Biotechniques 373 Pre Mid term Notes Review
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Gradually
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
In A Sephadex g-75 Column, It has an Exclusion limit of 3 and 80 KdA If a molecule is 90kd and 100 Kda what will happen when it runs through the column
Both Molecules that are over the exclusion limit of 80 KDa will elute together at the beginning of separation
Which Buffer choice could you use while preforming an ion exchange chromatography with a cation exchanger, Such as Carboxymethyl (PKA:3.5)?
At pH 5 would be the Ideal Buffer pH since the PH would be larger than the pH/pka giving us a Negative charge that would be eluted out since of the Chromatography allowing amino acid samples to enter the The mobile Phase.
What is the Total Volume in the GFC?
(VT)- is the total Volume of the fraction where the Separation ends.
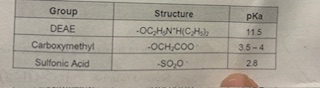
Which if the Following is a Cation exchanger ?
E) both Carboxymethyl and sulfonic acid. Deemed to have A lower PKA creating more Positive charged amino acids thats stays attractive within the column beads
Which of the following proteins would cause a higher absorbance with Coomassie blue?
D) All of the Above
lysine rich ,Arginine , and Histidine-rich proteins Absorbance increases when binded with basic Amino Acids
Where is Colorimetric Assay most USed??
Is deemed to be evaluated/used in most Crude (Impure protein Samples )
How does ninhydrin work?
It binds to the Amino group of Amino Acids
You have isolated some GFP from Bacteria. Which of the following tells you about the purest sample?
Known as the Highest ratio between the Total Amount of GFP over the Total Proteins.
What is Responsible For the Florescence of GFP?
A Sequence of 3 Amino Acids.
How does Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 Dye make proteins quantifiable after binding with them??
it switches the Protein sample absorbance from 465 nm to 595 nm
When making a buffer by titration, you can start only from the weak base
False
Using BSA as Bradford standard is an issue with pure Proteins, not with protein mixes.
True. Since BSA is a purified protein and has a high concentration of basic amino acids can change the Outcome of adding A Bradford assay to the protein solution.
The Kd Value of a Molecule is Always the Same.
True As the resin carries a Certain Exclusion limit the KD( Distribution coefficient will be the same).
How does the Bradford Assay Binding occurs ?
Known through the Dye Coomassie brilliant Blue g-250 within the assays is placed in a Acidic Conditions reacts with the proteins known to be interacted with the Basic Amino Acids through the Aromatic hydrophobic ( water fearing groups ).
How are most Practical buffer made within the Lab?
Known to be Created by the titration when evaluated and used for Lab evaluation
You prepare The Phosphate Buffer By mixing two different Amount of weak acids and conjugate base at the same concertation to the buffer , and the Tris buffer by titration. Why could you adjust the pH with a strong acid/base with the Tris buffer?
e.) the Phosphate buffer created was already at the final volume, the Tris buffer was Not.
Adding HCL (Strong acid) will get to the tris buffer DESIRED PH more quicker
Explain and provide an example of a Cation exchange ?
Known AS Dowex 50 As well As sulfonic Acid and Carboxymethyl. Known to have a smaller PKA . Attractive Positive(+) charged amino acids to stay stationary in the Chromatography. Has negatively (-) charged porous beads placed in the chromatography that binds to opposite charges .
What should be included in a good Buffer ?
Known to be PKA +-1 from its desired pH. The reactivity (should not be able to have a reaction ) within the solution. HAs small minor effect of Changed by temperature and Ionic strength. Chemical Stable and High purity
Describe Anion Exchanger ?
Deemed as the DEAE. Has a Higher PKA known to be attached to negatively charged (-) amino acids. COntains (+) charged Resin beads tend and attracted opposite charges
Detecting AMino acid Sample Eluted Fractions on WHatman paper ?
Known as the molecule of ninhydrin. It turns purple when an amino acid is present. Known to bind with The AMino groups within an amino Acid .(NH2). The darker the Purple colour the more presence of amino acid is detected within the fraction.
Explain the Thin layer Chromatography?
known as the separation process of an amino acids through their degree on polarity based on their R- Group.
Explain the Normal Phase Chromatography ?
Known as the least Polar Amino acid that are taken up with the Solvent and migrated from the stationary more polar molecules and moved closer to the solvent front.
Explain the reverse phase Chromatography ?
Deemed as the Amino acids with High polarity Are migrated Through the Paw solvent To move closer to the solvent front. While the least polar molecule stays stationary and have a lower polarity molecule remains closer to the point of origin.
What is the RF (retention factor Used as )
Known as a Amino acid distance travelled from the point of origin/ over the total distance of migration of a solvent ( also known as the Solvent front).
What is a true Statement about the RF value in the TLC?
Known as the proportional to the percent of time spent of one phase vs the other. Known as the time % spend on a molecule beginning in a mobile phase compared to the stationary phase.
analyzing RF data?
if RF=1 interpreted as a molecule whole duration being spent on at the mobile phase. An RF=0.5 explains a molecule spend 50% of the time within the Mobile phase.
What is the Gel filtration Chromatography ?
Known as a method used to separate A molecule on the basis of size
Explain the process of a protein being smaller then the exclusion limit ?
Example in a sephadex G-75 at 3000 Da/3KD has its lower Limit proteins smaller will cause elution to occur at the end of the separation from all other proteins since it would be stuck and too filled in the porous beads
Explain the process when a protein Mass is larger then the Exclusion limit ?
In a sephadex G-75 Which is upper limit is 80000Da/80kDa.Molecules larger then that limit will be too large to fit within the porous beads Causing the molecule to elute quickly from the column due to the large size.
Explain the VO (Void Volume)?
Known as the Blue-dextran Comes out MW(80,000 DA or more ) evaluated @ 650 nm Where the blue dextran samples appears to be used to evaluate on proteins thats is too big to enter the porous beads. VOlume separation starts
Explain VT (total Elution VOlume)?
Known as DNP -aspartate ( Yellowing) will elute for mw (3000 Da Or less). Evaluated @ 440 nm known as the slowest molecules. and is expressed at the end of the separation.
Explain the KD?
Known as the Distribution coefficient known to act as a Constant for a molecule that does not differ in various other columns. Can also be used to predict where a protein of a known size can be eluted out.
How is the Purity of the GFP ( Green Fluorescent protein evalued ?
Know to be Done through the Estimating of each sample of the GFP over the total mass of each protein.
How Does NTA (Nitrilotriacetic acid) operate in this process ?
Known as the divalent metal cations being immobilized to the beads of a column matrix through the hydrocarbon support.
How are Binding of Ni working when in the IMAC?
Known as Bonding to Two Histidine Molecules that are side by side Each other then when bonded with Ni2+ (Divalent Cation) It gets folded and turns into the NTA (Nitrilotriacetic acid) from the histidine molecules.
Where does the proteins being added to a Poly hIS -stretch?
Known to be bonded within the N (nitrogen) or C(Carbon) terminus. The protein recombinant are places @ 5’ or 3’ end of the polyhistidine sequence.
Use of Imidazole @ Higher concertation ?
Deemed as a way/process of eluting and Isolating the deemed his-tagged protein need for Evaluation
Issues with Imidazole ?
Deemed to have a higher affinity for the metal cations Resulting with it outcompeting with the histidine molecules out of the IMAC matrix
When preforming a Put -down experiment with Ni2+ NTA, How could you explain that you have too much GFP In the washes sample and almost Non in the Final elute sample?
The reasoning behind this could occur through the LAck of adequate bonding time of the Tagged proteins with the divalent CAtion NI 2+. As well Low Affinity or missing a Histidine which could of been inaccessible or degraded causing the Divalent cations to not having high attraction when bonding to a protein. Lastly Too much protein over stimulating the resin Leaving the GFP unbounded to the NTA Matrix