Digestion Structures (Anatomy and Physiology 12)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
time to clutch up.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Digestion (Physical and chemical)
physical/mechanical = breakdown of ingested food to particles in digestive tract (gut)
chemical = breakdown of food particles to small molecules that pass through epithelial cells to internal environment
Digestive Tract
- extracellular tube that food passes through
absorption
- passage of digested nutrients from gut into blood or lymph, which distributes them through body
elimination
- expulsion of indigestible residues from body
Upper Digestive System Structures Diagram (for labeling practice)
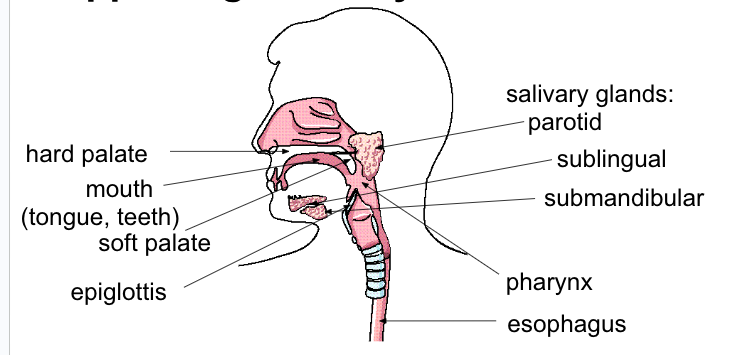
Upper digestive system (oral cavity)
mouth: receives food
tongue: helps break up food, aids in swallowing
teeth: breaking up food into small pieces (incisors bite, canines tear, molars grind)
salivary glands: secrete lubrication (water, mucus) to moisten food
pharynx
chamber where both food and air reside
epiglottis:
flap of skin, closes during swallowing to ensure that food does not enter respiratory system (sphincter)
esophagus
muscular tube which takes food from pharynx to stomach
Bolus
lump of chewed lubricated solid food in mouth
Swallowing:
reflex action that moves bolus from pharynx to esophagus
soft palate moves back to cover upper air passages
epiglottis covers lower air passages
impossible to breathe & swallow at same time
Peristalsis:
rhythmic contractions of circular/longitudinal muscles surrounding esophagus
squeezes bolus down to stomach
Lower Digestive System Structures Diagram (for labeling practice)
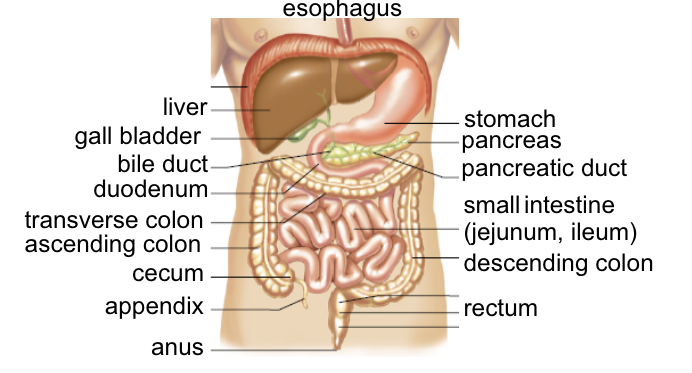
Stomach Components (cardiac sphincter)
ring of muscle, gateway from esophagus to stomach
Structure:
J-shaped bag for food storage/digestion
3 layers of muscle to break up food
glands that secrete gastric juice
pyloric sphincter
ring of muscle, gateway from stomach to small intestine
chyme
partially digested food in stomach (liquid/paste form)
Small Intestine Sections:
duodenum
first 25 cm of intestine, receives secretions from liver, gall bladder, pancreas
jejunum/ileum
middle/final sections where further peristalsis, enzyme secretion & nutrient absorption occur
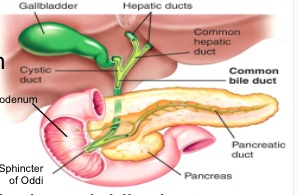
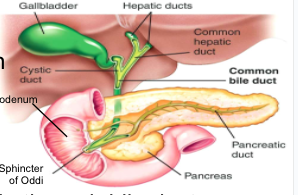
Pancreas
- secretes pancreatic juice into duodenum via pancreatic duct (chemical digestion)
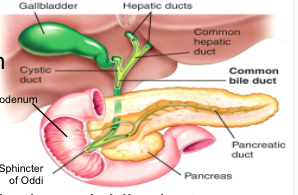
gallbladder
- stores bile (produced by liver), secretes bile through bile duct into duodenum (fat digestion)
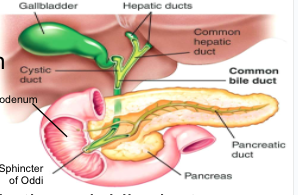
Sphincter of Oddi:
- gateway from bile duct & pancreatic duct to duodenum
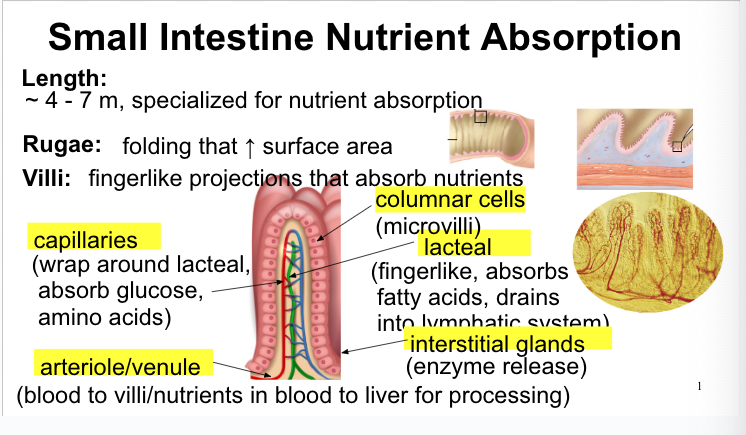
small intestine nutrient absorption
4-7m, specialized for nutrient absorption
Structures within:
Rugae: folding that increases surface area
villi: fingerlike projections that absorb nutrients
capillaries: wrap around lacteal, absorb glucose, amino acids
arteriole/venule: blood to villi/nutrients in blood to liver for processing
columnar cells: microvilli
lacteal: fingerlike, absorbs fatty acids, drains into lymphatic system
interstitial glands: enzyme release
liver functions
removes toxins (like alcohol) from blood
nutrients:
interconversion (carbs ↔ fats ↔ amino acids)
blood concentration (glucose ↔ glycogen)
manufacturing:
blood proteins fibrinogen & albumin
cholesterol and other lipids
red blood cells in vertebrate embryos
destruction:
deamination of amino acids to make waste ammonia excreted as urea, uric acid)
old red blood cells
bile production:
bile secreted into duodenum through bile duct, aids in physical digestion of fats
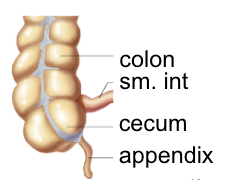
Large intestine/colon
~ 2m long
designed for water reabsorption (90% - 95%)
too much water reabsorbed = constipation
not enough water is reabsorbed = diarrhea (watery feces)
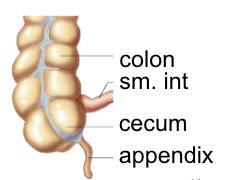
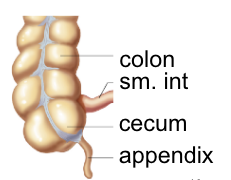
cecum
- blind end of colon after junction betwee ileum and colon (ileocecal sphincter)
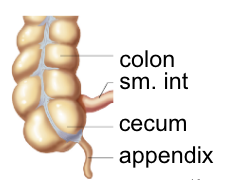
appendix
- projection from cecum, immune properties
rectum and anus
Rectum: where feces are stored before evacuation
Anus: sphincter made of double rings of muscles, controls defecation