NEU 101 Test 6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:35 PM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
motoneuron
a neuron that passes from the central nervous system or a ganglion toward a muscle and conducts an impulse that causes movement.
2
New cards
motor unit
it is 1 motoneuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
3
New cards
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
a synaptic connection between the terminal end of a motor nerve and a muscle.
4
New cards
electromyography (EMG)
records the electrical activity of muscles.
5
New cards
What is a Central Pattern Generator
neural networks formed by inhibitory and excitatory interconnected neurons that generate a highly reproducible, rhythmic, sequence of muscle activations.
6
New cards
Differences between reflexes and compensatory postural adjustments
Reflexes are involuntary, a sequence of movements, and elicited by sensory stimulus. Compensatory postural adjustments respond to unexpected perturbations, have polysynaptic loops which start from a variety of receptors, and can be perfected.
7
New cards
Pyramidal Tract
A tract that carries motor info from the primary cortex to the spinal cord. It will begin with a primary motor neuron at the primary motor cortex to the internal capsule, from their it goes to the brain stem where it passes through the midbrain and medulla, and finally from the medulla is where the pyramidal tract begins and from the medulla to just before the spinal cord the neuron will decusate.
8
New cards
Which neuron degenerate with Parkinson’s Disease?
The dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra degenerates, which causes a resting tremor, slowness of movements, and difficulty to intiatite movements. Levodopa helps regulates the level of dopamine which helps with alleviating the symptoms caused by parkinson’s disease.
9
New cards
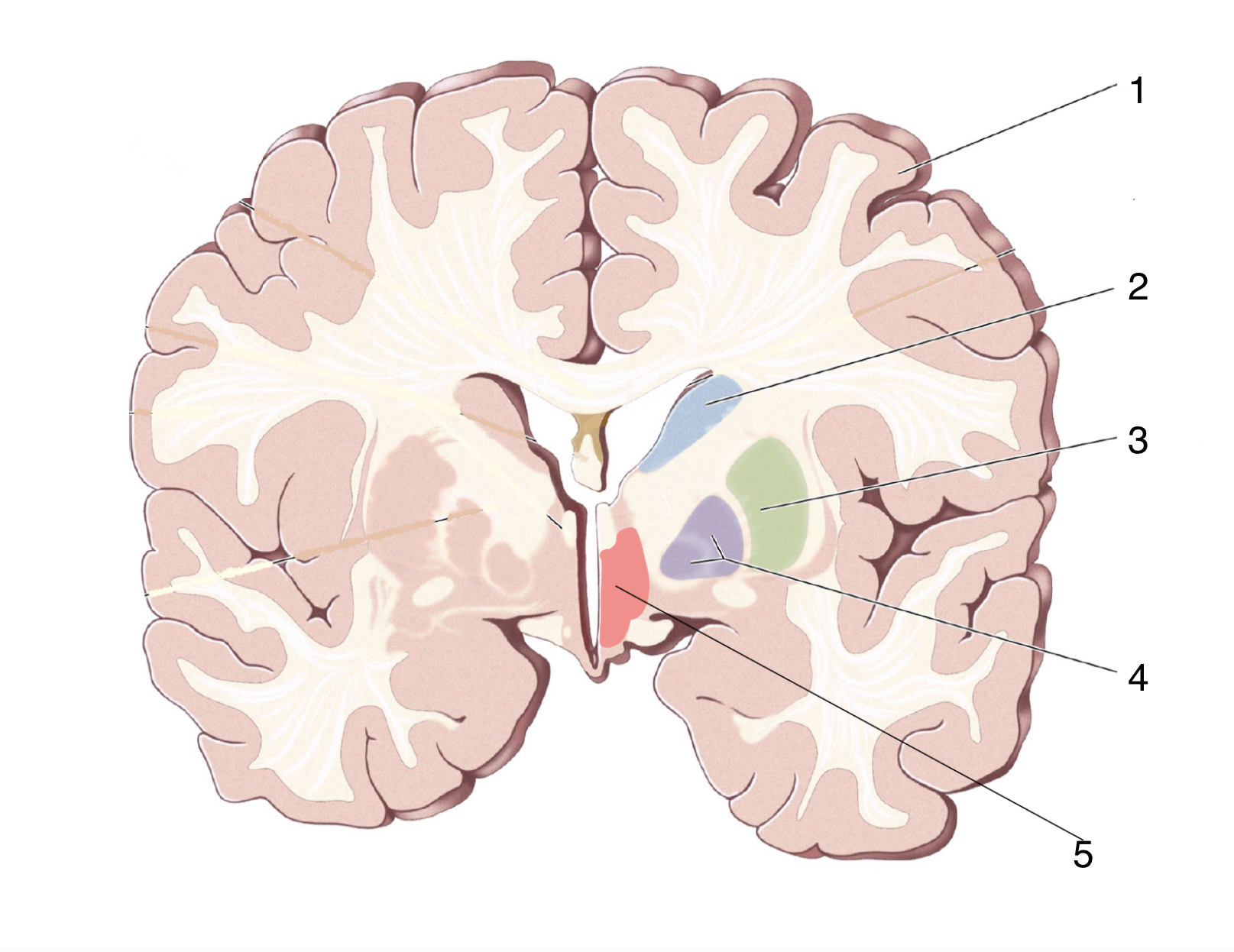
What is 1?
Cerebral Cortex
10
New cards
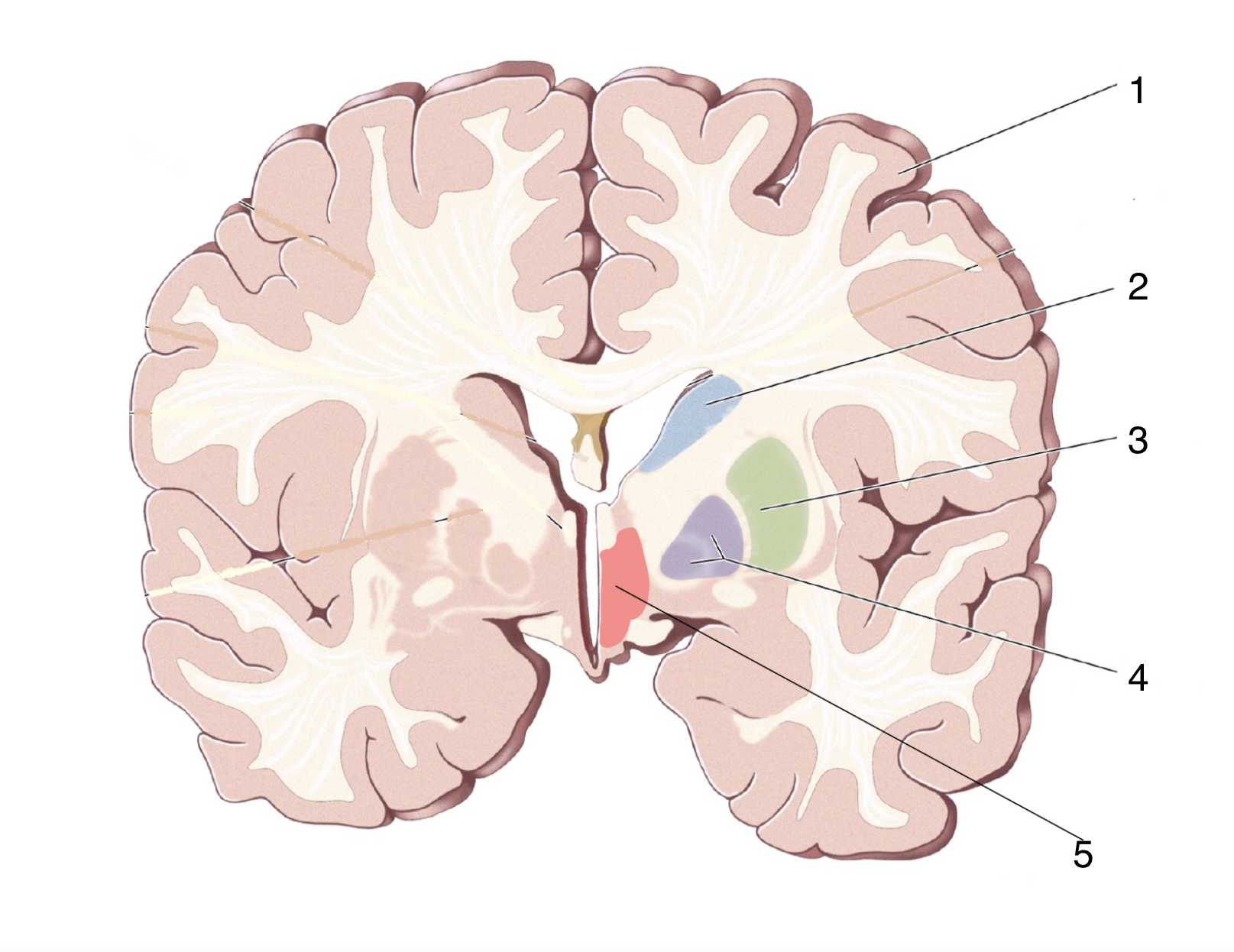
What is 2?
Caudate Nucleus
11
New cards
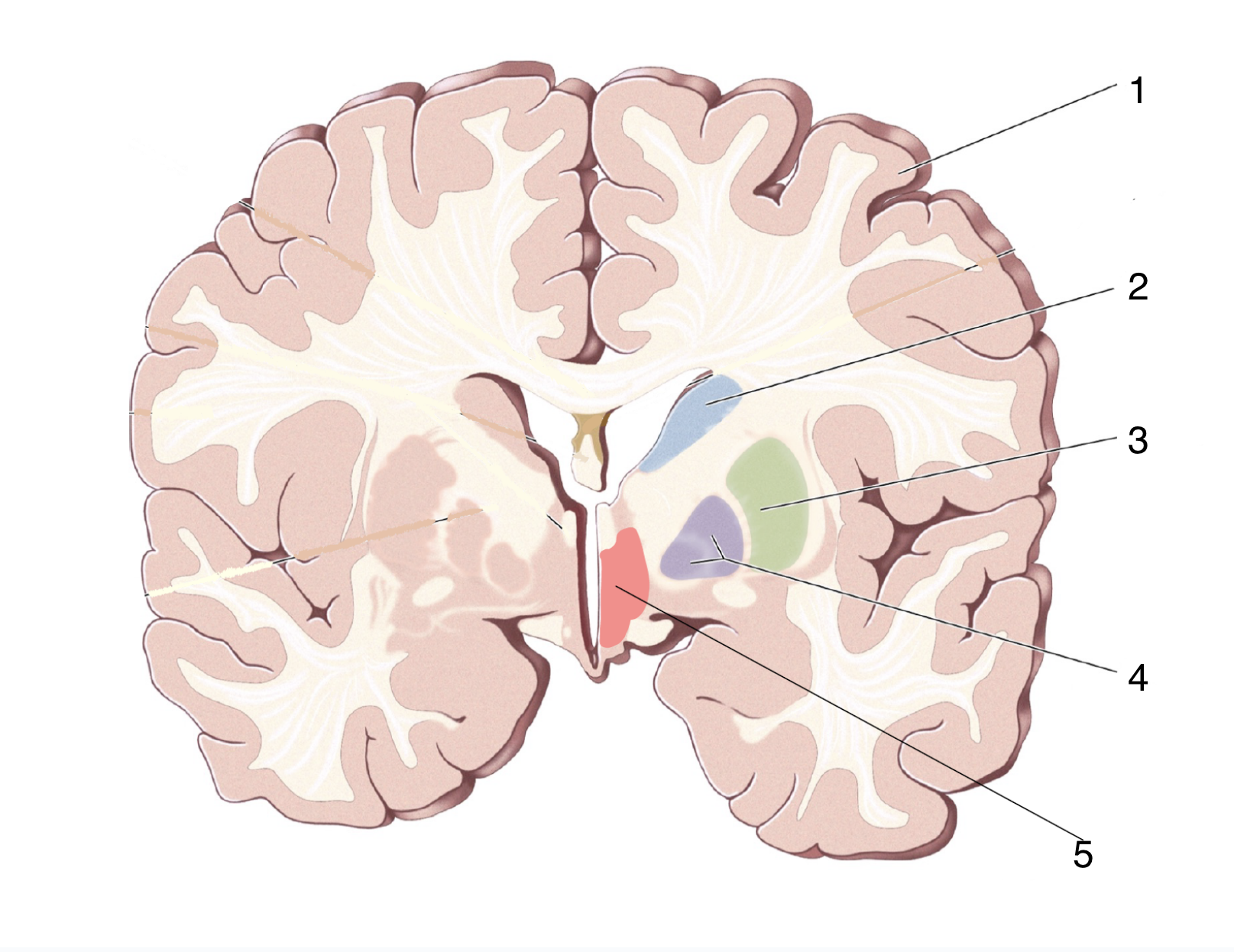
What is 3?
Putamen
12
New cards
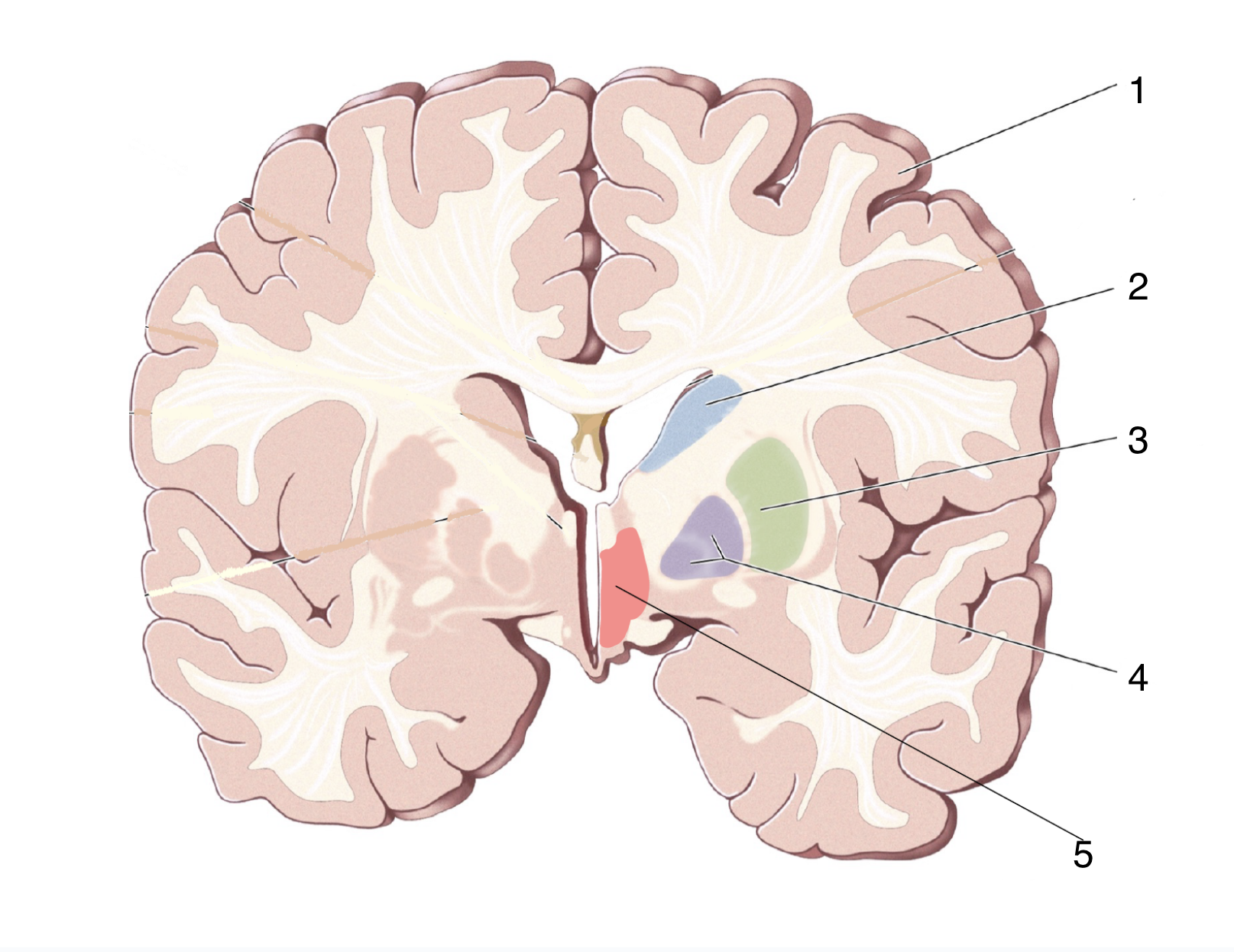
What is 4?
Globus Pallidus
13
New cards
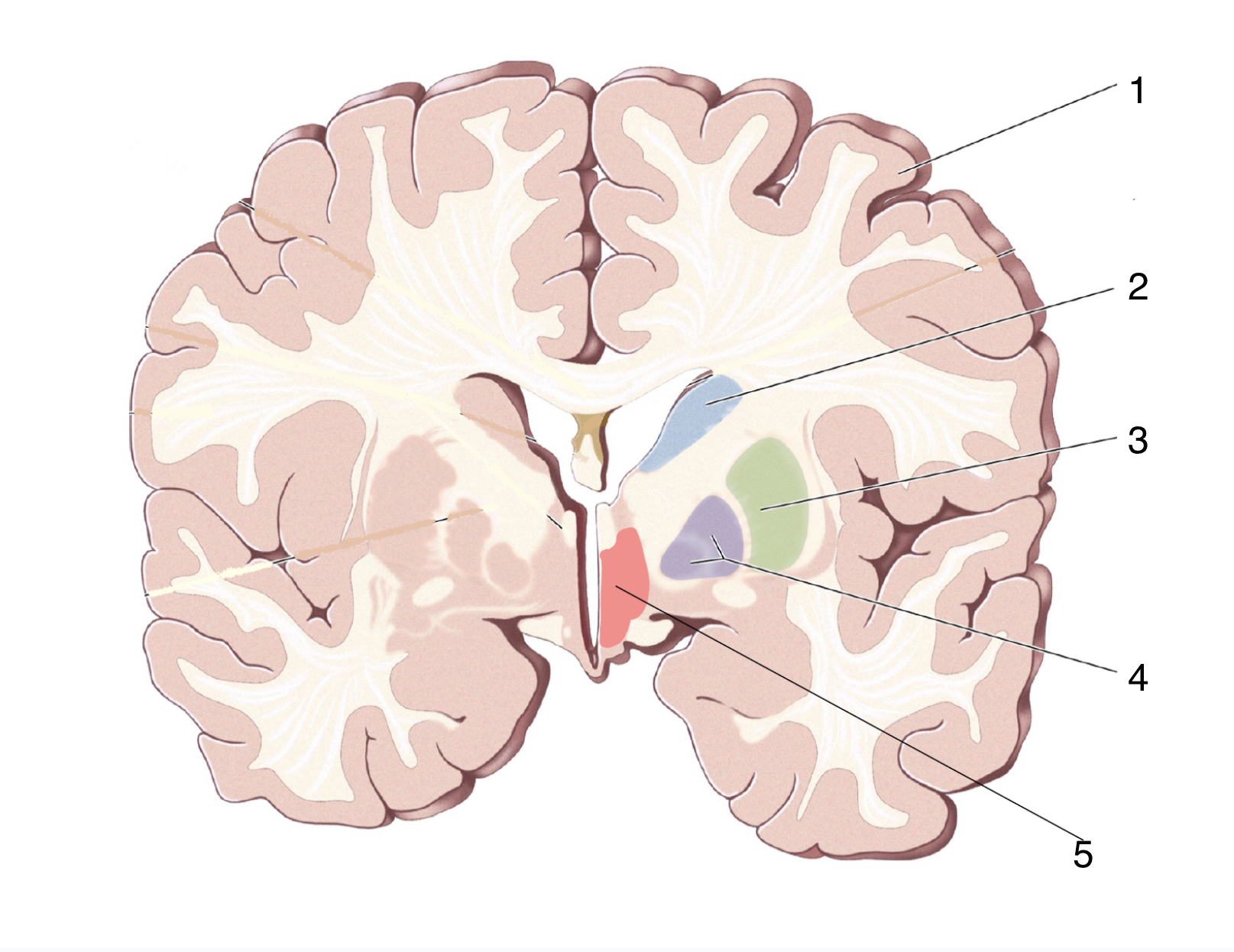
What is 5?
Thalamus
14
New cards
What is striatum?
Consists of the caudate nucleus and putamen.
15
New cards
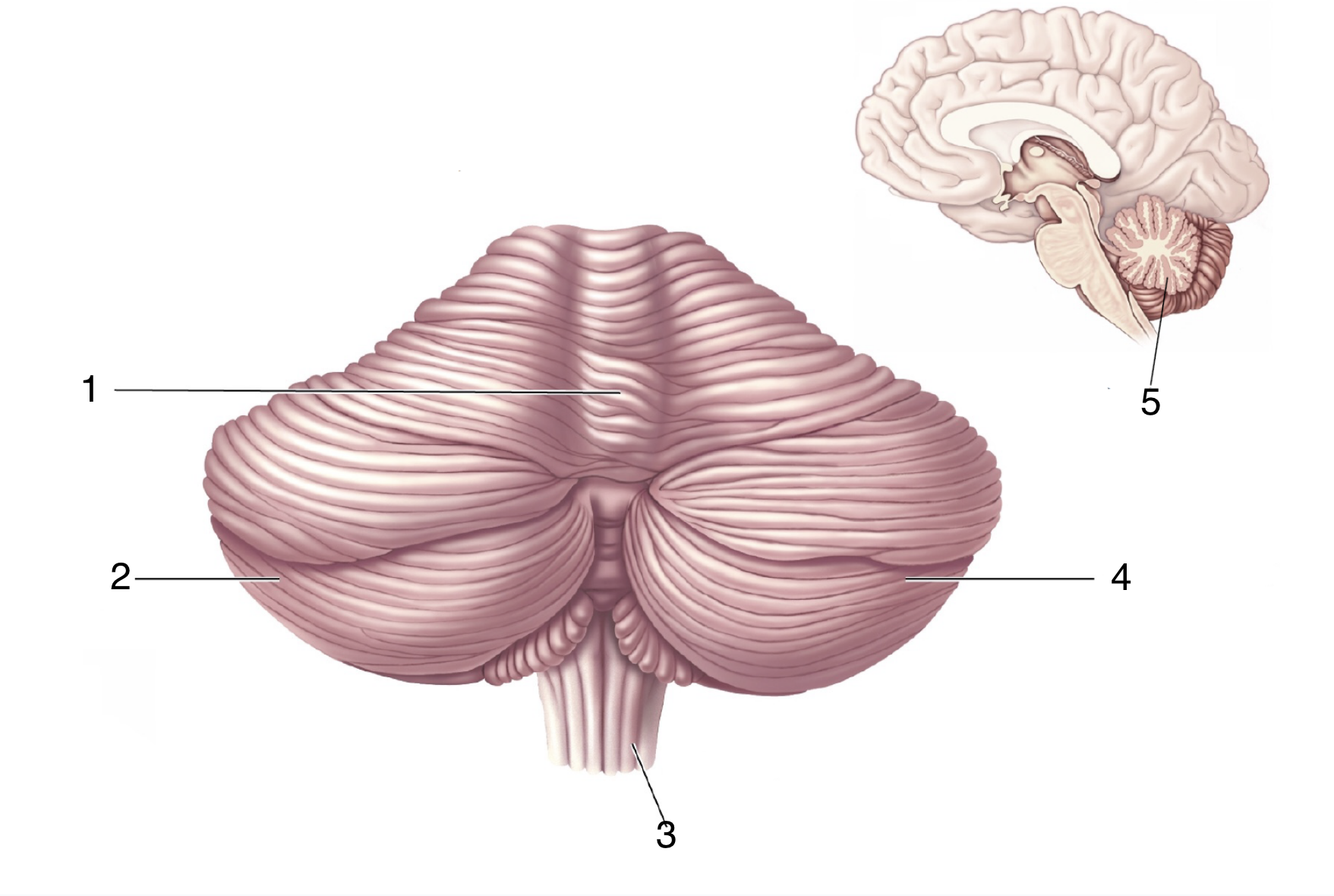
What is 1?
Vermis
16
New cards
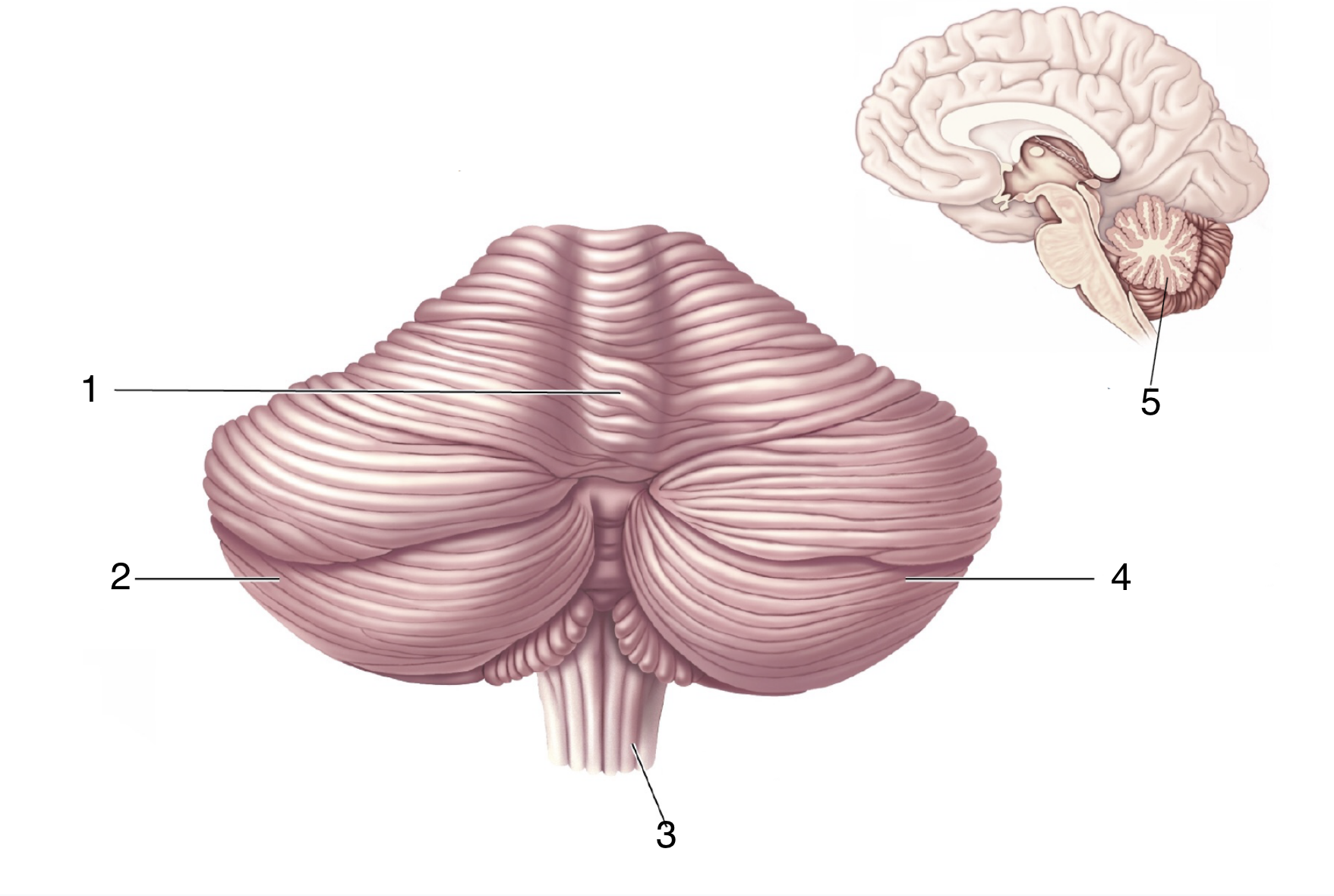
What is 2?
Left cerebellar hemisphere
17
New cards
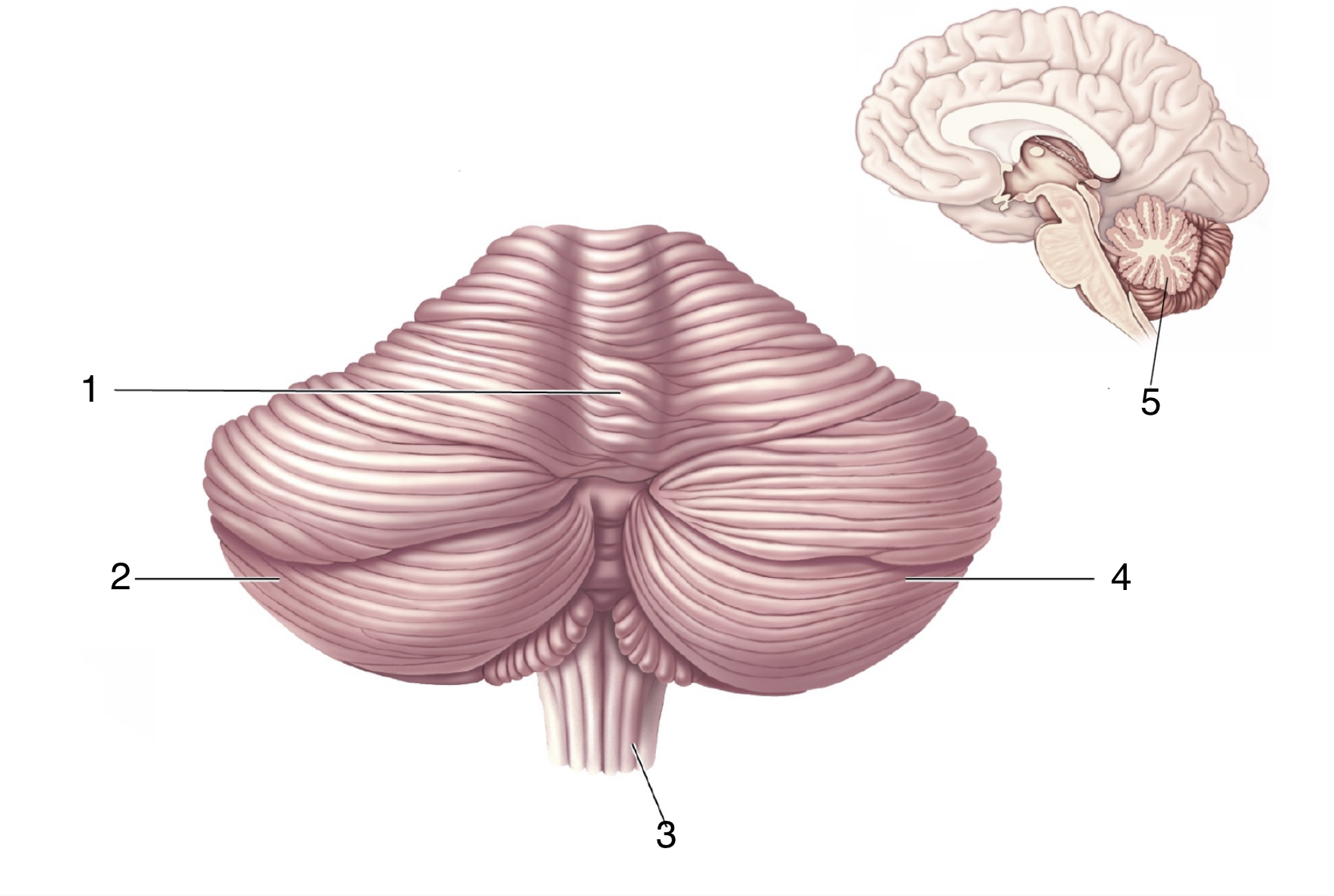
What is 3?
spinal cord
18
New cards
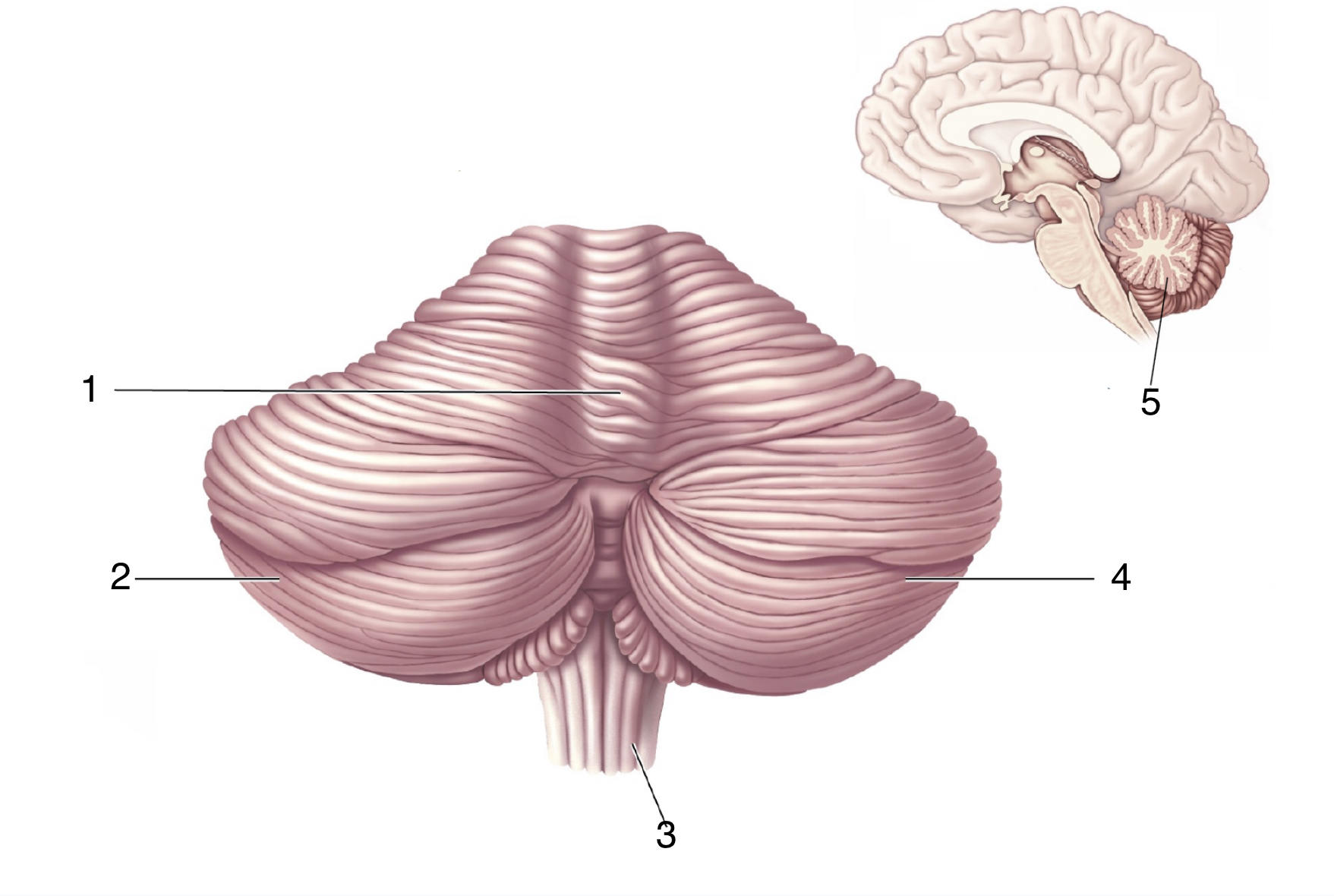
What is 4?
right cerebellar hemisphere
19
New cards
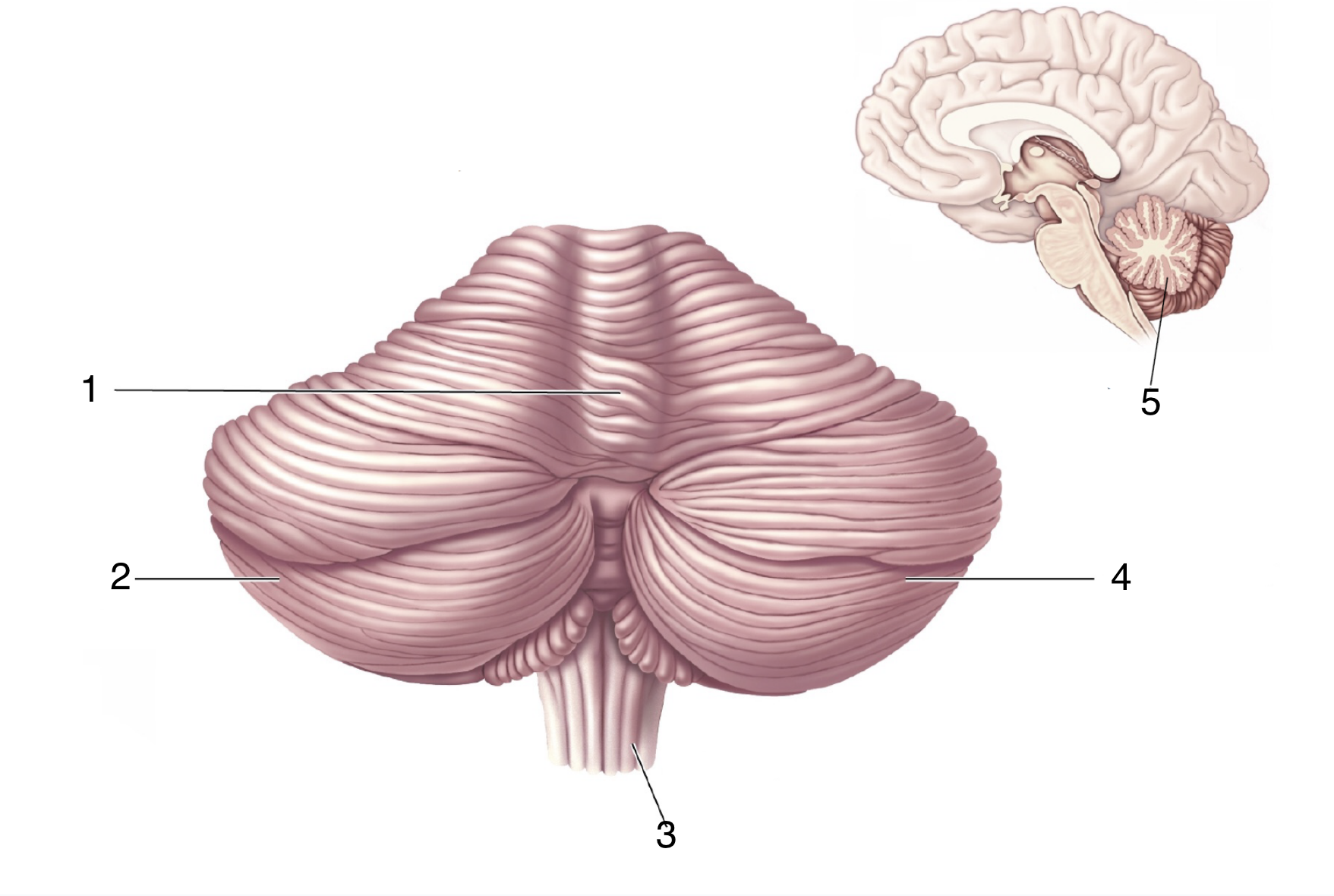
What is 5?
Cerebellum
20
New cards
Decussation
Information crosses by intersections of pathways.
21
New cards
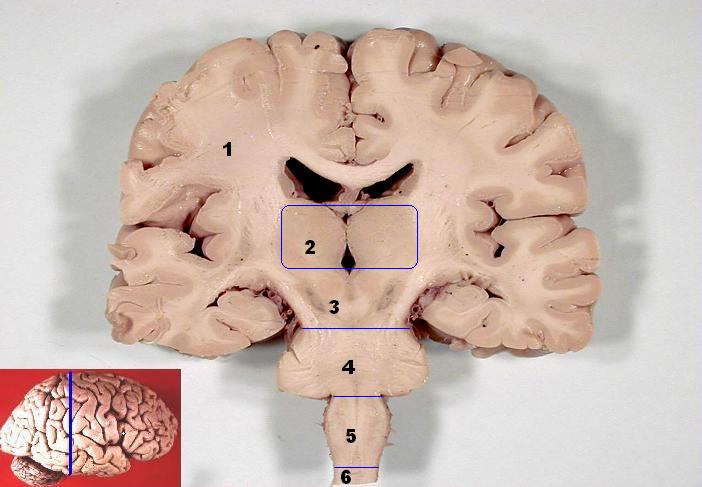
Thalamus
Works as a relay which is located within the brain above the cerebral cortex and brainstem.
22
New cards
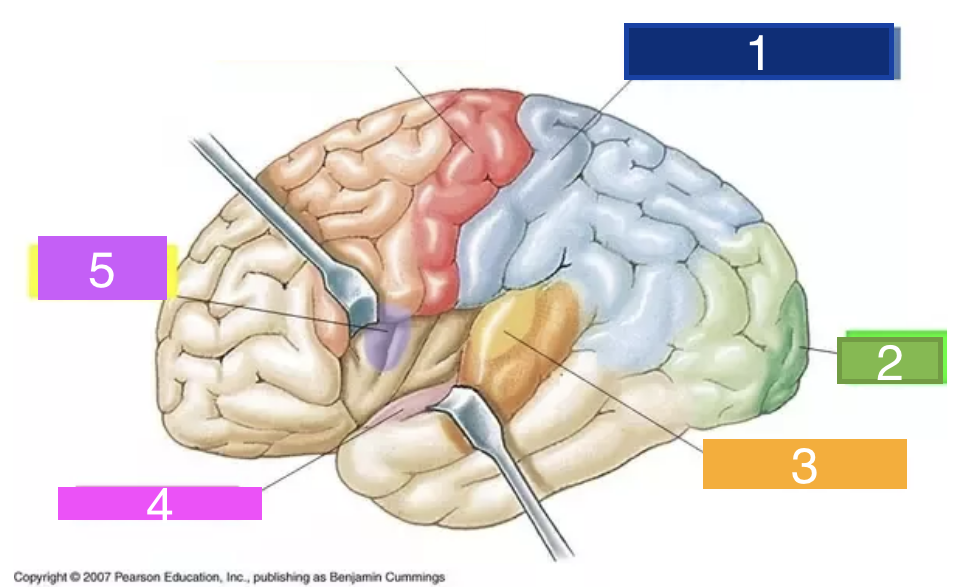
What is 1?
Primary sensory cortex
23
New cards
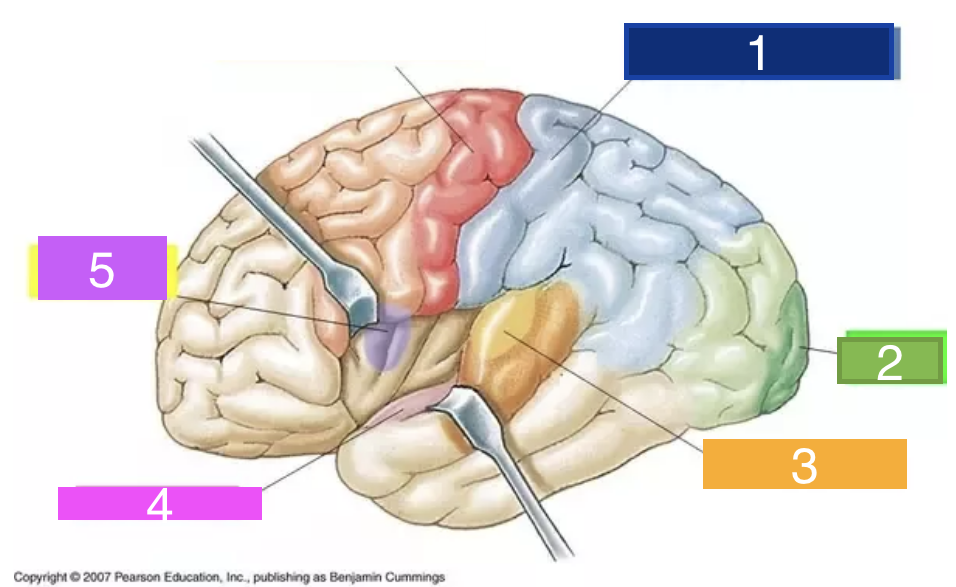
What is 2?
visual cortex
24
New cards
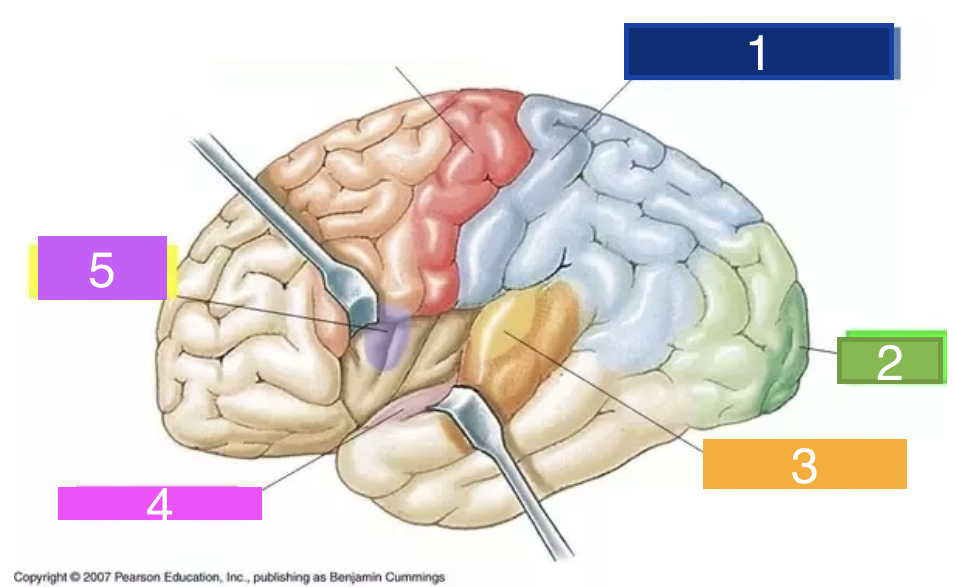
What is 3?
auditory cortex
25
New cards
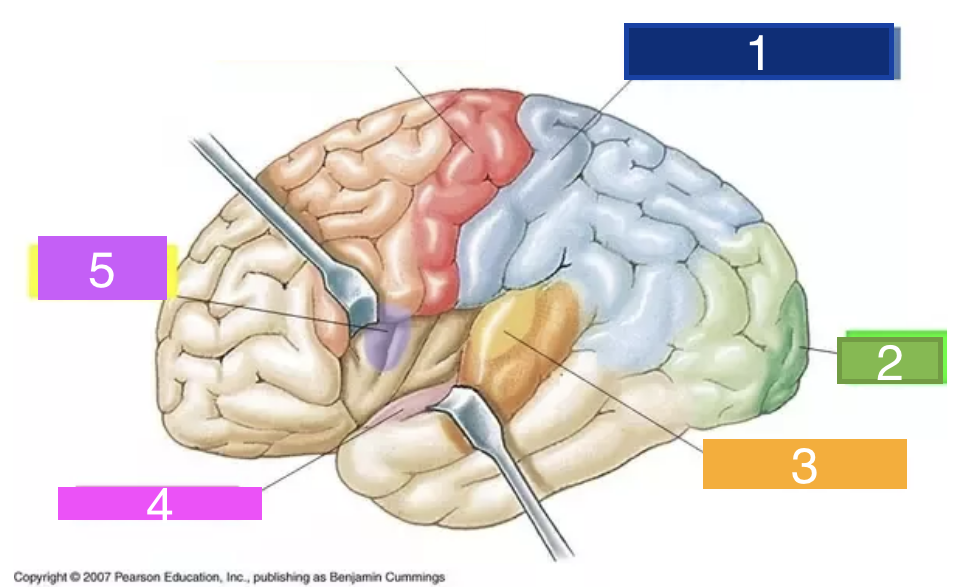
What is 4?
olfactory cortex
26
New cards
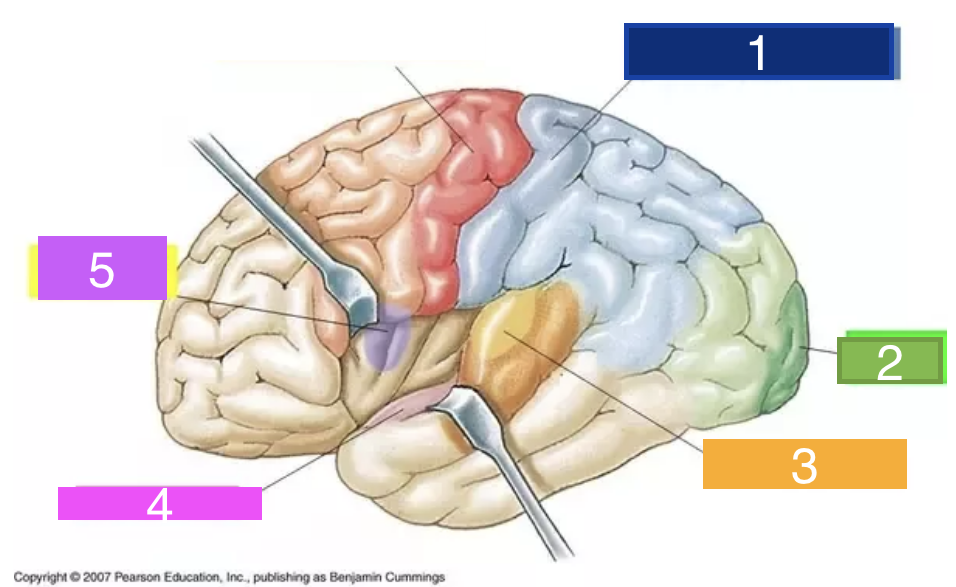
What is 5?
gustatory cortex
27
New cards
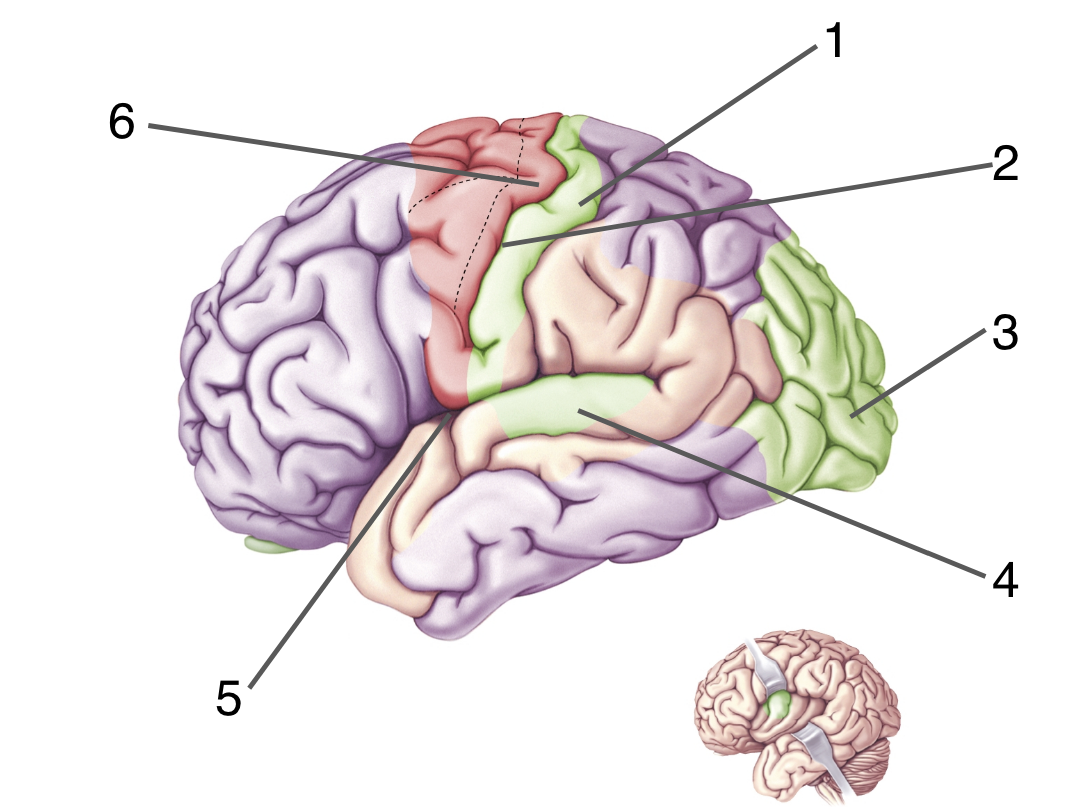
What is 6?
Primary motor cortex.
28
New cards
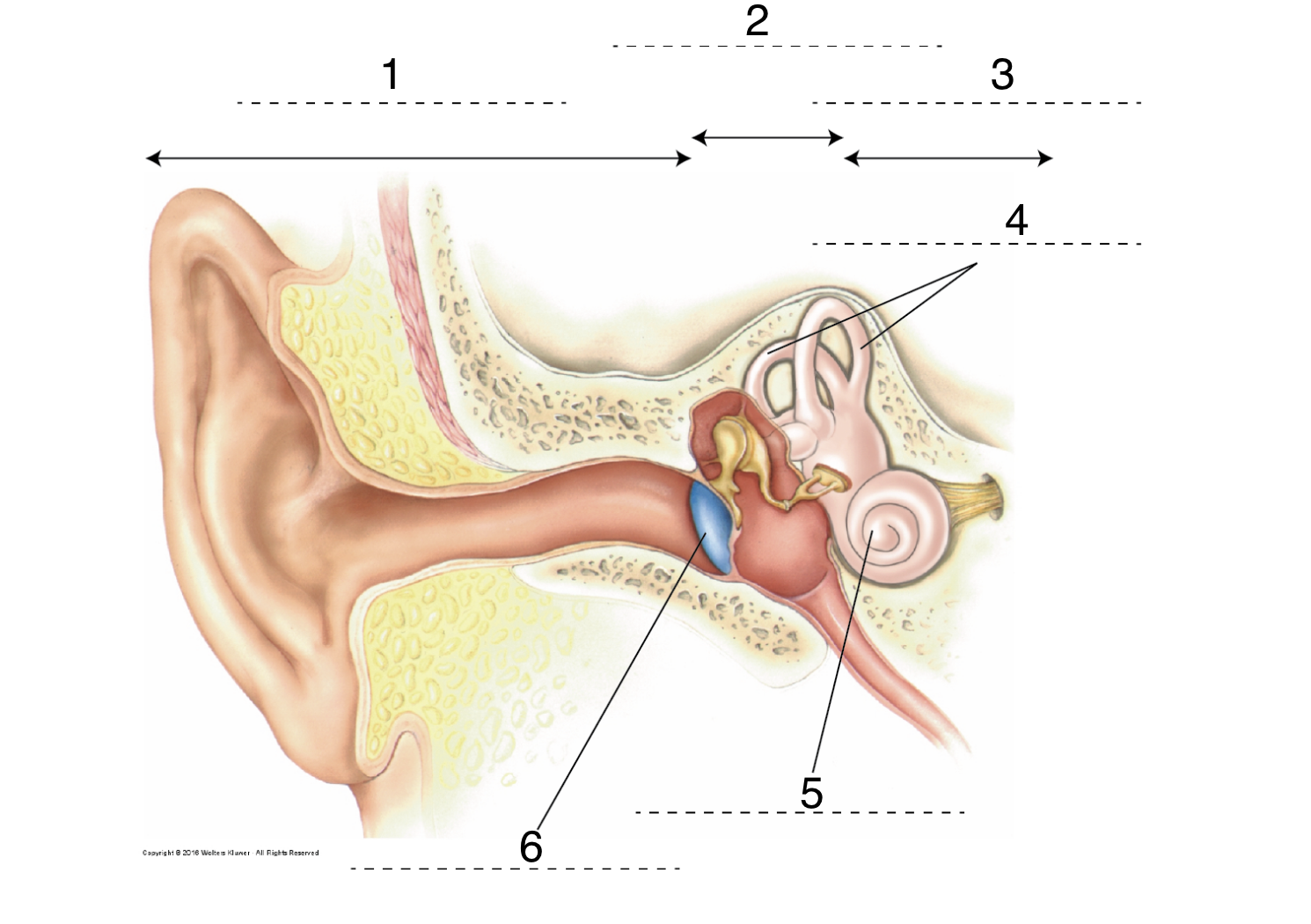
What is 1?
Outer ear
29
New cards
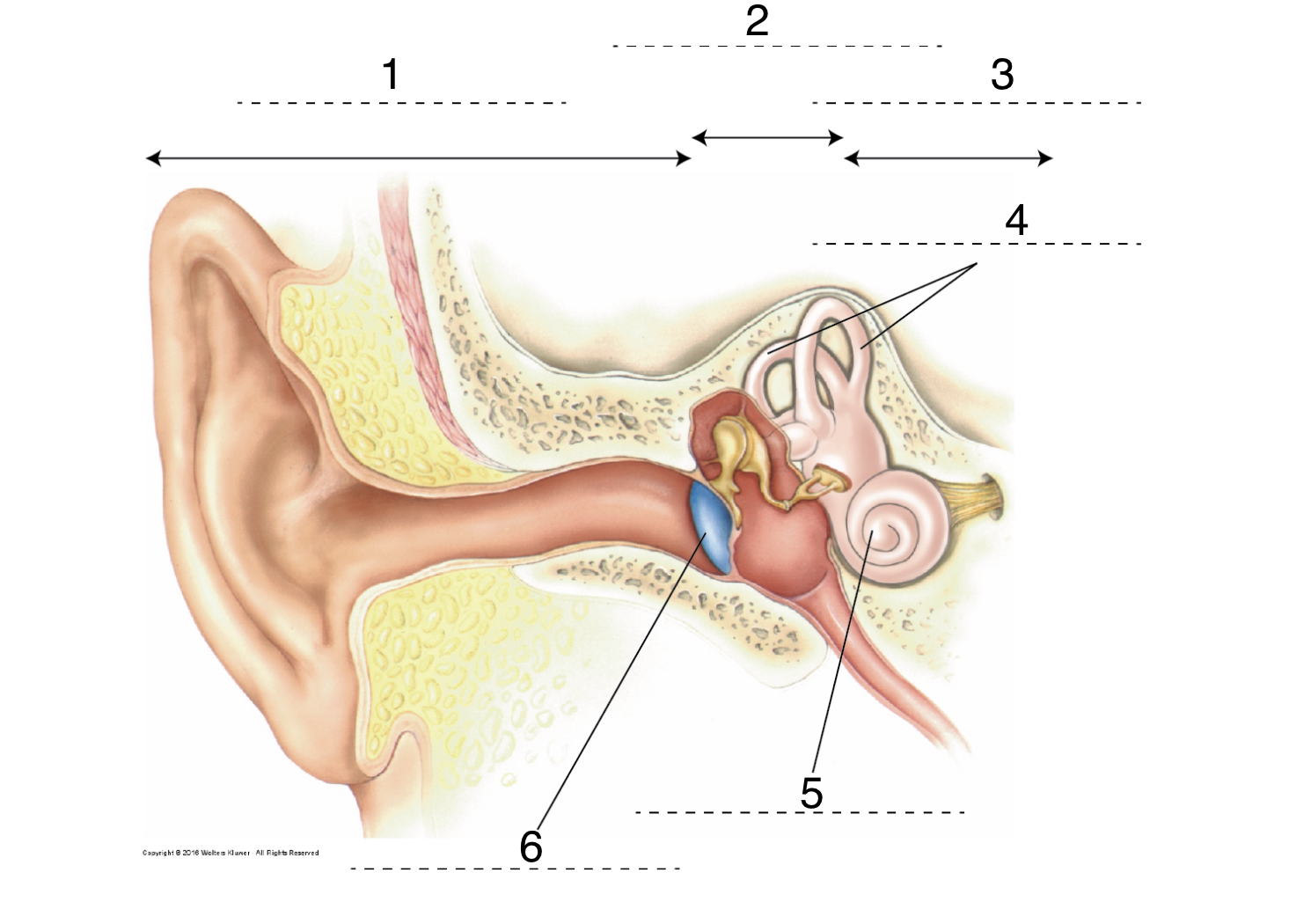
What is 2?
Middle ear
30
New cards
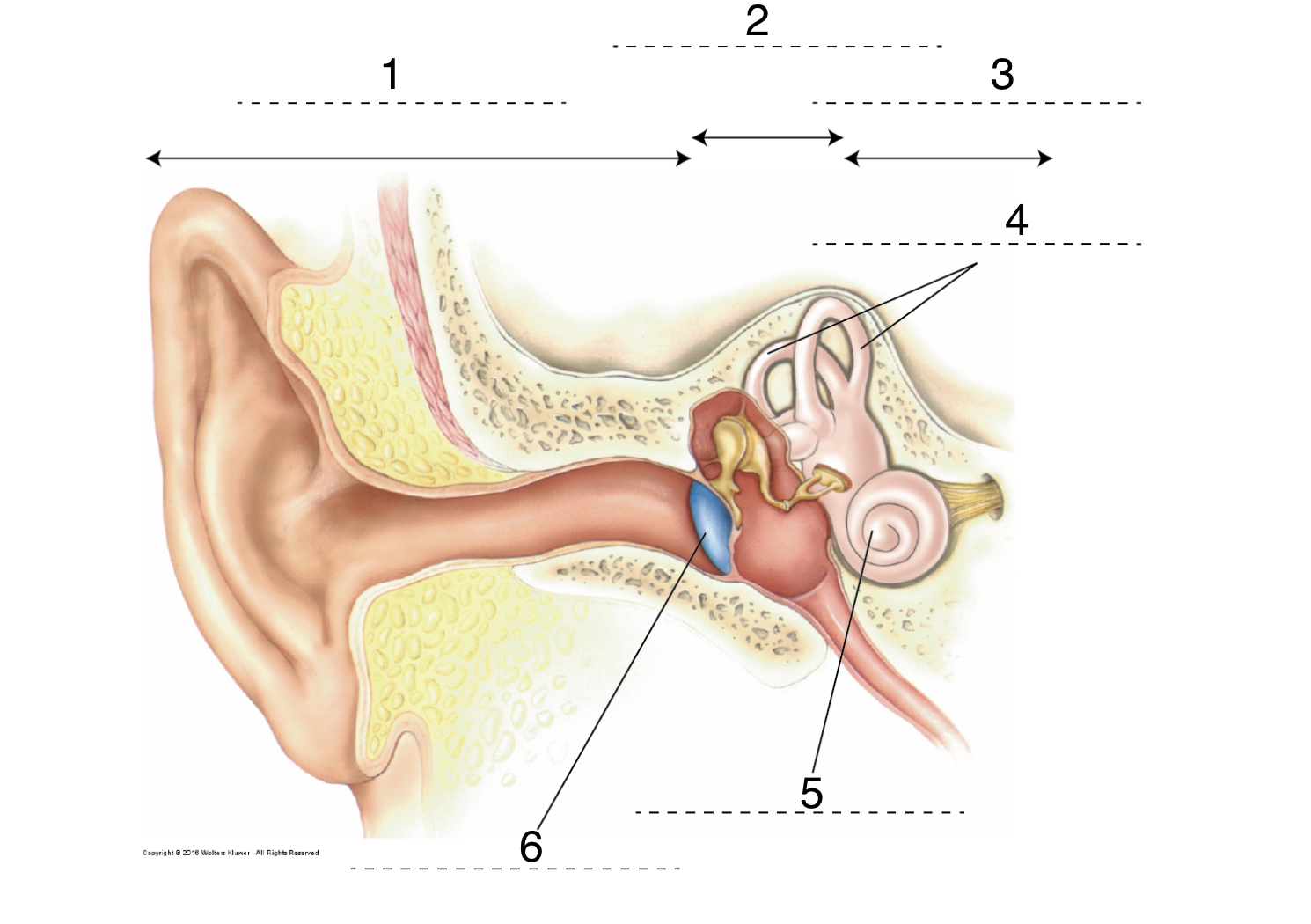
What is 3?
inner ear
31
New cards
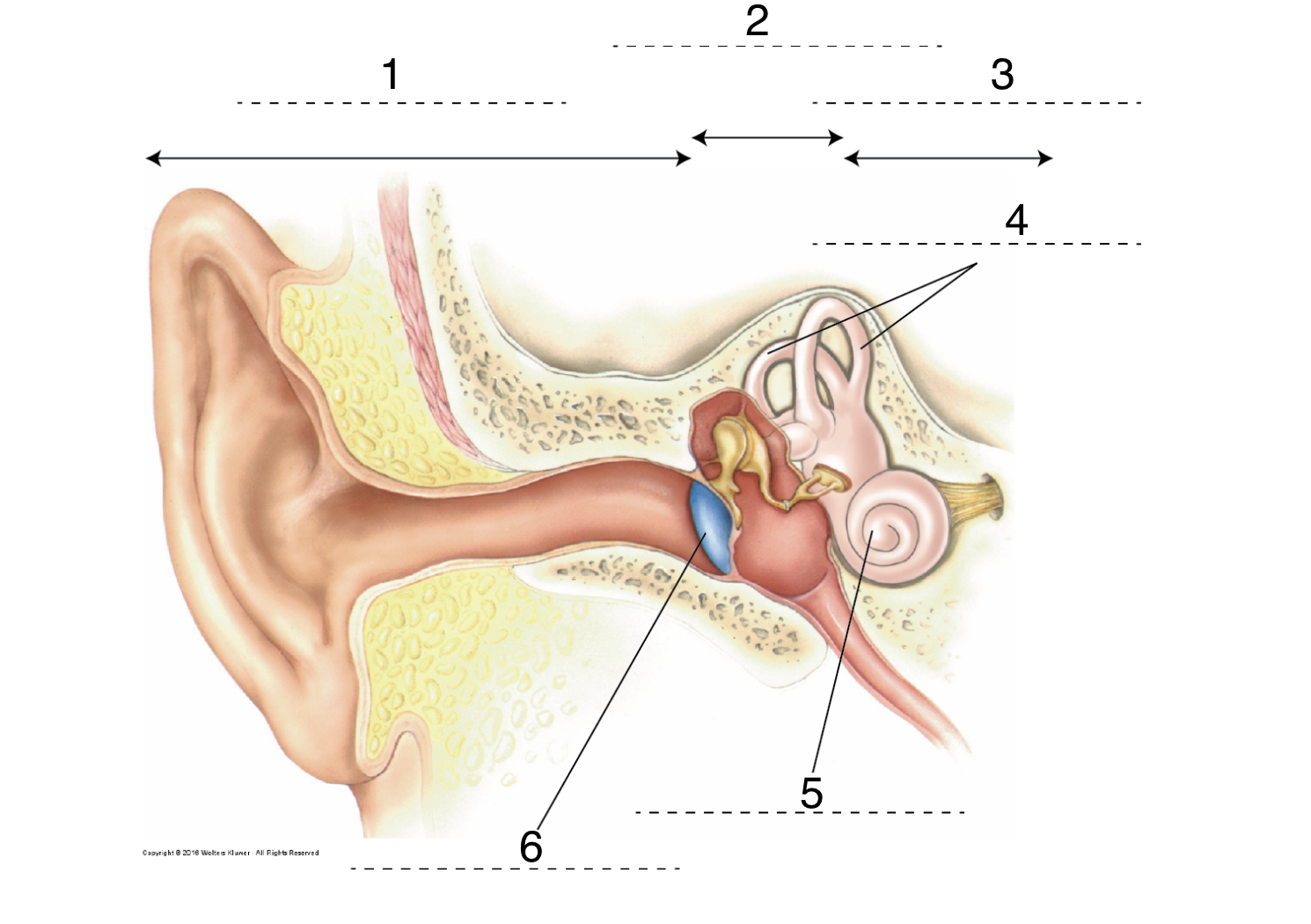
What is 4?
semicircular canals
32
New cards
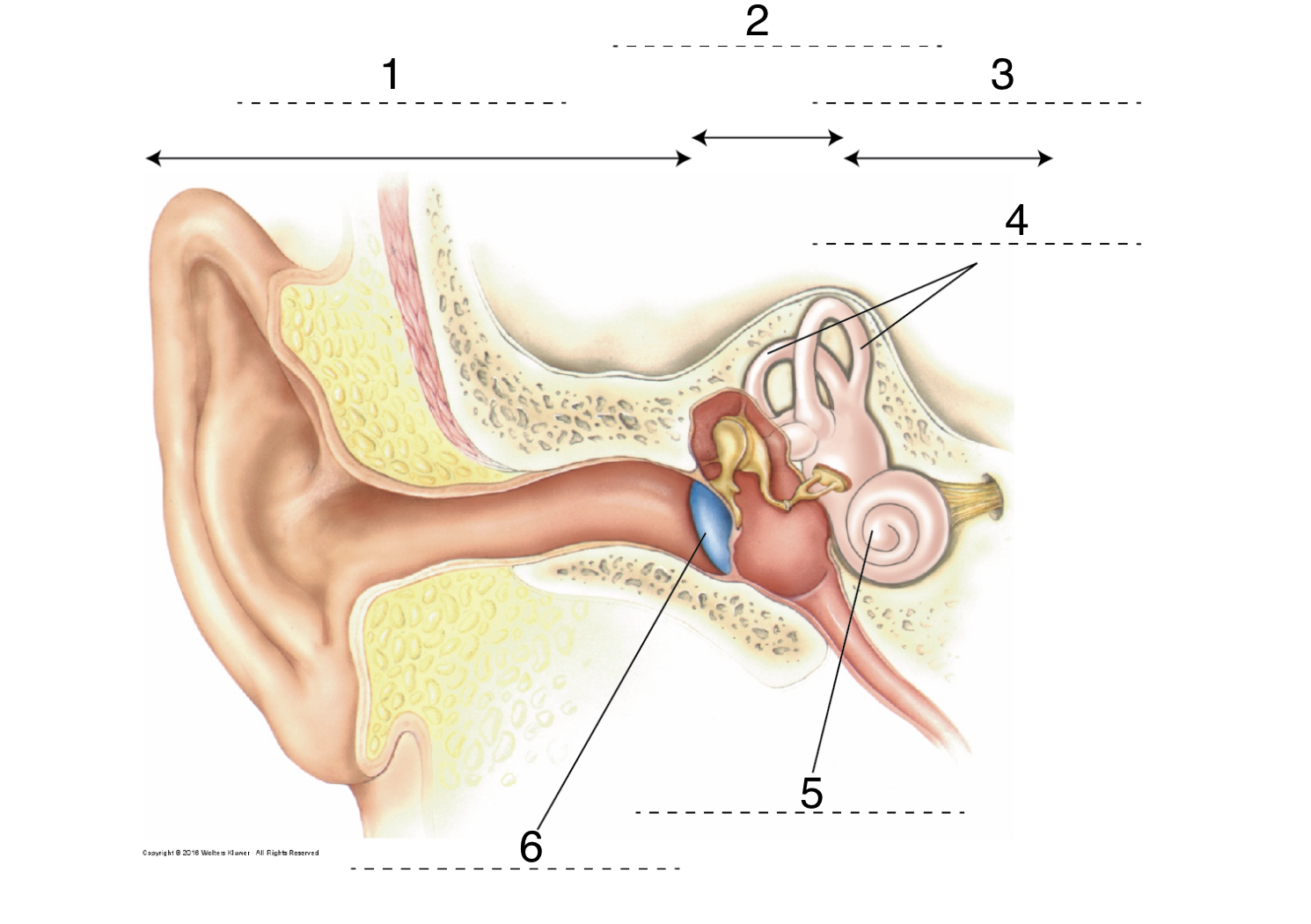
What is 5?
cochlea
33
New cards
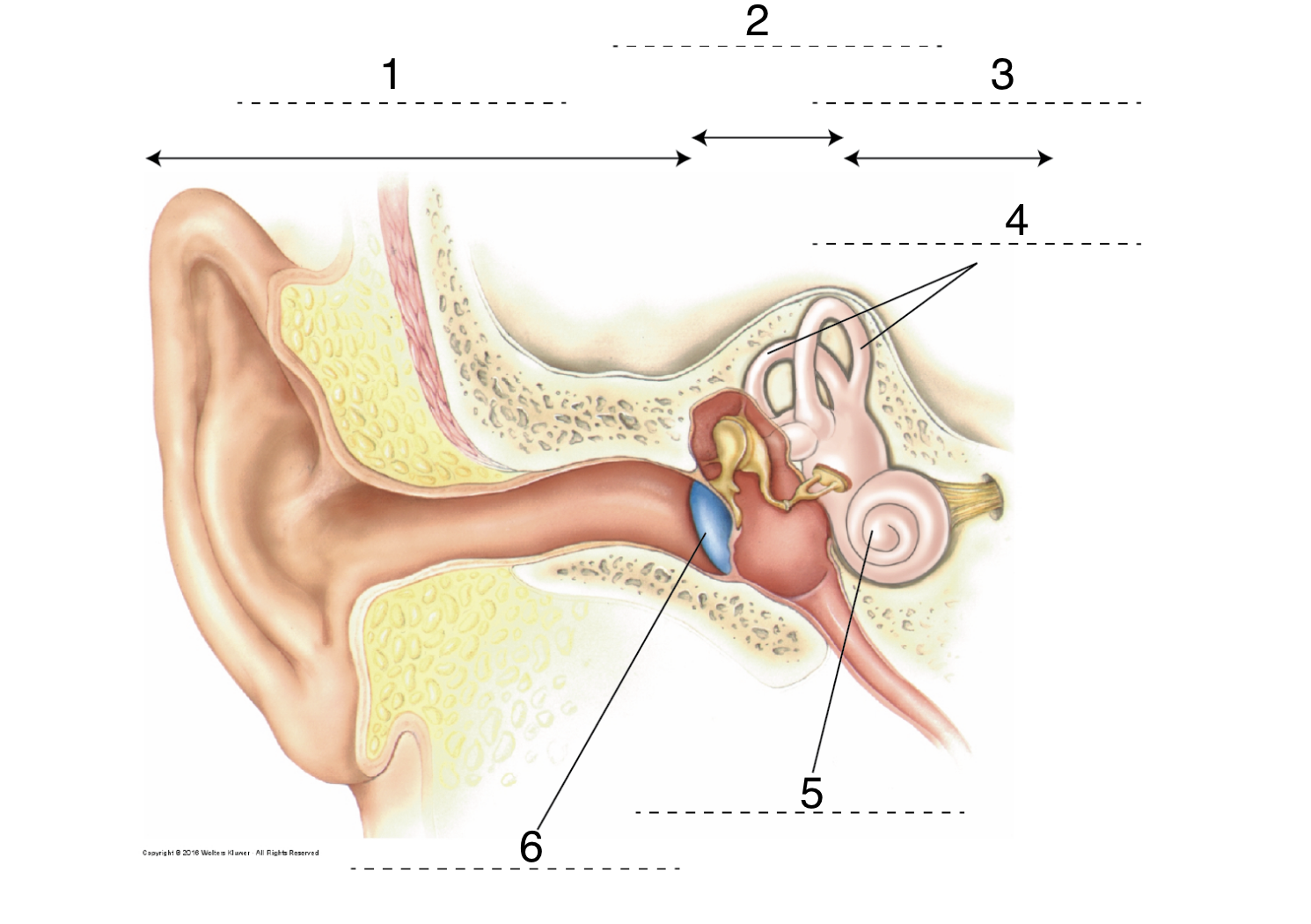
What is 6?
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
34
New cards
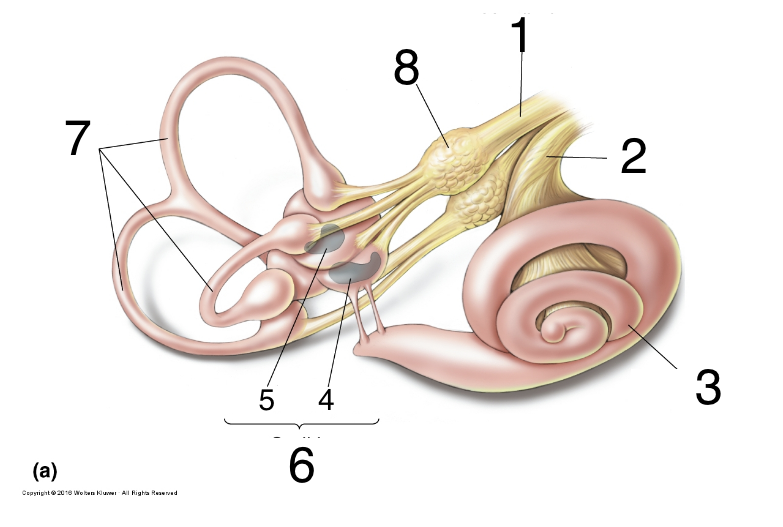
What is 1?
vestibular nerve
35
New cards
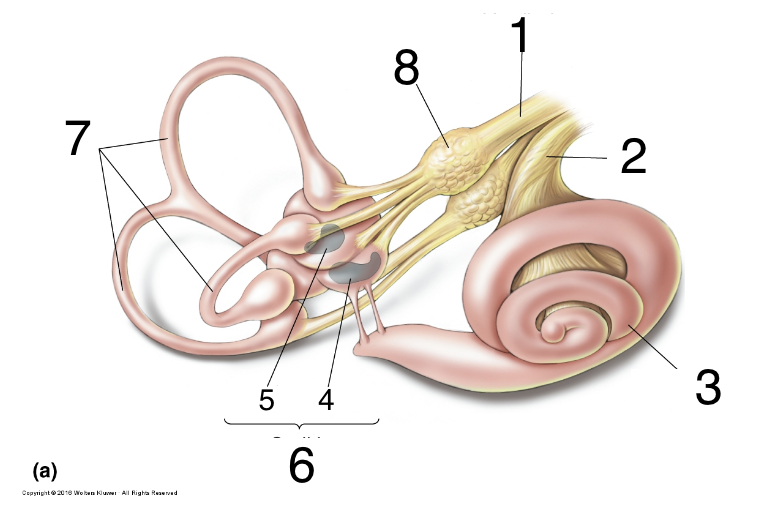
What is 2?
auditory nerve
36
New cards
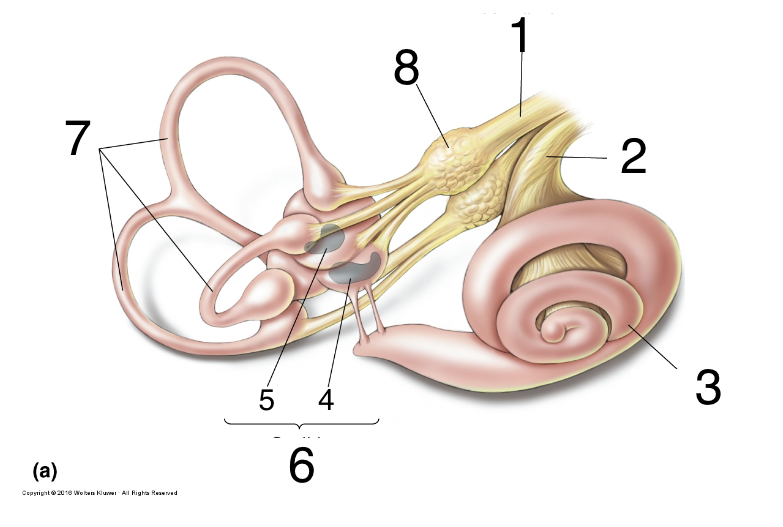
What is 3?
cochlea
37
New cards
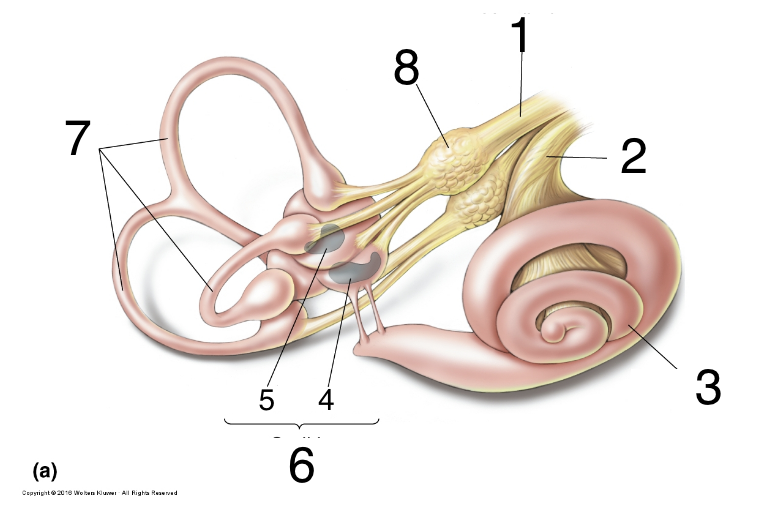
What is 4?
saccules
38
New cards
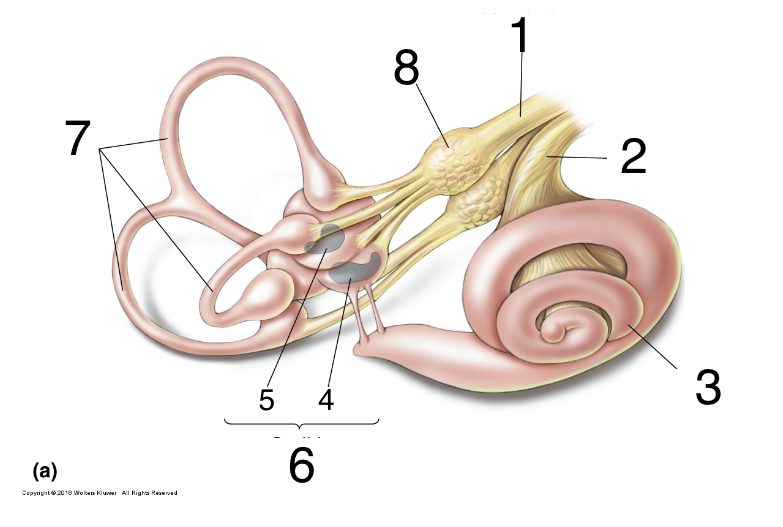
what is 5?
utricle
39
New cards
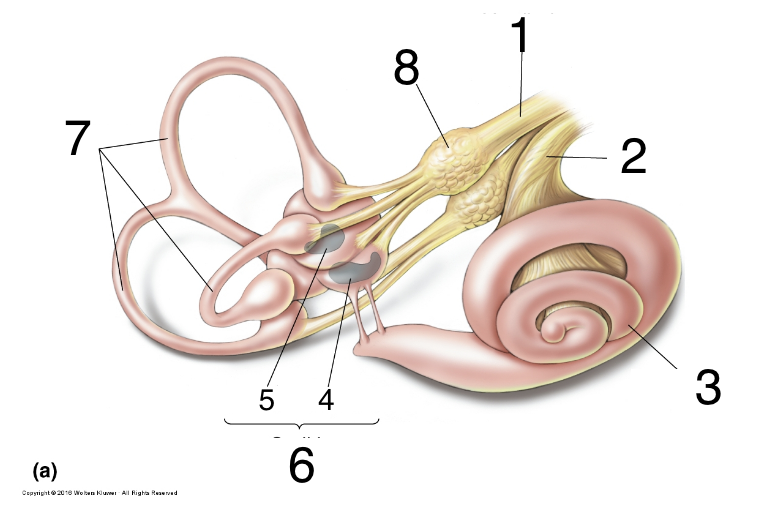
What is 6?
otolith organs
40
New cards
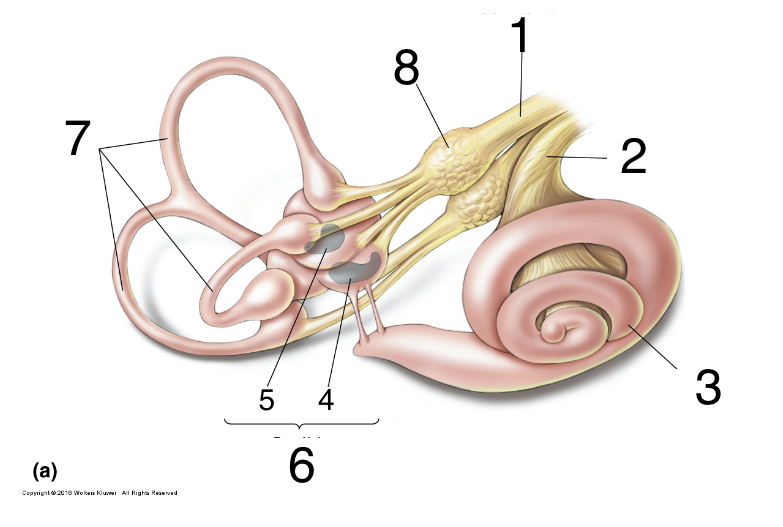
What is 7?
semicircular canals
41
New cards
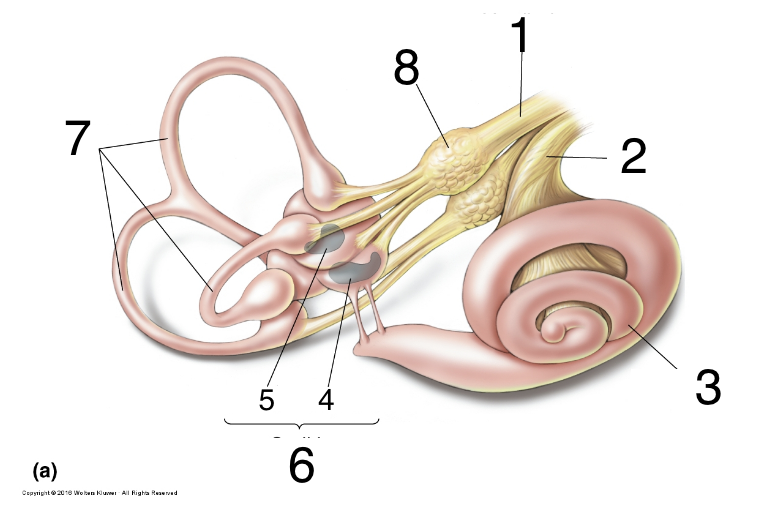
What is 8?
scarpa’s ganglion
42
New cards
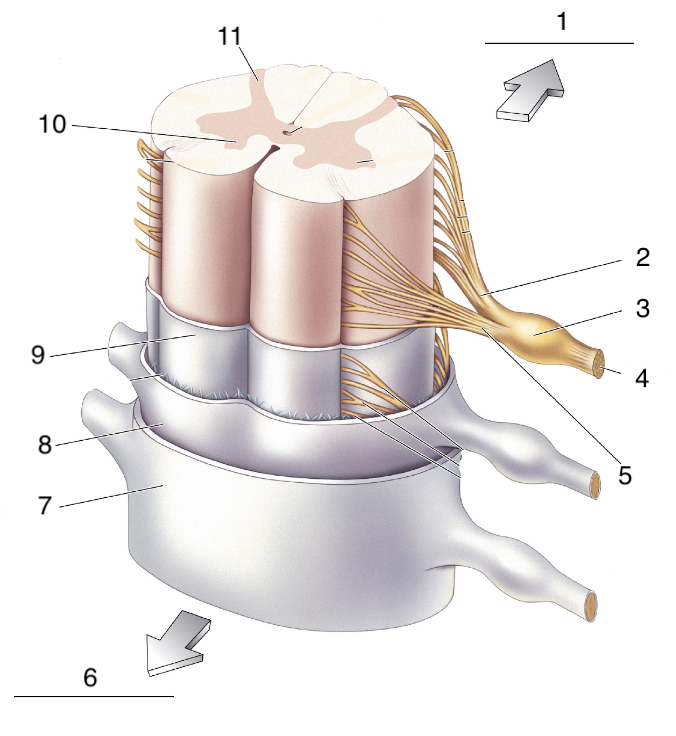
What is 1?
Dorsal
43
New cards
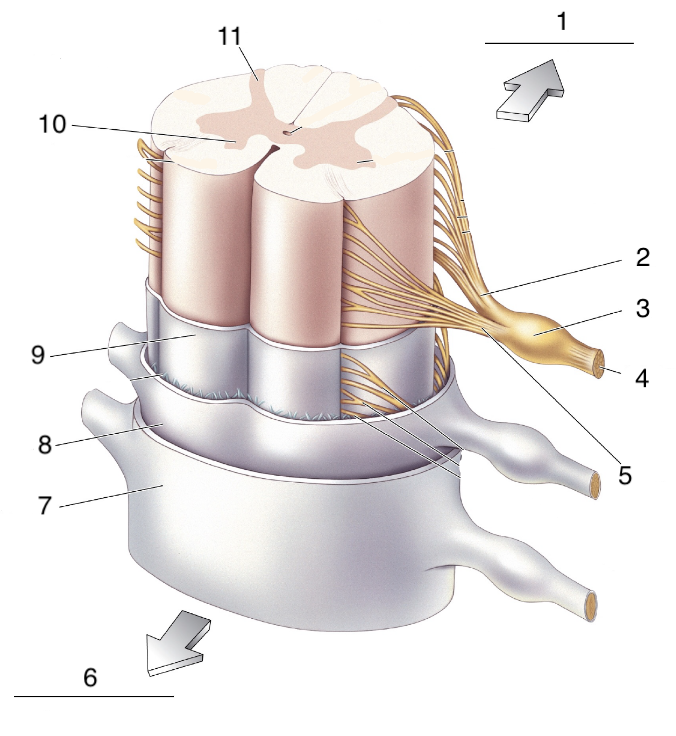
What is 2?
Dorsal roots
44
New cards
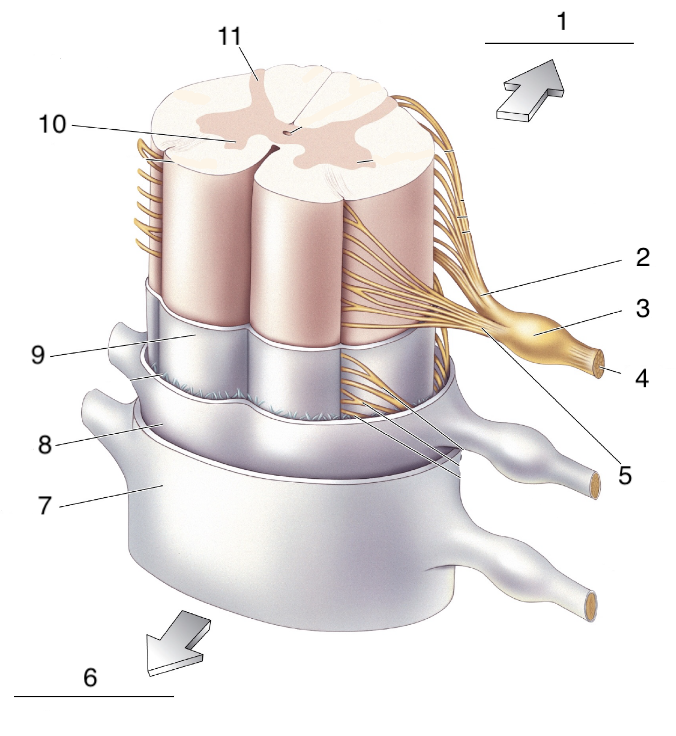
What is 3?
Dorsal root ganglion
45
New cards
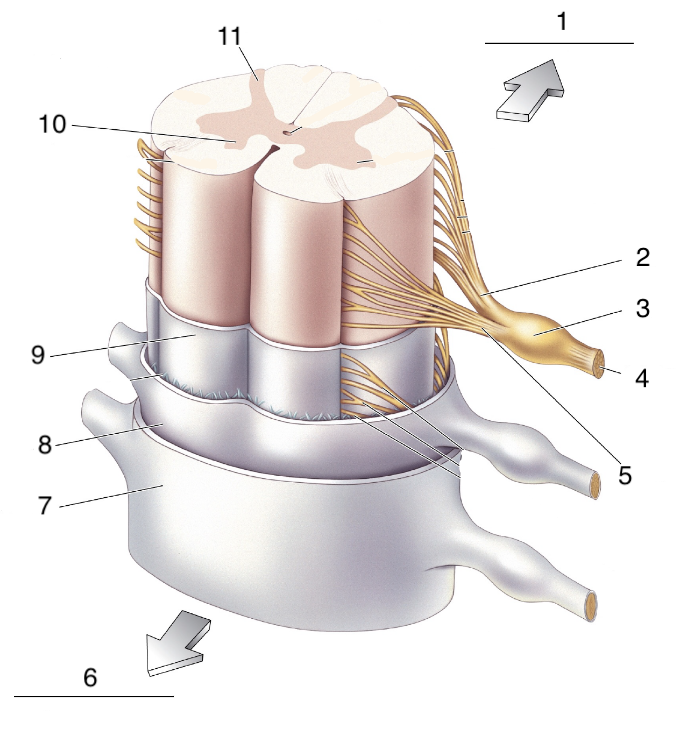
What is 4?
spinal nerve
46
New cards
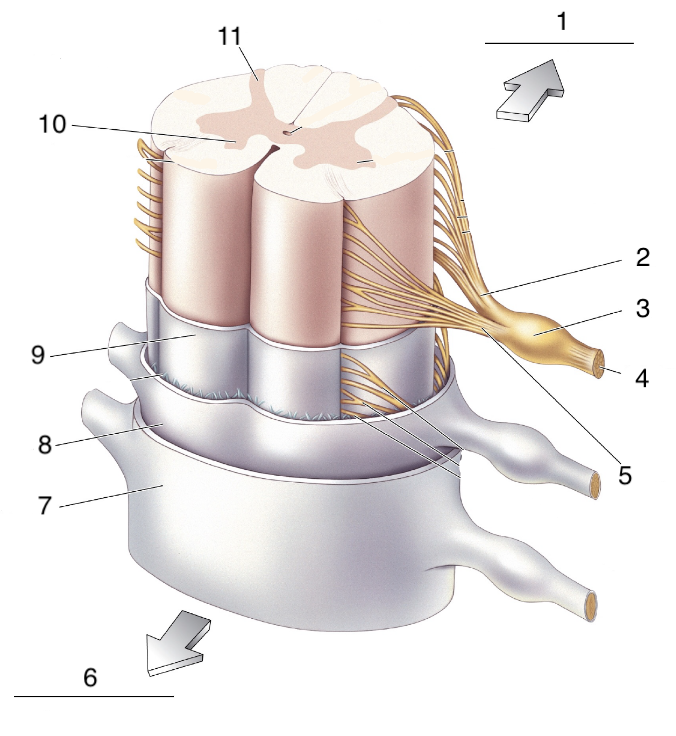
What is 5?
ventral root
47
New cards
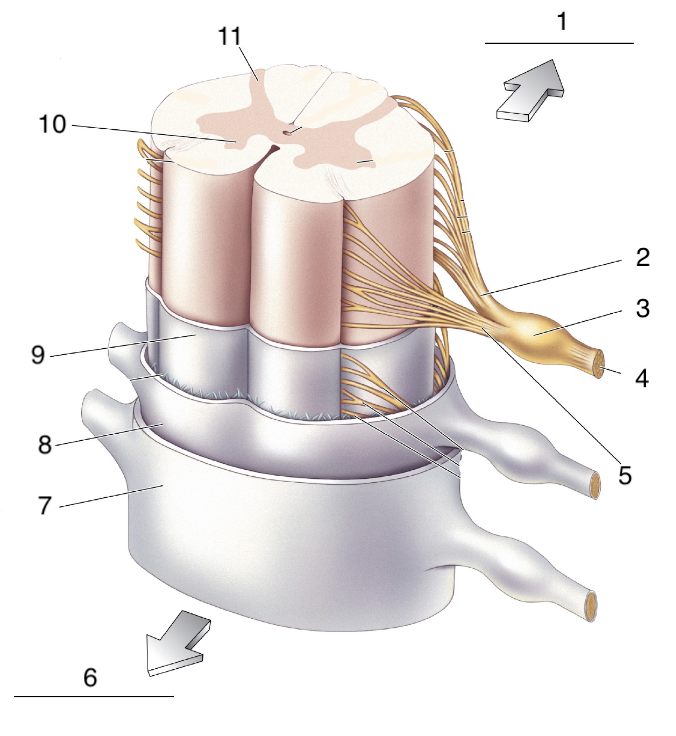
What is 6?
ventral
48
New cards
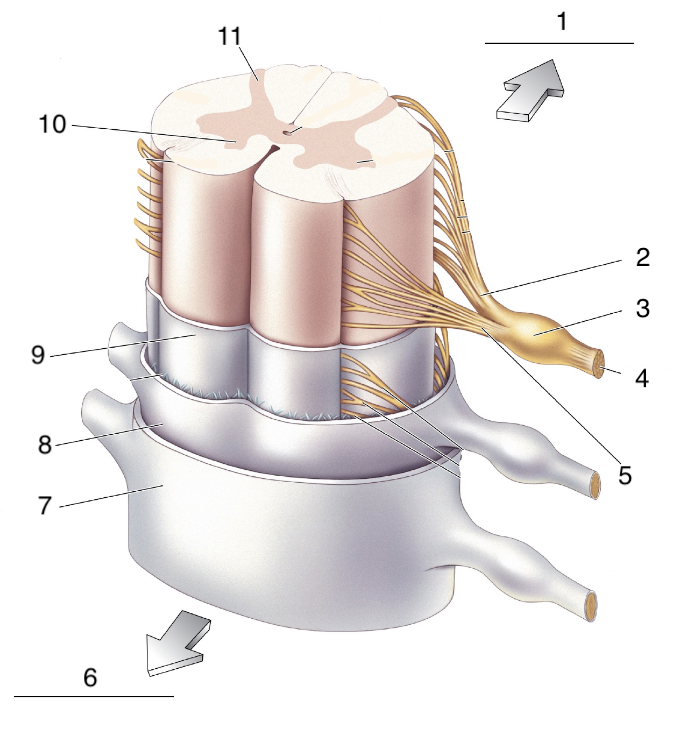
What is 7?
spinal dura mater
49
New cards
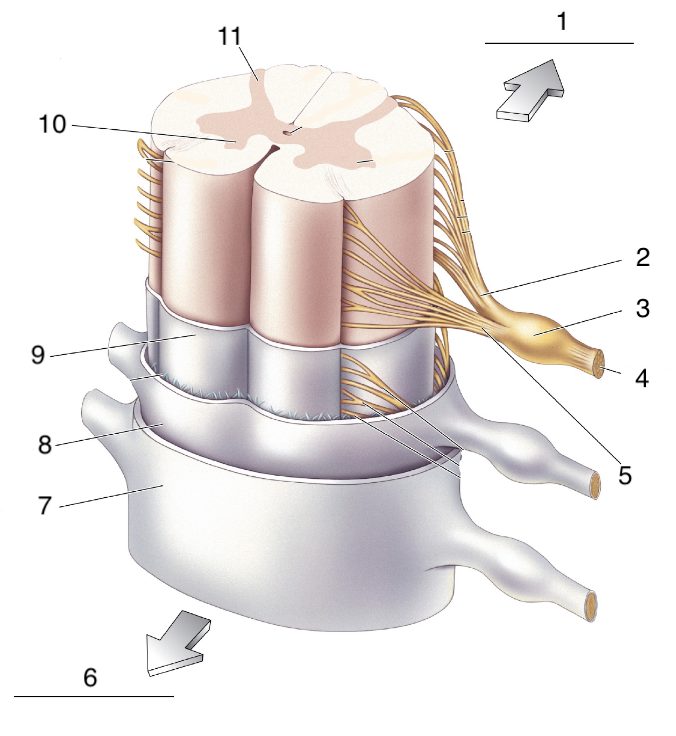
What is 8?
spinal arachnoid
50
New cards
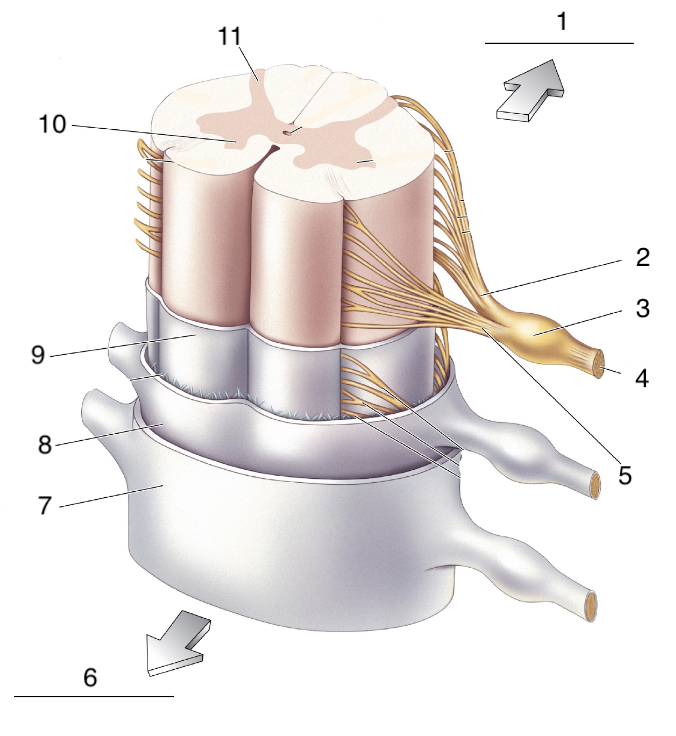
What is 9?
Spinal pia mater
51
New cards
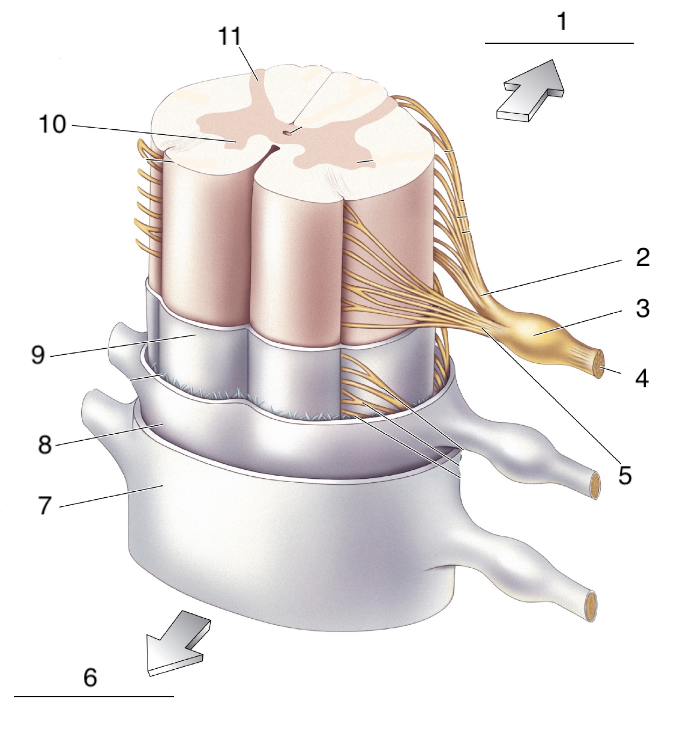
What is 10?
ventral horn
52
New cards
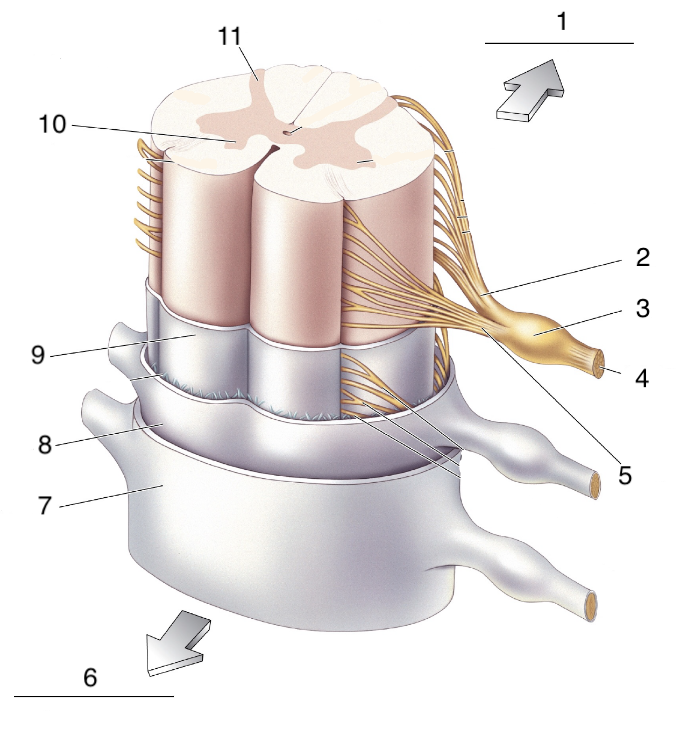
What is 11?
dorsal horn
53
New cards
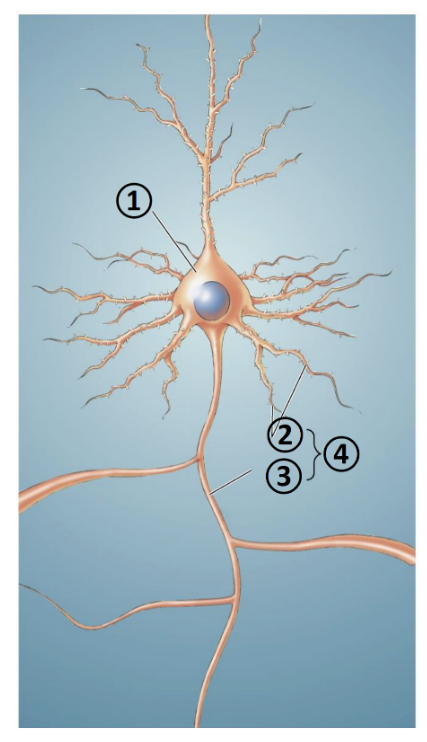
What is 1?
Soma
54
New cards
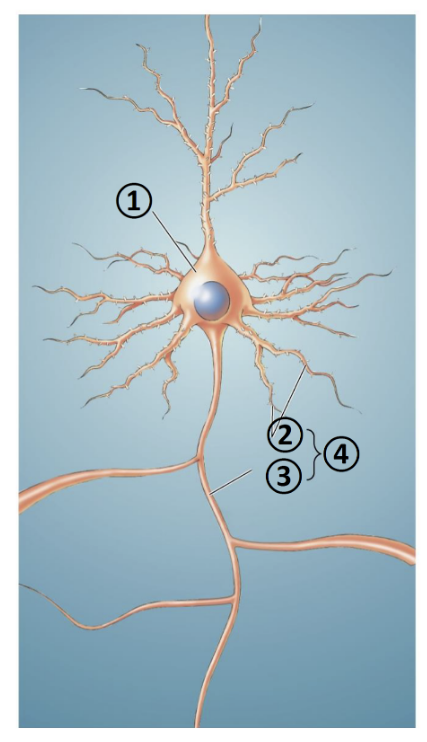
What is 2?
Dendrites
55
New cards
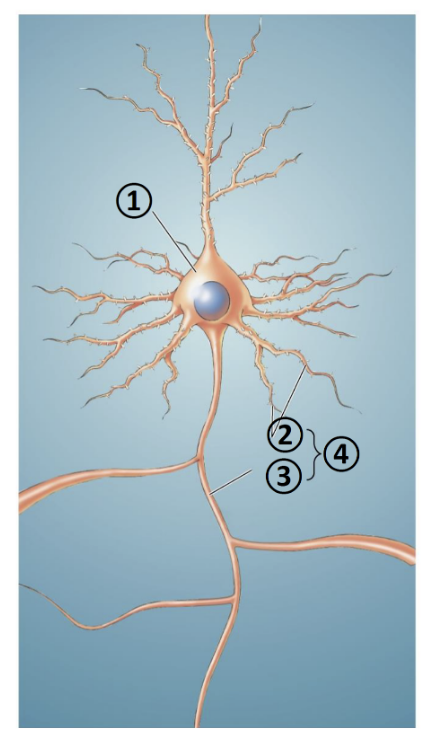
What is 3?
axon
56
New cards
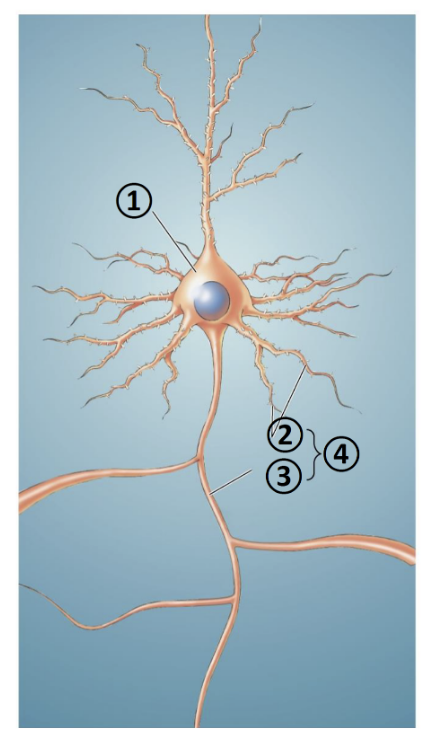
What is 4?
neurites
57
New cards
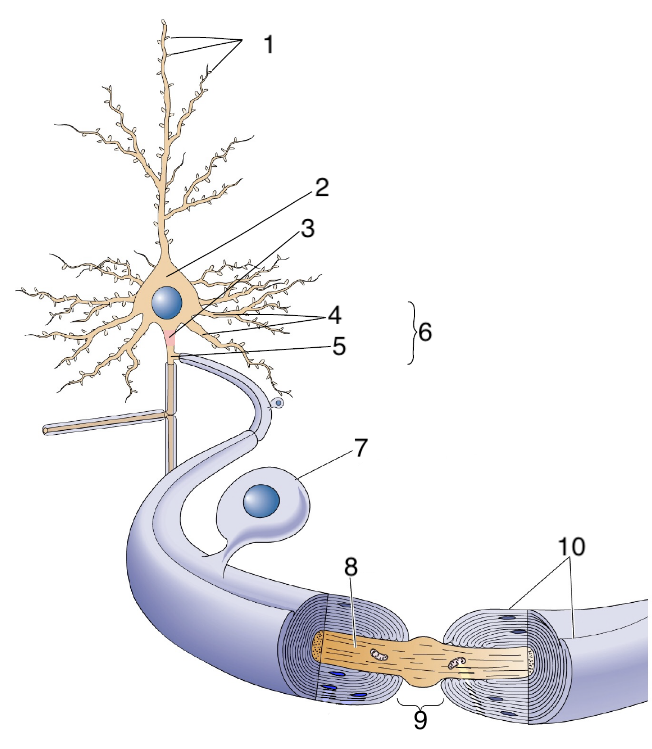
What is 1?
dendritic spines
58
New cards
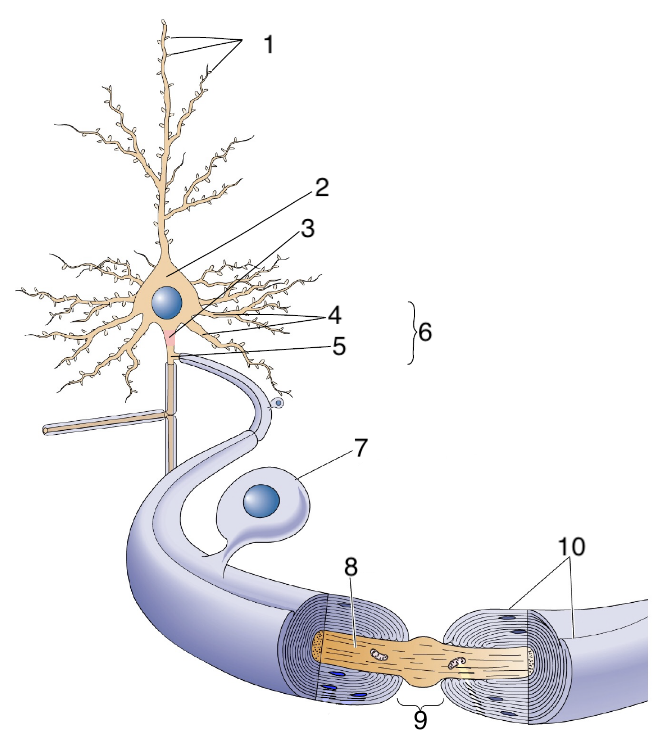
What is 2?
soma
59
New cards
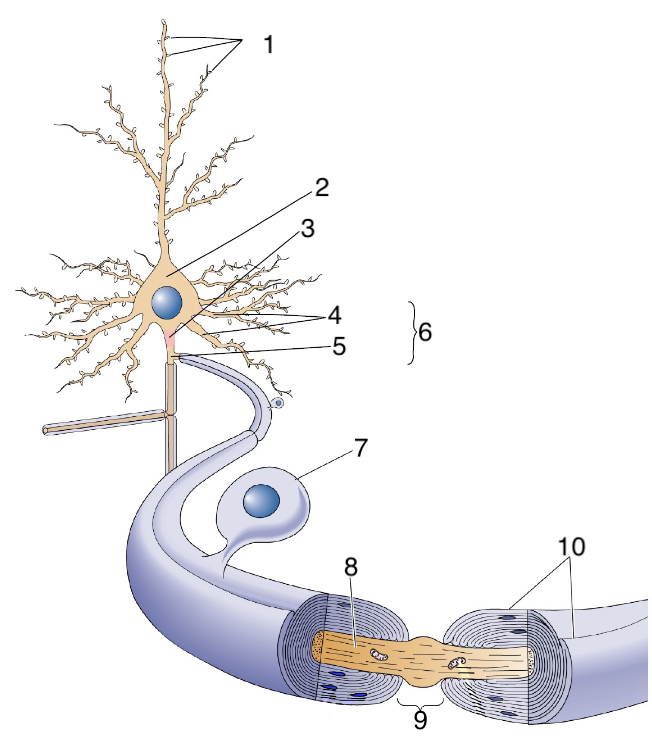
What is 3?
axon hillock
60
New cards
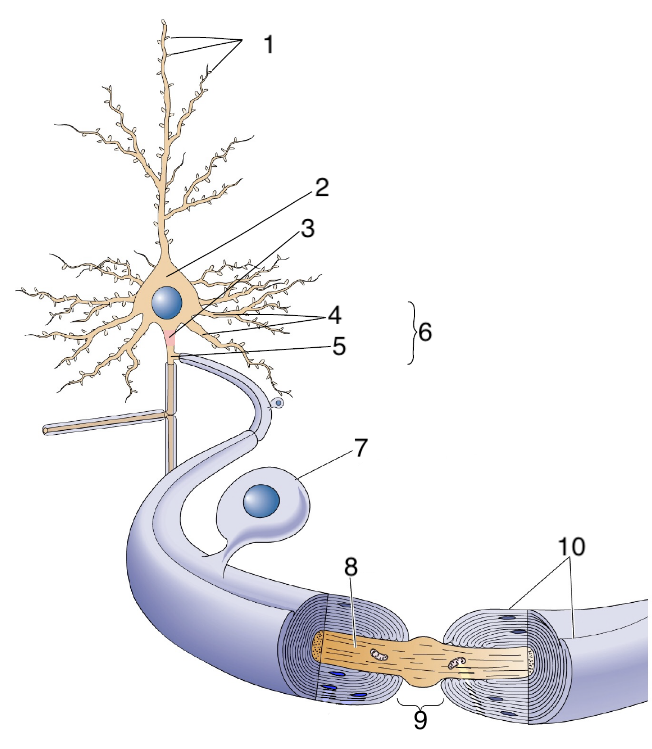
What is 4?
dendrites
61
New cards
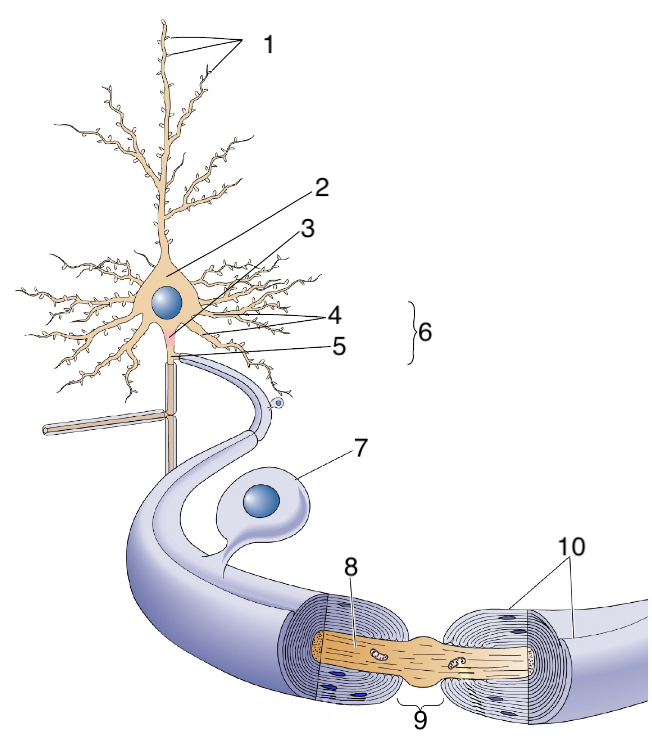
What is 5?
axon
62
New cards
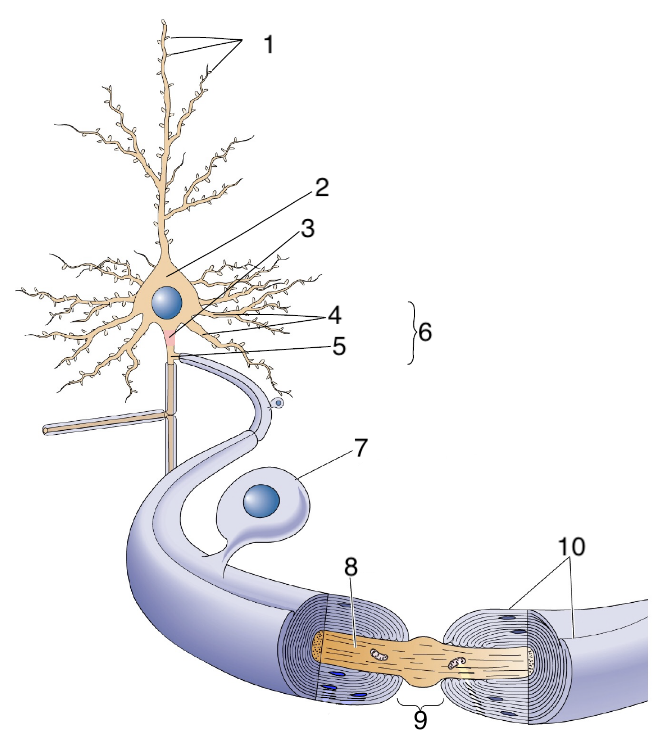
What is 6?
neurites
63
New cards
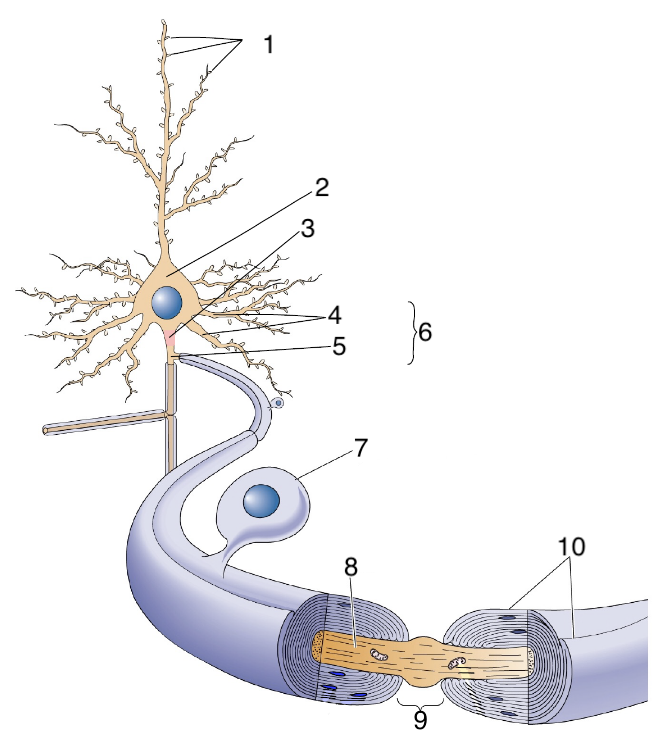
What is 7?
schwann cells
64
New cards
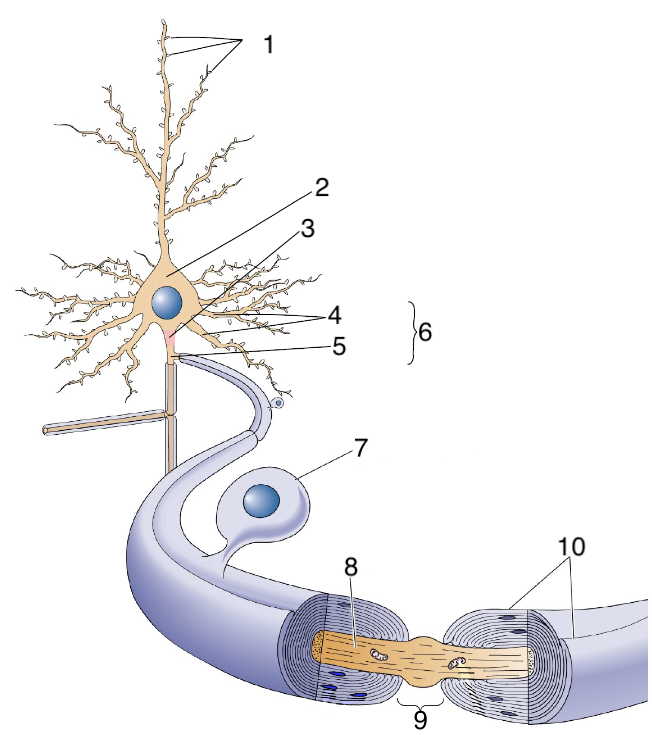
What is 8?
axon
65
New cards
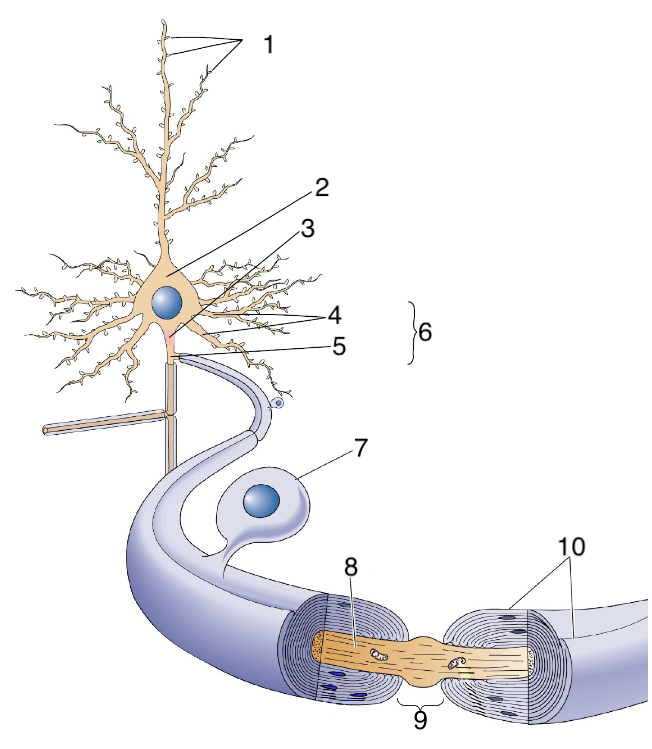
What is 9?
Node of Ranvier
66
New cards
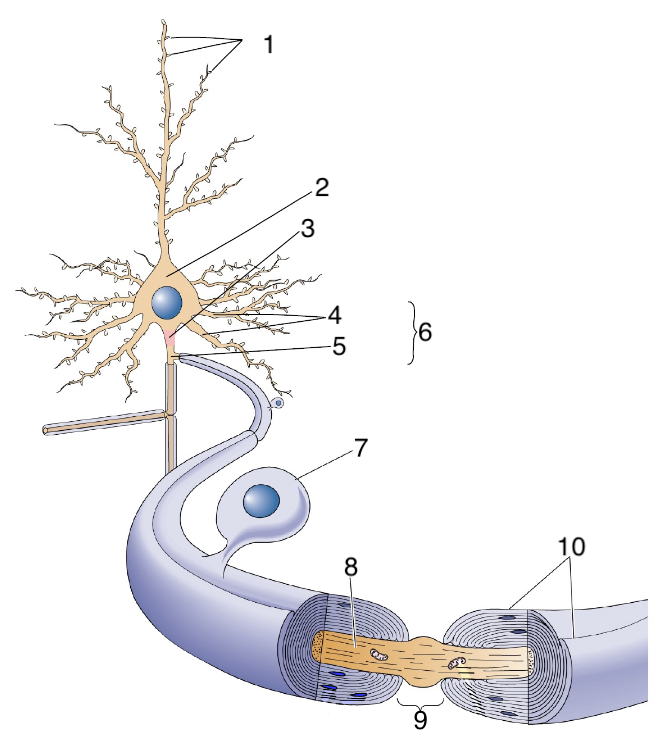
What is 10?
myelin sheath
67
New cards
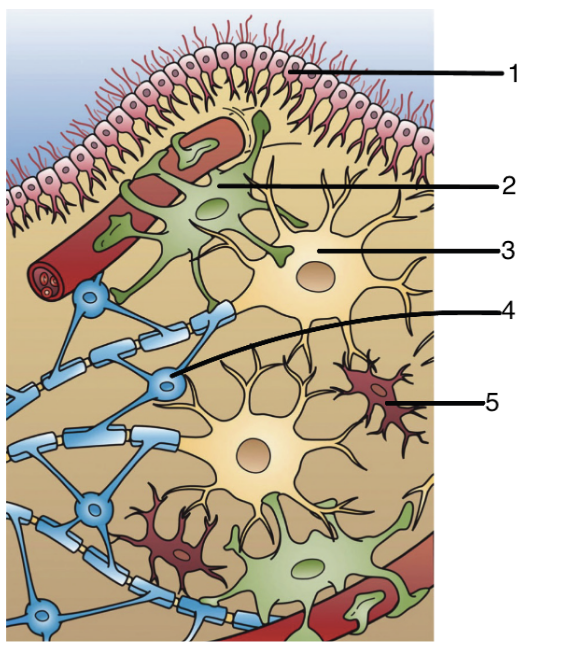
1
ependymal cells
68
New cards
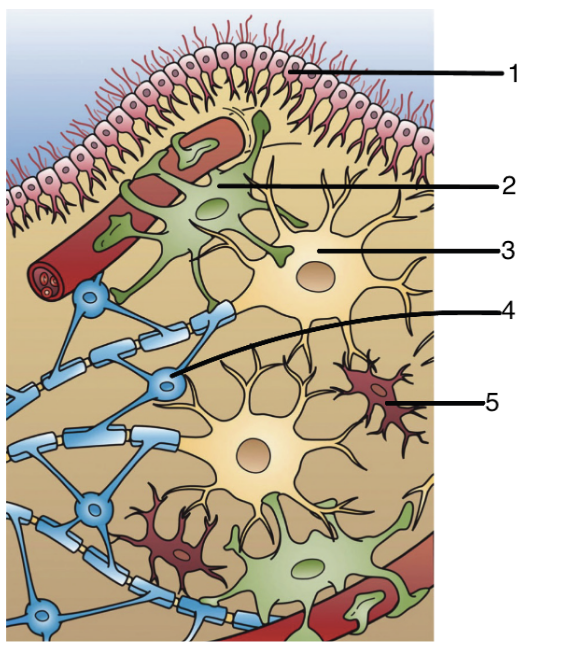
2
astrocytes
69
New cards
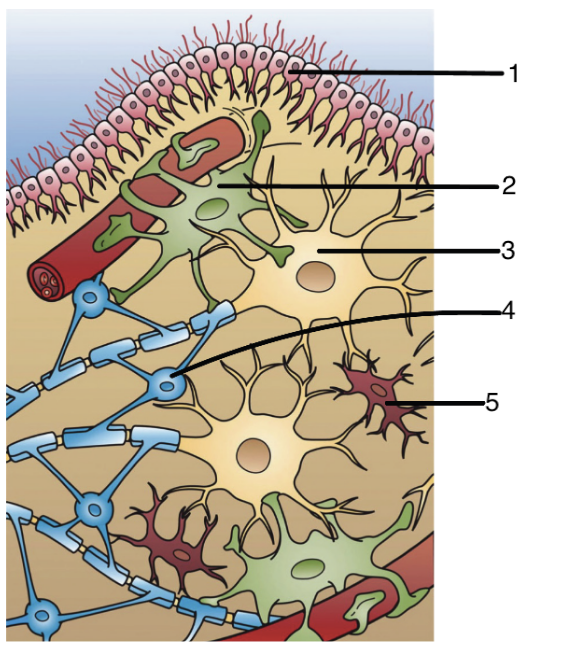
3
neuron
70
New cards
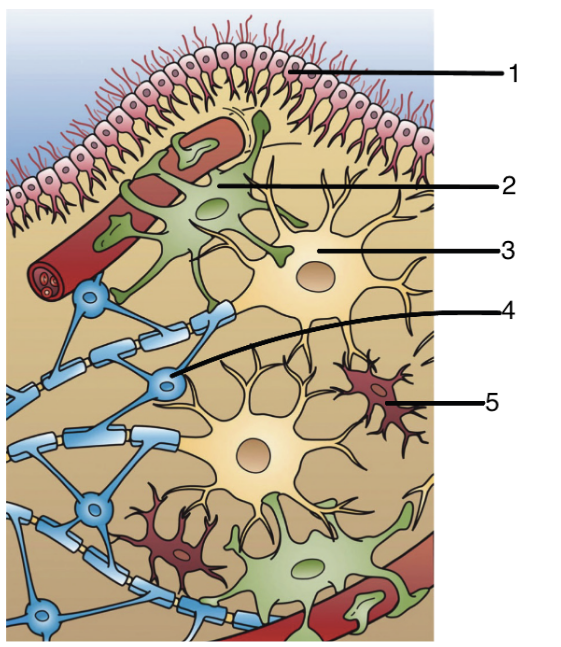
4
oligoendocytes
71
New cards
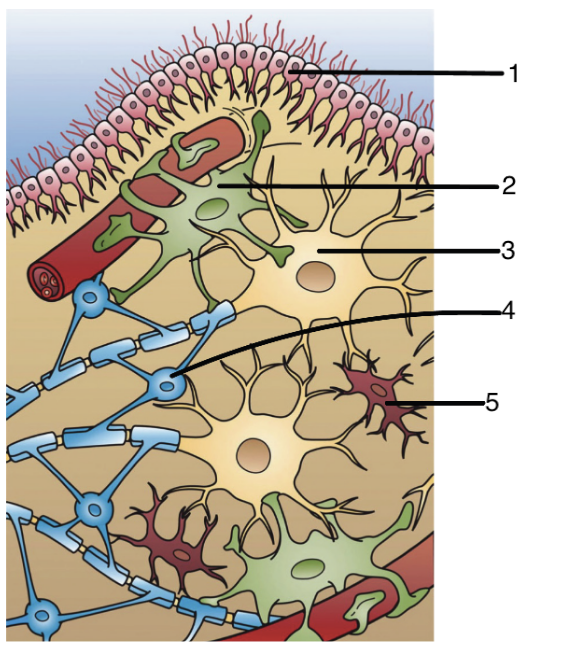
5
microglia
72
New cards
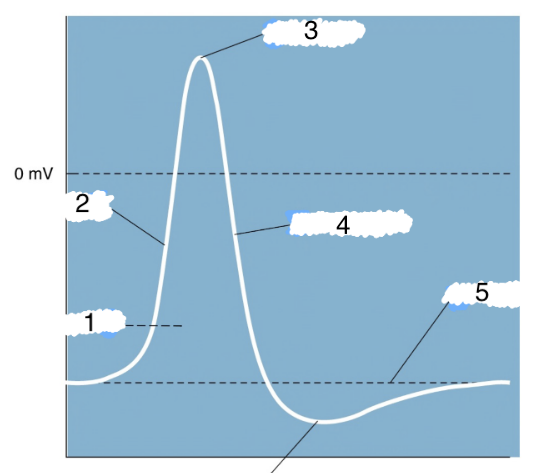
1
action potential
73
New cards
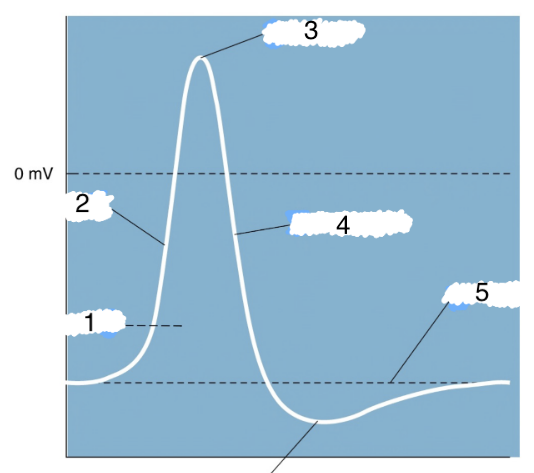
2
depolarization
74
New cards
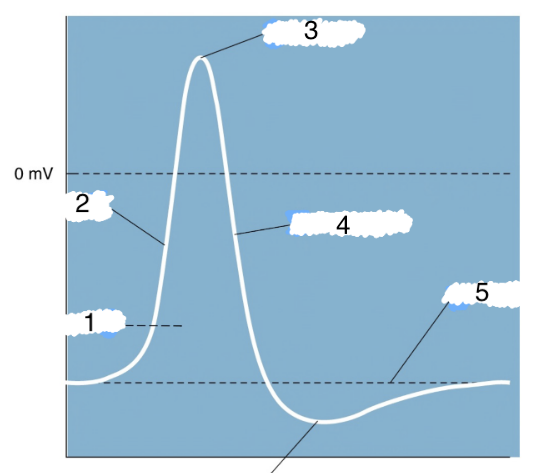
3
peak
75
New cards
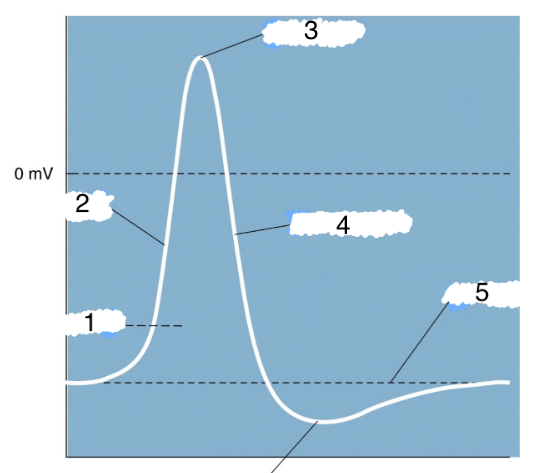
4
repolarization
76
New cards
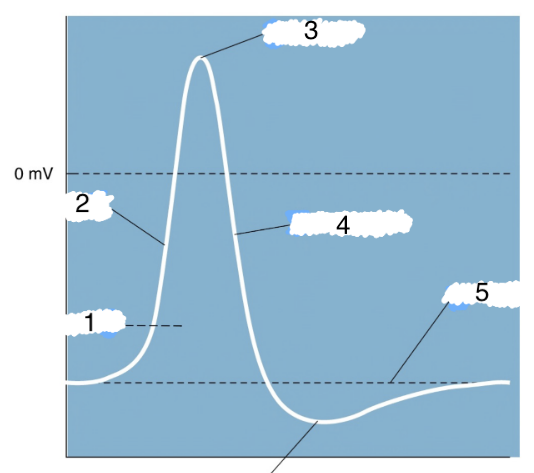
5
threshold
77
New cards
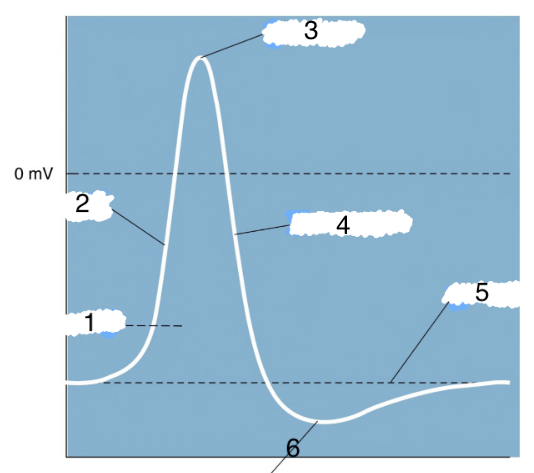
6
hyperpolarization
78
New cards
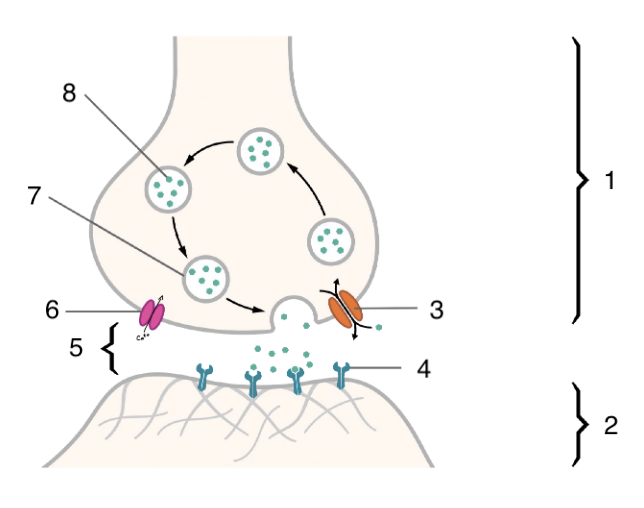
1
presynaptic cleft
79
New cards
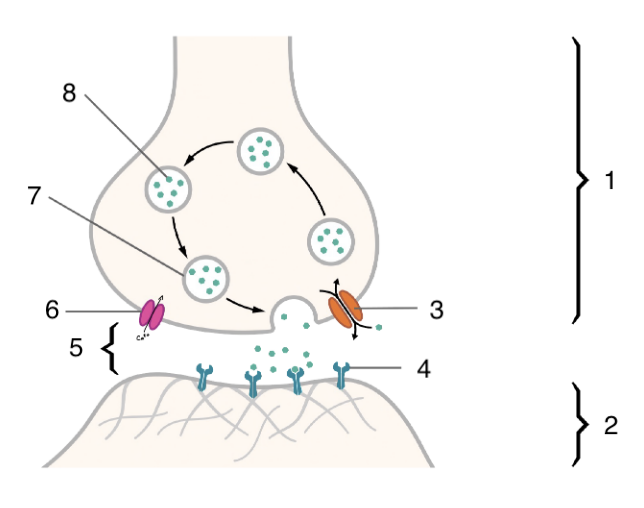
2
postsynaptic cell
80
New cards
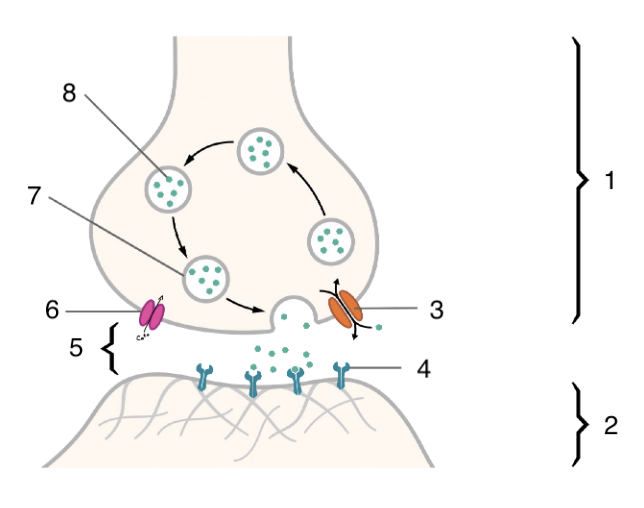
3
neurotransmitter pump
81
New cards
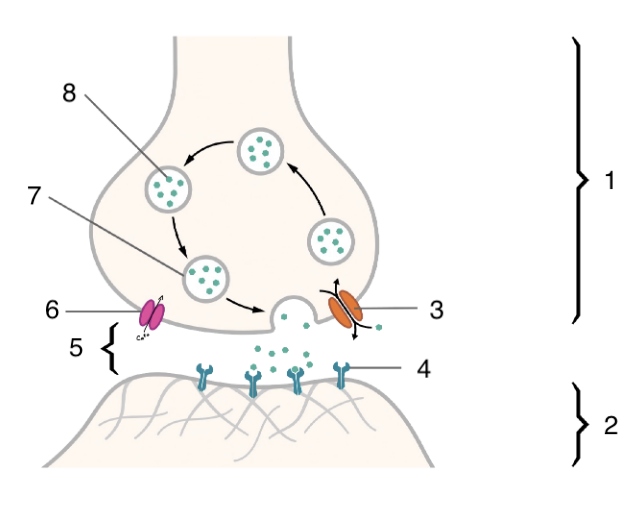
4
Neurotransmitter receptor
82
New cards
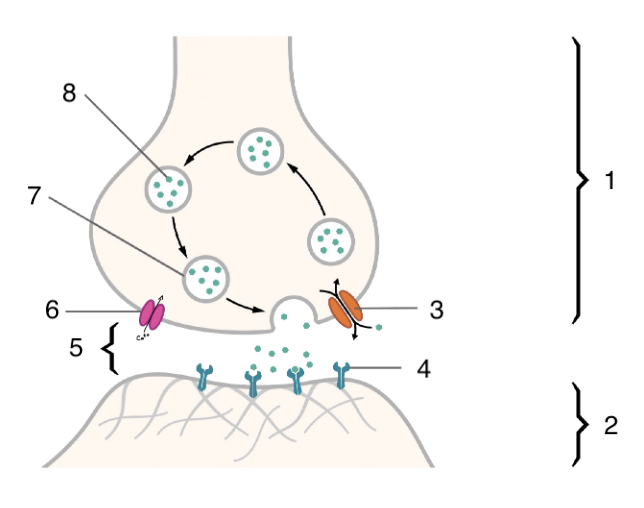
5
synaptic cleft
83
New cards
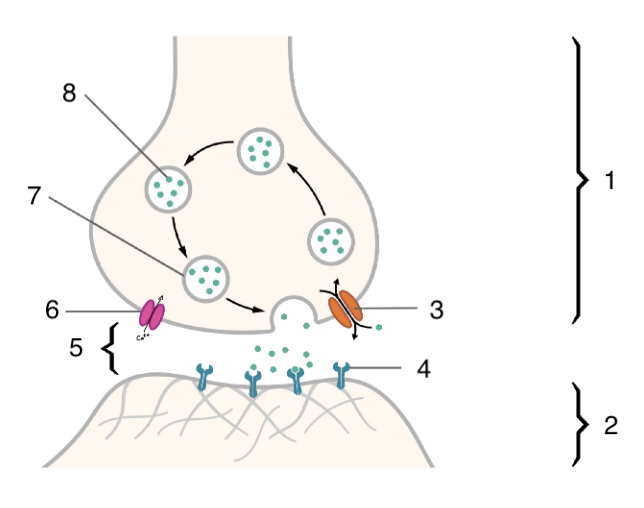
6
voltage gated calcium channel
84
New cards
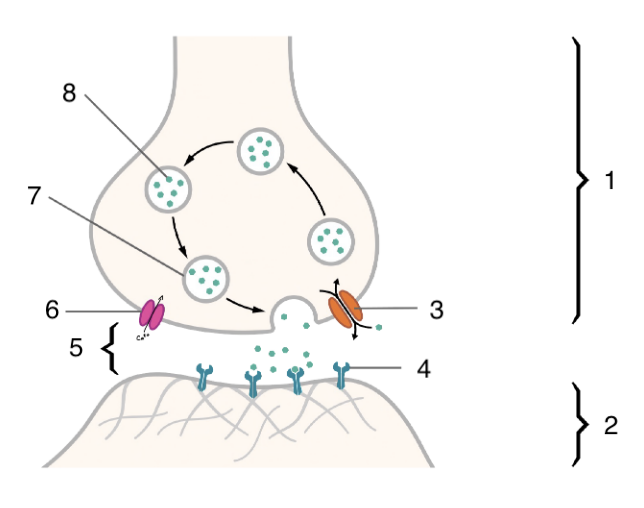
7
neurotransmitter vesicle
85
New cards
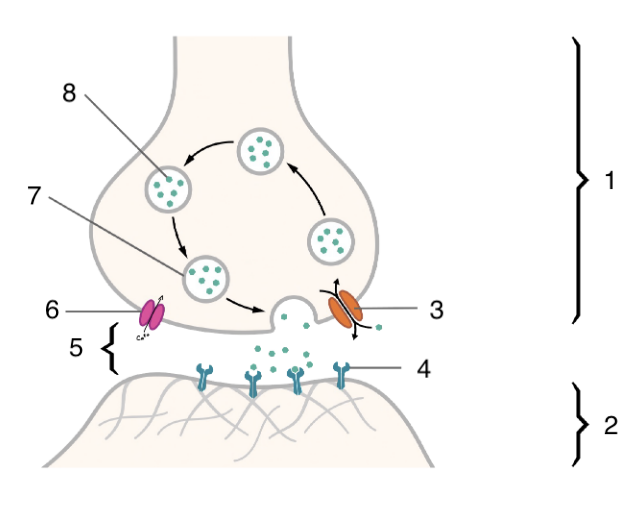
8
neurotransmitter
86
New cards
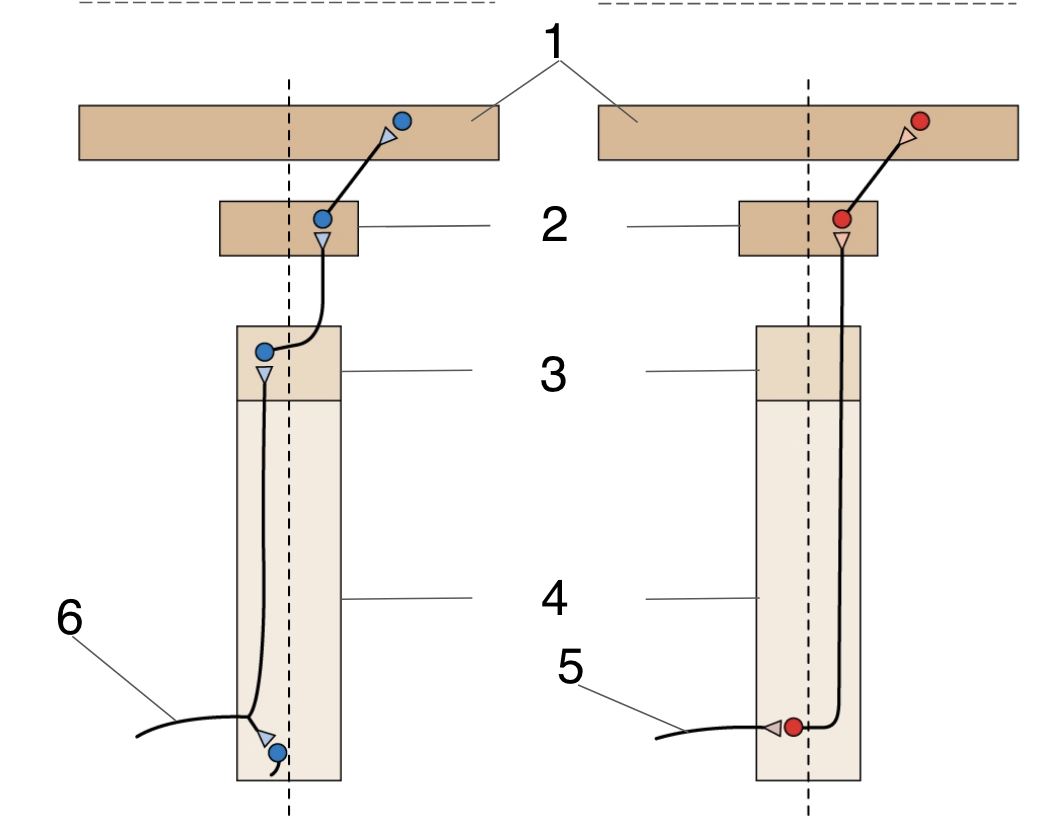
What is 1?
Cerebral cortex
87
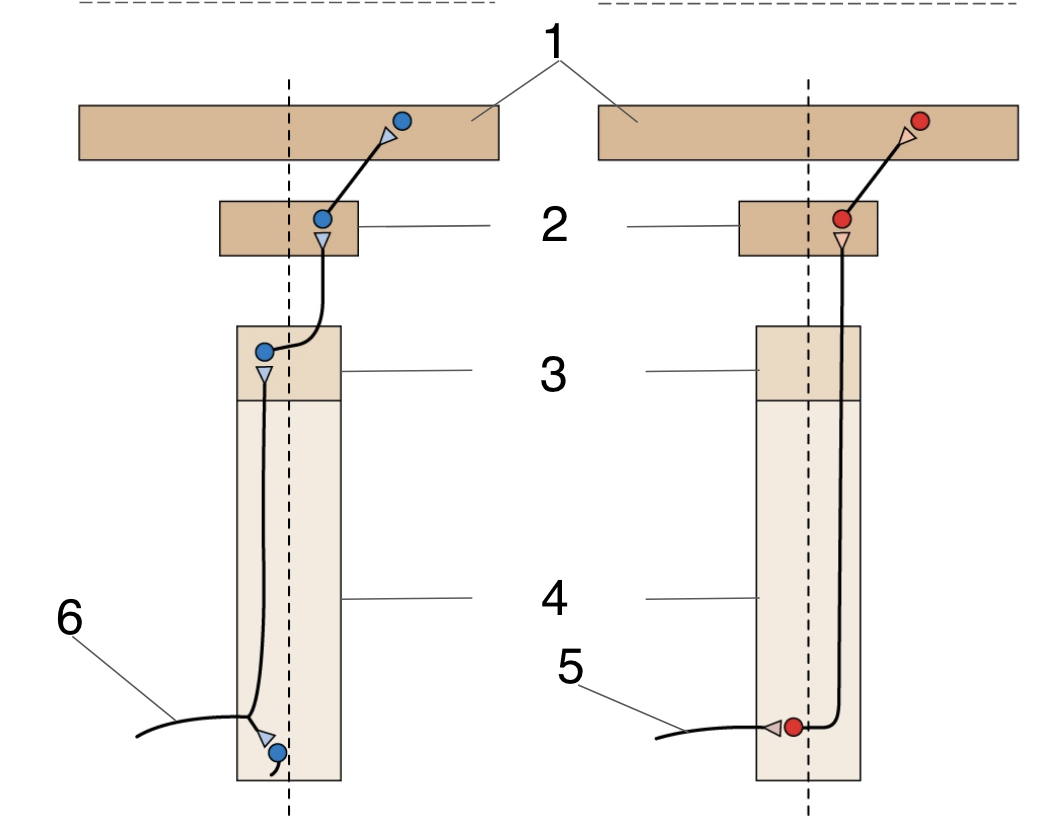
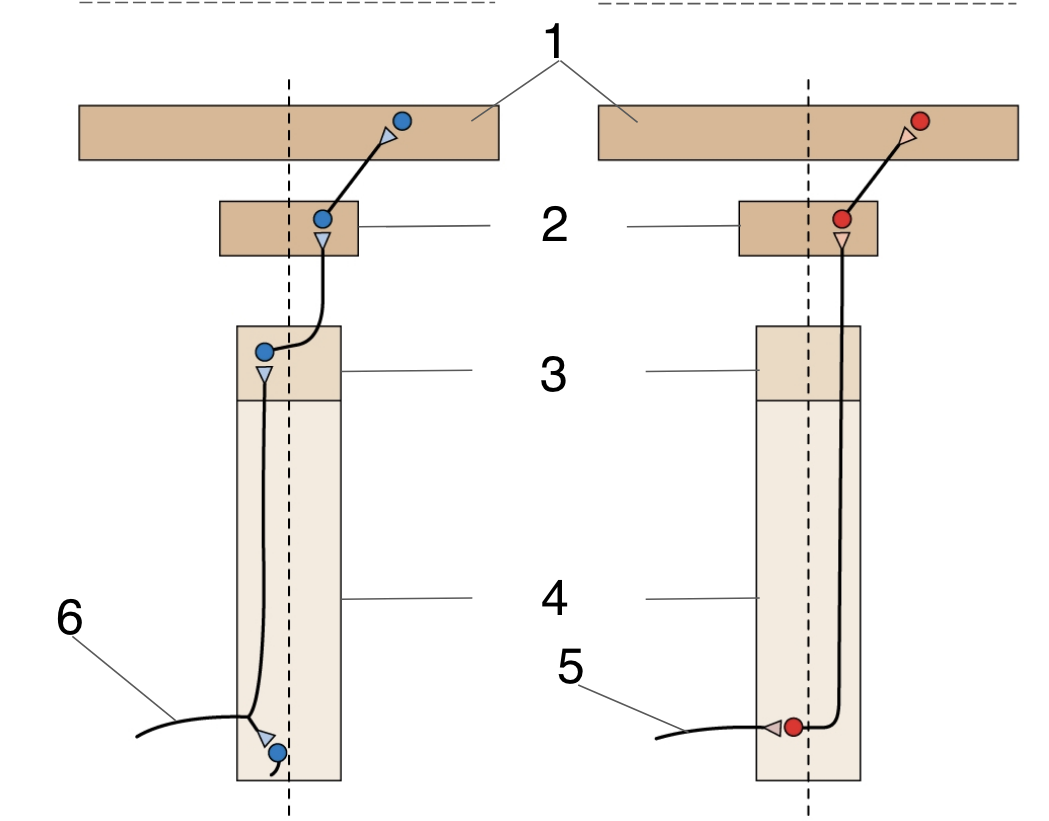
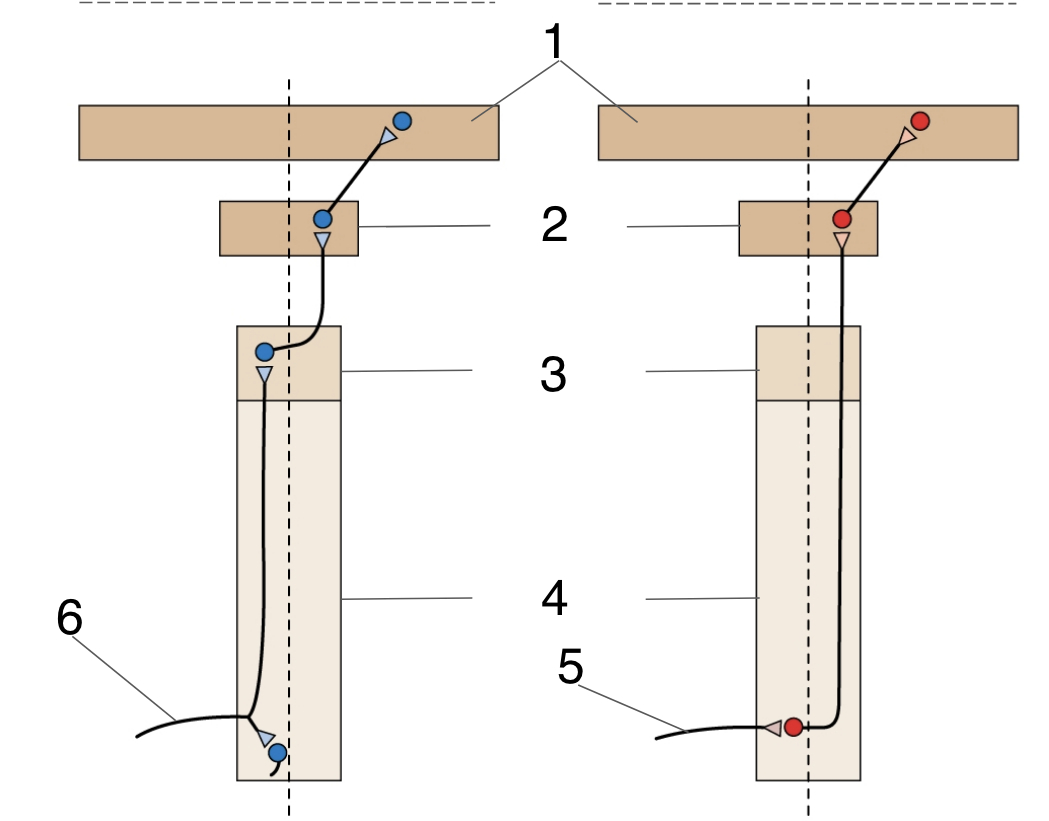
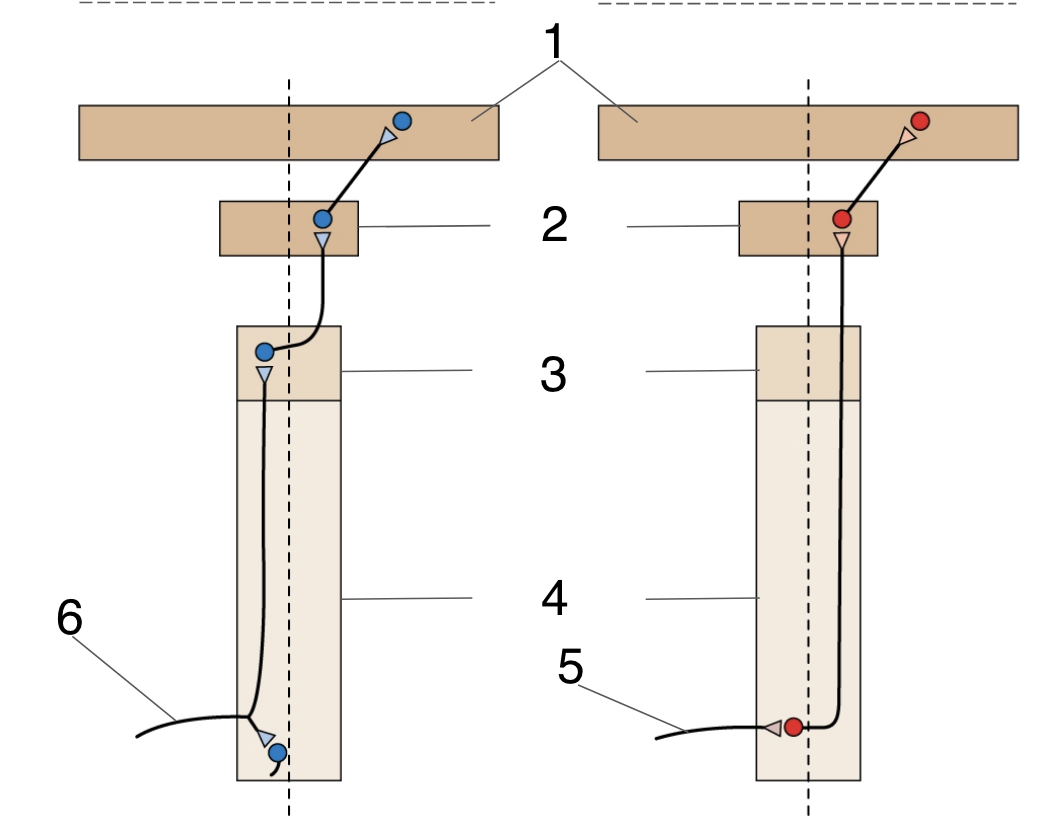
New cards
What is 2?
Thalamus
88
New cards
What is 3?
Medulla
89
New cards
What is 4?
Spinal cord
90
New cards
What is 5/6?
Dorsal root axon
91
New cards
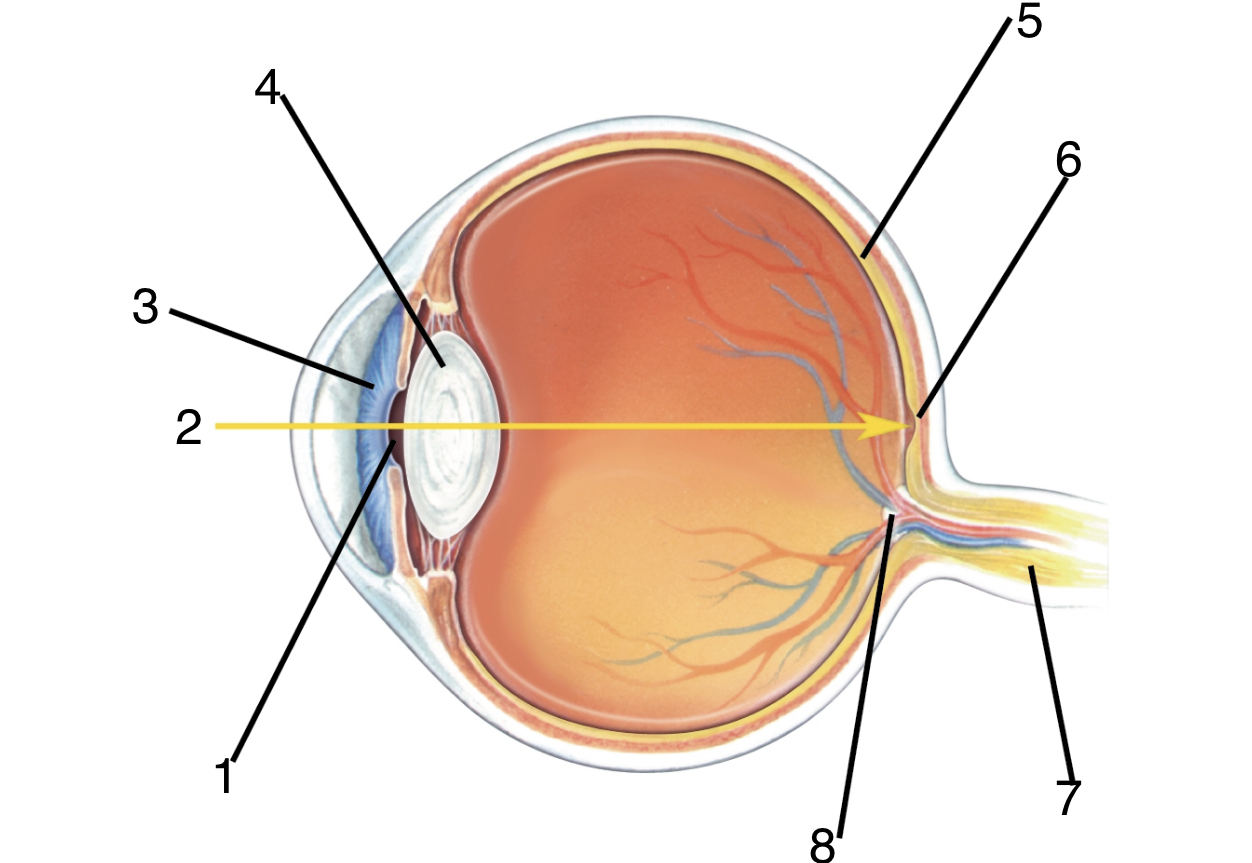
What is 1?
pupil
92
New cards
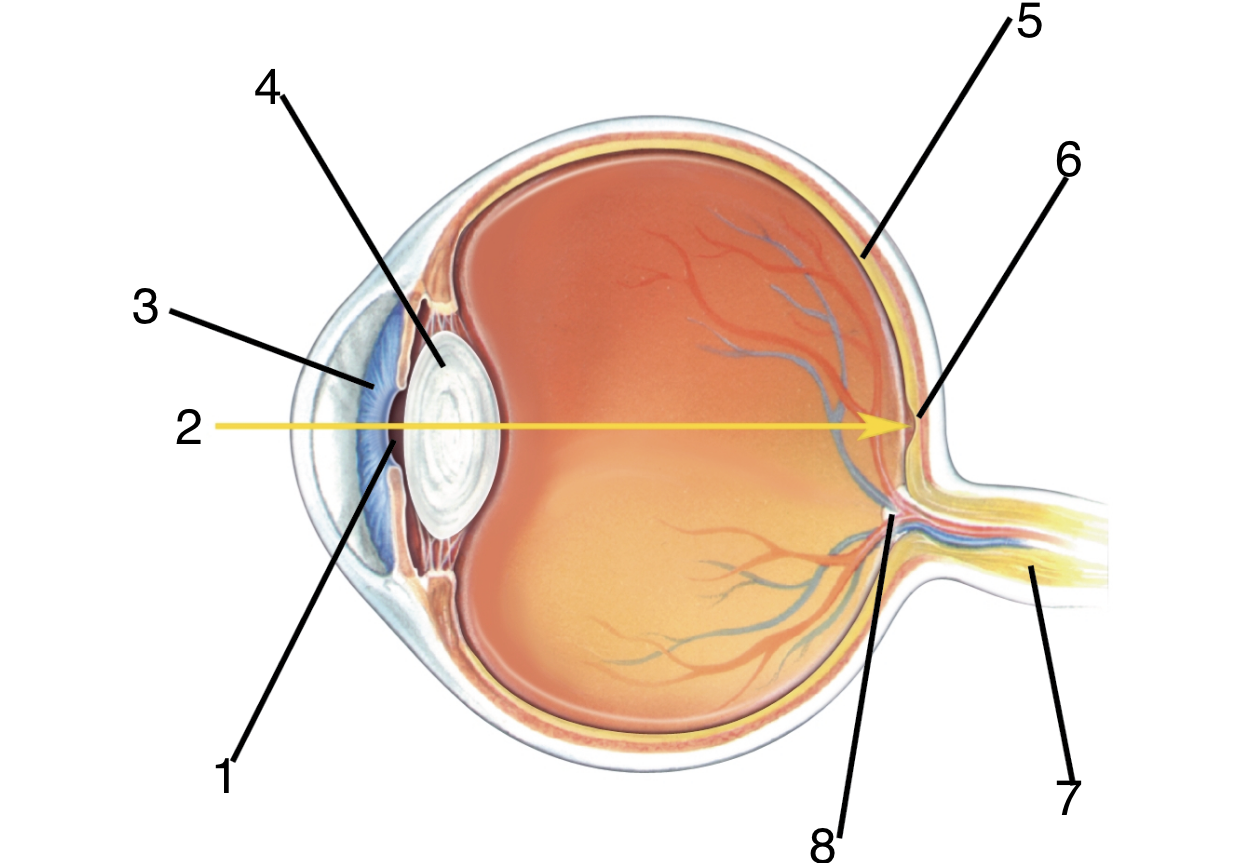
What is 3?
Iris
93
New cards
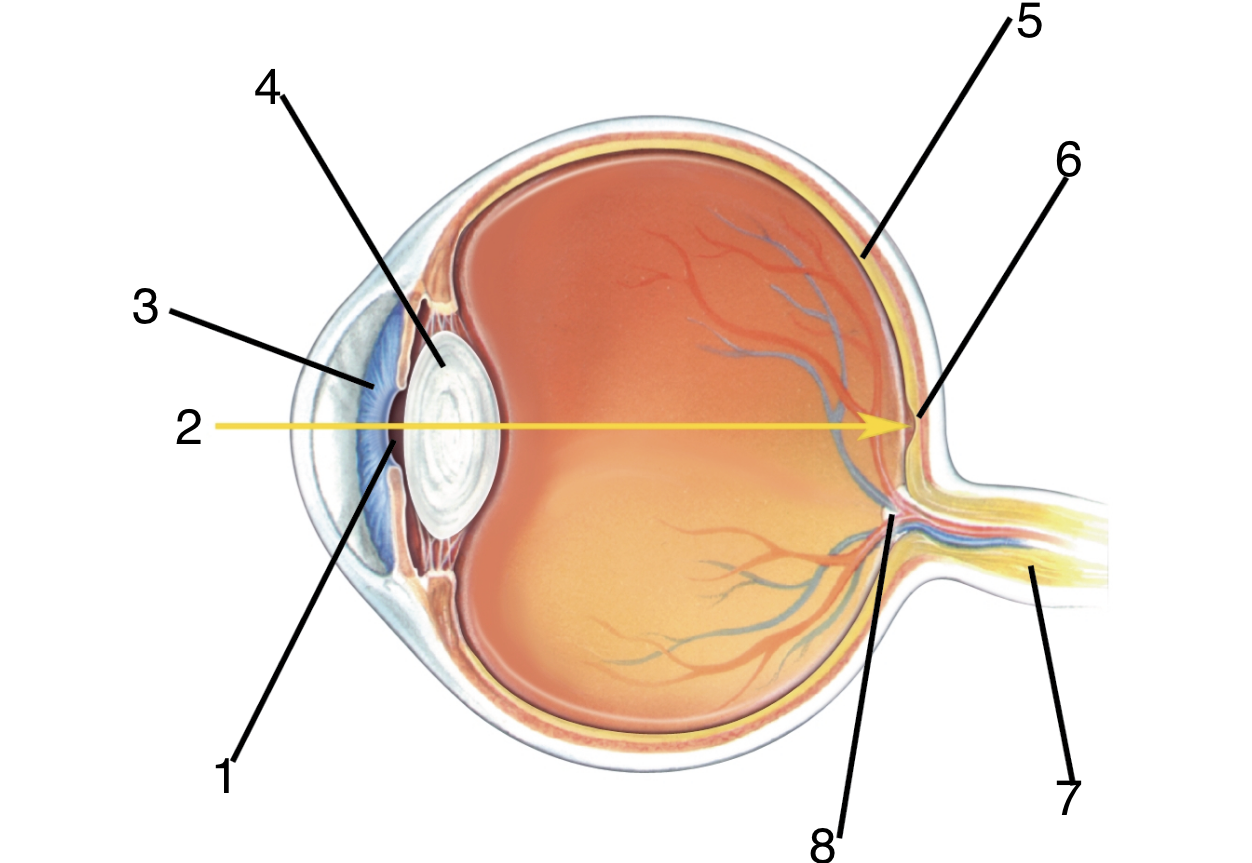
What is 4?
lens
94
New cards
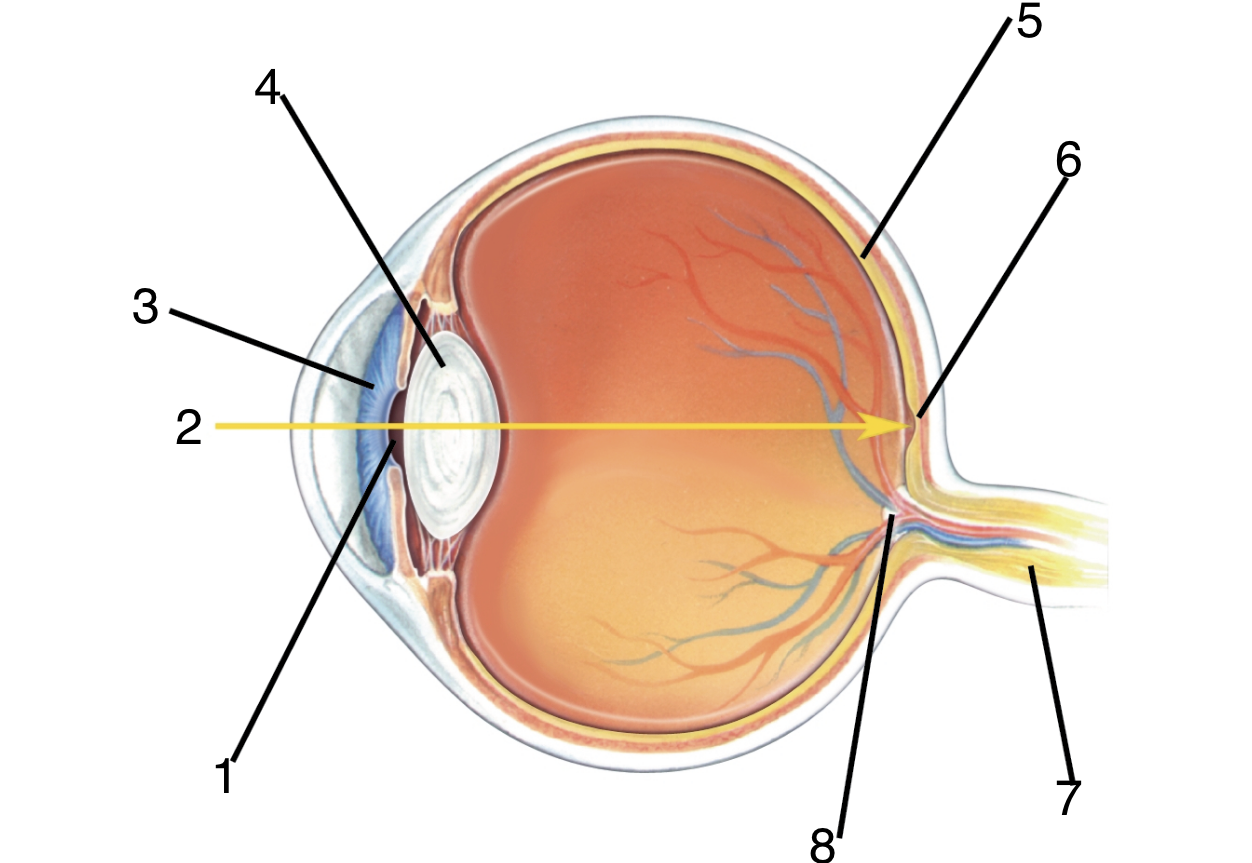
What is 5?
Retina
95
New cards
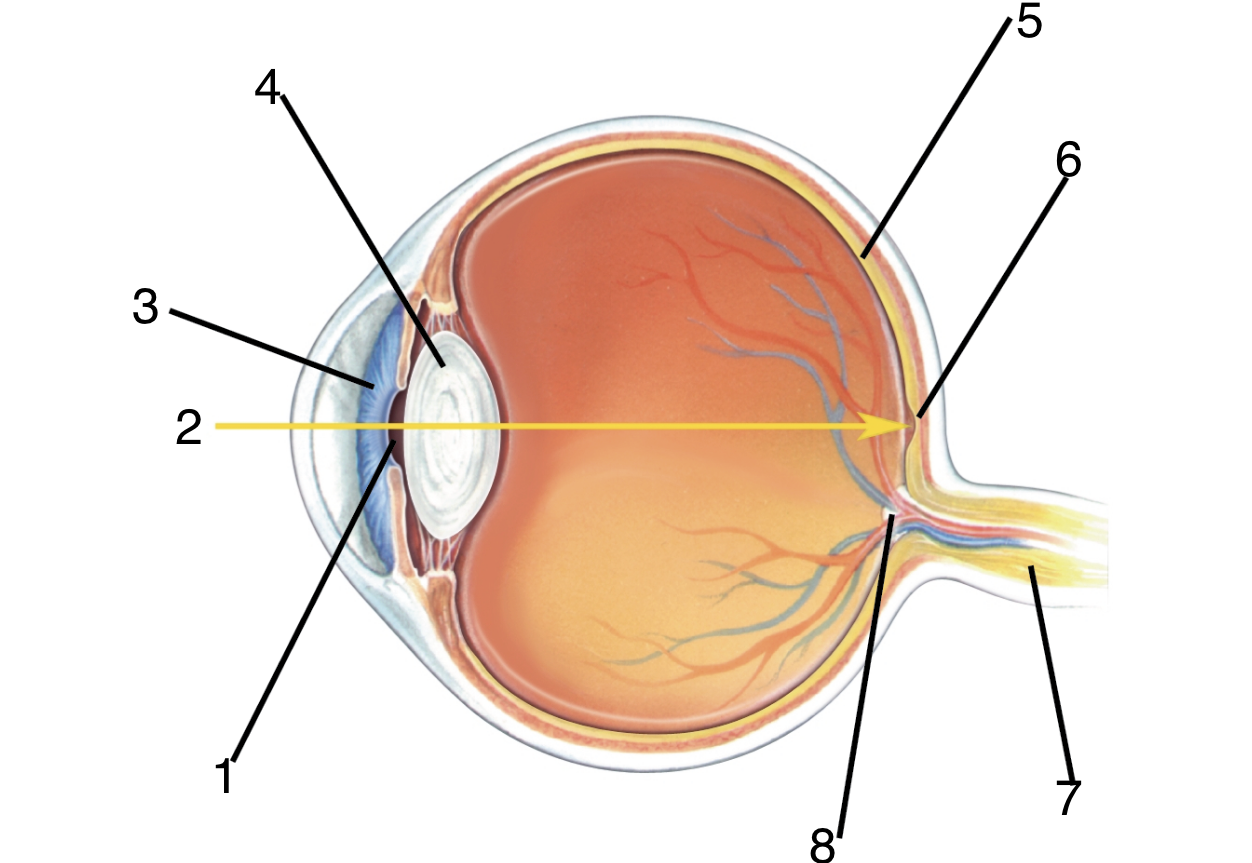
What is 6?
Fovea
96
New cards
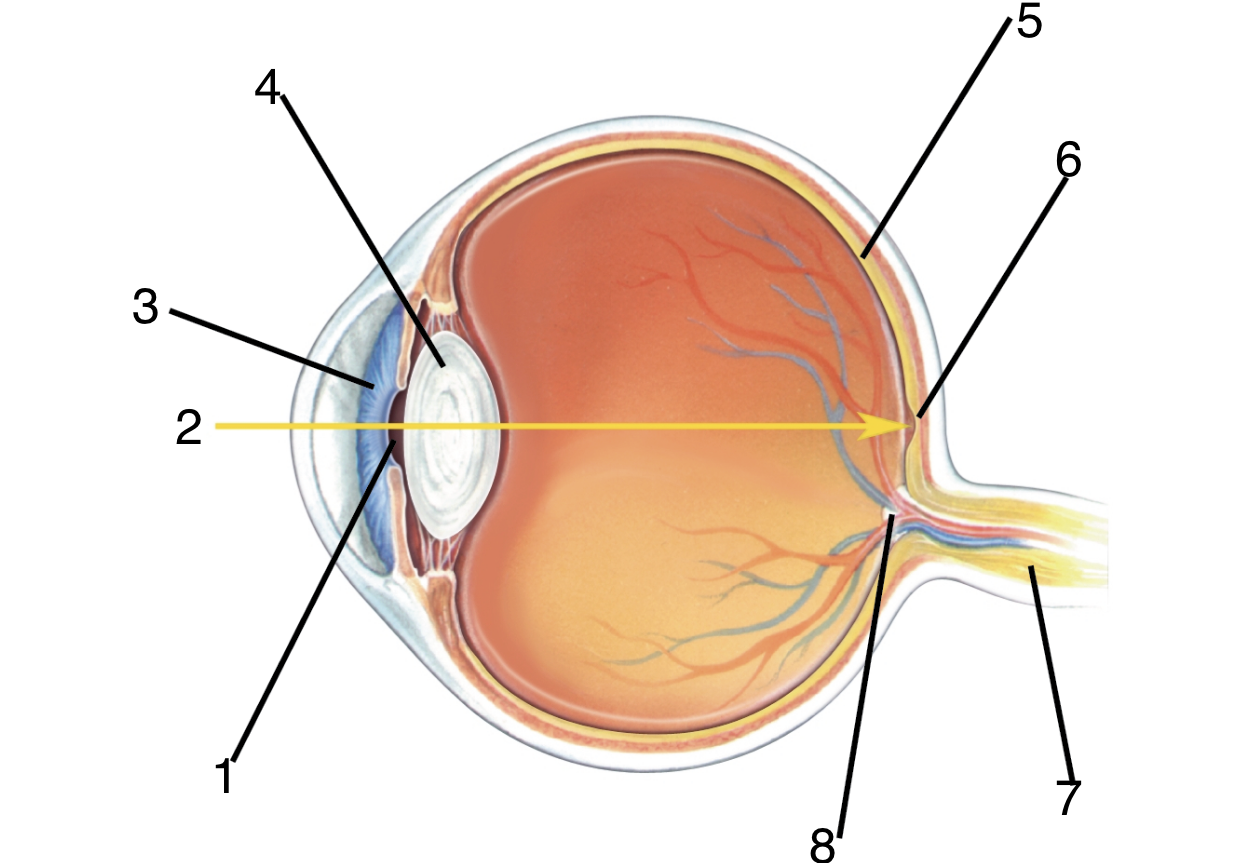
What is 7?
Optic nerve
97
New cards
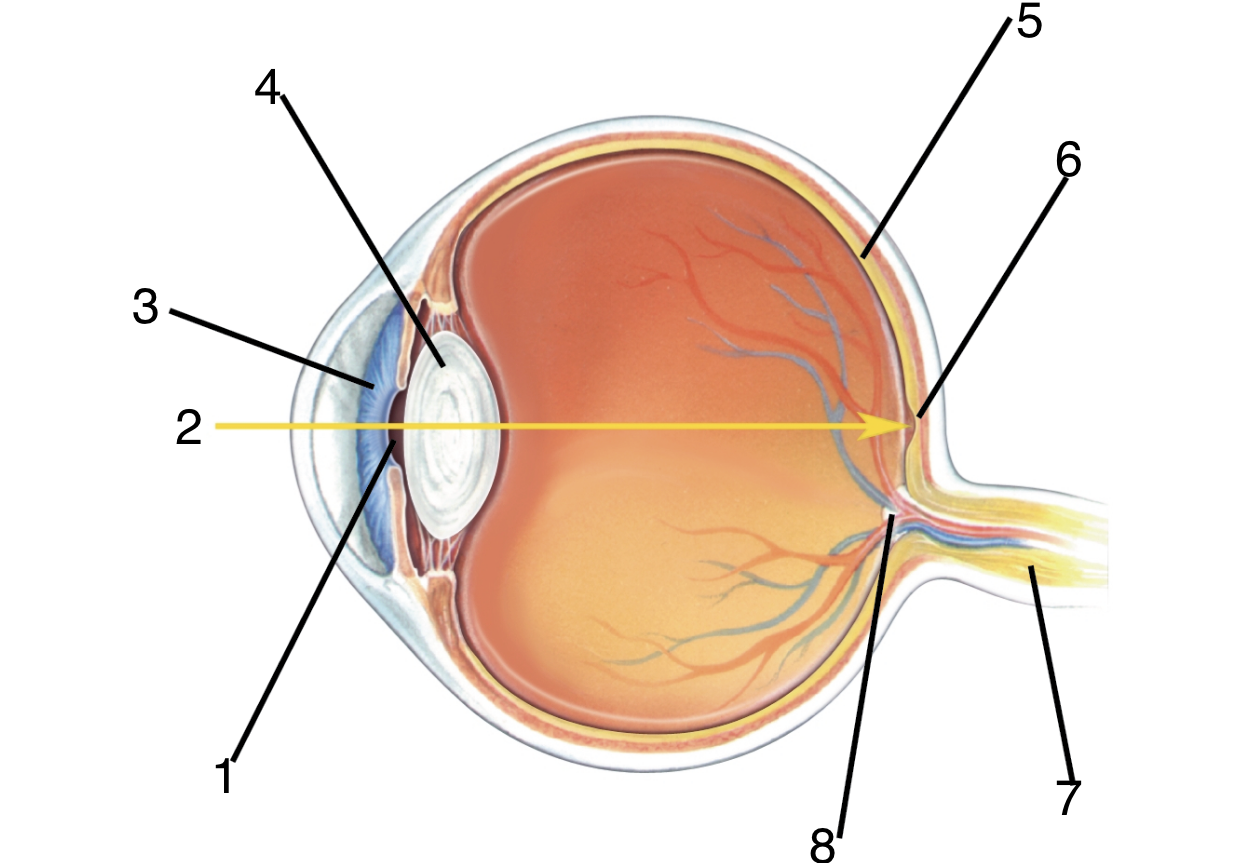
What is 8?
optic disc
98
New cards
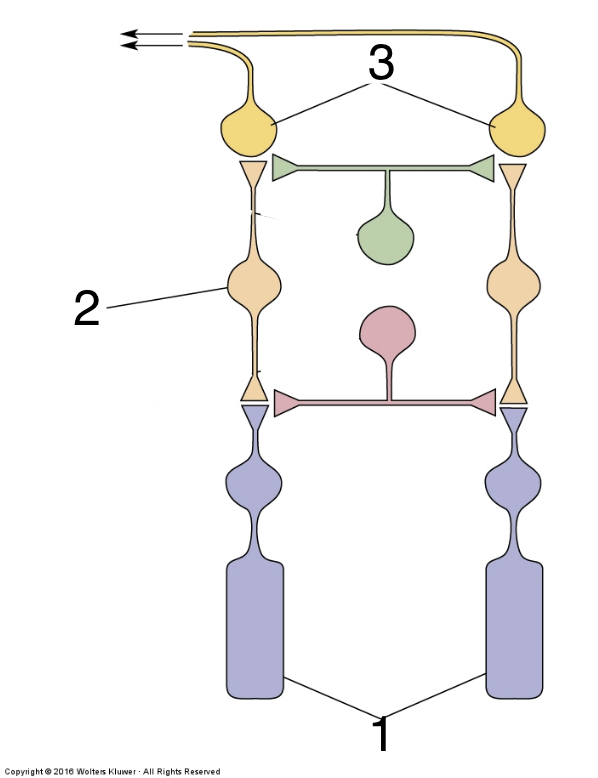
What is 1?
Photoreceptors
99
New cards
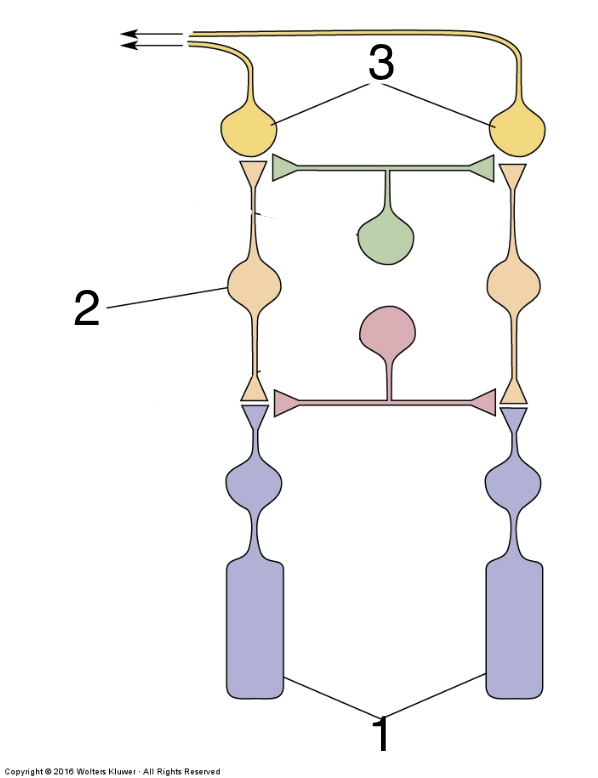
What is 2?
bipolar cell
100
New cards
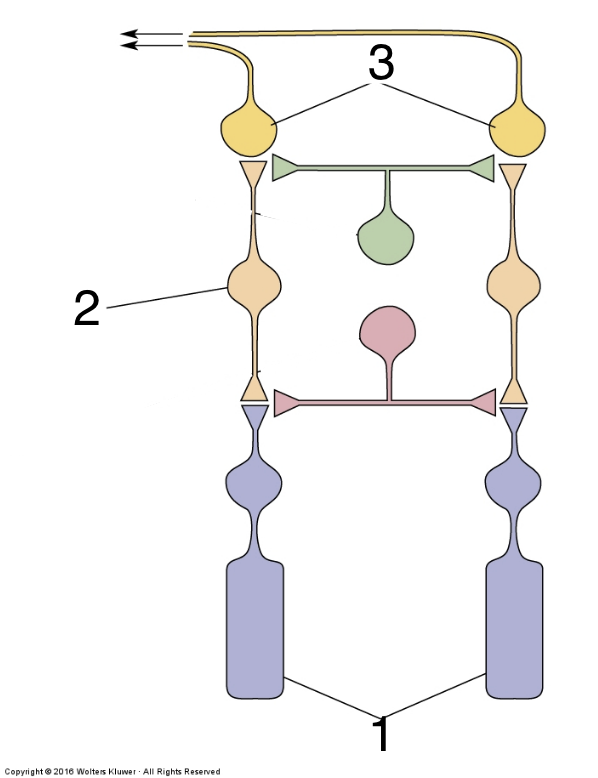
What is 3?
ganglion cells