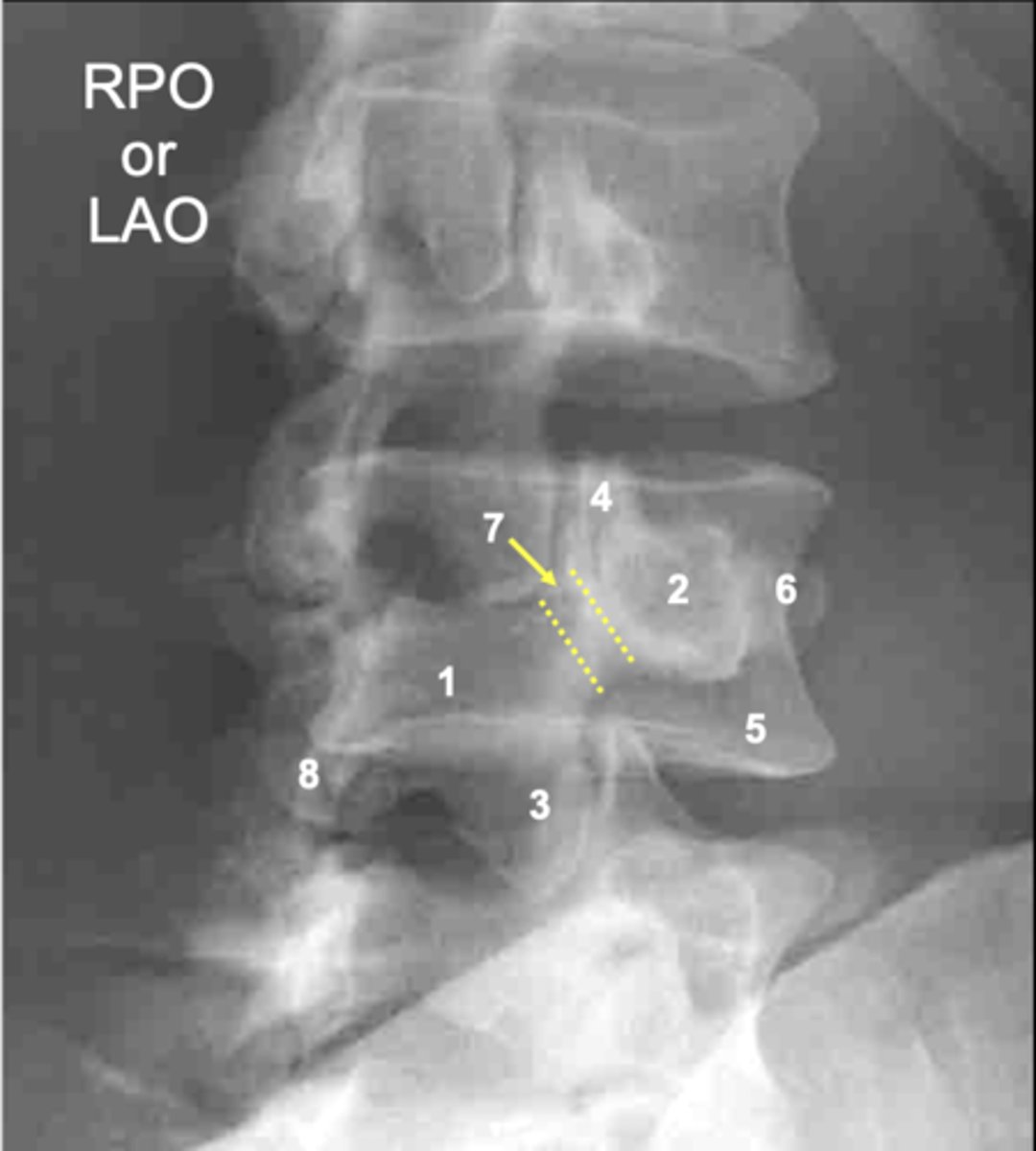
L4 vertebral body
ID 5
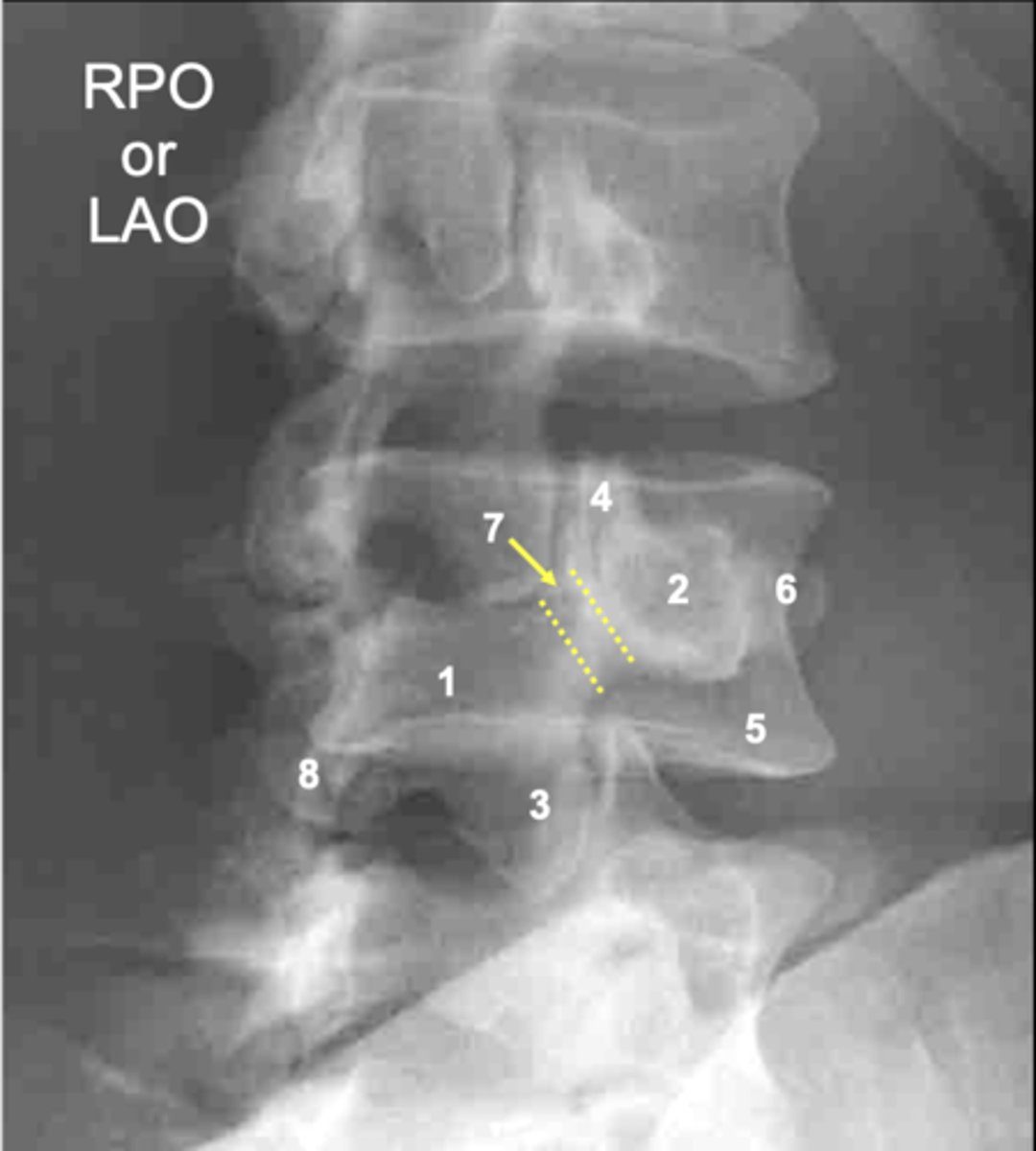
L4 transverse process
ID 6
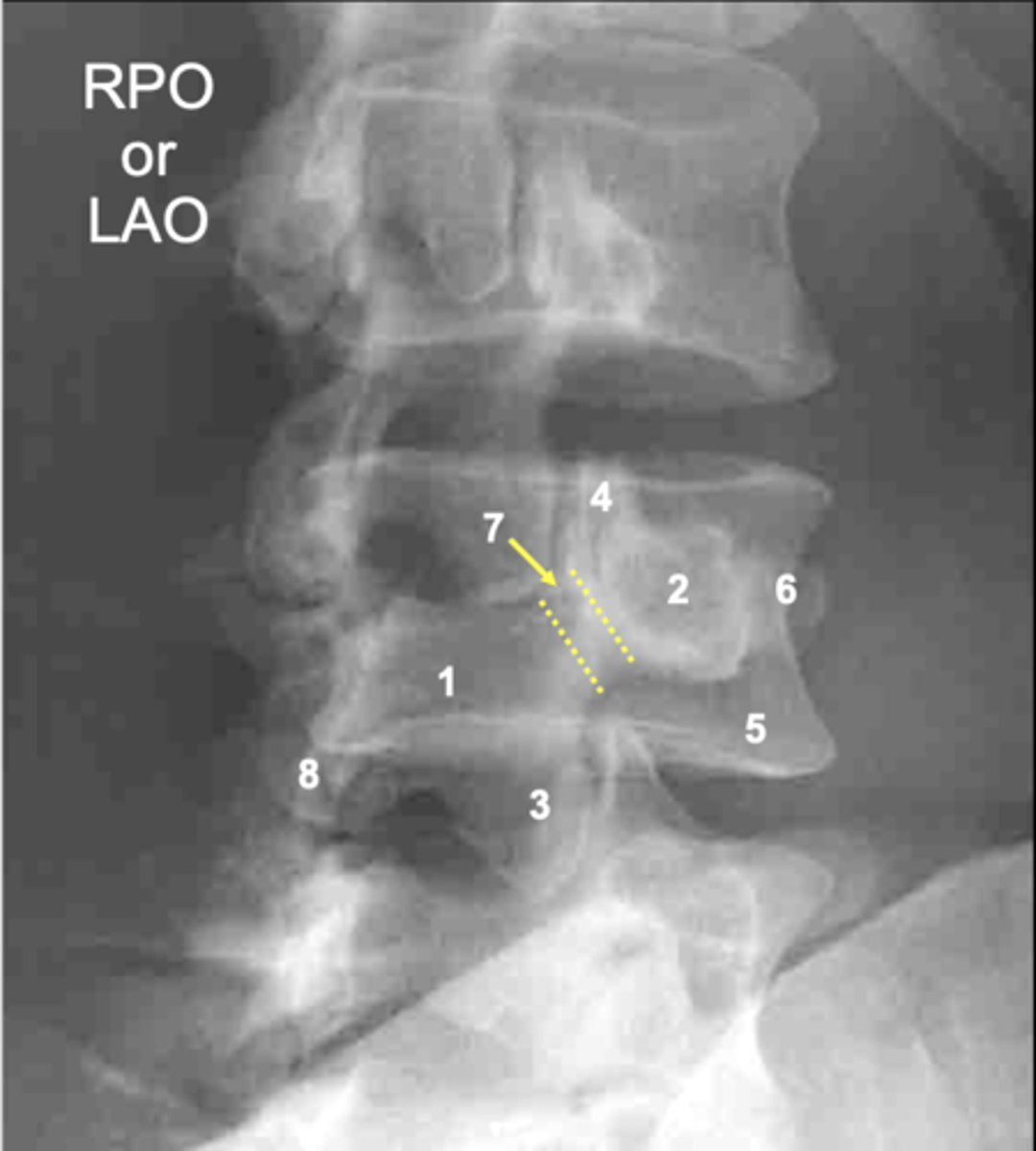
L4 pars interarticularis
ID 7
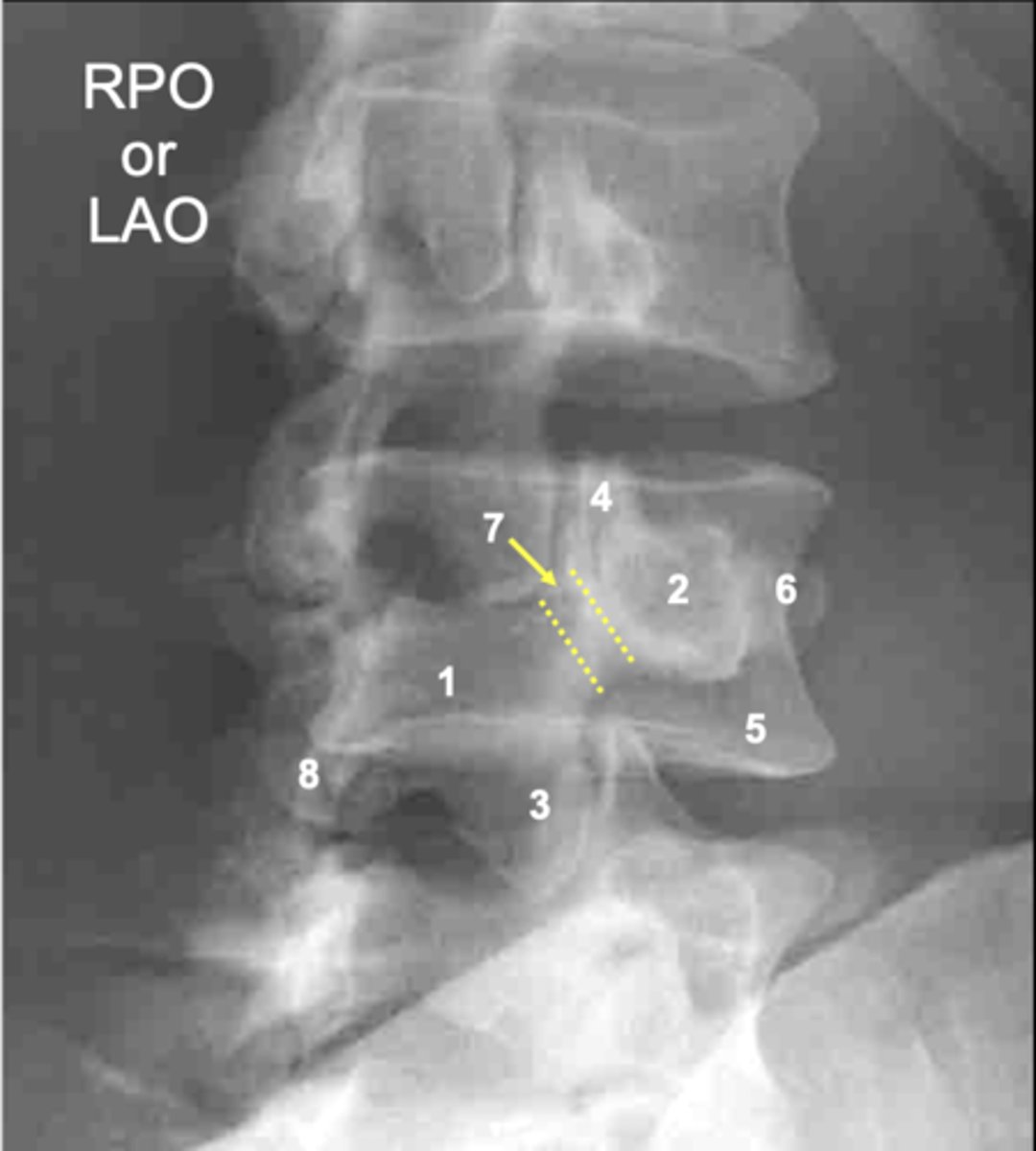
L4 other inferior articular process
ID 8
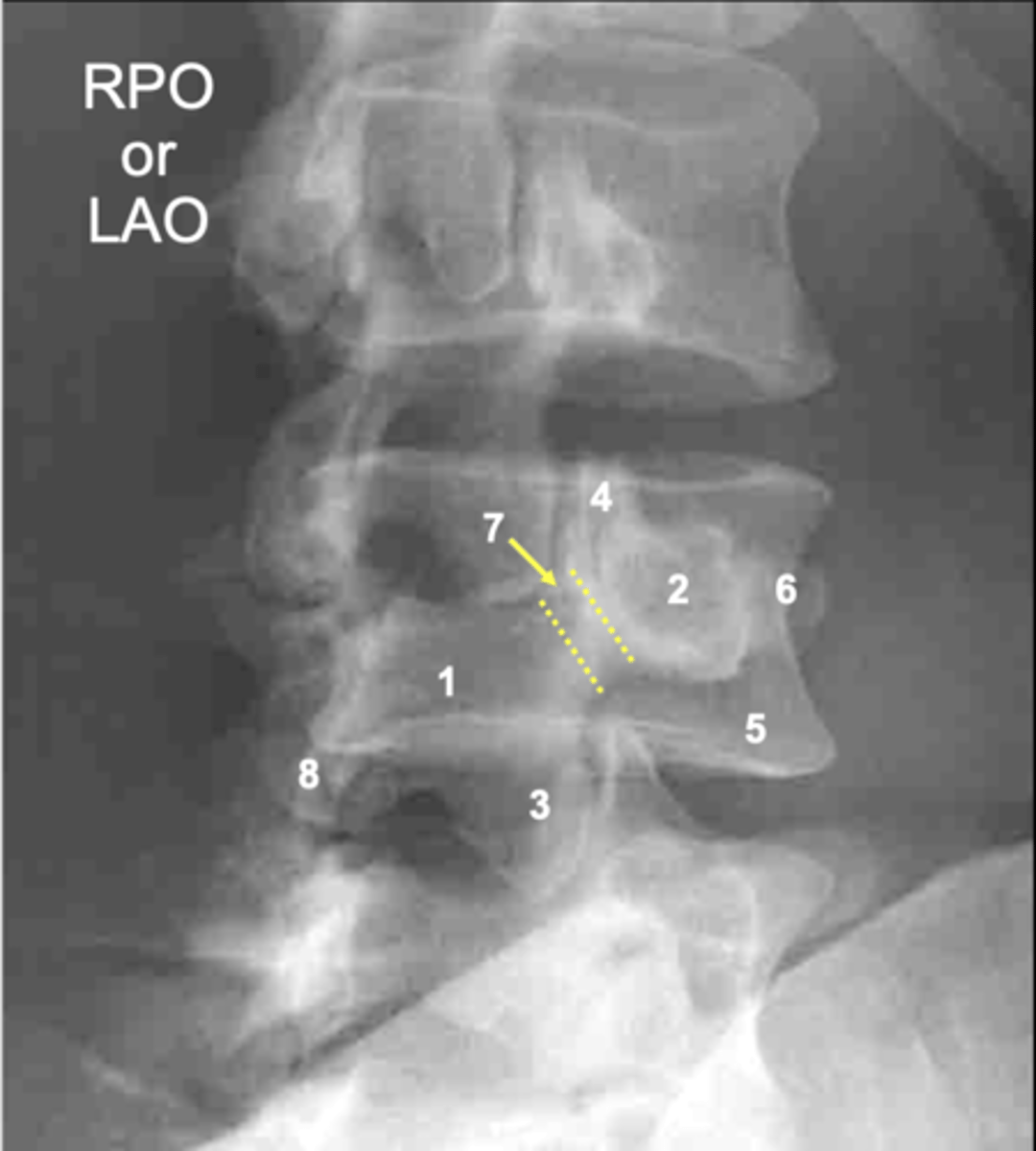
Pars interarticularis
A break in the _____ occurs as a stress fracture in adolescence, usually in very active children that do sports with repetitive hyperextension (gymnasts, wrestlers, football players, etc.)
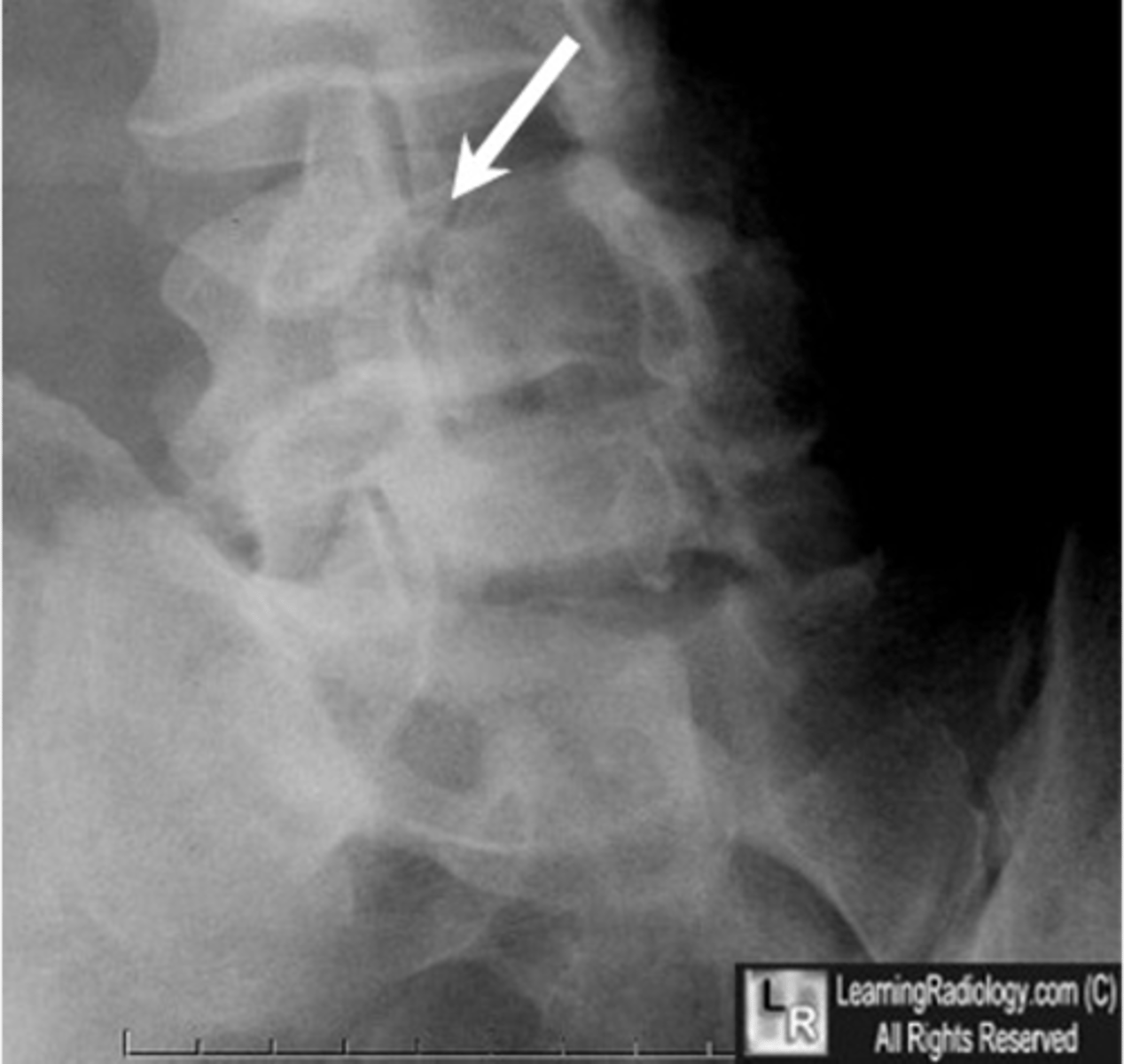
Left
LPO --> _____ Pars
Right
RPO --> _____ Pars
Right
LAO --> _____ Pars
Left
RAO --> _____ Pars
L1
L1/L2 IVF nerve root
L2
L1/L2 disc herniation
L2
L2/L3 IVF nerve root
L3
L2/L3 disc herniation
L3
L3/L4 IVF nerve root
L4
L3/L4 disc herniation
L4
L4/L5 IVF nerve root
L5
L4/L5 disc herniation
L5
L5/S1 IVF nerve root
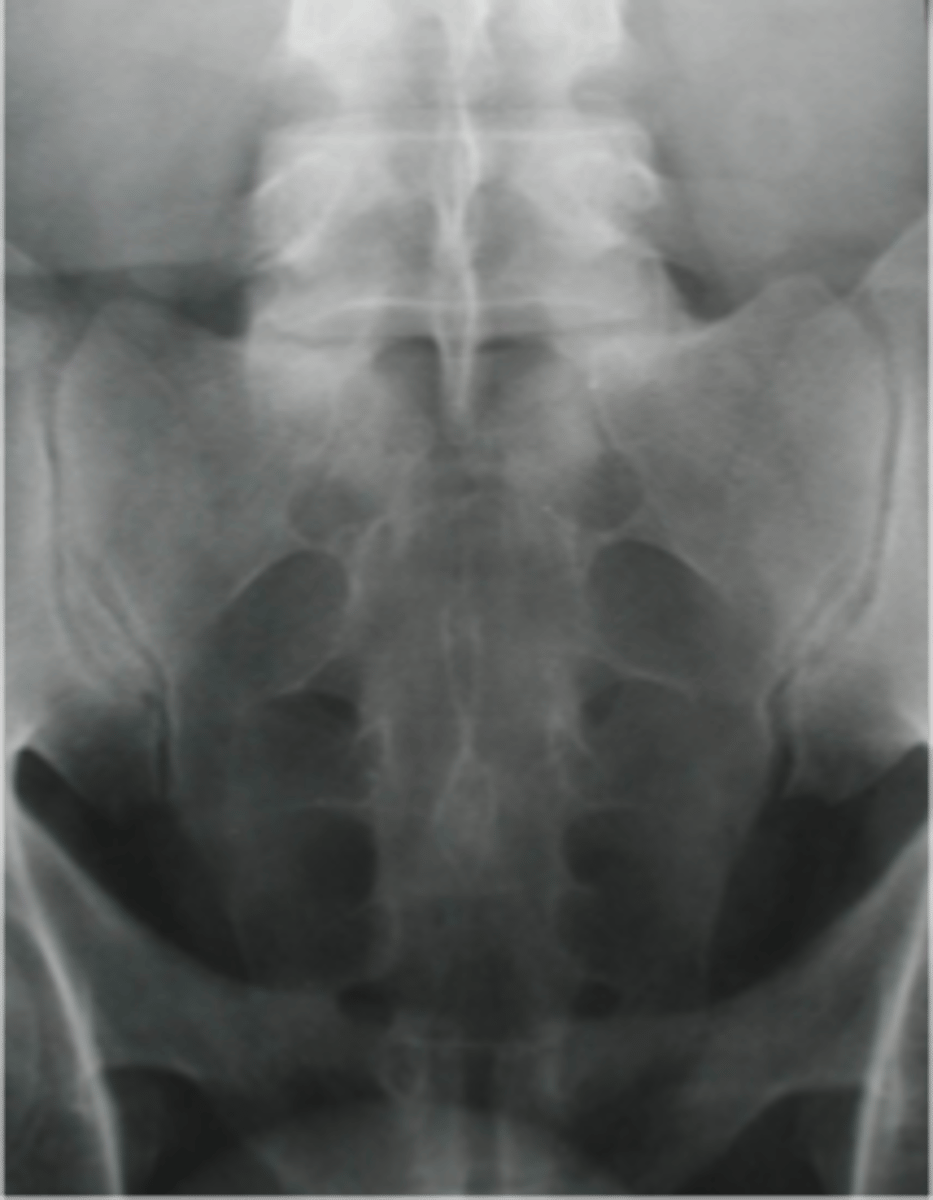
AP sacrum
ID view
Lateral sacrum
ID view
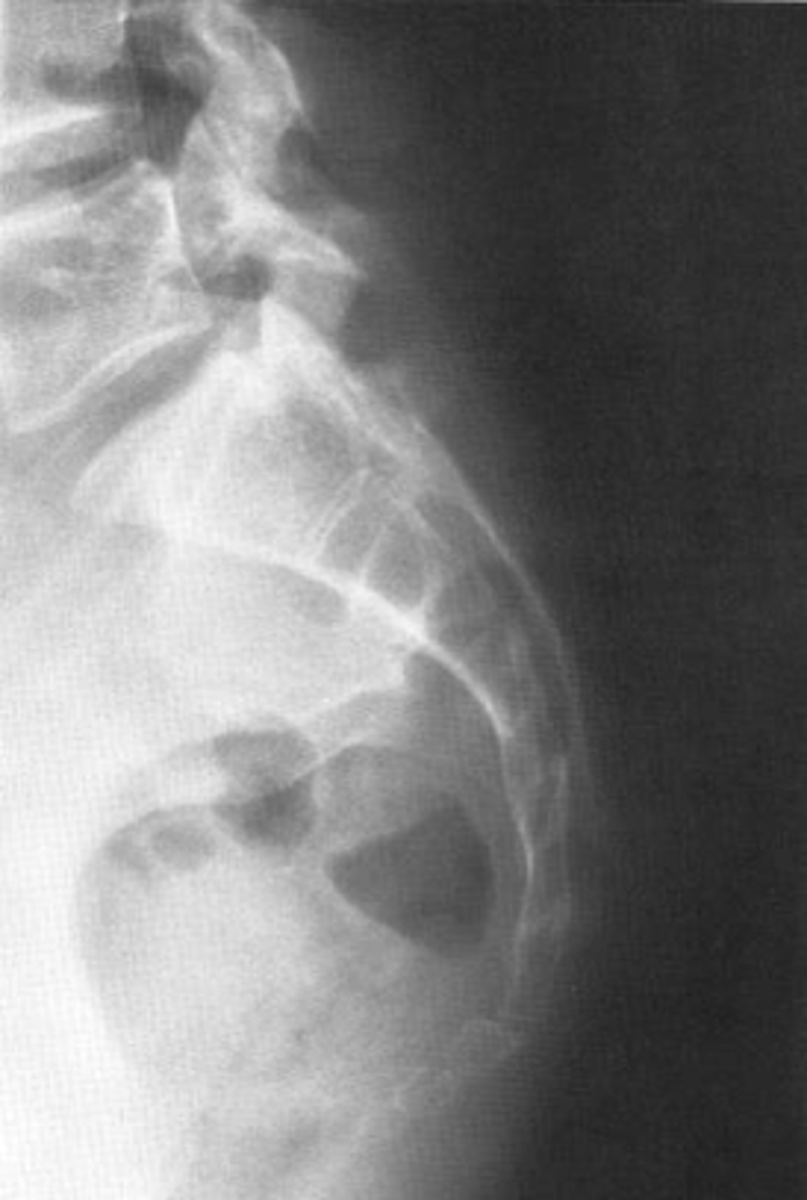
50-60˚
Normal lumbar lordosis
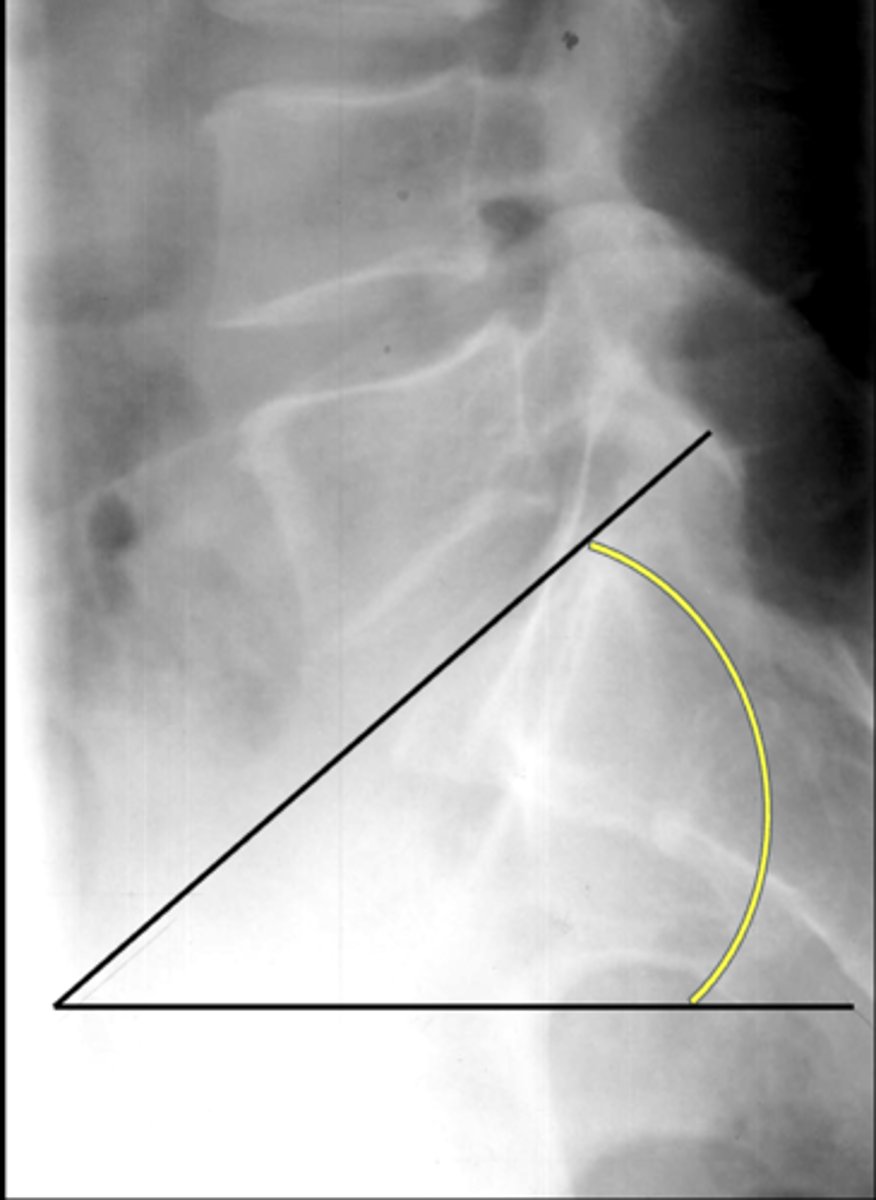
Angle created by the superior endplate of L1 and the superior endplate of S1
How is the lumbar lordosis measurement line drawn?
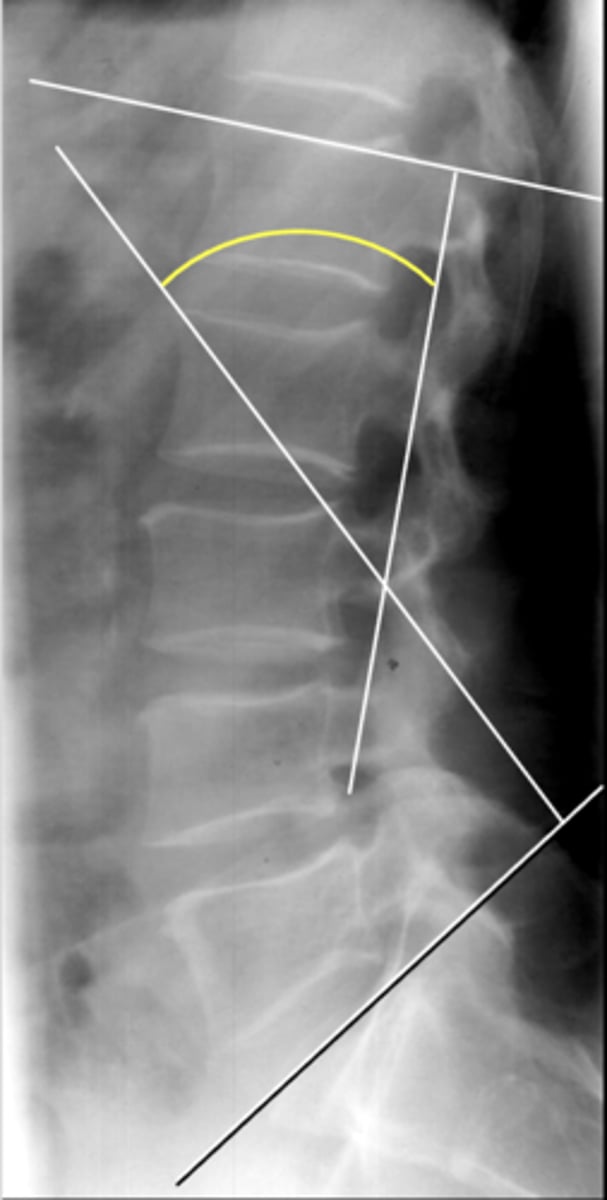
Line drawn from the superior endplate of the sacrum met by a horizontal line
How is the lumbosacral angle drawn?
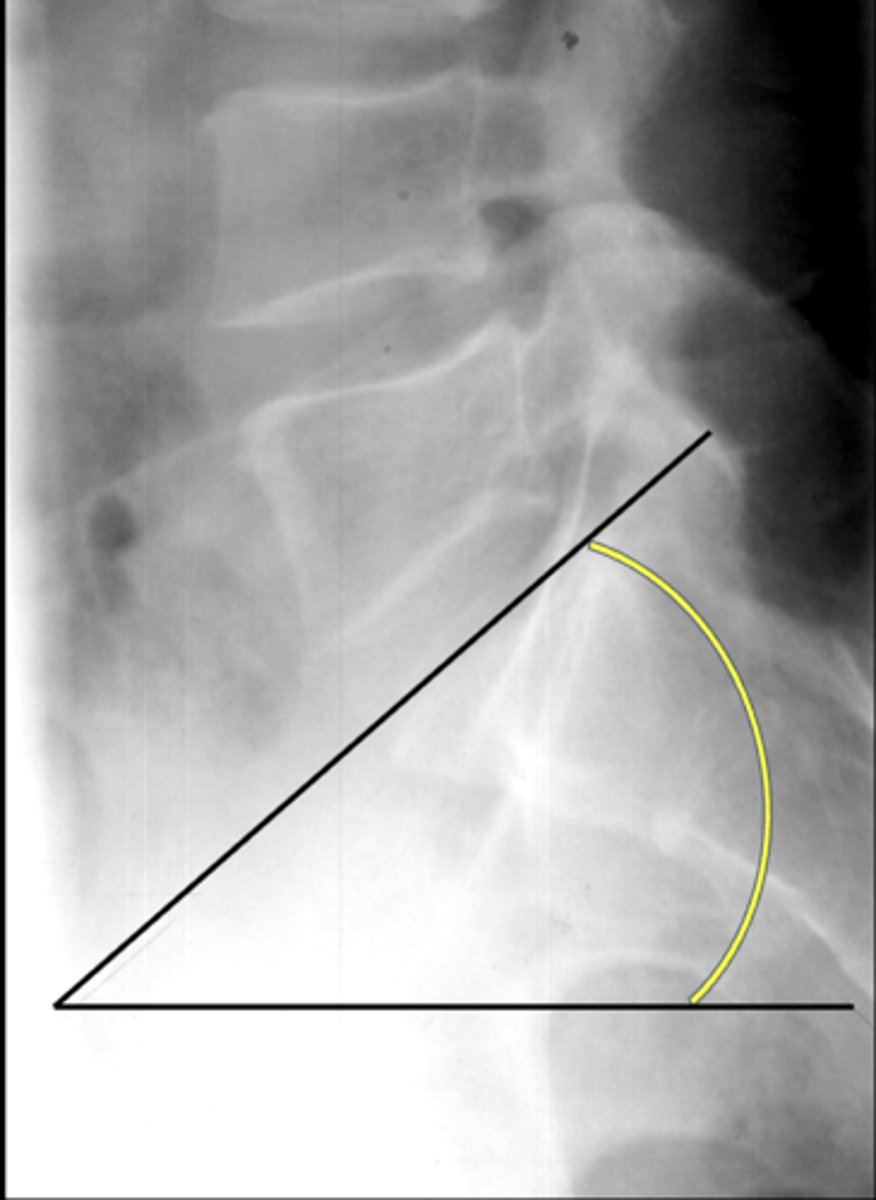
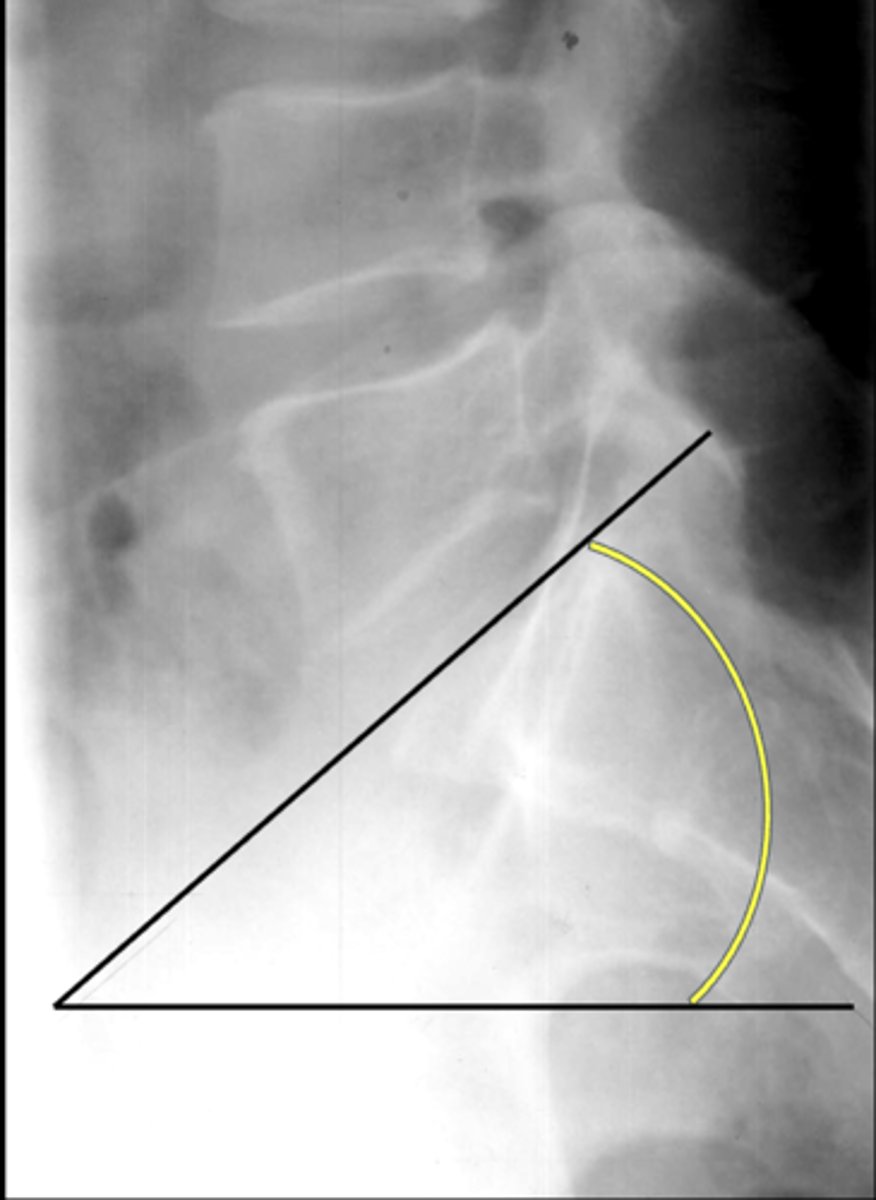
Ferguson's angle, sacral base angle
Another term for lumbosacral angle
26-57˚
Normal lumbosacral angle
Facet syndrome & spondylolisthesis
Significance of an increased lumbosacral angle
Hyperlordosis
ID lumbar lordosis
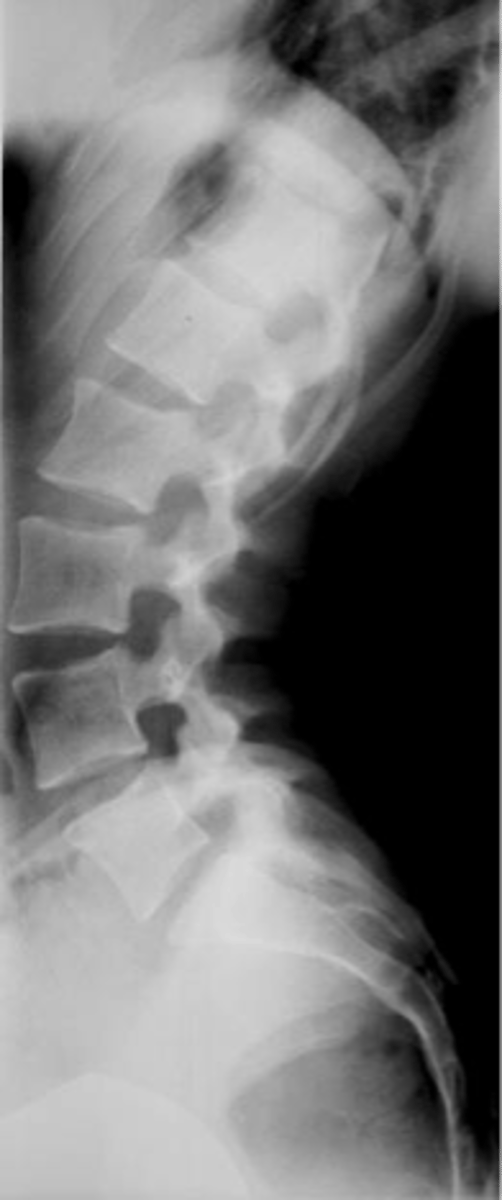
Sway back
ID lumbar lordosis
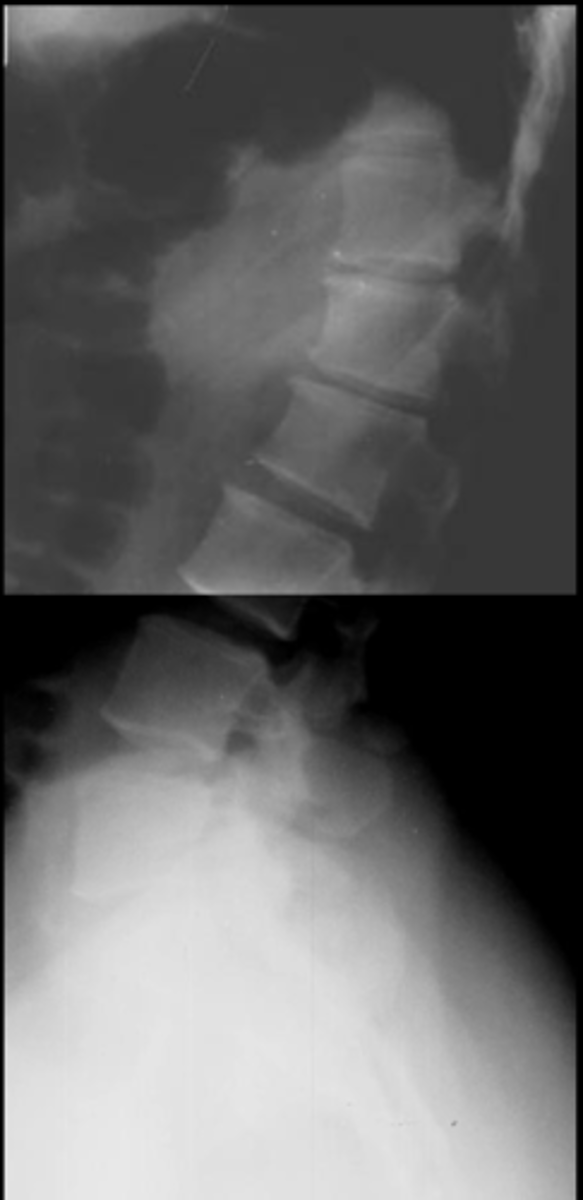
Antalgic hypolordosis/list
ID lumbar lordosis
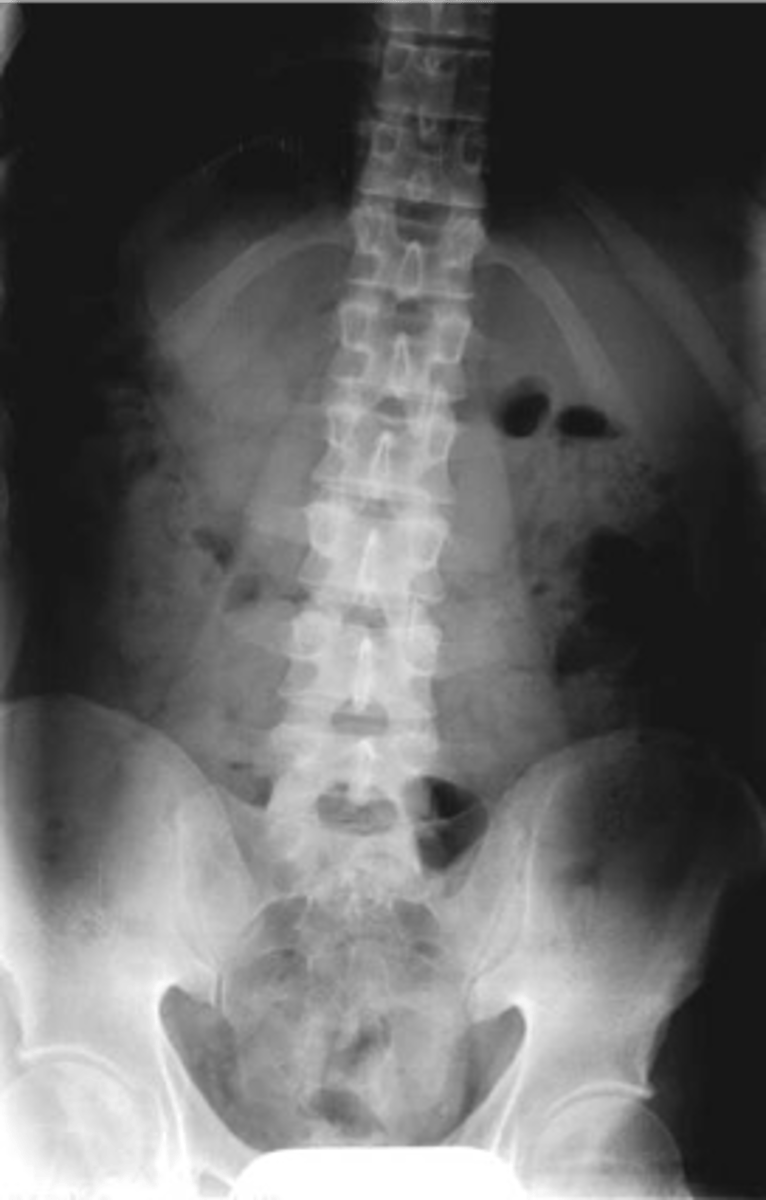
Lumbosacral disc angle
The _____ measures the lumbosacral disc
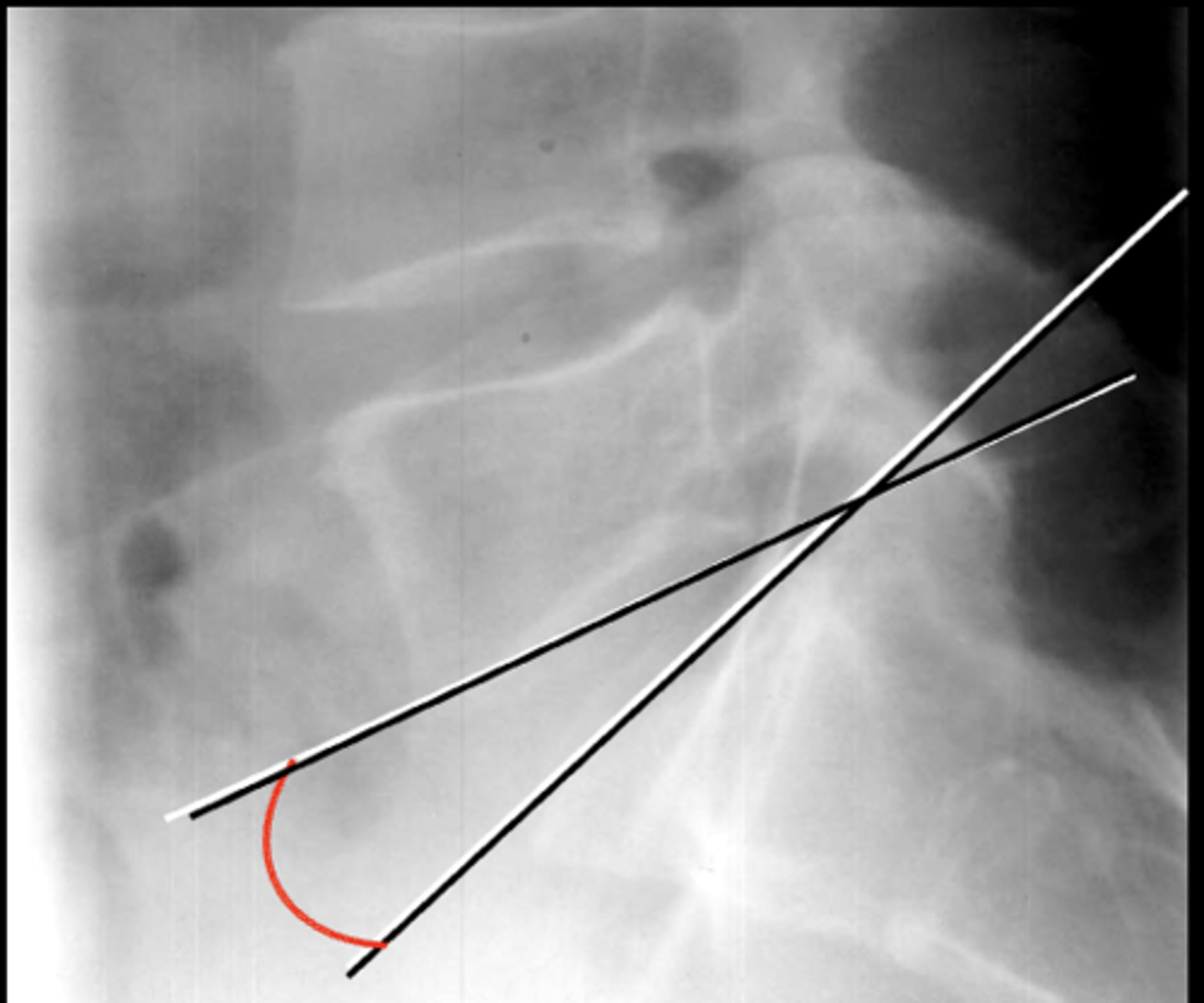
Inferior L5, superior S1
What landmarks are used for the lumbosacral disc angle?
10-15˚
Normal lumbosacral disc angle measurement
Facet syndrome
Significance of an increased lumbosacral disc angle
Ullmann's Line
ID spondylolisthesis measurement
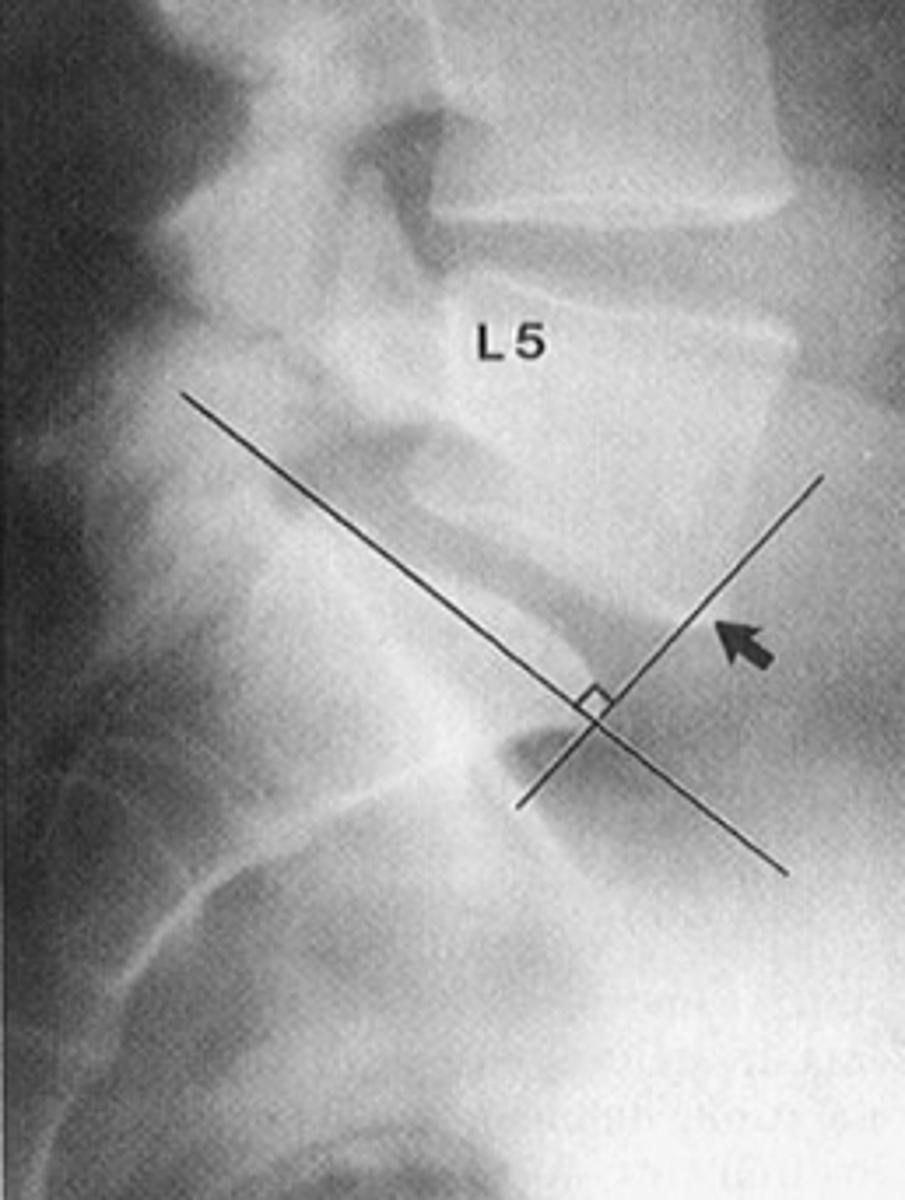
Line drawn across the top of the sacrum, 90˚ angle at anterior tip
How is Ullmann's Line drawn?
Myerding's Method
ID spondylolisthesis measurement
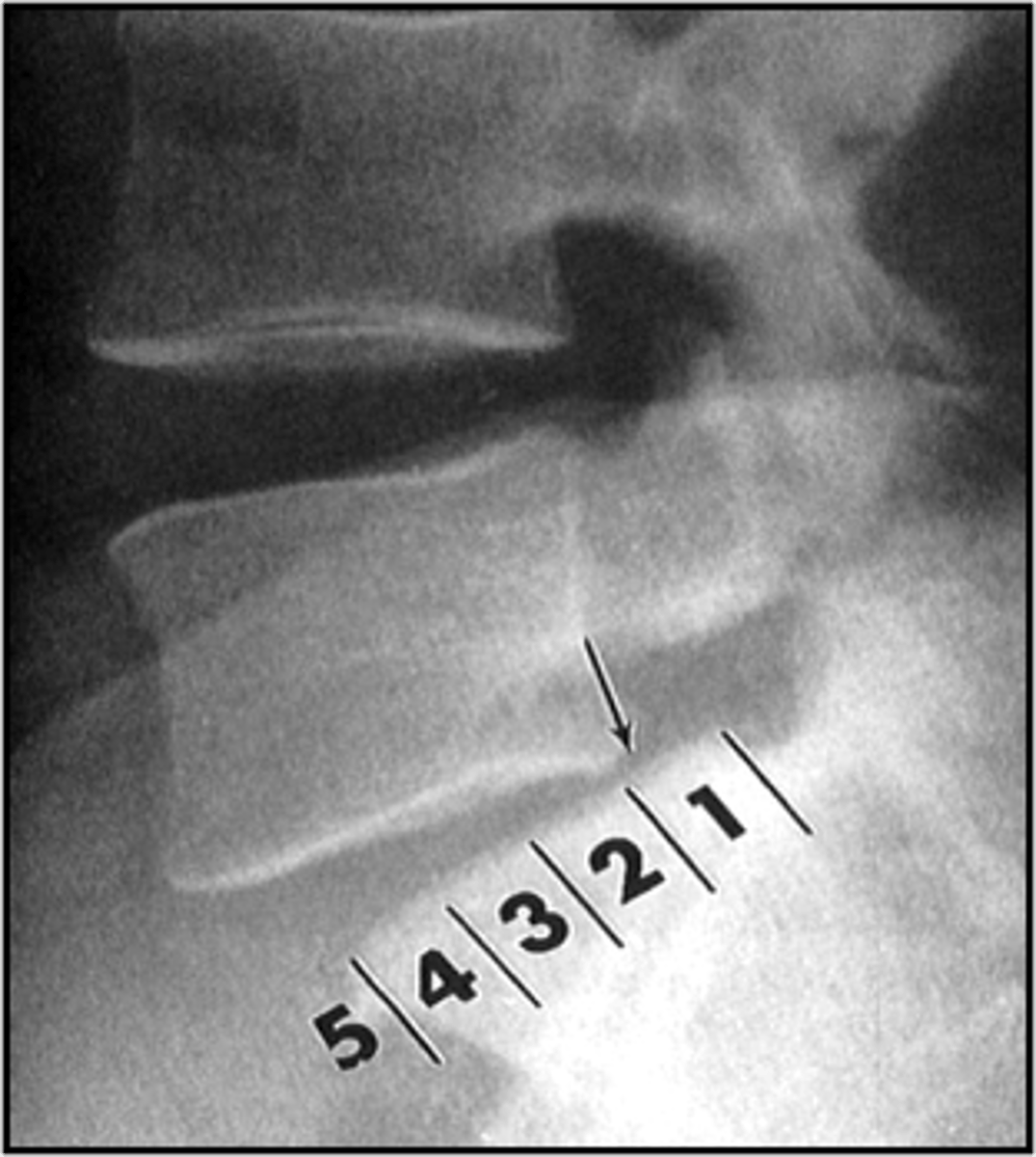
Determine the grade of spondylolisthesis
What is the purpose of Myerding's Method?
I
Grade _____: <25% degree of displacement
II
Grade _____: 26-50% degree of displacement
III
Grade _____: 51-75% degree of displacement
IV
Grade _____: 76-100% degree of displacement
V
Grade _____: >100% degree of displacement
Lumbar gravity line
ID lateral lumbar projection
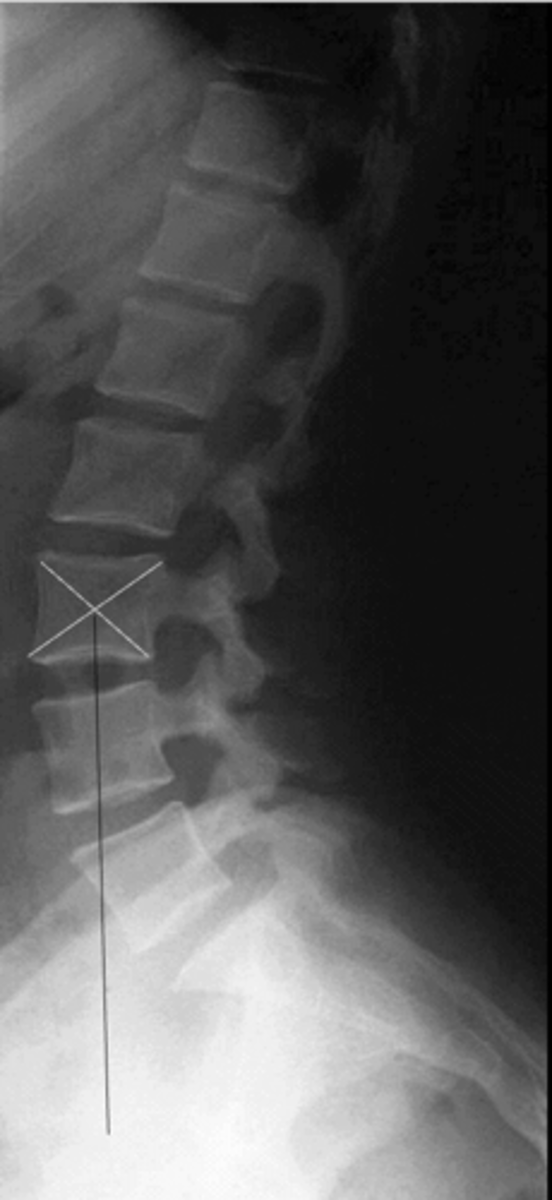
Vertical line from the center body point of L3. Should intersect with anterior 1/3 of the sacral base (<10 mm anterior to base)
How is the lumbar gravity line drawn?
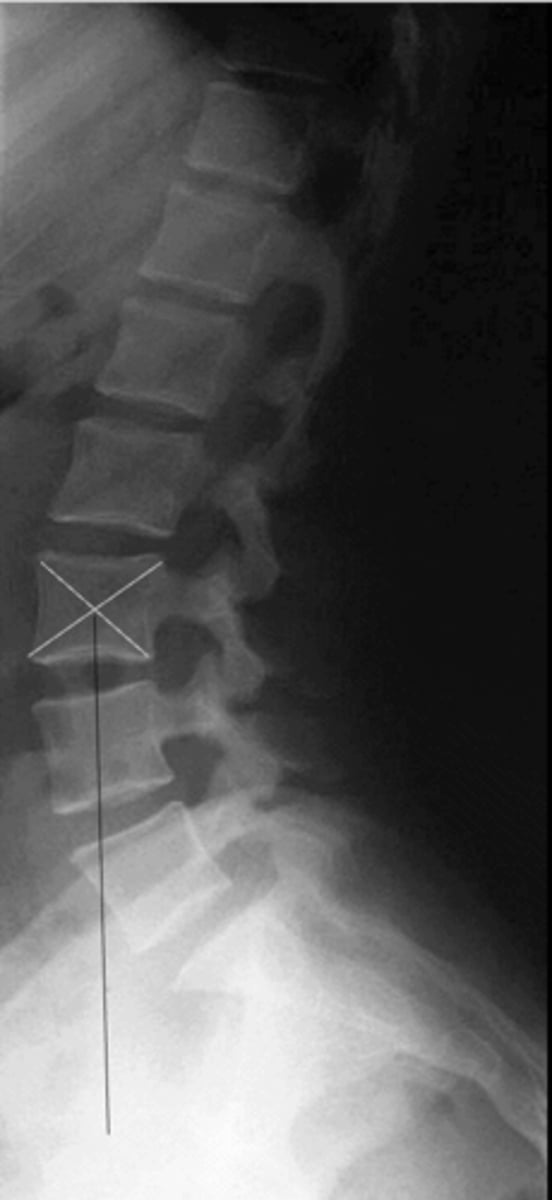
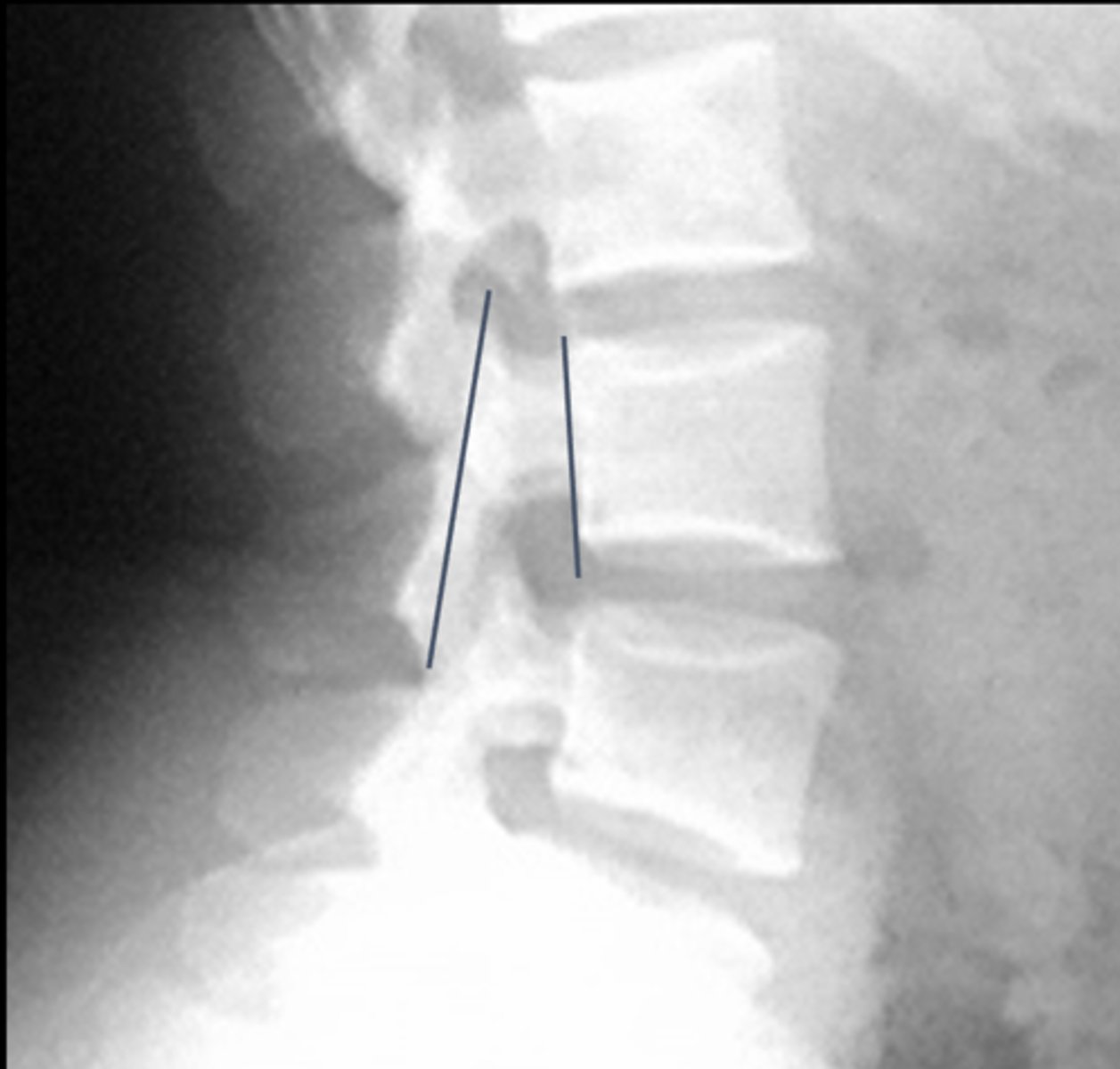
Eisenstein's Method
_____ is a sagittal canal measurement
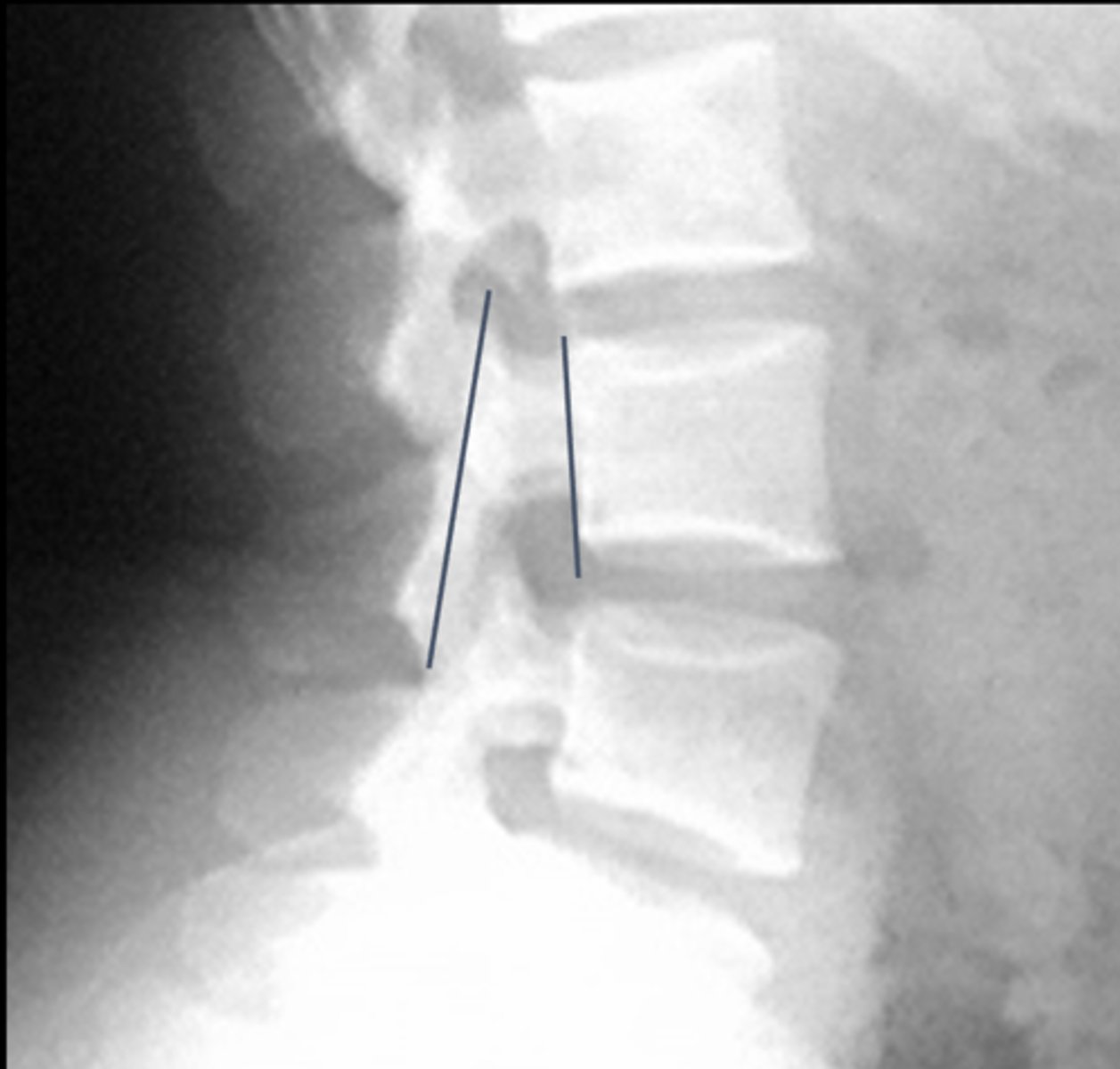
Lines joining the tips of the superior and inferior articular processes at a given level. Distance between line and back of vertebral body measured
How is Eisenstein's Method drawn?
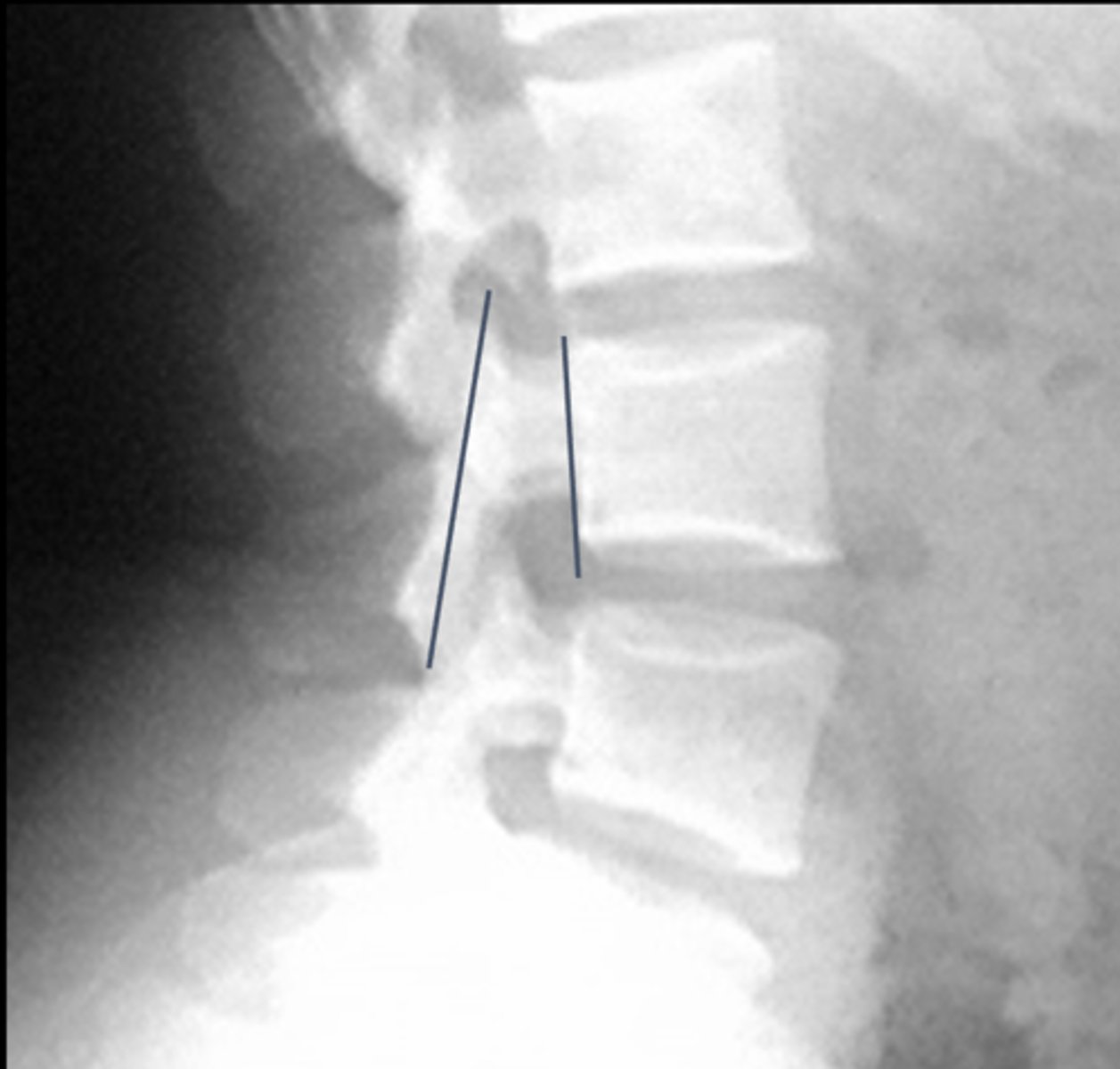
>15 mm
Normal Eisenstein's Method measurement
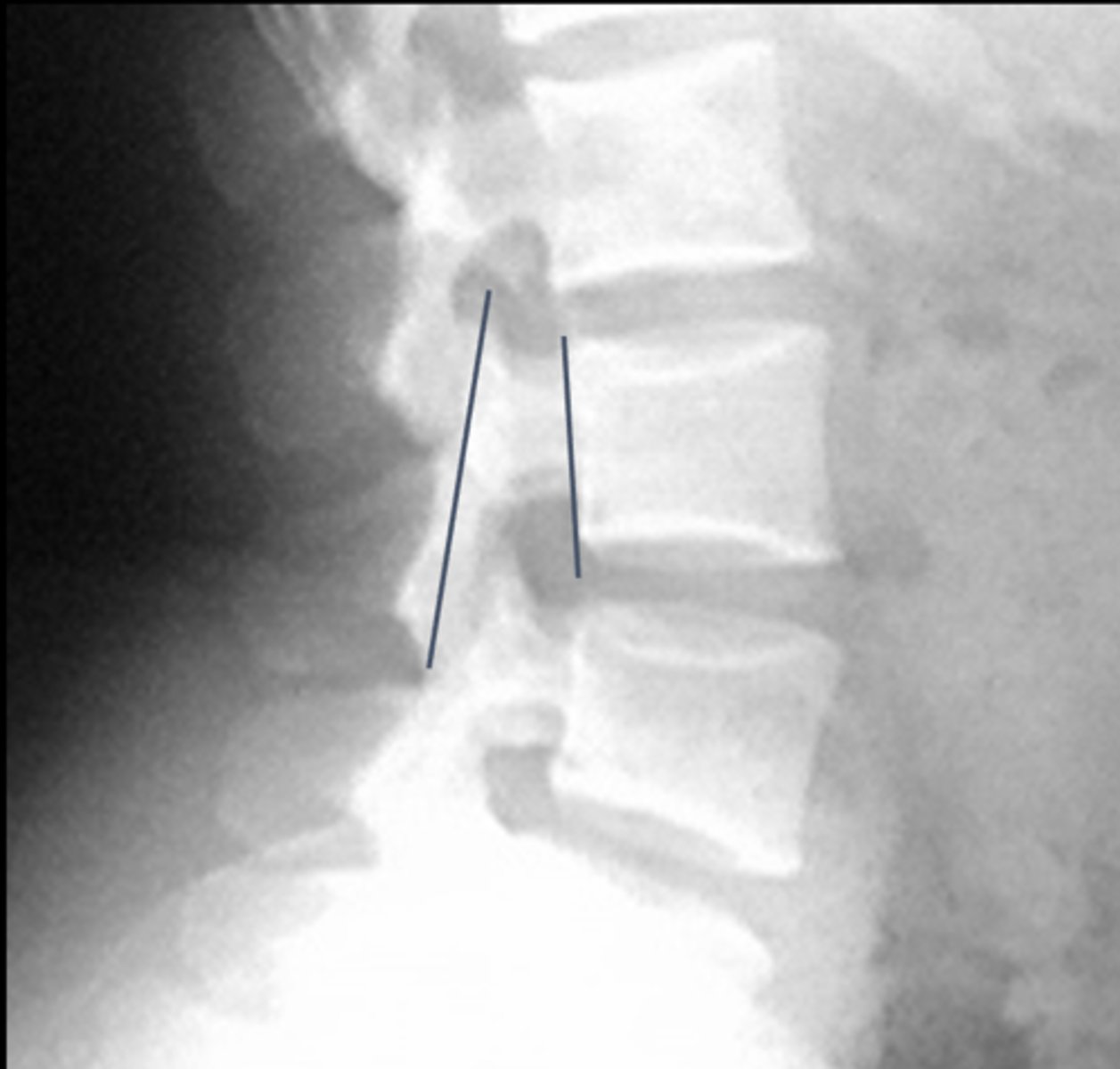
Central canal stenosis
An Eisenstein's Method measurement <15 mm means there is _____
Wider
The interpedicular distance should get _____ as you descend the lumbar spine
Space occupying lesion, congenital anomaly, burst fracture
If the interpedicular distance above is wider, it may be secondary to a _____, _____, or a _____ at that segment
Achondroplasia
_____ is when the interpedicular space narrows as you descend the lumbar spine
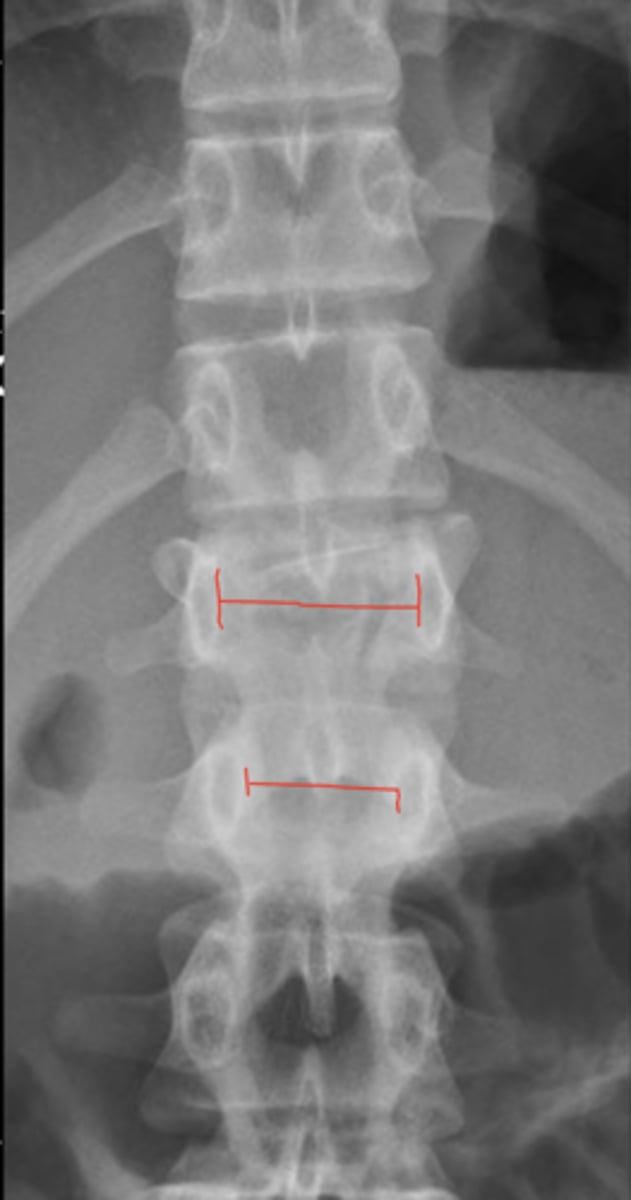
Stenosis
People with achondroplasia are prone to _____
Congenital dwarfism
People with _____ typically exhibit achondroplasia