Biology Exam Grade 11
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
Last updated 10:31 PM on 12/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Cycle
\n
a series of steps during which the chromosomes and other cell material double to make two copies.
a series of steps during which the chromosomes and other cell material double to make two copies.
2
New cards
Mitosis
Where all of the cells chromatids are evenly divided and they move to opposite ends of the cell to form new cells for growth and repair of damaged tissue
3
New cards
Chromatids
Uncoiled Chromosomes
4
New cards
Chromosomes
A structure found inside the nucleus of a cell. Made up of proteins and DNA organized into genes. Each cell normally contains 23 pairs
5
New cards
Centromere
a chromosome constricted region which separates it into a short arm and a long arm.
6
New cards
Prophase
Chromatin sondense and thickens, nuclear membrane and nucleus disappears, centriole migrate to opposite poles, spindle fibres start to form
7
New cards
Metaphase
Spindle fibres attach to centimetre, chromosomes guided to middle of the cell
8
New cards
Anaphase
Spindle fibres pull chromatids to opposite poles of the cell
9
New cards
Telophase
Chromatids reach opposite poles, begin to unwind
10
New cards
Cytokenesis
The cell divides all the cytoplasm and organelles then it forms new cell membranes
11
New cards
Meiosis
The process by which sex cells or gametes are made. This process is also called gameto genesis
12
New cards
Haploid
a cell that contains a single set of chromosomes
13
New cards
Diploid
the presence of two complete sets of chromosomes in an organism's cells, with each parent contributing a chromosome to each pair.
14
New cards
Autosome
one of the numbered chromosomes, as opposed to the sex chromosomes. Humans have 22 pairs of ________ and one pair of sex chromosomes
15
New cards
__**Spermatogenesis**__
**The process by which male testes germ cells undergo meiosis to form sperm. Each diploid primary spermatogonium forms two haploid secondary spermatocytes, which divide to produce four haploid sperm.**
16
New cards
__**Oogenesis**__
The process by which a diploid oogonium germ cell in the ovary undergoes meiosis to form ovum. This results in one haploid ovum and three haploif polar bodies.
17
New cards
__**Fertilization**__
Occurs when a haploid sperm (N) enters a haploid egg (N). Fertilazation forms a diploid zygote. The zygote is the first somatic cell.
18
New cards
Sex Chromosome
type of chromosome involved in sex determination.
19
New cards
homologous Chromosome
The chromosomal pair which contains the maternal as well as the paternal chromatid of the same length and gene position, and are joined by the centromere
20
New cards
sex-linked inheritance
haracteristics (or traits) that are influenced by genes carried on the sex chromosomes.
21
New cards
crossing Over
Occurs during meiosis prohase I. When homologous chromosomes overlap and exchange portions o their chromatids.
22
New cards
Allele
Alternate forms of genes
23
New cards
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism due to the alleles present in the genes
24
New cards
Phenotype
A particular physicial appearance produced by the alleles in a gene
25
New cards
Co-dominance
Both alleles are expressed at the same time,
26
New cards
Incomplete Dominance
Occurs when 2 alleles are equally domimant and the heterozygous individuals produce a new phenotype
27
New cards
random assortment
Happens when pollen fertilizes ovum from a different plant
28
New cards
__**Law of Segregation**__
States that inherited traits are determined by pairs of genes and that each of the genes separates into separate gametes
29
New cards
__**Law of Independent Assortment**__
States that inheritance of one trait does not affect the inheritance of alleles for another trait
30
New cards
Multiple Allele
Some traits have more than two alleles, creating more phenotypic combinations. Example Blood
31
New cards
Genome
The whole hereditary info of an organism that is encoded in the DNA
32
New cards
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms.
33
New cards
Mutation
alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA
34
New cards
Recessive
relating to a gene (= chemical pattern) that causes a particular characteristic only when it is passed on by both parents.
35
New cards
Dominant
An allele of a gene when it effectively overrules the other (recessive) allele.
36
New cards
Sex Linkage
Genes located on a sex chomosome
37
New cards
Non-disjuction
the failure of the chromosomes to separate, which produces daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes.
38
New cards
Albinism
reduced amount of melanin, or no melanin at all.
39
New cards
muscular dystrophy
group of muscle diseases caused by mutations in a person's genes. Over time, muscle weakness decreases mobility, making everyday tasks difficult.
40
New cards
karyotype
an individual's complete set of chromosomes
41
New cards
Down Syndrome
a condition in which a person has an extra chromosome.
42
New cards
Gene Therapy
a medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material.
43
New cards
genetic engineering
a process that uses laboratory-based technologies to alter the DNA makeup of an organism. This may involve changing a single base pair (A-T or C-G), deleting a region of DNA or adding a new segment of DNA
44
New cards
Segregation
describes how pairs of gene variants are separated into reproductive cells.
45
New cards
heterozygous
Express or show the dominant allele, the recessive allele is not able to be expressed
46
New cards
Homozygous
Pure breeding individuals (both dominant or both recessive)
47
New cards
Hybrid
An individual formed by mating between unlike forms, usually genetically differentiated populations or species.
48
New cards
Pedigree
A diagram of family history that uses standardized symbols.
49
New cards
hemophilia
an inherited bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly
50
New cards
kingdom
***the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain***.
51
New cards
domain
highest taxonomic rank in the hierarchical biological classification system, above the kingdom level.
52
New cards
taxon
each kingdom is subdivided into a series of progressively smaller groups
53
New cards
Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms. Developed by Carolus Linnaeus. Used simple characteristics to identify species and organize them into groups.
54
New cards
phylogeny
a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor.
55
New cards
hierarchical classification
a system of grouping things according to a hierarchy, or levels and orders.
56
New cards
binomial nomenclature
the biological system of naming the organisms in which the name is composed of two terms, where, the first term indicates the genus and the second term indicates the species of the organism
57
New cards
morphology
the study of the size, appearances, and internal relationships of animals, plants, and microbes.
58
New cards
species
a group of organisms that can reproduce with one another in nature and produce fertile offspring.
59
New cards
Prokaryotes
organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Divided into two distinct groups; the bacteria and the archaea
60
New cards
eukaryote
any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus.
61
New cards
autotroph
an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals.
62
New cards
heterotroph
an organism that eats other plants or animals for energy and nutrients.
63
New cards
Plantae
includes all the plants. They are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic organisms.
64
New cards
Animalia
Largest kingdom, multicellular eukaryotes. Do not possess chlorophyll or a cell wall
65
New cards
Protista
Simple eukaryotic organisms. Mostly unicellular, most live in water, damp terrestrial environments or even as parasites.
66
New cards
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms such as yeasts, moulds, and mushrooms. Contain a cell wall, and are heterotrophs.
67
New cards
Bacteria
single-celled organisms
68
New cards
Archaea
a group of prokaryotic life, lack cell nuclei and therefore prokaryotes
69
New cards
Virus
Do not have cells, can’t make protein themselves. Can’t use energy. Without hosts they are simple group of chemicals.
70
New cards
lytic cycle
A reproduction process, where the the virus attaches to the cell surface, and chemically recognizes the host. Then makes proteins and nucleic acids, using the host cell as a slave. New viruses are assembled, and new virus particles are released into the infected cells
71
New cards
Lysogenic Cycle
Where a virus can insert their genome into the host cell genome for long periods of time. These viruses are called proviruses. Can switch into lytic cycle
72
New cards
capsid
the protein shell of a virus particle surrounding its nucleic acid.
73
New cards
methanogens
Microorganisms that create methane as a byproduct of their metabolism
74
New cards
halophiles
microorganisms that require certain concentrations of salt to survive, and they are found in both Eubacterial and Archaeal domains of life
75
New cards
thermoacidophiles
microorganisms that have developed mechanisms to successfully persist in unusually hot, acidic environments
76
New cards
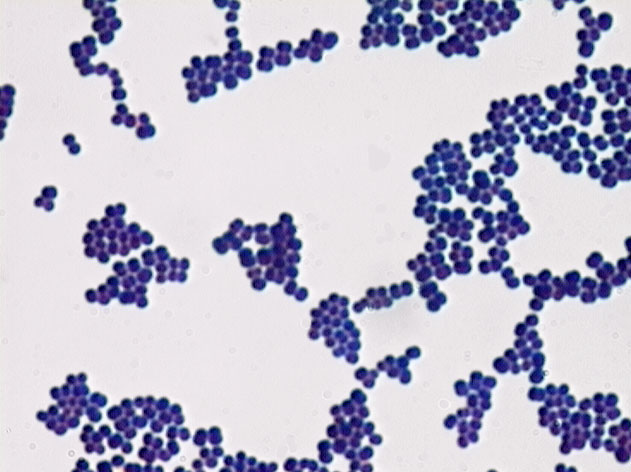
Coccus
a spherical-shaped bacterium
77
New cards
Spirilli
curved-shaped bacteria which can range from a gently curved shape to a corkscrew spiral
78
New cards
diplo-
a combining form used like a prefix meaning “double” or “in pairs.”
79
New cards
staphylo-
Cells arranged in clusters resembling grapes
80
New cards
Strepto-
Cells arranged in a chain
81
New cards
Gram stain
a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial species into two large groups (gram-positive purple and gram-negative pink).
82
New cards
binary fission
asexual reproduction by a separation of the body into two new bodies.
83
New cards
Conjugation
the process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact.
84
New cards
pili
short, hair-like structures on the cell surface of prokaryotic cells.
85
New cards
transformation
specific process where exogenous genetic material is directly taken up and incorporated by a cell through its cell membrane.
86
New cards
endospore
A differentiated cell formed within cells of certain Gram-positive bacteria that are extremely resistant to heat and other harmful conditions and agents.
87
New cards
Antibiotic
Medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria in humans and animals by either killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply
88
New cards
bacillus
rod-shaped, endospore-forming aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, Gram-positive bacteria;
89
New cards
protozoa
one-celled animals found worldwide in most habitats.
90
New cards
algae
a group of predominantly aquatic, photosynthetic, and nucleus-bearing organisms that lack the true roots, stems, leaves, and specialized multicellular reproductive structures of plants
91
New cards
slime moulds & water moulds
Fungus-like protists that grow as slimy masses on decaying matter. fungus-like protists present in moist soil and surface water; they live as parasites or on decaying organisms.
92
New cards
cilia
small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of all mammalian cells
93
New cards
flagella
microscopic hair-like structures involved in the locomotion of a cel
94
New cards
hyphae
The fine, branching tubes which make up the body (or mycelium) of a multicellular fungus
95
New cards
mycelium
the vegetative part of a fungus or fungus-like bacterial colony, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae.
96
New cards
septa
The two sides of the heart are separated by a thin tissue wall
97
New cards
zygospore
The spores produced by fungus and protists
98
New cards
Fruiting Body
spore-containing fungal structures. part of the sexual phase of a fungal life cycle.
99
New cards
lichen
a small group of plants of composite nature, consisting of two dissimilar organisms, an alga and a fungus living in a symbiotic association.
100
New cards
seed
the part that develops from the ovules after fertilization.