DNA manipulation (3)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are the ways to manipulate DNA based on knowledge of DNA replication?
PCR
gel electrophoresis
What is PCR?
polymerase chain reaction
Takes few small copies of DNA to make billions of copies in a few hours
Look at properties of DNA by looking
What is PCR used for?
allows researchers to amplify, or replicate, a targeted region of a DNA molecule into as many copies as desired
Sensitive and selective → used to amplify and detect small quantities of nucleic acids
Can analyze starting sample of single molecule of DNA
How do you look at the properties of DNA
Look at properties of DNA by looking at products of PCR through separated products through gel where you can size it (gel electrophoresis)
Separate products through gel electrophoresis
Where does PCR process take place?
in a small plastic tube containing a solution that includes four essential components
What are the necessary components for the tube solution?
Template DNA. At least one molecule of double-stranded DNA containing the region to be amplified serves as the template for amplification.
DNA polymerase. The enzyme DNA polymerase is used to replicate the DNA.
All four nucleotides. Nucleotides (deoxynucleoside triphosphates) with the bases A, T, G, or C are needed as building blocks for the synthesis of new DNA strands.
Two primers. Two short sequences of single-stranded DNA are required for the DNA polymerase to start synthesis. Enough primer is added so that the number of primer DNA molecules is much greater than the number of template DNA molecules
What are Oligonucleotides?
Short stretch of nucleic acid; in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the primer sequence produced by chemical synthesis, which is typically 20–30 nucleotides long.
Base sequences chosen to be complementary to ends of the region of DNA to be amplified??
short, single-stranded sequences of synthetic DNA (or RNA) that act as primers to initiate the amplification of a specific target DNA sequence
What are the steps of PCR?
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
What is Denaturation?
pulling apart of parental strands
Solution containing double-stranded DNA (template DNA) is heated (usually 98C)—> separates DNA into two individual strands
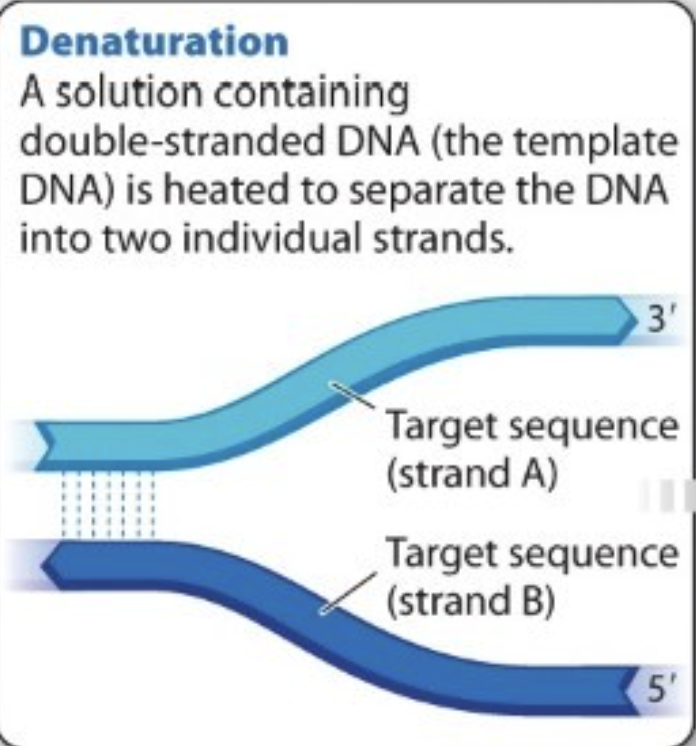
How are the two parental strands broken apart?
heat breaks hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
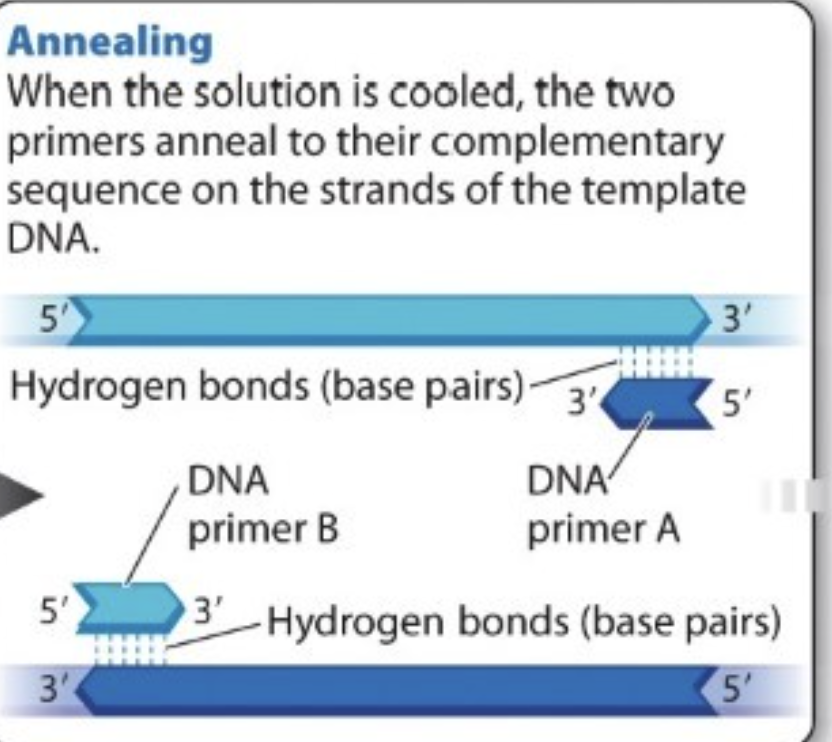
What is annealing?
Solution is cooled —> two primers anneal to their complementary sequence on the strands of template DNA
supply RNA nucleotide primers into the tube of reaction —> Primers will find complementary sequence on the parental strand and anneal (base pair with)
3’ of each primer point toward targeted region → one of primer pairs with one strand of template DNA and other pairs with other strand of template DNA
two primers bind (anneal) to complementary sequence on DNA
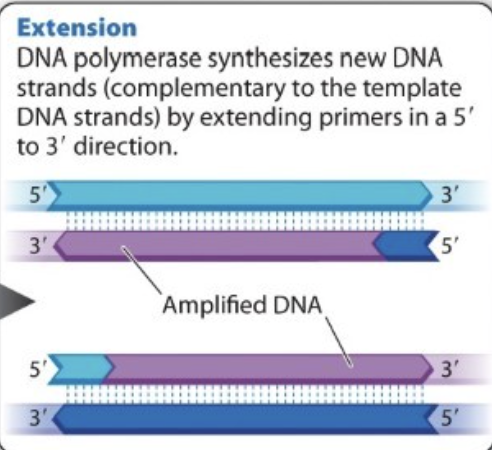
What is extension?
solution heated to optimal temp for DNA polymerase
Now two primers sticking to respective complementary sequence
add nucleotides, polymerase, and energy into the tube --> polymerase build (elongates each primer) new DNA strand off of the RNA nucleotide with deoxynucleoside triphosphates--> extension —> extension is now amplified DNA
What is the result of PCR?
One parental strand --> two copies (amplified DNA)
doubling every round of PCR --> billions of copies (30 rounds) --> calculate amnt of DNA
How do you calculate the amount of DNA?
2^m (m=# of cycles of PCR)
What are the components of PCR?
Template DNA
DNA Polymerase: makes DNA
The four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (A, T, G, or C): Building blcoks
Two primers: one anneals to each of the two strands
What long are primers for PCR?
20-30 nucleotides
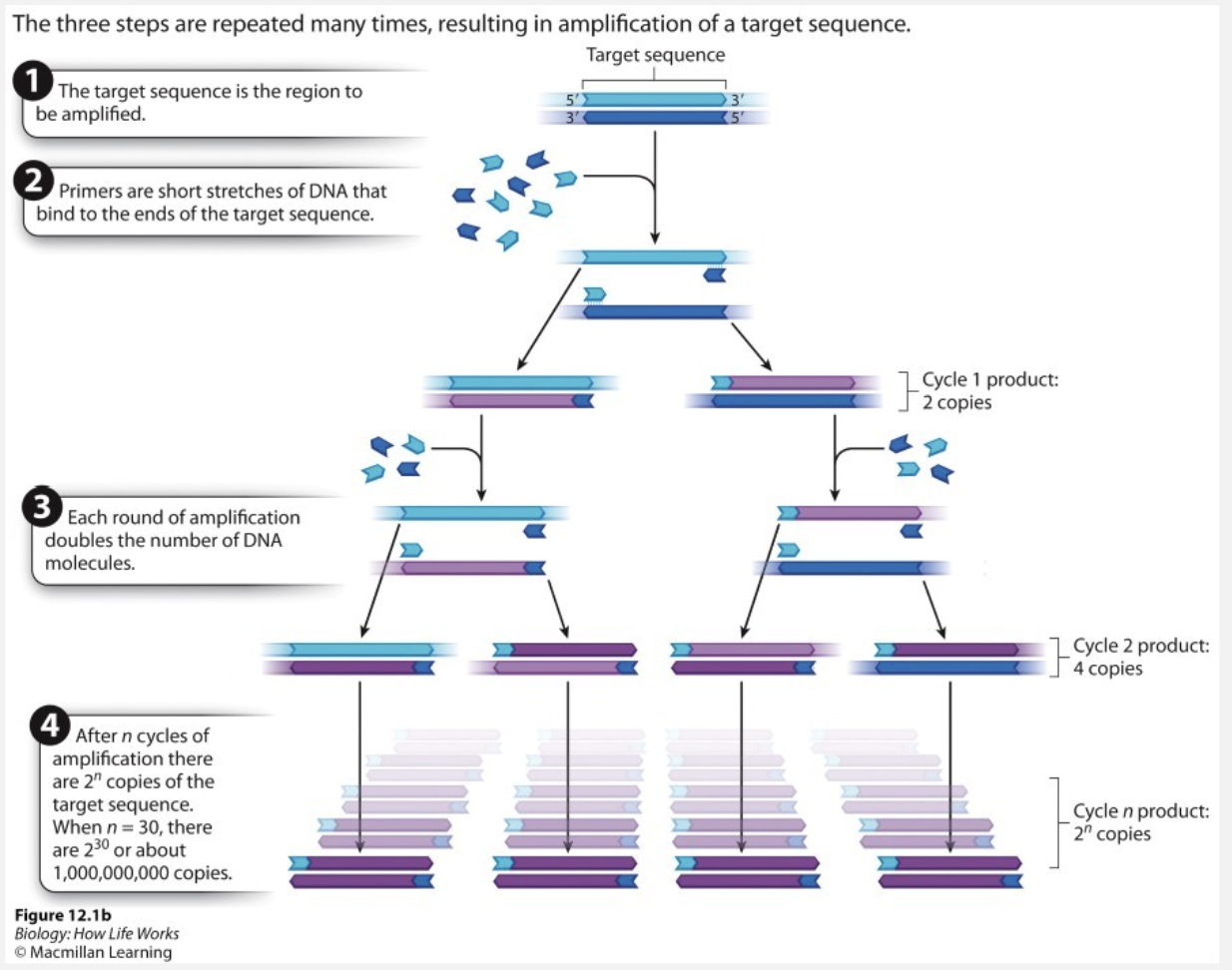
What happens in cycle 1 of PCR?
primers are chosen to base pair with one or the other strand of the template duplex
primers are added to the reaction mixture in great excess compared to DNA template strand
Why is an excess of primers added?
When separate strands by heat (denaturation) by 98C --> primers in excess can go find complementary sequences --> RNA primers binding to parent DNA prevents parental strands from coming back together
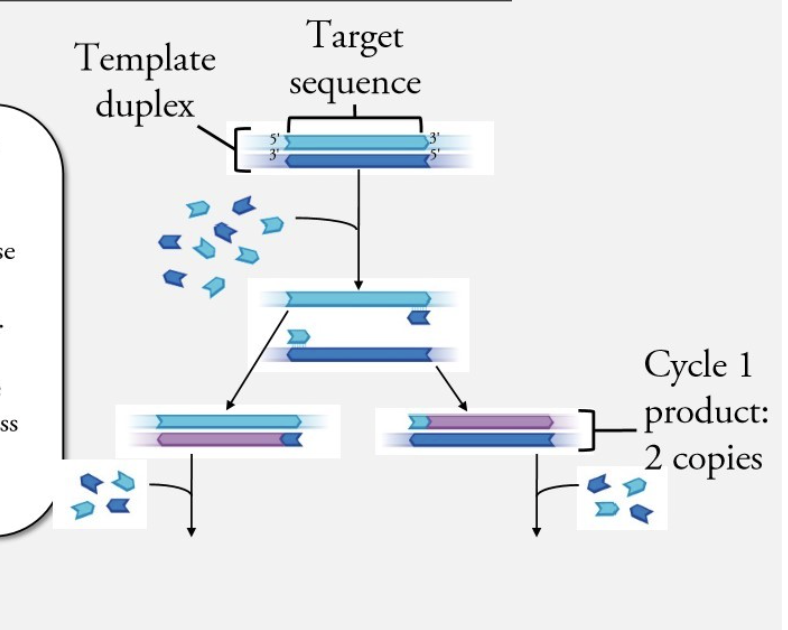
What is the product of PCR cycle 1?
2 copies (one for each parental strand)
What is this doubling called?
amplification
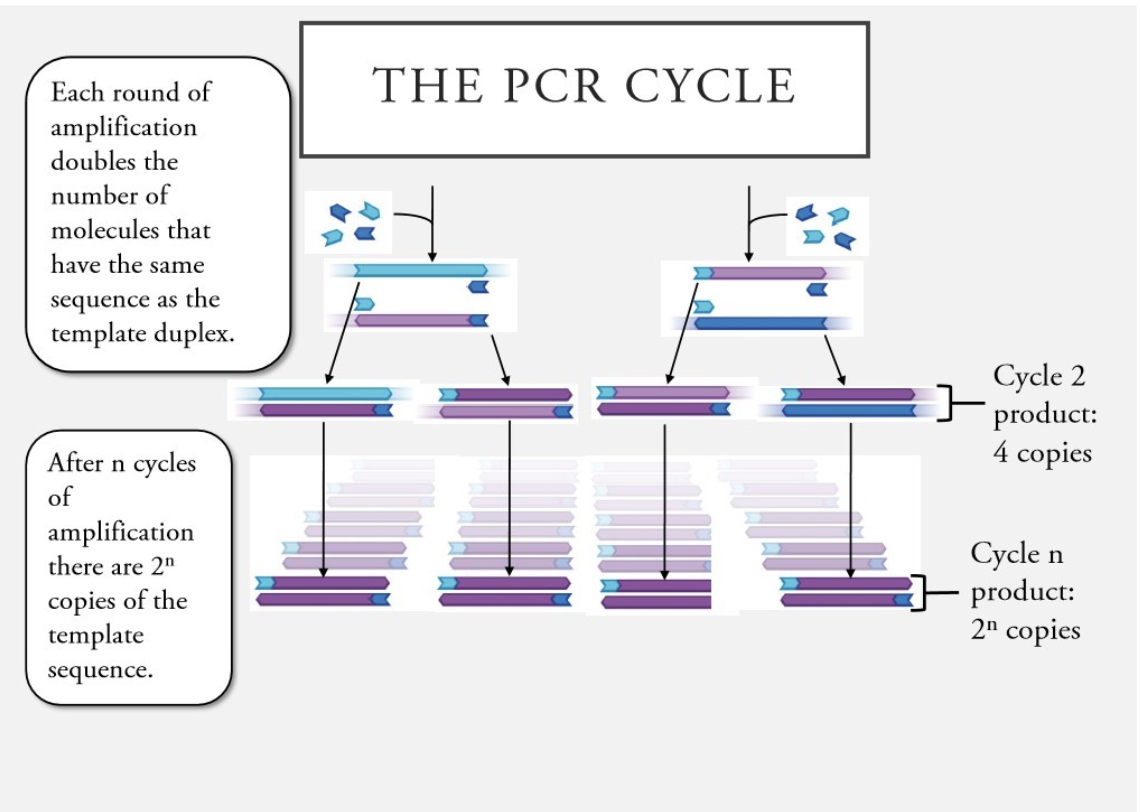
What does each cycle of PCR do?
Each round of amplification doubles the number of molecules that have the same sequence as the template duplex.
What happens after the third round of PCR?
Second round: made full copies of the template DNA that act as templates for replication
only produce molecules as long as region of the template flanked by sequences complementary to primer → doubling number of amplified fragments each cycle = chain reaction
What represents the number of copies of the template sequence in CPR?
after n cycles of amplification there are 2^n copies of template sequence
What is Taq DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase from Taq bacteria that lives in springs
Why is Taq polymerase often used in PCR?
Start heating human DNA polymerase to denature it and do it 30 times --> after 2nd time kills all DNP
98 boils ourself and DNP falls apart --> can't use DNA or most bacterial DNA all the time
Rely on bacteria that live in harsh environments
Taq: evolved to have DNP that can handle 98 and does not denature at 98
Can separate DNP from this bacteria and use it for denaturing in PCR
What does the Taq DNP also show?
conserved function and enzyme evolution
PCR steps summary
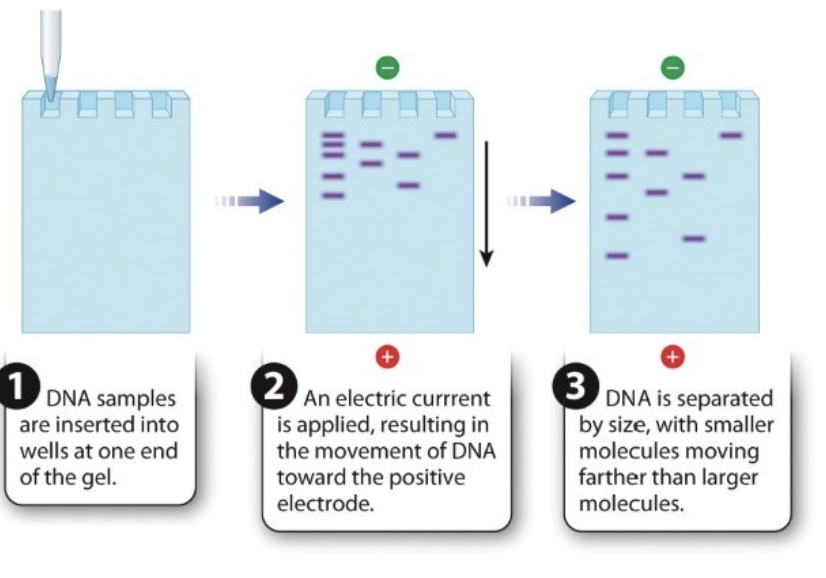
What is gel electrophoresis?
A technique that is used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on size and/or charge, using an electric current passed through a jelly-like substance
Why is gel electrophoresis used?
PCR can cause wrong sequence (anneal improper), anneal to multiple sites and multiple fragments amplified→ to show if PCR showed expected product → must determine size of amplified DNA molecules
What is the process in gel electrophoresis?
DNA samples are inserted in wells at one end of the gel
an electric current is applied —> movement of DNA toward positive electrode
DNA is separated by size
smaller molecules move further down than larger molecules
What is the gel like?
Gel is porous (consists of tangle of polymers) → tangle make it difficult for large molecules to pass through
Why do DNA samples move down in different ways?
Sugar- phosphate backbone negatively charged --> sample of DNA in porous gel matricies --> apply electric current --> DNA sample added at top will want to migrate towards positive charge at the bottom of the gel
Tiny DNA molecule gets through porous matrix quickly –> goes further down in gel
Larger may stay close to top of gel --> seperation of DNA molecules based on size
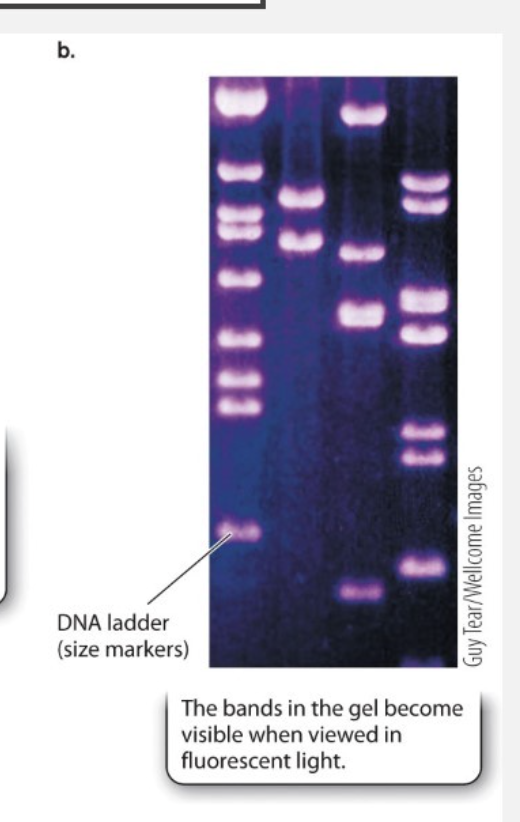
What unit is used to find DNA fragments size?
kb = kilobase pairs (thousands of base pairs)
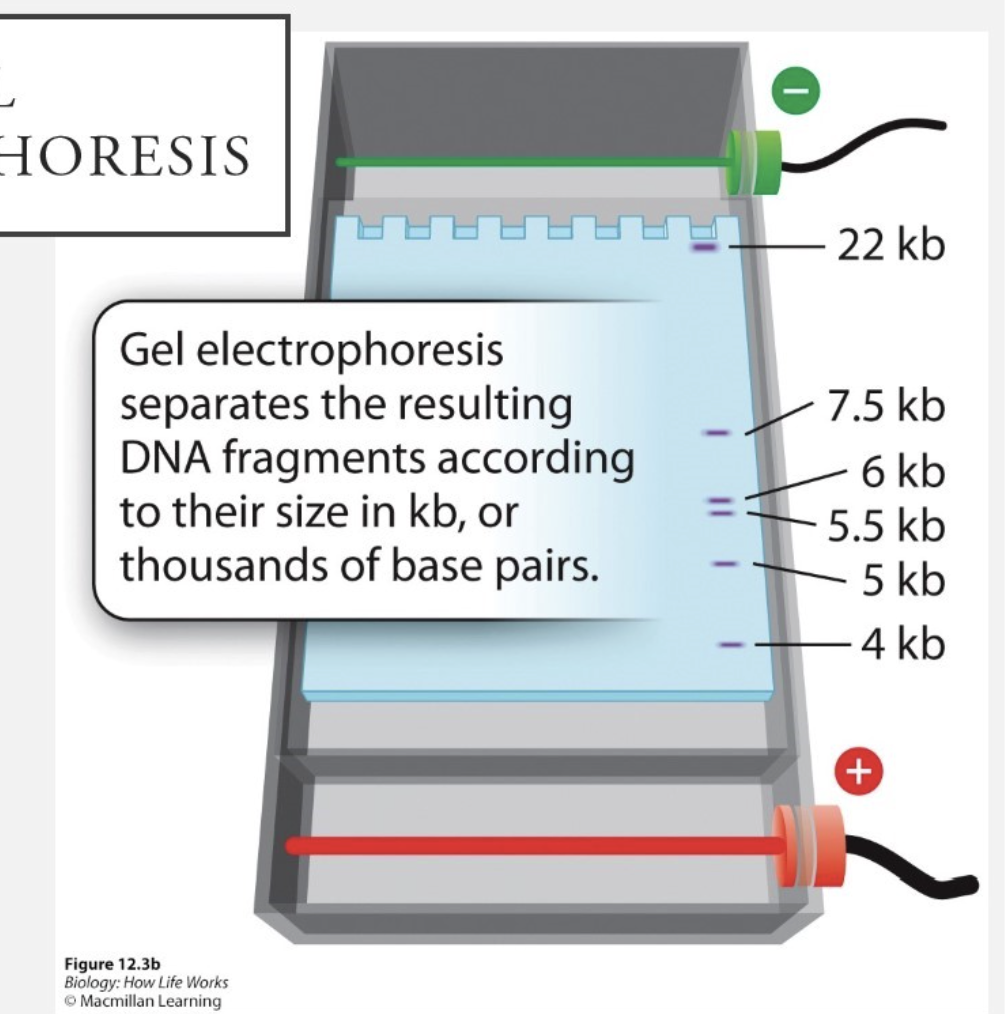
What are the DNA fragments compared to?
sets of standards (DNA that we know the size of the bands)
Look for certain length of PCR product to see if the correct DNA fragment was created during PCR?
One of the lanes contains DNA fragments of known length → results in series of bands called a ladder
Ladder used for estimating lengths of fragment in other lanes
What does CRISPER (overall system) rely on for DNA editing?
the bacterial enzyme Cas9
What are the parts of CRISPER machine?
Three types of molecules are introduced at different points in process into cell containing target DNA
Guide RNA that has been engineered to be complementary to the target DNA
Cas9 (gene for protein) that cleaves DNA when it associates with the guide RNA
Piece of DNA: acts as template with desired new sequence for target DNA
Target DNA identified by guide RNA, cleaved by Cas9, replaced with sequence of template DNA
What does Cas9 have?
Guide RNA attached to it that can express the cas9
What is the first step in CRISPER machine?
Transform cell with plasmid that contains the code for CRISPIEr guide RNA and Cas9
Guide RNA contains a region that can form a hairpin-shaped structure and a region that researchers previously engineered to have bases complementary to the target DNA
What is the process of CRISPER?
Guide RNA combines with CAS9 protein
CRISPERcas9: RNA can find target in genome
Design guide RNA that is complementary to a region of gene in our cells —> finds that and base pair with it
Cas9 enzyme cuts the DNA above and below the base pair region on DNA (cleavage)
Region of complementary can be removed from genome
exonuclease widens gap in target DNA
Add another template (editing template) to the cell (double stranded DNA)
Top and bottom of it complements DNA at either side of the break
Repair reponse for cell uses the editing template to recreate that piece of DNA based on that template
Trick the cell to change the sequence of whatever was being added in (template has a diff sequence of what we og cut out ) --> maybe fixed mutation
Editing template usually degraded by cell mechanisms
Expresses gene that is normal
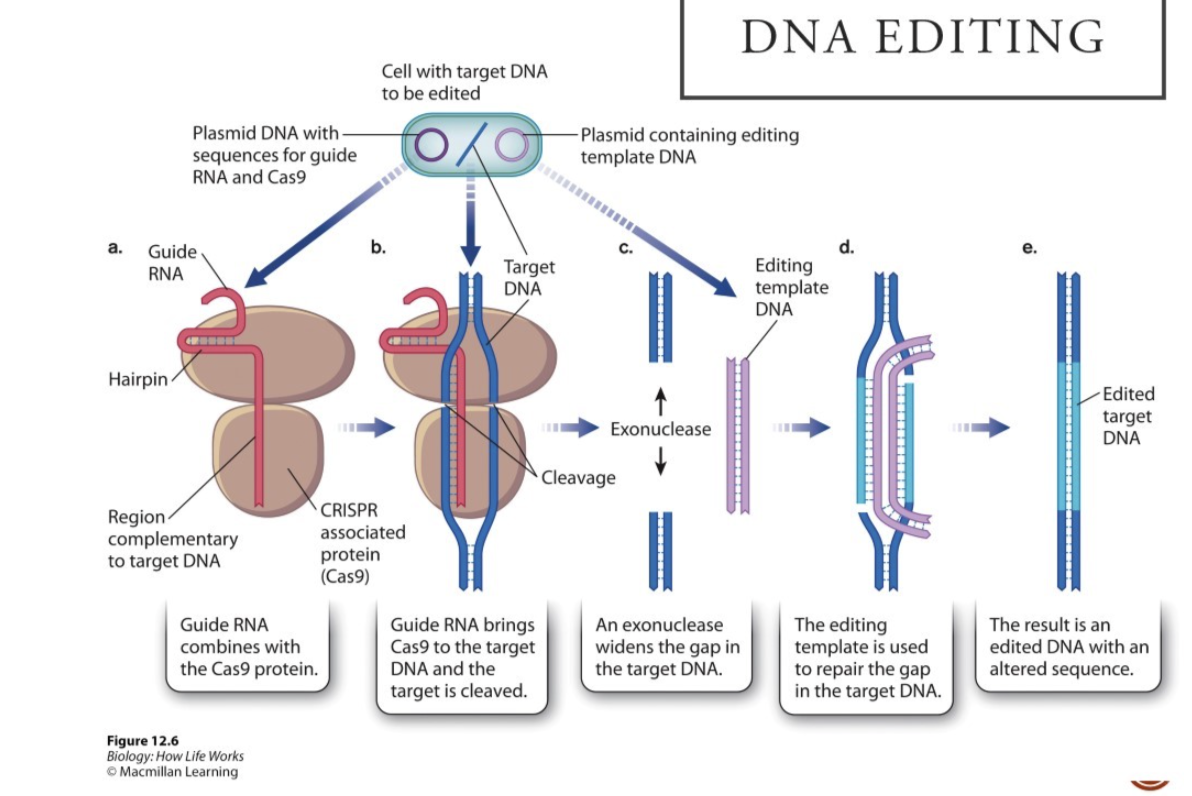
What is the process of CRIPSER gene editing (book)?
Identify sequence to edit
Three types of molecules are introduced at different points in process into cell containing target DNA
Guide RNA that has been engineered to be complementary to the target DNA
Cas9 (gene for protein) that cleaves DNA when it associates with the guide RNA
Piece of DNA: acts as template with desired new sequence for target DNA
Target DNA identified by guide RNA, cleaved by Cas9, replaced with sequence of template DNA
More detailed steps?
Transform cell with plasmid that contains the code for CRISPIEr guide RNA and Cas9
Guide RNA contains a region that can form a hairpin-shaped structure and a region that researchers previously engineered to have bases complementary to the target DNA
Guide RNA undergoes base pairing with target DNA
Cas9 cleaves target DNA
Exonucleases in cell expand gap
Gap repaired using newly introduced template DNA for editing target DNA
Editing template DNA contains sequences of interest to replace the degraded sequence of the target DNA and is flanked by sequences complementary to the target
Strands of gapped target DNA undergoes base pairing with complementary ends of editing template
DNA synthesis elongates target DNA strands and closes gap
Target DNA restored
But sequence altered according to the sequence present in the editing template
What are the issues associate with CRISPER gene editing?
ethical issues with editing human embryos
It can sometimes change genes other than the intended ones = risks?
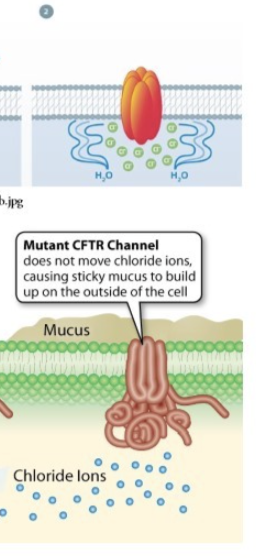
What is Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTDR)?
chloride ion channel
What does a properly working CFTR work and why is it important?
chloride ions move out of cells —> water follows path of ions (osmosis —> water moves to area with higher solute concentration) —> water moves to things like the inside of intestines
Keeps intestines hydrated and helps the mutate of mucus
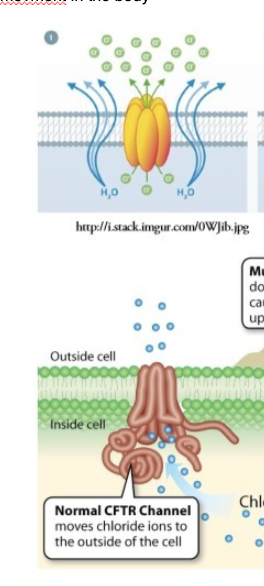
What is cystic fibrosis?
mutation in gene that leads to a non-functional CFTR
What happens due to a non-functional CFTR?
no chloride ion transport —> water remains inside cell
intestines and airways dehydrated —> bacteria replicate in mucus as it replicates —> can cause life threatening bacterial disease
What are organoids?
“mini guts”
sections of intestine of CFTR patients
Form shape of intensities (cells surrounding cavity (lumen) where it needs to be hydrated and absorb food) --> created in lab
What happens if CFTR ion channel is functional/not functional?
-if ion channel functional à ions and fluid enter the “lumen”
-if ion channel nonfunctional à no ions or fluid enter the “lumen”
How can functional CFTR be activated?
by a chemical named forskolin
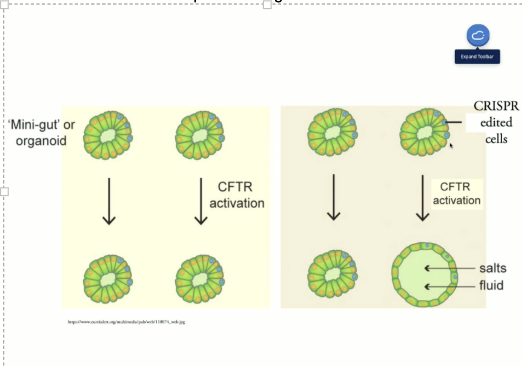
Cystic Fibrosis example
CFTR F508Del = mutation in CF patients
These cells taken from the patient’s intestine
Compared to cells that were edited with CRISPR to correct the mutation = F508Del-Corrected clone (S1-c1 and S1-c2)
What does the previous example show?
expansion of corrected clones
non functional —> does not expand due to mutation
Few cells corrected —> helps entire organoid
What does genetic information in DNA direct?
activities in the cell
What is the central dogma?
DNA —> RNA —> Protein
What is transcription?
RNA from DNA —> specifically mRNA
What is mRNA recognized for?
mRNA recognized by ribosome to build proteins