BIOL 2 CUMULATIVE FINAL
1/381
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
382 Terms
driven by geologic processes and by photosynthesis and the respiration of plants and animals
describe the major events in the global cycling of carbon
liquid water evaporates into water vapor, condenses to form clouds & precipitates back to earth in the form of rain/snow
describe the major events in the global cycling of water
nitrogen fixation, nitrification, ammonification, & denitrification
describe the major events in the global cycling of nitrogen
weathering, absorption by plants, consumption by animals, decomposition, leaching/runoff, & sedimentation
describe the major events in the global cycling of phosphorus cycle
photosynthesis pulls carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere/allows for the continuous cycling of carbon between its organic and inorganic forms
explain how the coupling of photosynthesis & respiration result in the cycling of carbon
burning fossil fuels, changing land use, and using limestone to make concrete all transfer significant quantities of carbon into the atmosphere
explain how human activities impact climate change by disrupting the global carbon cycle
too much nitrogen and phosphorus in water can cause algae to grow too fast
explain the problems when excess phosphorus & nitrogen make their way into ecosystems
energy decreases as it moves up trophic levels because energy is lost as metabolic heat when the organisms from one trophic level are consumed by organisms from the next level
explain the change in available energy at progressively higher trophic levels
the top has the least amount of energy
explain why there is typically less biomass and fewer individuals & species at the top of a food chain than at the bottom
they show the relative amounts of various parameters (such as number of organisms, energy, and biomass) across trophic levels
explain the concept of “ecological pyramids“
gross is the total which material is produced & net is the rate at which material is accumulated in excess os respiration
explain the difference between gross and net primary productivity
efficiency with which organism converts what it has eaten into its own biomass (the energy transferred)
explain the concept of ecological efficiency
short term atmospheric conditions (ex: sunny with clear skies)
what is weather & give an example
the weather of a specific region averaged over a long period of time (ex: tropical climate characterized by consistently warm temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall throughout the year, as found in the Amazon Rainforest)
what is climate & give an example
air deflects to the right in the northern hemisphere & air deflects to the left in the southern hemisphere (curved paths)
describe how the Coriolis Effect deflects moving parcels of air in the northern & southern hemispheres
the earth’s tilted axis causes the seasons
why do the Northern & Southern Hemispheres have opposite seasonal patterns?
they regulate global climate, helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth's surface
how do ocean currents affect climate?
mountainous areas tend to have more extreme weather because it acts as a barrier to air movements and moisture.
explain the effects of topography (mountains) on climate
the higher the altitude, the colder the climate becomes
explain the effects of altitude on climate
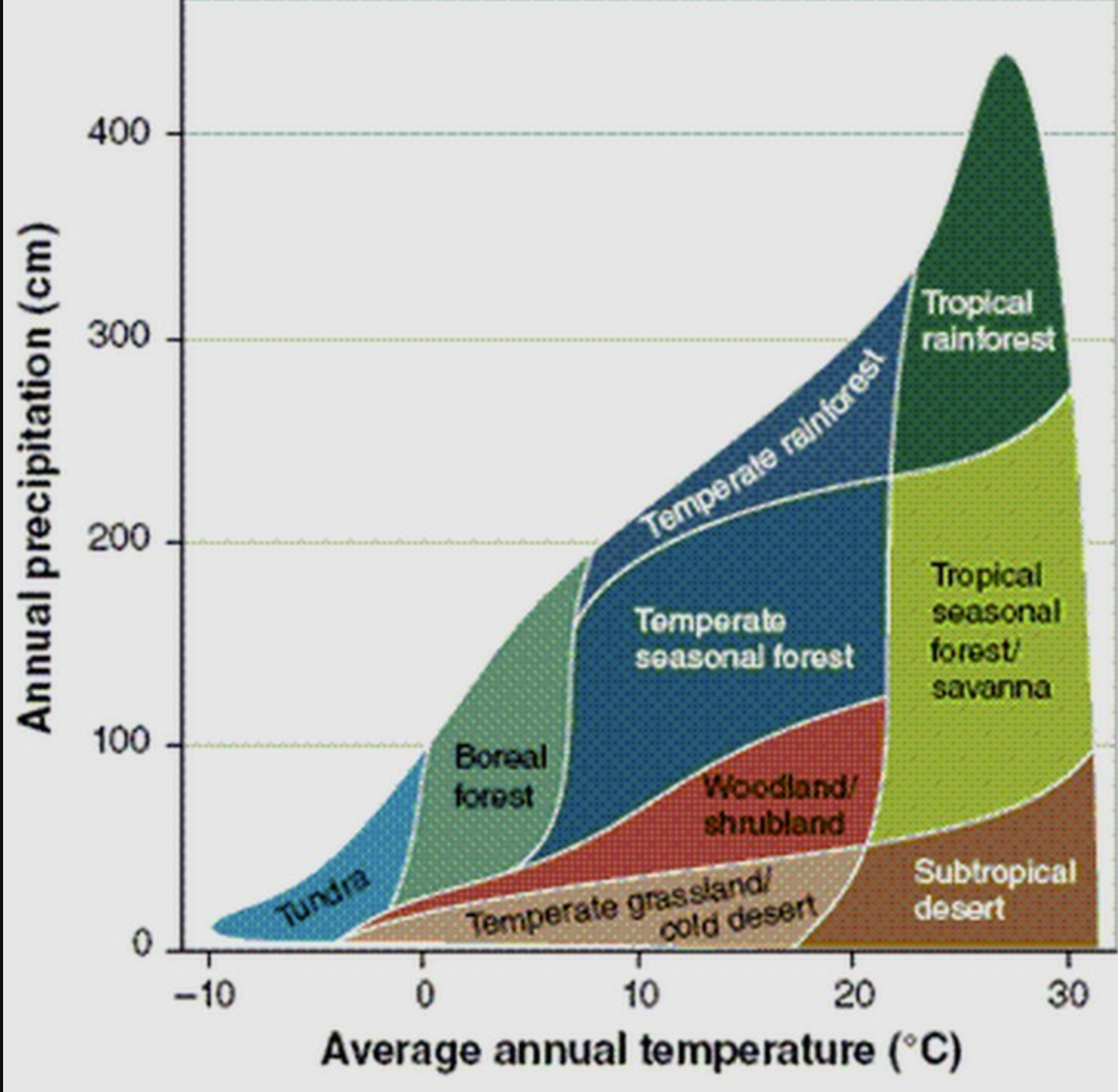
aquatic, grassland, forest, desert, & tundra biomes
evaluate the position of biomes on the Whittaker diagram
climate determine plant growth & the number/variety of other organisms in a terrestrial biome
what is the relationship between climate and biome distribution
causation (mechanistic), development, adaptive function, & evolutionary history
what are Tinbergen’s 4 questions that should drive studies of animal behavior
a trade-off exits between the energy provided by larger prey, and the time and energy required for their capture and handling.
how does foraging involve trade-offs between nutrients acquired and the costs of energy required & risk?
Males often evolve traits and displays that advertise their ability to provide direct and indirect benefits, and females evolve preferences for these traits
explain how differences in the reproductive strategies of males & females can foster sexual selection for certain characteristics in males
determines who reproduces by competition with who to mate with
what is sexual selection?
polygamy
a mating system with 2 basic types are polygyny (males mate with multiple females) & polyandry (females mate with multiple males)
costs: increases competition with each other; benefits: foraging efficiency & reduced risk of predation
explain the costs & benefits of living in groups
benefits: increase the colony's chance of survival by promoting and safeguarding reproduction above all else
explain how altruism could’ve evolved & its benefits to the individual & group
altruism increases in a group when its members are more closely related to each other
relate the concepts of inclusive fitness & kin selection to altruism
altruism occurring among organisms who share a given percentage of genes enables those genes to be passed on to subsequent generations
how can individual & inclusive fitness between individuals of different relatedness promote altruistic behavior?
group of individuals of the same species within a given area that have the potential to interbreed & interact with each other
what is a population?
individuals in patches = uneven amount of distribution of nutrients/resources in the environment (wolves)
describe conditions that may result in clumped dispersion of individuals in a population
individuals are evenly spaced out = competition (penguins)
describe conditions that may result in uniform dispersion of individuals in a population
independent of other individuals (dandelions)
describe conditions that may result in random dispersion of individuals in a population
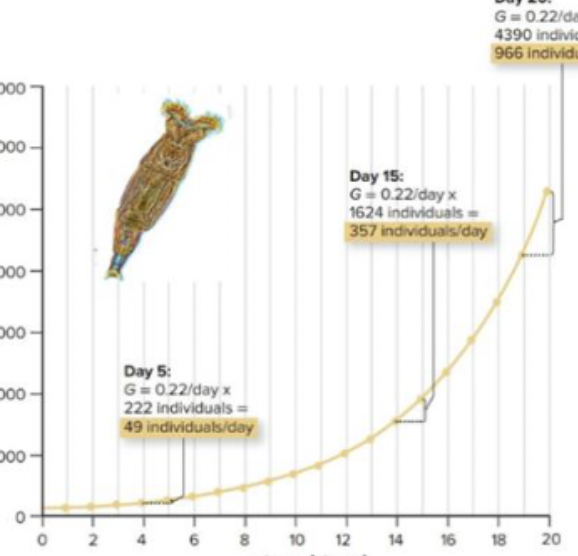
average growth rate over an interval of time; J-shaped
what is exponential population growth equations & the resulting growth curve?
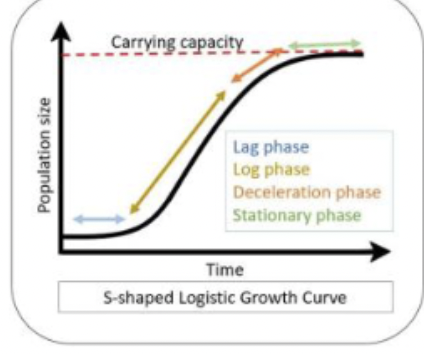
carrying capacity; S-shaped
what is logistic population growth equations & the resulting growth curve?
explain how carrying capacity affects exponential growth
density-dependent growth regulation of populations
birth rate decreases when a population increases
density-independent growth regulation of populations
death rate increases when a population increases
Type I
live until they’re old/die & usually have few offspring; low death rates during early & middle life and increases death rates in older age groups (ex: humans)
Type II
constant death rate over lifespan (ex: fish/sea life)
Type III
either die off at a young age/if they survive they’ll live a long time then die, usually have many offspring; high death rate for young & lower death rate for survivors
trade-off: usually the animal with more children will die sooner than the animal with less children bc the animal with more children is using more energy to reproduce, support, & take care of itself
how can limited resources & trade-offs affect life histories?
semelparity
reproduces one huge batch of offspring & then dies
iteroparity
produces several smaller batches of offspring distributed over time
r-selected species
species with a capacity for a high rate of population increase; density-dependent selection, it selects for life history traits that are sensitive to population density
K-selected species
reproduce later in life & have a small number of offspring with fairly long life spans; density-independent selection, it selects for life history traits that maximize reproduction
metapopulation
a group of subpopulations of a species living on patches of habitat connected by an exchange of individuals
source habits
a local demographic surplus arises in good quality habitats
sink habits
a local demographic deficit occurs in habitats of poor quality
community ecology
all the populations of all the different species found in a given place at a given time
dominant species
species that have the highest abundance/biomass within a particular community/ecosystem
keystone species
species that have a disproportionately large impact on their environment relative to their abundance
invasive species
species that are introduced to a new habitat/ecosystem, often by human activities, & have negative impacts on the environment, economy, or human health
ecological niche
a specific role of a species within an ecosystem, including its use of resources, and relationships with other species
fundamental niche
the requirements needed by a species to survive & reproduce under ideal conditions
realized niche
a set of conditions actually used by a given animal, after interactions with other species have been taken into account
competitive exclusion
if two species are competing for a limited resource, the species that uses the resource more efficiently will eventually eliminate the other locally
resource partitioning
similar species develop ways to partition/divide resources in order to coexist
character displacement
trait evolution stemming from selection to lessen resource competition between species & acts on traits associated with resource use; two similar species inhabit the same environment
interspecific competition
competition between individuals of different species (ex:woodpeckers & squirrels compete for nesting sites in the same holes in trees)
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species (ex: two oak trees growing too close together, fighting for sunlight & nutrients OR two male deer competing for mates)
predators decrease numbers of prey; lack of dood resources in turn decrease predator abundance & lack of predation pressure allows prey populations to rebound
explain why predator & prey population can cycle over time
detection and prey-capture prowess (heightened sensory, speed, agility, fangs, claws), poison (venom), & mimicry (camoflage)
describe mechanisms (adaptations) species use to avoid predation
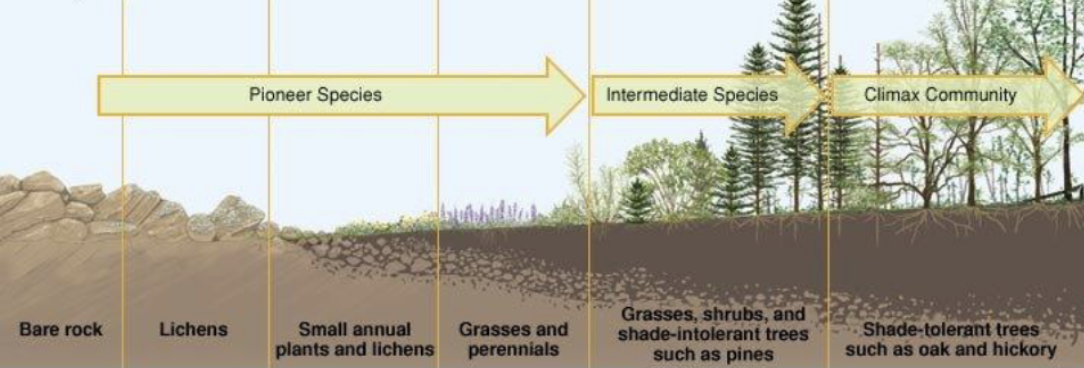
primary succession
newly exposed/formed rock is colonized by living things
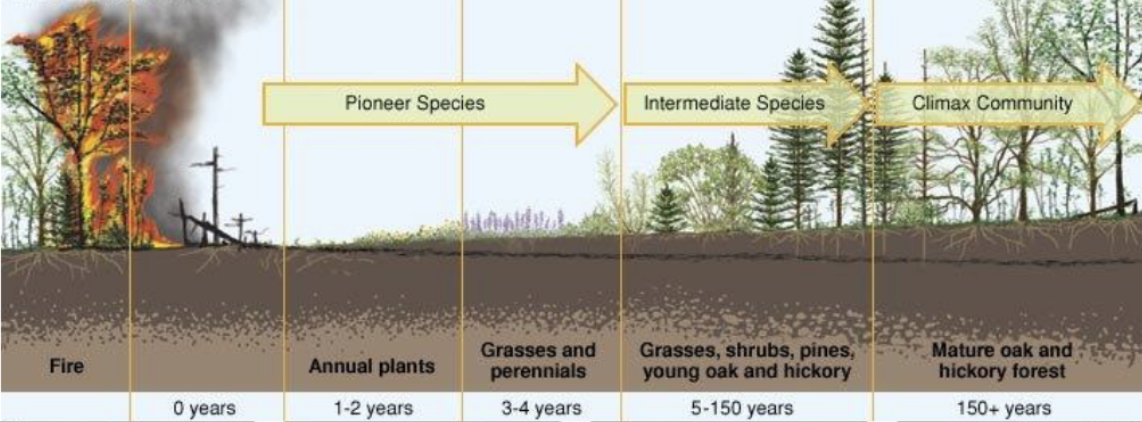
secondary succession
an area that was previously occupied by living things is disturbed, then re-colonized following the disturbance
to represent the common ancestors of those descendants
what are the importance of nodes on a phylogenetic tree in determining evolutionary relationships
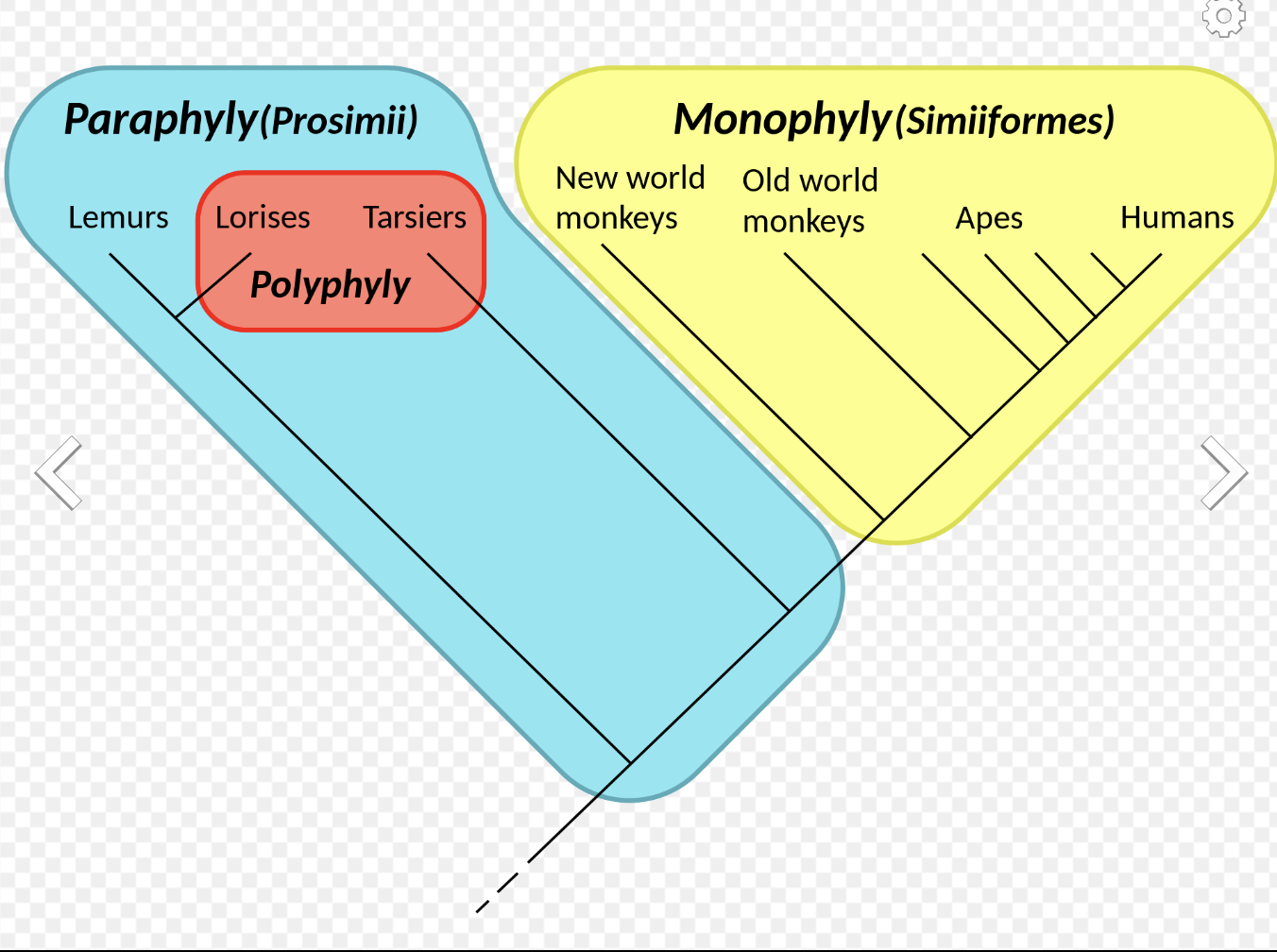
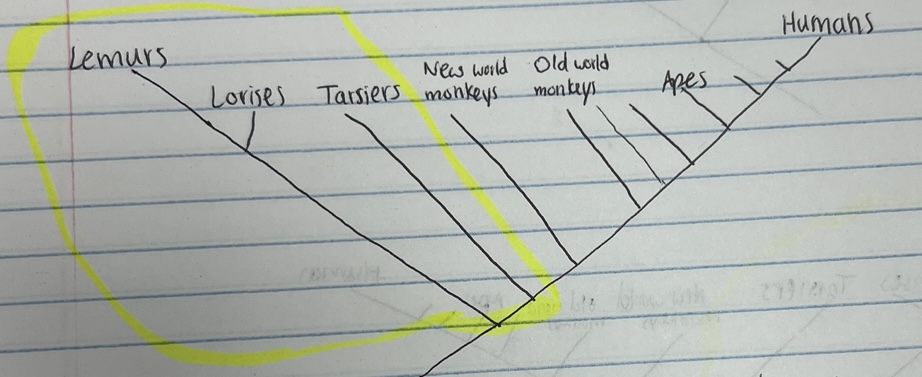
monophyletic group
a group of organisms that share a common ancestor
paraphyletic group
includes a single ancestor and some of its descendants
polyphyletic group
includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but doesn’t include their most recent common ancestor
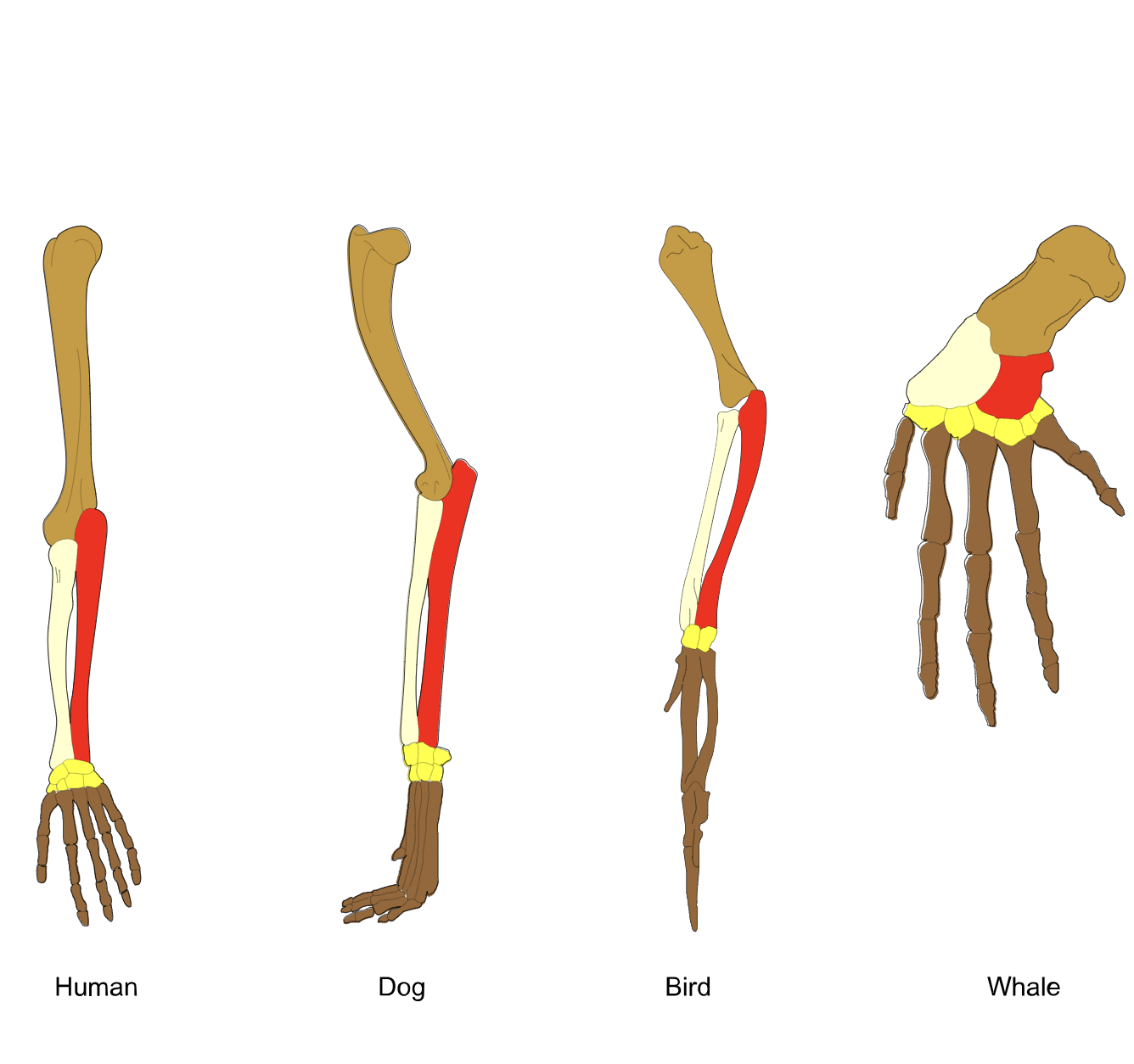
homologous characters
similarity due to shared ancestry
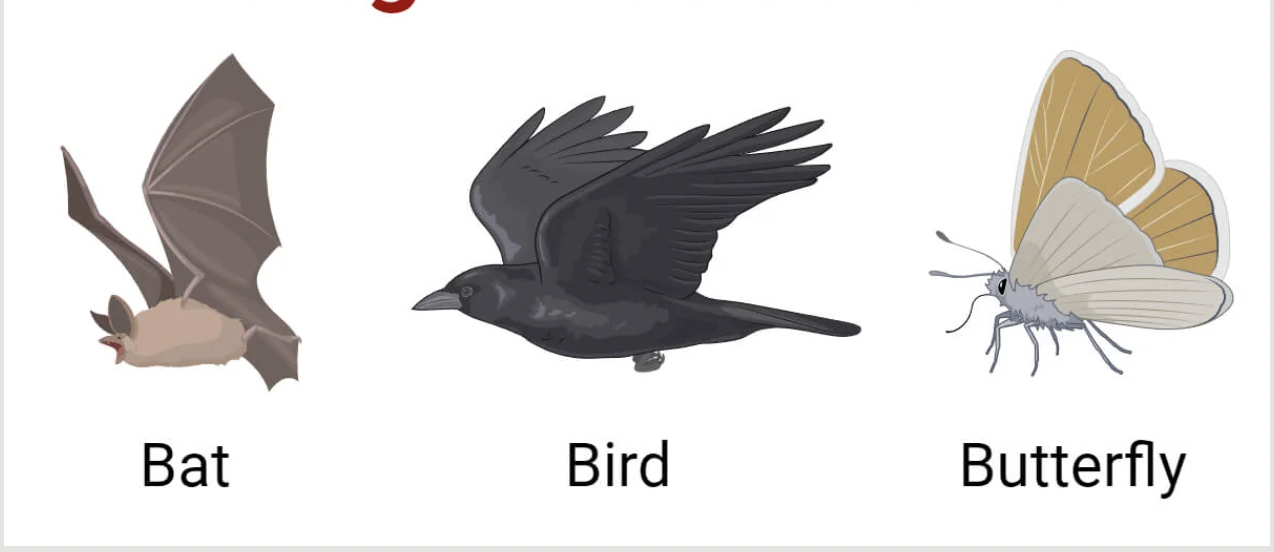

analogous characters
similarity due to convergent evolution or evolutionary reversal
ancestral characters
belongs to everyone in the group
derived characters
new trait that appears on the tree
they create evidence for historical relationships & their associated hierarchical structure (a marker for the most recent common ancestor of the monophyletic group consisting of a set of taxa)
what is the role of synapomorphies (derived characters) in constructing a phylogenetic tree?
Provides more details because there are more characters that can vary among the species
explain the utility of molecular data in constructing a phylogenetic tree
all other things being equal, the best hypothesis is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary changes
explain the principle of parsimony regarding phylogenetic trees
explain the importance of nodes on a phylogenetic tree in determining evolutionary relationships
they represent the common ancestors of those descendants
includes all the groups we are interested in figuring out relationships
ingroup
a group of organisms that don’t belong to those being studied
outgroup

contains an ancestor and all of its descendants
monophyletic group
contains a common ancestor and only some of the descendants of that ancestor
paraphyletic group

do not share a common ancestor
polyphyletic group
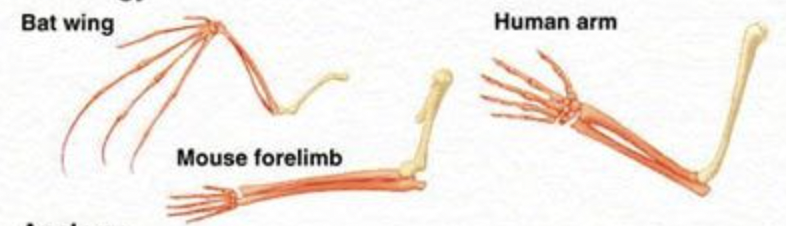
save function & evolutionary origin
homologous characters
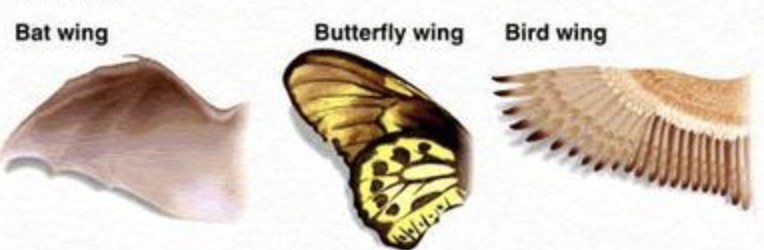
similar function but different evolutionary origin
analogous characters
belongs to everyone in the group
ancestral characters
new trait that evolved within a smaller group of organisms
derived characters
what is the role of synapomorphies (derived characters) in constructing a phylogenetic tree
they provide evidence of evolutionary relationships & help determine which groups share a common ancestor
explain the utility of molecular data in constructing a phylogenetic tree
they compare the sequences of their evolutionary related genes/proteins
explain the principle of parsimony regarding phylogenetic trees
2 hypotheses about vertebrate relationships
what is the importance of sex in maintaining genetic diversity?
allows for the mixing & combination of genes from 2 individuals, creating new genetic combinations in offspring (it does not always increase variation)
zygotic meiosis
haplontic life cycle
gametic meiosis
diplontic life cycle
sporic meiosis
haplodiplontic life cycle (alternation of generations)
explain why protists are a paraphyletic grouping of organisms
it doesn’t contain all descendants of its most recent common ancestor
what are the different modes of locomotion & nutritional strategies of protists
flagella, cilia, & pseudopodia
explain why protists, algae, and protozoa form paraphyletic groups within the eukaryotes
the representative taxa don’t contain all the descendants of their stem species
explain the importance of surface area-to-volume ratio in cell size
to ensure that the exchange of resources & waste occurs quickly enough for the cell to survive
single celled micro-organisms with a defined nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles
unicellular
Composed of multiple cells that are similar to one another, often found in algae
Colonial organisms
simple multicellular