OB Final
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
The skeletal system develops from
mesoderm
By what process is the skeletal system maintained
homeostasis
what is patterning
blueprint
which ossification center develoops earlier
primary
what are the second ossification centers that develop prenatally
distal femoral epiphysis
syndactyly
residual tissue- extra skin
typical limb development is
prox to distal
humerus/femur
radius.ulna & tibia/fibula
carpals and tarsals
meta
phalanges
what forms at 7 weeks
limb buds
what forms at 8 weeks
clavicle and mandible osteogenesis
what forms at 11/12 weeks
primary ossification centers of long bones
what forms at 12/14
hands and feet
what happens at 9-10 weeks
fetal movement
lateral bone
radiusme
medial bone
ulna
for the femur, measure the
proximal onewhat
is the medial larger bone on the side of the big toe
tibia
what is the lateral thinner bone
fibula
if you see the foot of the baby
club- foot should be perpendicular to the tib/fib
ratio of femur
1
oligiohydraminos
affects all systems (lung maturity, MSK development, GI tract)- not enough surfactant in lungs
normal amniotic fluid promotes
normal skeletal development
condensed mesoderm
cartilage—> bone
long bone
metaphysis
where is the primary ossification center on the bone
shaft (diaphysis)
where is the secndary ossification center on the bone
epiphysis
what does condensed mesoderm form
cartilage
GI tract in the baby, you notice the stomach is full and will not empty; what is most likely wrong with the baby? you also see a lot of amniotic fluid
duodenal atresia/ectasia
omphalocele
umbilical abdominal wall defect
how many arteries and veins are in the umbilical cord?
2 arteries, 1 vein
what plate is the chorionic
faces the baby
which plate is the basil
brook
overfilled bladder causes
artificial lengthening of the cervix
cervix should normally measure
2.5-3cm
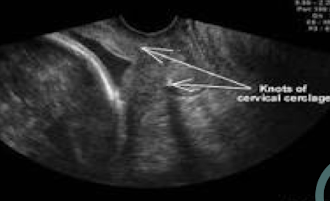
cervical cerclage
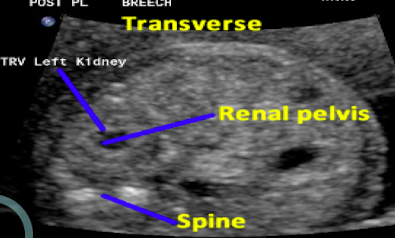
what is this image
transverse image of the kidneys
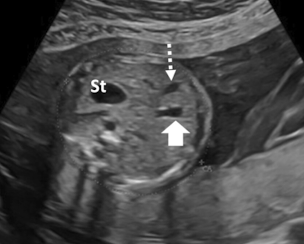
what is the top arrow
gallbladder
what is the umbilical cord colour on US
3 vessels seen- Red, blue, red
what is gastrocesis
abdominal wall defect which does not involve the umbilical cord
what is omphalocele
defect through the umbilical cord, organs go outside of body, membrane covering defect
what is the candy cane view
aortic arch and neck vessels and descending aorta
hockey stick view
ductal arch view
what vessels are seen in the ductal arch view
ductus arteriosis
how wide should the cervix be for the pushing stage
10cm
the cervix should measure more that
2.5cm
should the bowel of the fetus be hyperechoic
no
is an umbilical cord cyst normal in the 1st trimester
yes
is an umbilical cord cyst normal in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters
no- indicated chromosomal abnormalitites
oligoamniotic fluid affects
all systems
during the birthing process, is decrease pH of fetal blood a sign of distress
yes
basal plate calcifications
grade 2
fetal birthing
30seconds
what forms the placenta
chorion frondosum and basalis
a thickness of greater than 4cm before 24 weeks is
abnormal
decidual spiral arteries are responsible for providing blood to the
intervillous spaces
size of gestational sac seen transabdominally
25mm
how will you know if the viteline sace (AKA yolk sac) is too big
usually measures 3-5mm- anything over 6mm is abnormal
double decidual sac sign
capsularis and parietalis
can you tell the difference between vernix and meconium
no
polyhydraminos
tooooo much amniotic fluid- >8cm
normal amniotic fluid
2-8cm
oligohydraminos
too little amniotic fluid- <2cm
AFI- amniotic fluid index
Q1+Q2+Q3+Q4 should add up to >50mm
single vertical >2cm is still considered a fail as per he BPP criteria
true
why is PROM without labour concerning?
infection
what term is given to the normal hardening/ toughening of the skin that occurs in the 2nd trimester
keratinized
what does normal amniotic fluid volume tell us about renal function
that they are working and there is no obstruction
what are sloughed off skin cells in amniotic fluid called
vernix
is AFV measurement of 10cm considered normal?
no
biophysical profile is scored out of 8. what do you need to pass?
it includes fetal breathing movements, fetal movement, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume. need 8/8
fetal breathing
3 or more movements in 30 minutes
fetal tone
flex extremity and make sure they extend and go back to normal
NST and breathing are the first factors to be affected by
asphyxia
modified BPP is normal if NST is reactive and AFI is >5cm
true
fetal breathing decreases significantly
up to 3 days before labour
most important view includes
head, stomach, bowel
what does sparing mean?
decreased resistance to brain
diastolic flow need to be present in
umbilical cord doppler
what does lightening mean
when the baby drops lower in the pelvis- can occur weeks before labour
active labour is when the cervix measures between
4-8cm
what stage is occuring when contractions last longer than 1 minute
transition
which fetal lie gives you more risks
transverse
umbilical cord prolapse is an
emergency
fetal blood pH (acidosis)
results from a lack of oxygen to the fetus
passing of fetal stool
mecondium
twins deliver at
35-36 weeks
quadruplets deliver at
30 weeks
triplets deliver at
32 weeks
what hormone causes the cervix to soften
relaxin
what hormone causes contractions to start
oxytocin
what term is used for softening of the cervix
rippening
what is “false labour” known as
braxton hicks contraction
what 3 vessels are shown in 3 vessel view
pulmonary, aorta, SVC
parity =
of pregnancies carried to 20 weekswh
at structure lies between the thalami and contains CSF
3rd ventricle
whats between the 3rd and 4th ventricle
aqueduct of sylvius and it carries CSF
is double decidual sac sign normal in early pregnancy
yes
during skeletal genesis, what will develop into mesoderm
cartilage
what is the structure that lines the chorion and feeds the fetus
amnion
what is the shunt called in the babys liver that connects to the IVC
ductus venosus
what is the purpose of the ductus arteriosus
connects pulmonary trunk to the aorta