WBC 2: BM, Non-Malignant WBC Disorders
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
____ refers to the ratio between red marrow and yellow marrow.
cellularity
phagocytic cells in connective tissue:
histiocytes
a ____ refers to an aspirate collection where there is no liquid available.
dry tap
a BM evaluation of an aspirate specimen is examined under low power (x10) to detect the presence of ____.
spicules
____ refer to relatively intact marrow consisting of hematopoietic and stromal cells.
spicules
____ stain dark blue/purple in the BM.
spicules
aspirate differential is performed under ____ magnification.
x100
the ____ series includes blasts, segs (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils).
myeloid
all stages of development should be present but within their anticipated distribution during a BM differential count. true or false?
true
what is the range for normal M:E ratio?
1.5:1 to 3.3:1
the ____ tissue occupies 1.5 to 3.3 times more space than the erythroid precursors.
granulopoietic
the reason granulopoietic tissue occupies 1.5 to 3.3 times more space than erythroid precursors is because of the ____ survival of granulocytes in circulation.
shorter
____ objective lens refers to low power.
x10
____ objective lens refers to high power.
x50 and x100
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when assessing peripheral blood dilution?
x10
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when finding bony spicules and areas of clear cell morphology?
x10
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when observing fat to marrow ratio and estimate cellularity?
x10
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when searching for tumor cells in clusters?
x10
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when examining and estimating megakaryocytes?
x10
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when observing myelocytic and erythrocytic maturation?
x50 and x100
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when distinguishing abnormal distribution of cells or cell maturation stages?
x50 and x100
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when performing differential count on 300 to 1000 cells?
x50 and x100
during a BM aspirate examination, which lens should be used when computing M:E ratio?
x50 and x100
megakaryocytes are too unevenly distributed to count in a differential. true or false?
true
clusters of megakaryocytes may indicate ____.
hyperplasia
<2 ____ per low power field may indicate hypoplasia or poor quality aspirate.
megakaryocytes
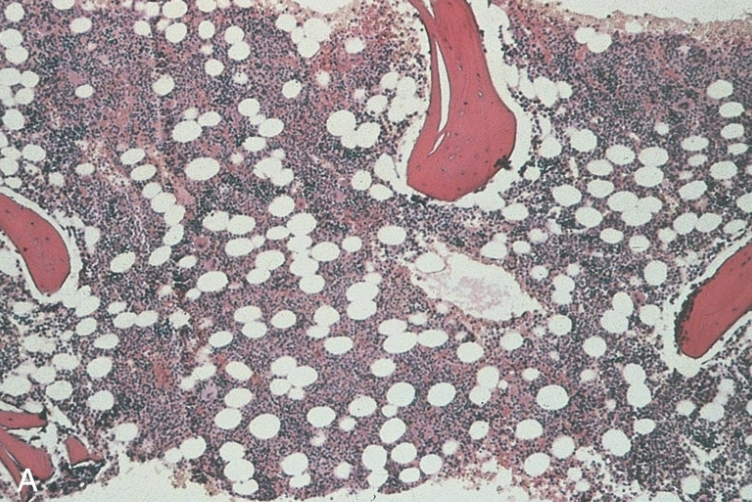
classify the cellularity. include ratio.
normal; 1:1
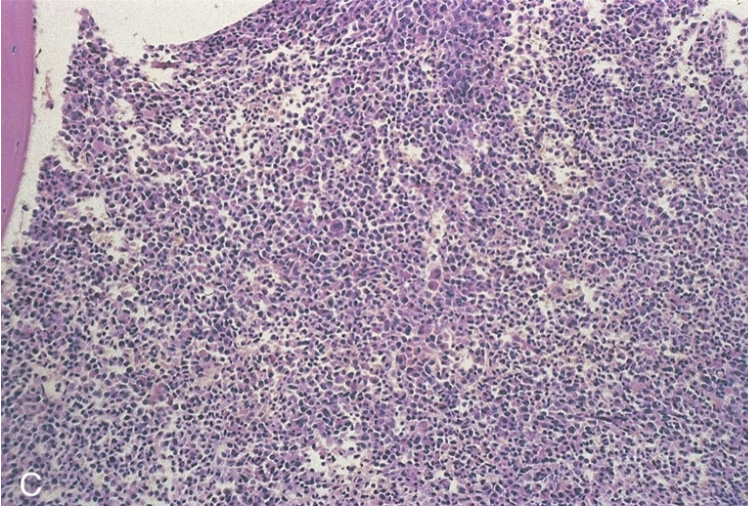
classify the cellularity. include ratio.
hypercellular; 10:1
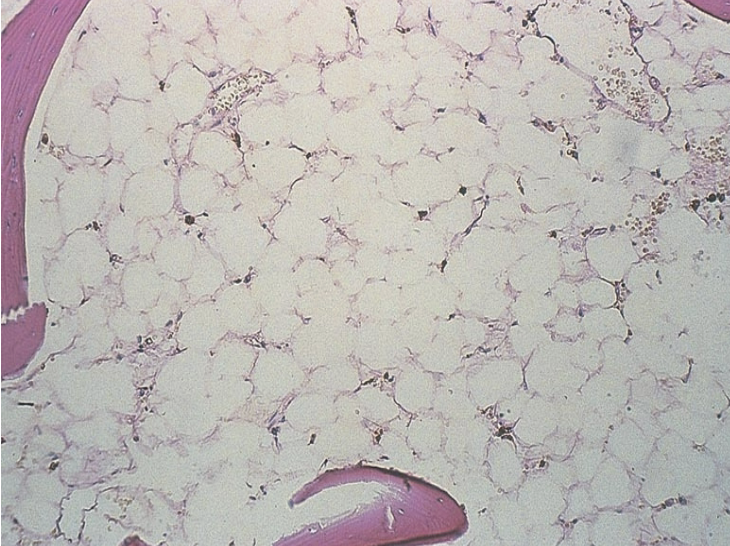
classify the cellularity. include ratio.
hypocellular; 1:10
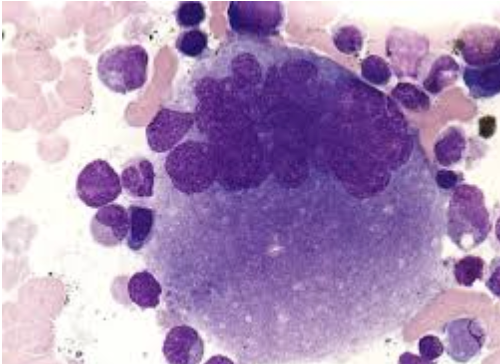
is this an early or late megakaryocyte?
early
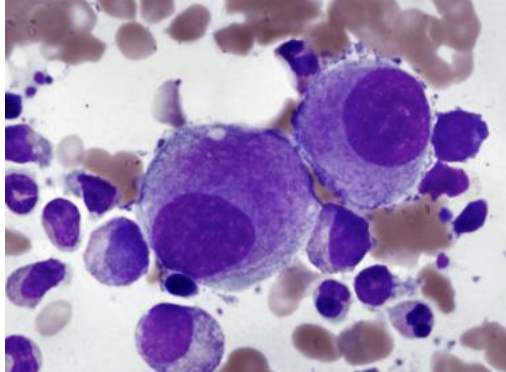
is this an early or late megakaryocyte?
late
identify this cell.
mitotic cell
the ratio of all nucleated hematopoietic cells (ANC/red marrow) to fat cells (yellow marrow):
cellularity
general rule to estimate normal cellularity for age is ____.
100 - age (±10)
individuals ages 1-3 years old tend to have a higher relative amount of ____.
lymphocytes
absolute neutrophilia is benign. true or false?
true
____ refers to a shift in neutrophils from marginal into circulatory pool.
absolute neutrophilia
can be caused by stress, trauma, labor, strenuous exercise, shock, burn, or increase in epinephrine:
absolute neutrophilia
absolute neutrophilia cannot occur in infections. true or false?
false
the release of neutrophils from the storage pool to peripheral blood is associated with ____.
absolute neutrophilia
describes an increased number of immature cells as an indicator of infection:
left shift
refers to an increase in bands, metamyelocytes (possibly myelocytes):
left shift
usually seen with neutrophilia and toxic changes:
left shift
left shift is associated with an increased release from ____.
storage pool
refers to a reactive leukocytosis above 50 × 103/uL with neutrophilia and a marked left shift, bands, and often metas/myelo could have rare pro or blast:
leukemoid reaction
____ are mostly a result of:
severe and/or chronic infection (e.g., TB, pneumonia)
metabolic disease
inflammation
response to a malignancy
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: normal count and morphology of eosinophils and basophils?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: toxic granulation and dohle bodies often seen in neutrophils?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: normal PLT count?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: normal PLT morphology?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: normal hemoglobin?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: elevated LAP score?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: normal genetics?
leukemoid reaction
leukemoid reaction or CML: often elevated and may show granulation in eosinophils and basophils?
CML
leukemoid reaction or CML: may see pseudo-pelger huet forms?
CML
leukemoid reaction or CML: elevated early and decreased late for PLT counts?
CML
leukemoid reaction or CML: possible giant, hypogranular, and/or bizarre forms for PLT morphology?
CML
leukemoid reaction or CML: often anemic hemoglobin?
CML
leukemoid reaction or CML: decreased LAP score?
CML
leukemoid reaction or CML: positive for t(9;22), BCR-ABL?
CML
what test is used to differentiate leukemoid reaction and CML?
LAP score
associated with the presence of immature neutrophils, nRBCs, and teardrop RBCs in the same sample:
leukoerythroblastic reaction
leukoerythroblastic reaction is often accompanied by neutrophilia, but not always. true or false?
true
____ point to the possibility of a space-occupying lesion in the BM:
metastatic tumor
fibrosis
lymphoma
leukemia
leukoerythroblastic reaction
strongly associated with primary myelofibrosis:
leukoerythroblastic reaction
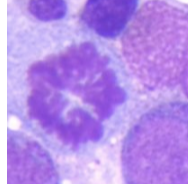
what nuclear abnormality is associated with the following:
chronic infections
megaloblastic anemia
drugs
hypersegmented neutrophils
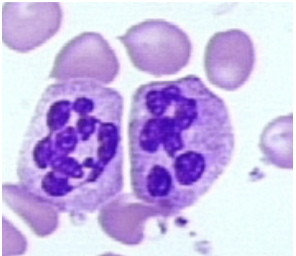
what nuclear abnormality is associated with the following:
myelodysplastic syndromes
asynchrony of nuclear maturation
very clumped chromatin
hyposegmented neutrophils
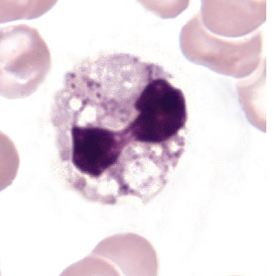
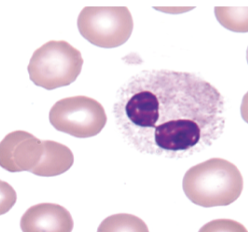
what nuclear abnormality is associated with the following:
dying cell
nucleus very dark/dense
filaments still visible
pyknotic neutrophils
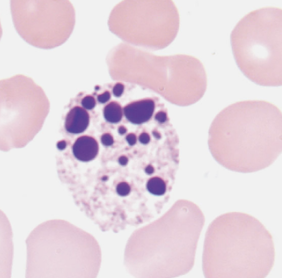
what nuclear abnormality is associated with the following:
dead cells
no filaments
necrotic neutrophils
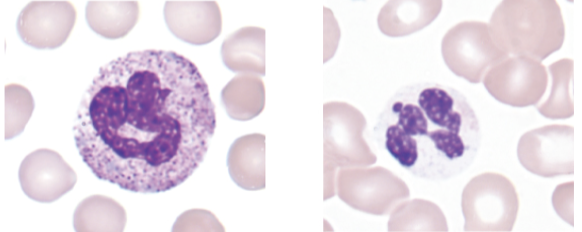
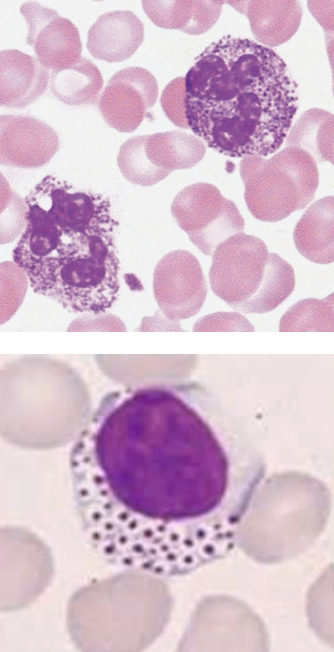
what image (left or right) shows the cytoplasmic abnormality associated with the following:
absence of granules
degranulation
hypo- or -agranular
right
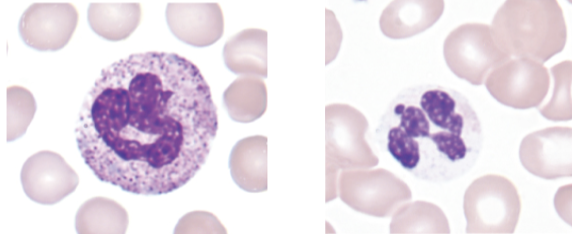
what image (left or right) shows the cytoplasmic abnormality associated with the following:
abnormal granules present
left
refers to dark, blue-black cytoplasmic granules present only in neutrophils:
toxic granulation
associated with inflammation, infection, administration of granulocyte colony stimulation factor (G-CSF):
toxic granulation
refers intracytoplasmic pale blue round or elongated bodies between 1 and 5 um in diameter, usually adjacent to cellular membranes:
dohle bodies
nonspecific finding or associated with bacterial infections, sepsis, and pregnancy:
dohle bodies
refers to small to large circular clear areas in cytoplasm, rarely may contain organism:
toxic vacuolation
associated with the following:
septicemia or other infection
autophagocytosis secondary to drug ingestion, acute alcoholism or storage artifact
sometimes seen in conjuction with toxic granulation
toxic vacuolation
often seen with toxic granulation and can indicate phagocytosis, may contain bacteria and other material:
toxic vacuolation
remnants of ribosomal RNA:
dohle bodies
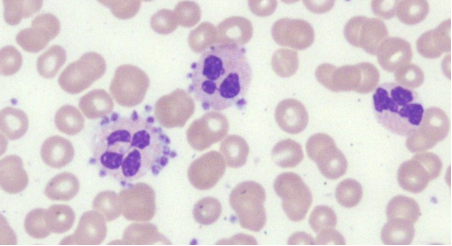
identify the image:
platelet satellitism
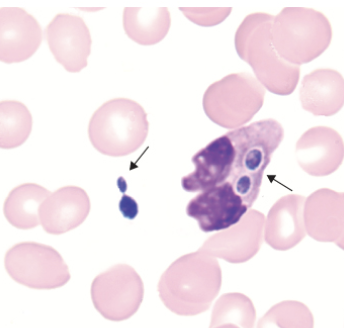
identify the image:
yeast
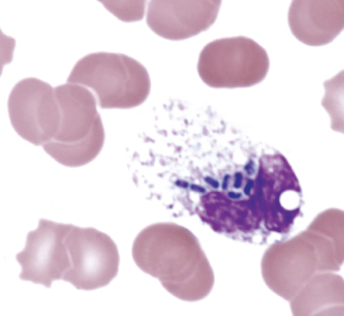
identify the image:
bacilli
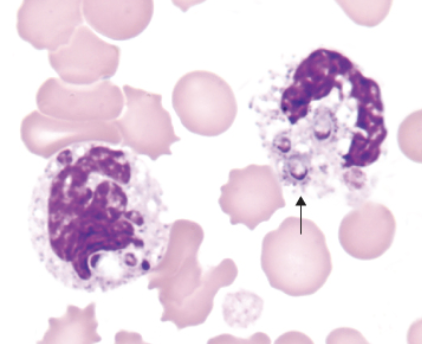
identify the image:
histoplasma capsulatum
autosomal dominant condition where there is hyposegmentation of neutrophils:
pelger huet anomaly
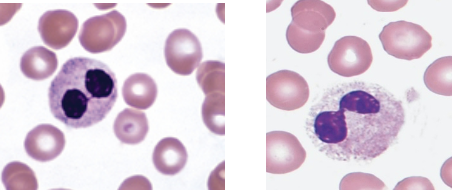
which state of pelger huet anomaly refers to the following:
bi-lobed nucleus
dense heterochromatin
incomplete nuclear segmentation
aka dumbbell or prince nez
heterozygous
which state of pelger huet anomaly refers to the following:
nucleus is round or oval
no segmentation
homozygous
in pelger huet anomaly, about what percent of neutrophils are affected?
70-90%
what condition can be caused by the following:
induced by drugs
seen in patients with HIV, tuberculosis and mycoplasma pneumonia, severe bacterial infections
secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome, acute leukemias and chronic myeloproliferative disorders
pseudo pelger huet
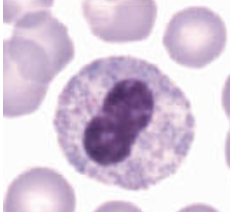
autosomal recessive condition characterized by abnormally large metachromatic granules in the cytoplasm of ALL types of WBCs (granulocytes, monocytes, lymphocytes):
alder reilly anomaly
incomplete degradation of mucopolysaccharides is associated with:
alder reilly anomaly
mucopolysaccharide deposits (granules) in most cells are associated with:
alder reilly anomaly
alder reilly anomaly affects leukocyte function. true or false?
false
deep purple to lilac granules that appear in all types of WBCs:
alder reilly anomaly
what condition may resemble promyelocytes or heavy toxic granulation?
alder reilly anomaly
neutrophilia, dohle bodies and left shift are associated with:
toxic granulation
autosomal dominant condition characterized by giant and bizarre platelets and may be hypogranular:
may hegglin anomaly
platelet disorder (thrombocytopenia with giant forms) that displays with leukopenia with large basophilic inclusions:
may hegglin anomaly
large basophilic inclusions:
dohle like bodies
patients are usually asymptomatic or have mild bleeding disorders:
may hegglin anomaly
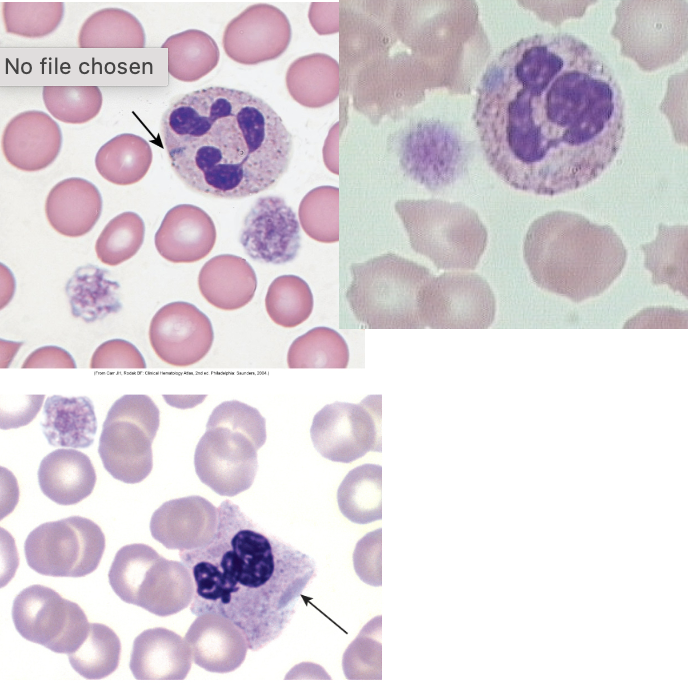
identify the image:
may hegglin anomaly