BIOCHEM 5614 ---[L3&4: Bioenergetics]
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro To Metabolism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Exergonic (free energy, spontaneous?)
Change in G < 0
Spontaneous
Endergonic (free energy, spontaneous?)
Change in G > 0
NOT spontaneous
Which reaction do regulations typically occur in?
Irreversible pathways
Irreversible pathways
Have high energy barrier to return to the original reactants and thus proceed primarily in one direction.
Thermodynamics is the relationships of what?
Reactants to products
Favorable Change in G (free energy) will occur AND it’ll tell you how quickly it goes (T/F)
False
It only tells you the occurence, NOT the speed
What tells you how quickly a reaction occurs?
Kinetics (activation energy)
Thermodynamic Equilibria (imageS)
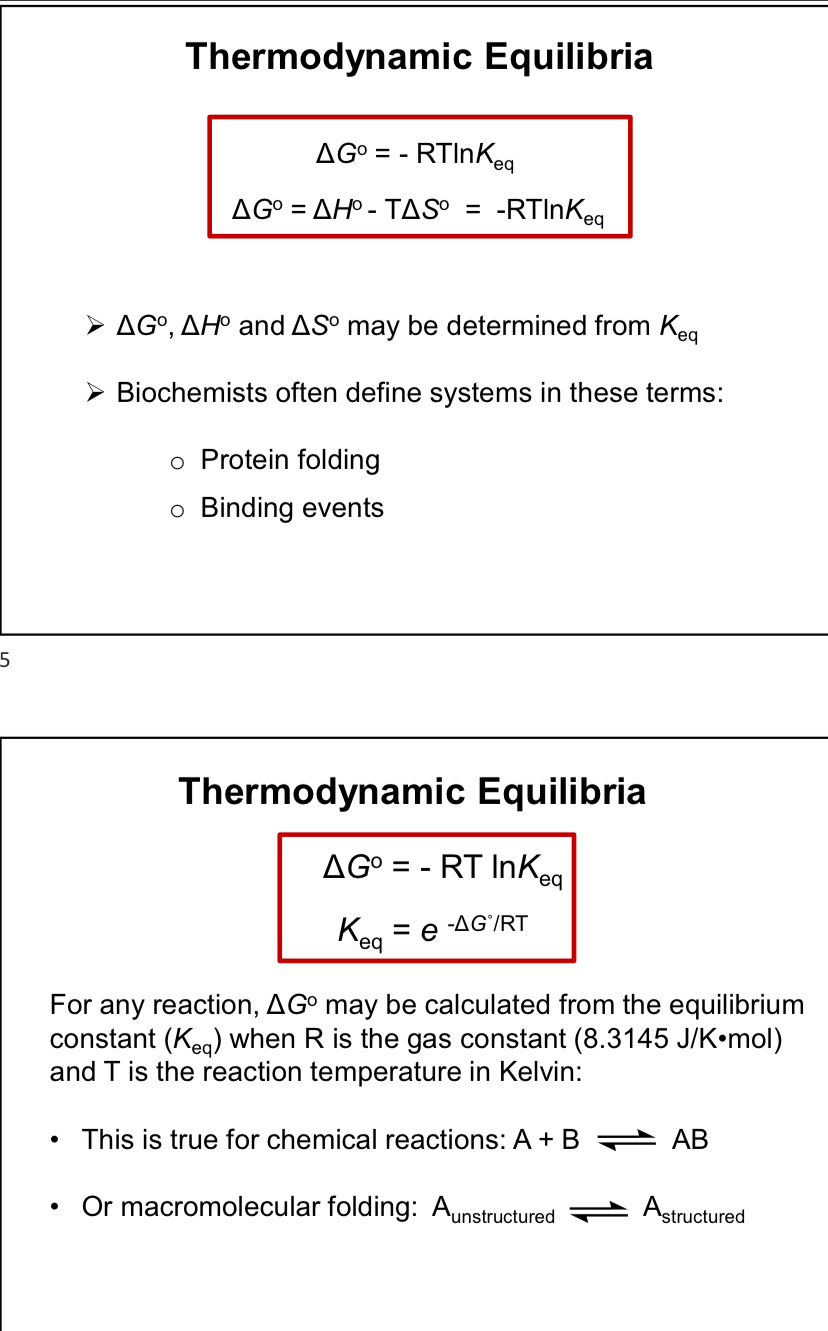
Standard Condition (In Chemistry)
P= 1 atm
All molecules= 1M
T= 298K (25ºC)
Standard Condition (In Biochemistry)
P= 1 atm
All molecules= 1M
T= 298K (25ºC)
Water= 55.5M
H+= 10^-7 M (7.0 pH)
*if needed, Mg2+= 1mM
remeber, realife components are rarely all at 1M
Reversible free energy amount must be…..
close to value of 0 so energy barrier is going to go through back and forth (not quite but almost like equilibria)
Discrete reactions may be ______ through a common ______
coupled
intermediate
What is the basis for metabolic pathways
coupled reactions
What can link different pathways together
coupled reactions
A coupled reactions can occur as long as the…..
Overall free energy is less than 0, it will be spontaneous
VERY important in metabolism
What drives Glucose phosphorylation?
ATP hydrolysis
First step of glycolysis does what
phosphorylates glucose entering an intestinal cell via transporters will become glucose-6-phosphate (endergonic) due to an reaction to trap the molecule within the cell
The trapping of glucose-6-phosphate isn’t energetically favorable. Discuss next step.
Couple with ATP Hydrolysis (exergonic), this will gain a net negative, so the reaction is spontaneous.
Note: The net reaction has high negative (energy barrier) so it will still be trapped inside the cell