Chapter 12 Nervous system
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
the nervous system contains
neurons and neuroglia
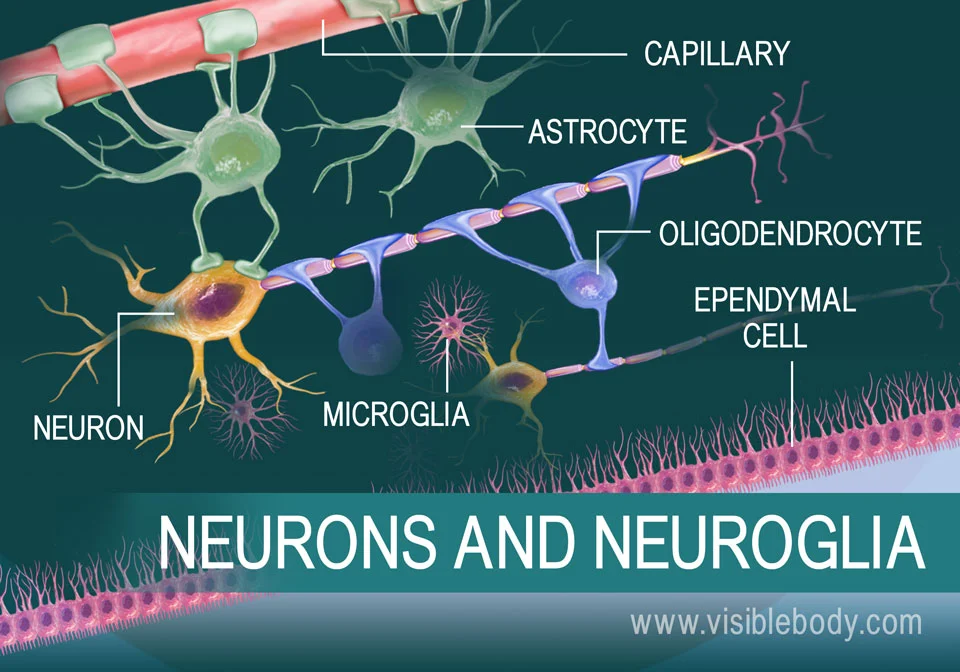
neurons
intercellular communication
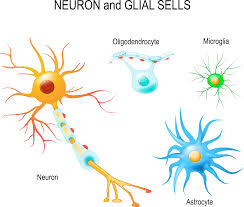
Neuroglia
essentials survival functions of neurons
preserve structure of nervous tissue
The brain and spinal cord consist of
nervous tissue connective tissue and blood vessels
The brain and spinal cord receive sensory information’s from
inside and outside body
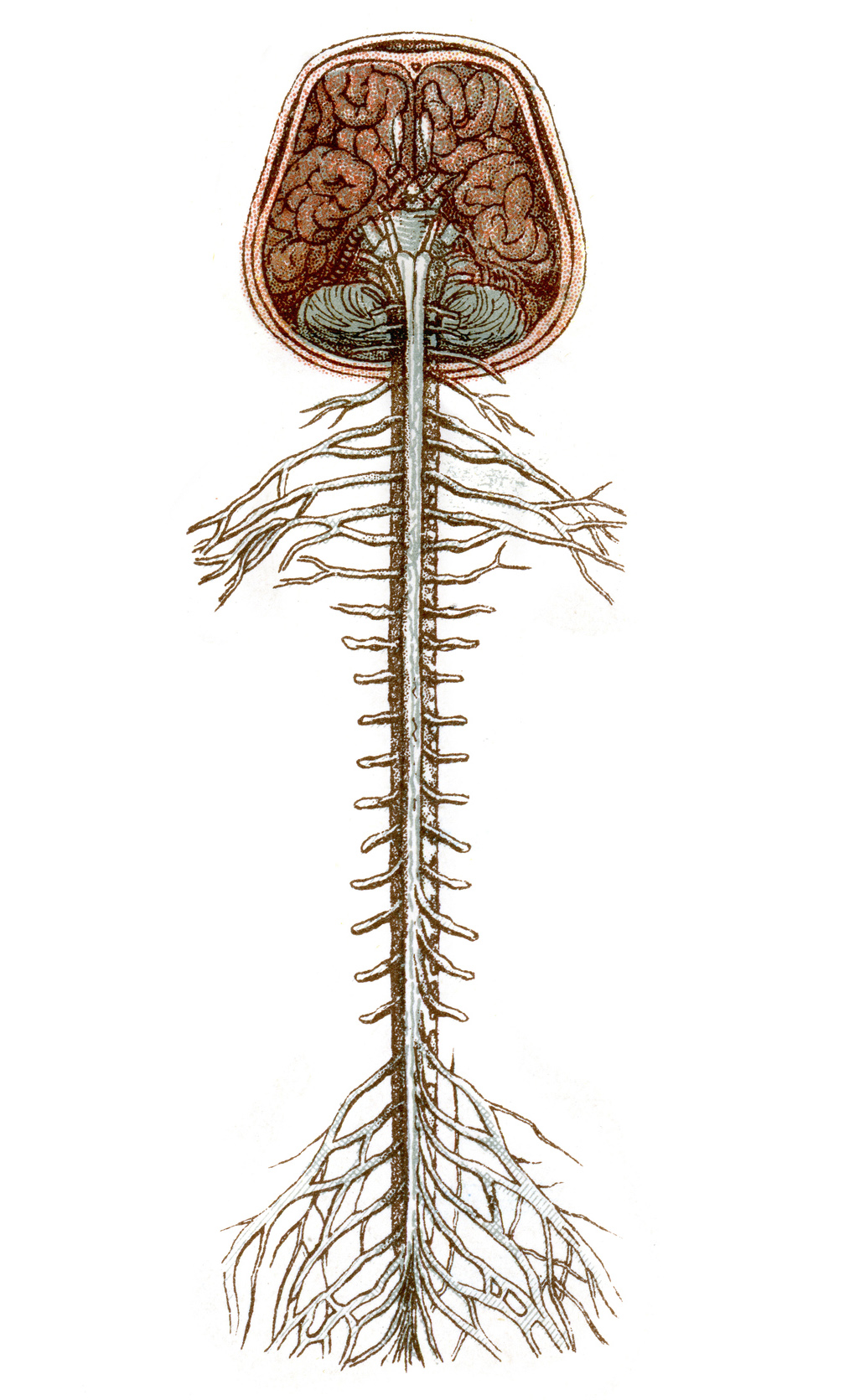
The brain and spinal cord functions to
process and coordinate sensory data
Brain spinal cord generates more commands to
control actives of peripheral organs (ex: skeletal muscles, glands, viscera)
Higher functions of the brain include
intelligence, memory, learning, and emotion.
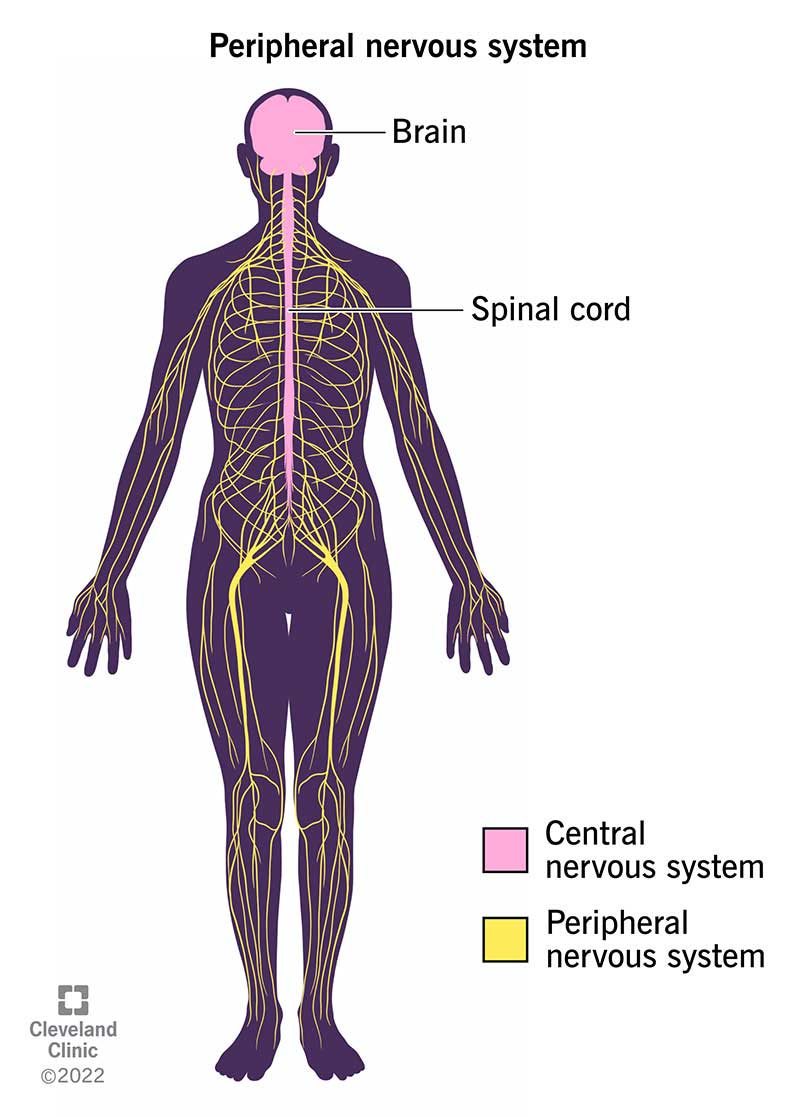
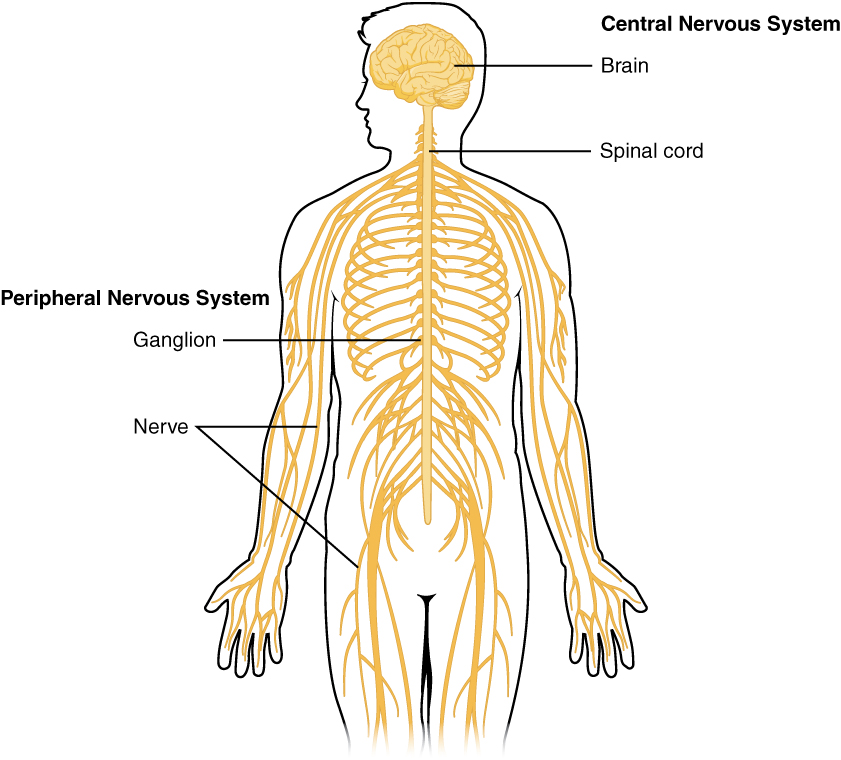
The Peripheral nervous system includes all nervous tissue outside the
CNS, and ENS
Where does the Peripheral nervous system deliver sensory information to
the Central Nervous System
Where does the Peripheral Nervous System carries motor commands to
peripheral tissue
Bundles of axons with
connective tissues and blood vessels
Carry sensory
information and motor commands
How many sensory Cranial Nerves connect to the brain
12 pairs
How many spinal nerves attach to the spinal cord
31 pairs
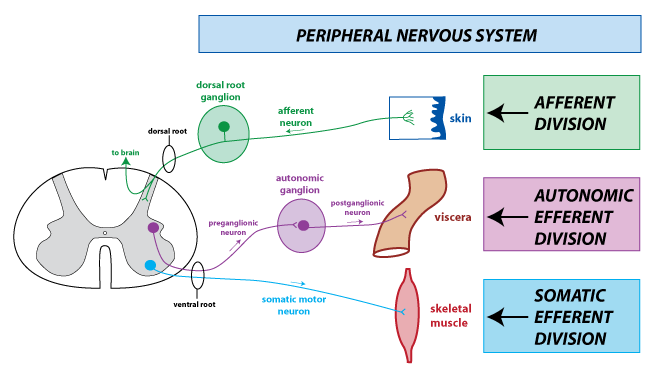
Afferent division
carries sensory information
Afferent division carry receptors in the
peripheral tissues and organs to the CNS
Efferent division
carries motor commands
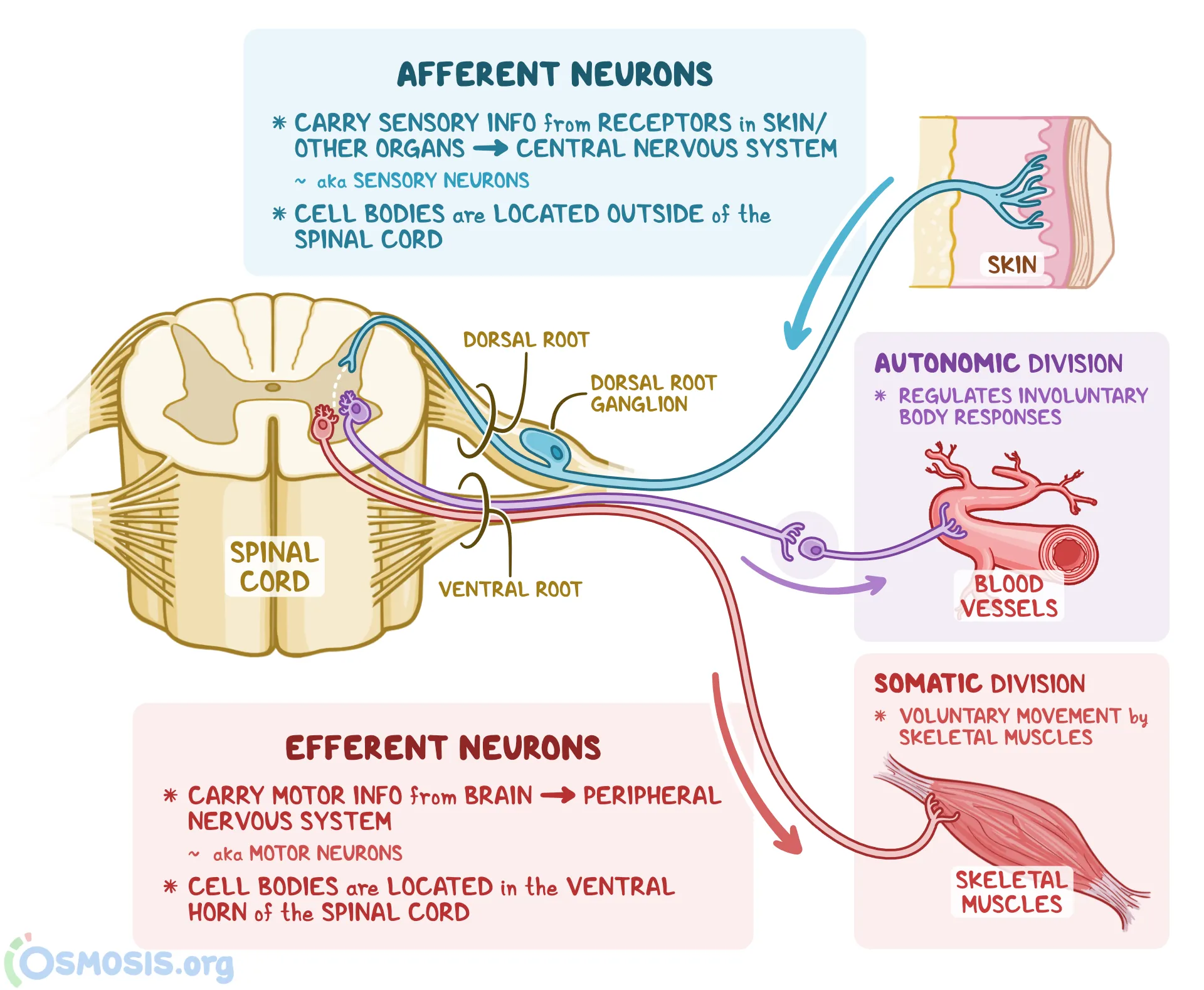
Efferent division from
CNS to muscles, glands, and adipose tissue
Divisions of the Nervous System are functional divisions of the
PNS
Receptors detect
changes respond to the stimuli
Receptors can be
neurons and specialized
Receptors may be
single cells or complex sensory organs (EG: eyes, ears)
Effectors target
organs that respond to motor commands
Examples of Effectors
skeletal, muscles, glands, viscera
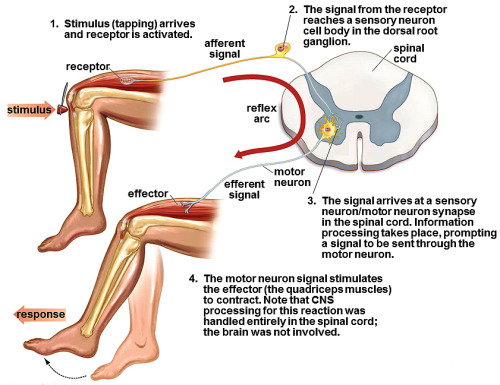
Efferent divisions of
PNS
Somatic nervous system controls
skeletal muscle contractions
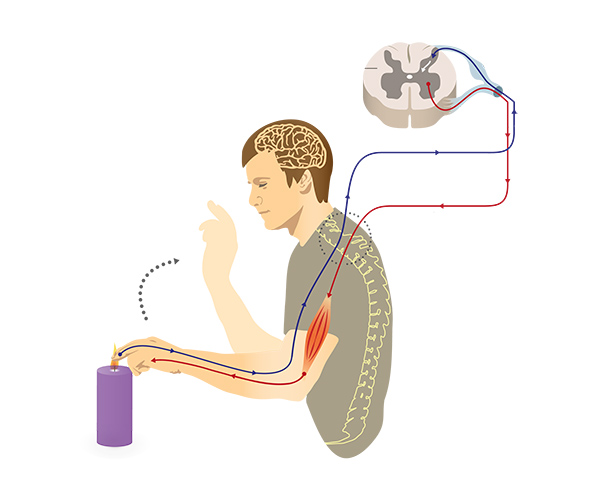
Somatic nervous system can be both
voluntary and involuntary (reflexes)
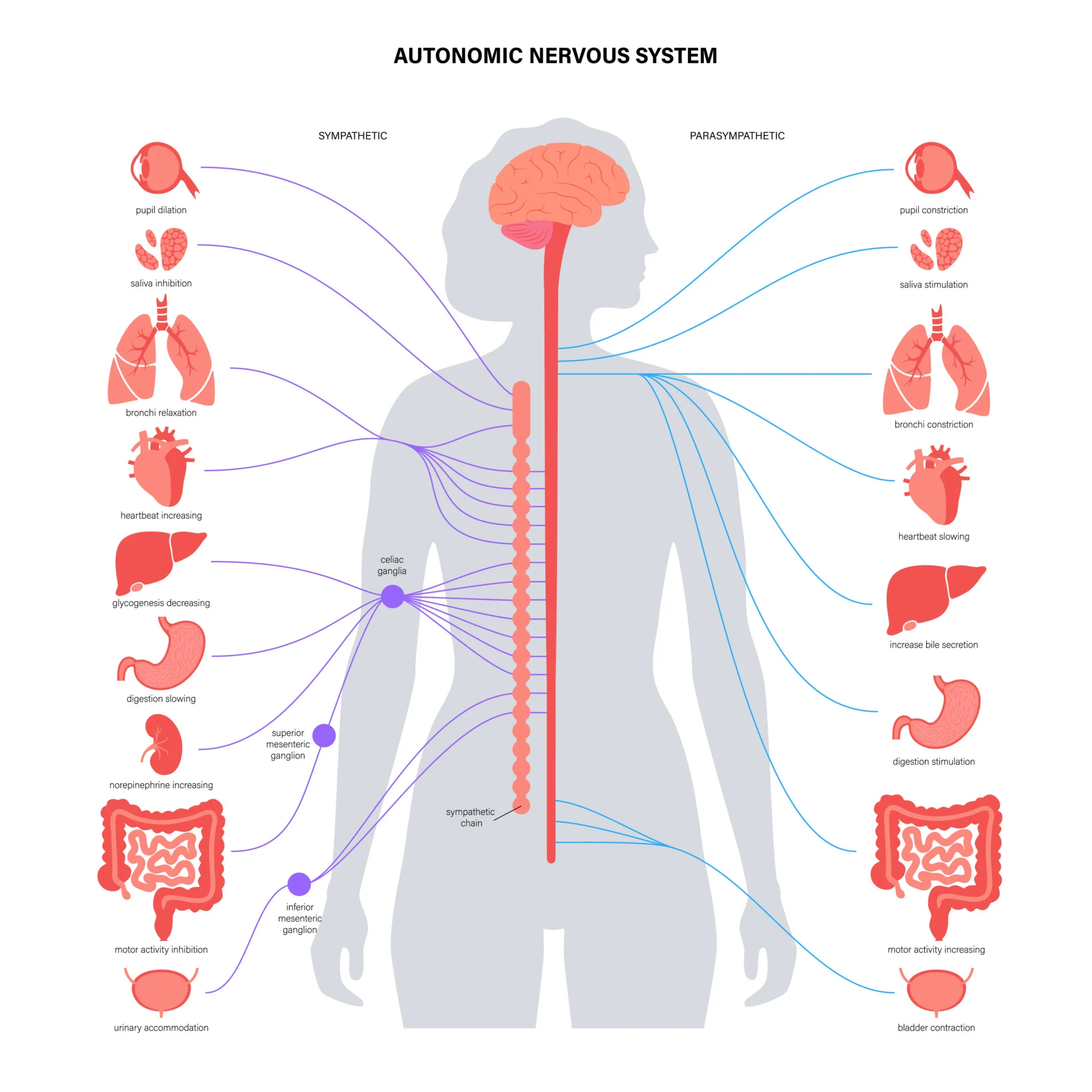
What do Automatic nervous system control
subconscious actions, contractions of smooth and cardiac muscle and glandular secretions
Sympathetic division
has stimulating effect (fight or flight response)
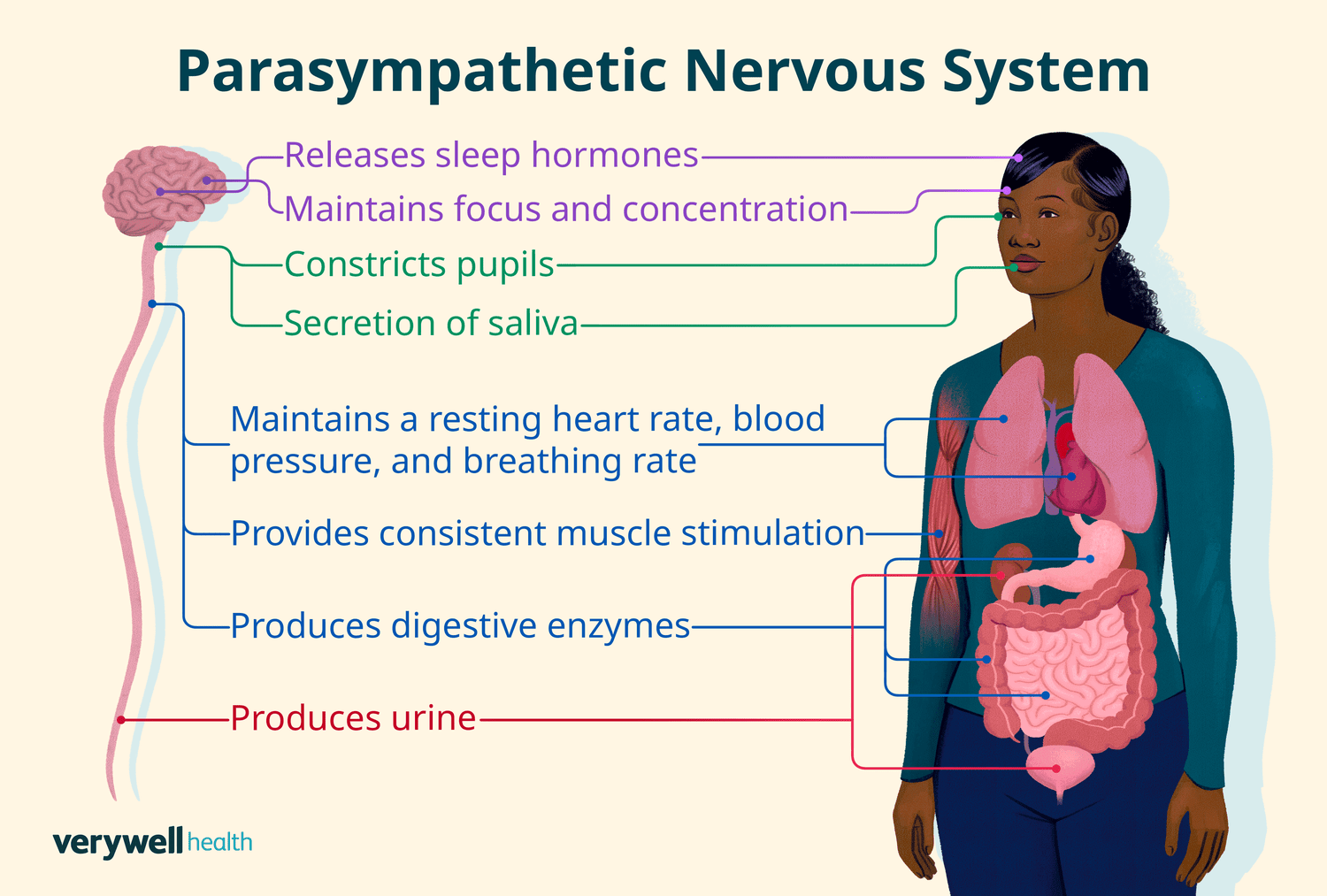
Parasympathetic
division has relaxing effect (rest and digest)
Nervous System
helps control the digestive system
What does the nervous system use, and which system is it common in
neurotransmitter common in the CNS
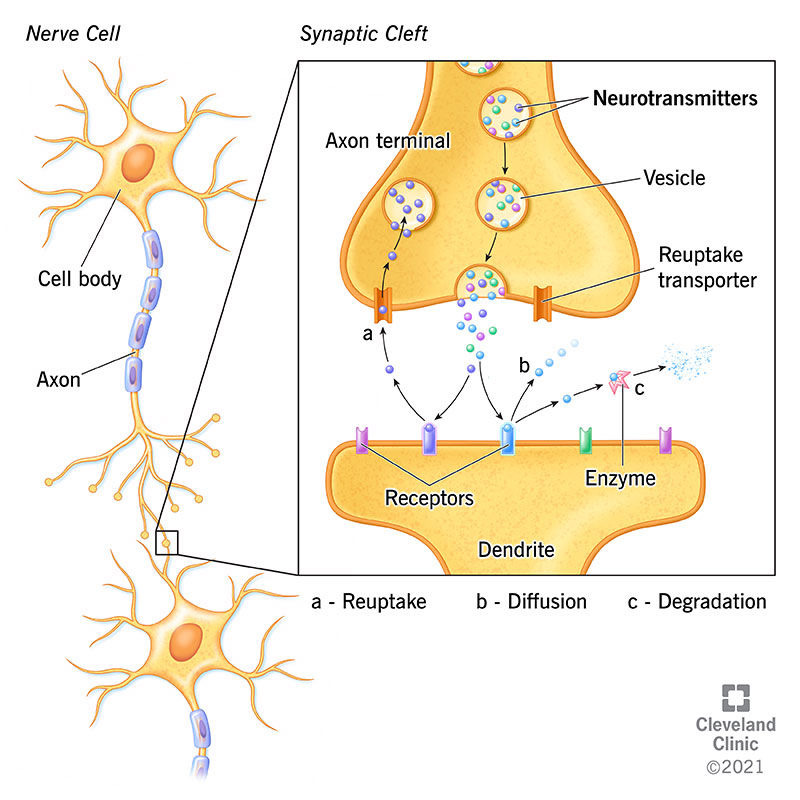
What else controls the Nervous System
the Autonomic nervous system
The basic functional units of the nervous system
Neurons
Send and receive signals
Neurons
Neurons generate
nerve impulses (also named action potential)
What are the function in the Neurons
communications, information processing, and control
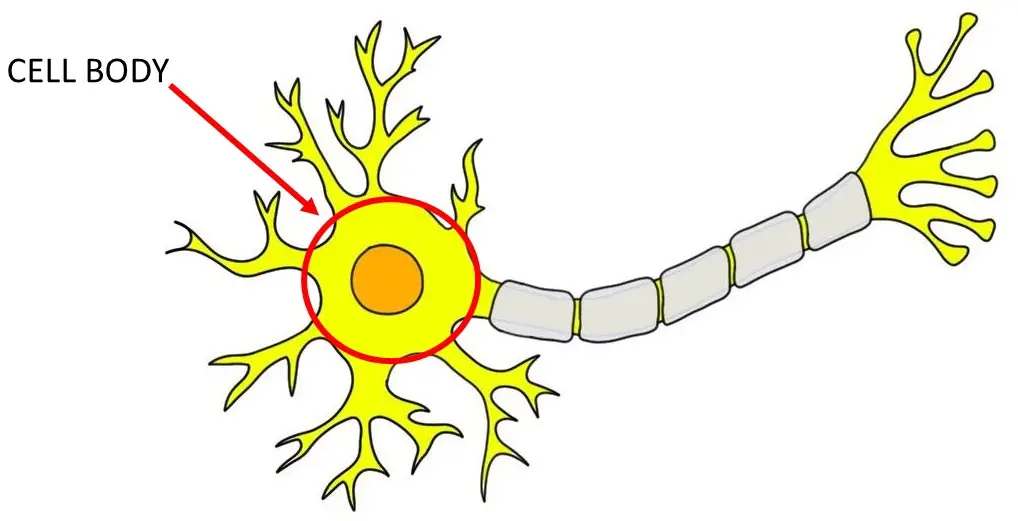
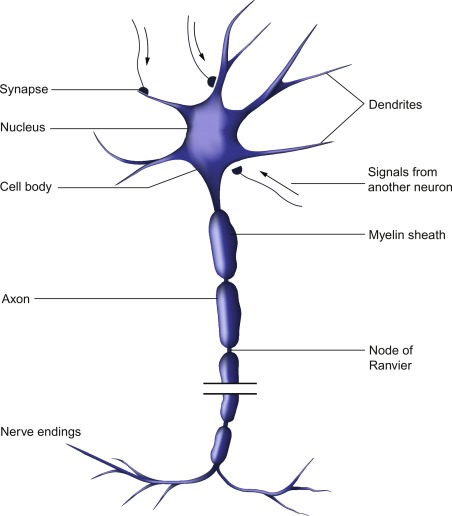
Cell Body (Soma)
Large nucleus and nucleolus
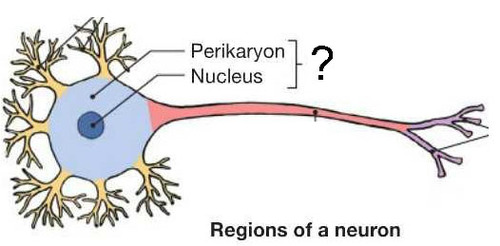
Perikaryon
the cytoplasm
Mitochondria
produce energy, ATP
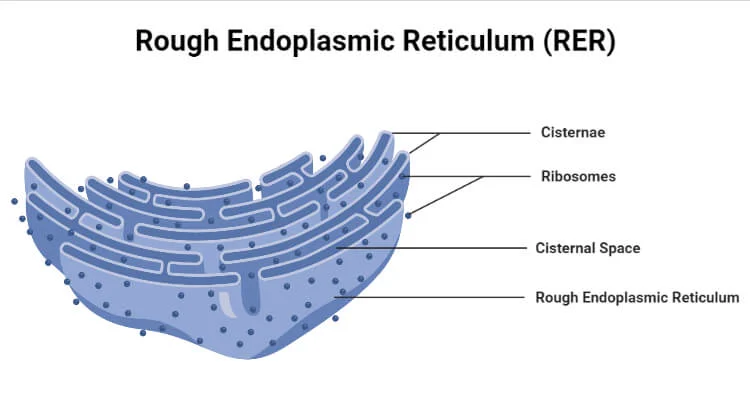
Synthesis proteins
R.E.R and ribosomes
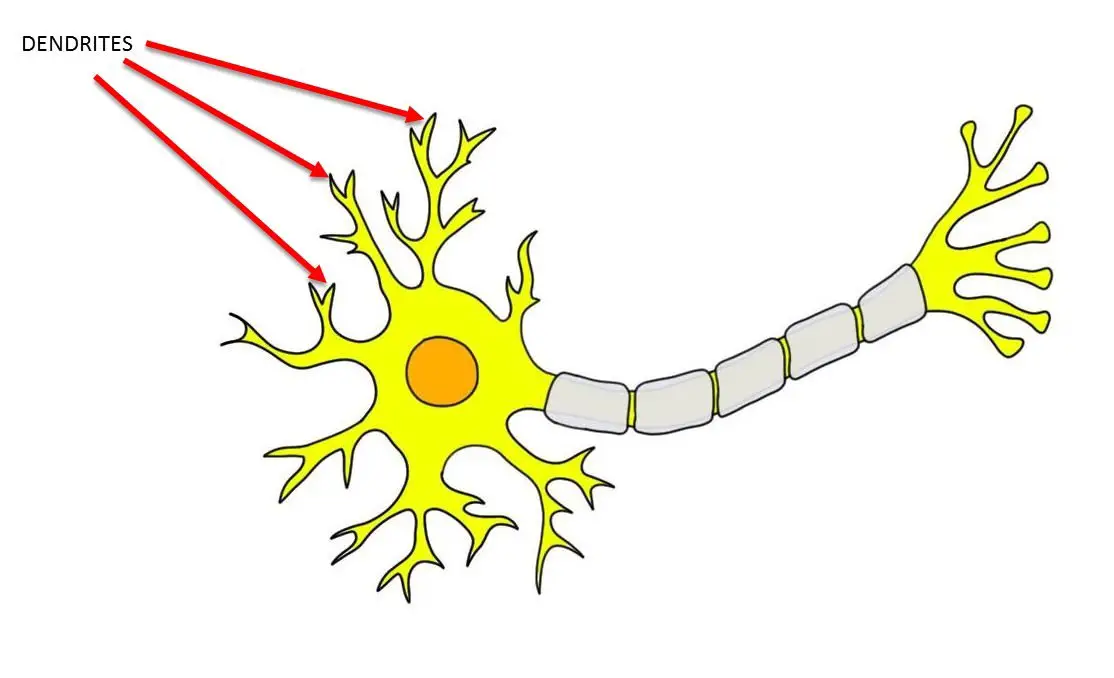
Short and highly branched processes extending from cell body.
Dendrites
Dendric cells are made of
Dendritic spines
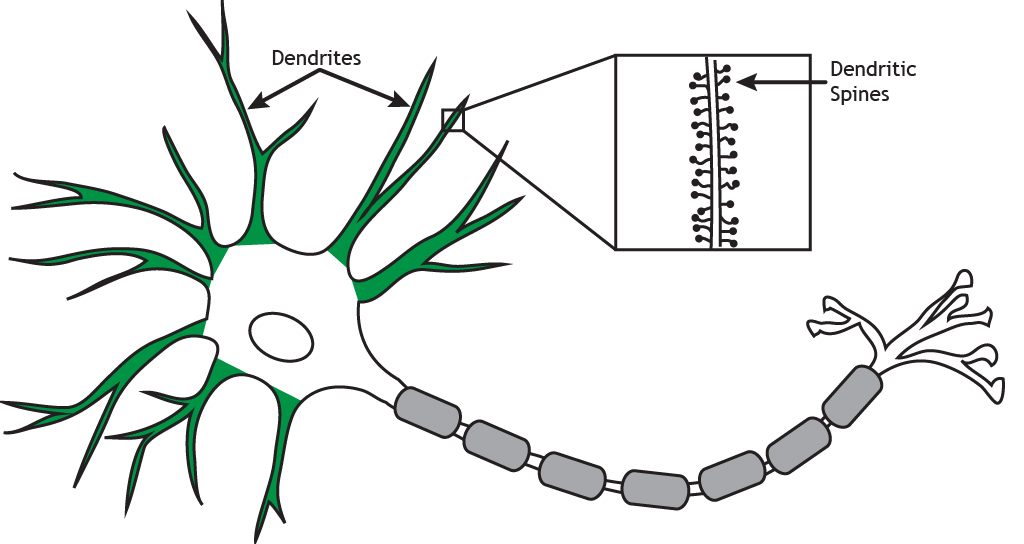
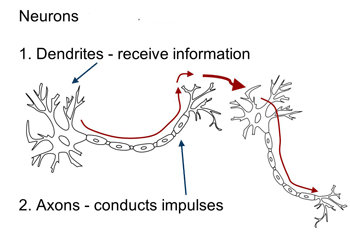
Dendrites receive information from other
neurons Afferent signal
What percent is the neuron surface area
80-90 percent
Single, long cytoplasmic process
Axon
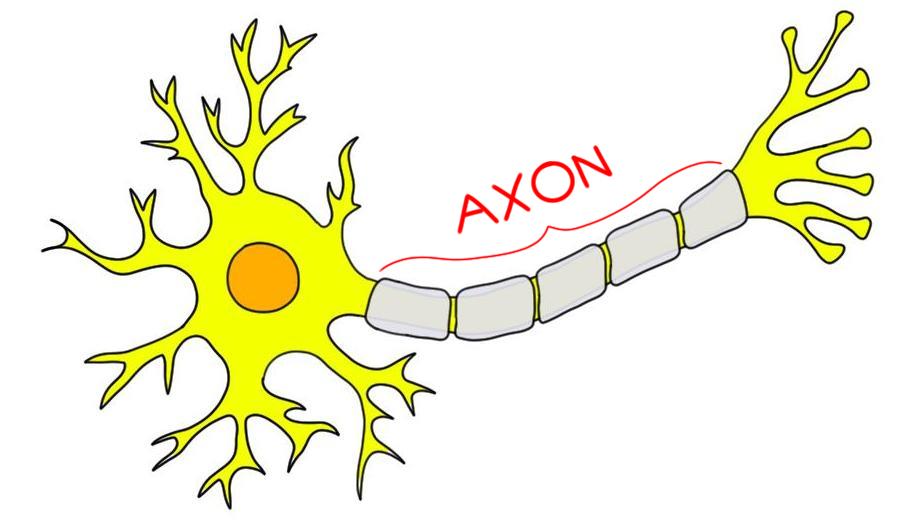
Axon propagates
electrical signals making them (Action Potentials)
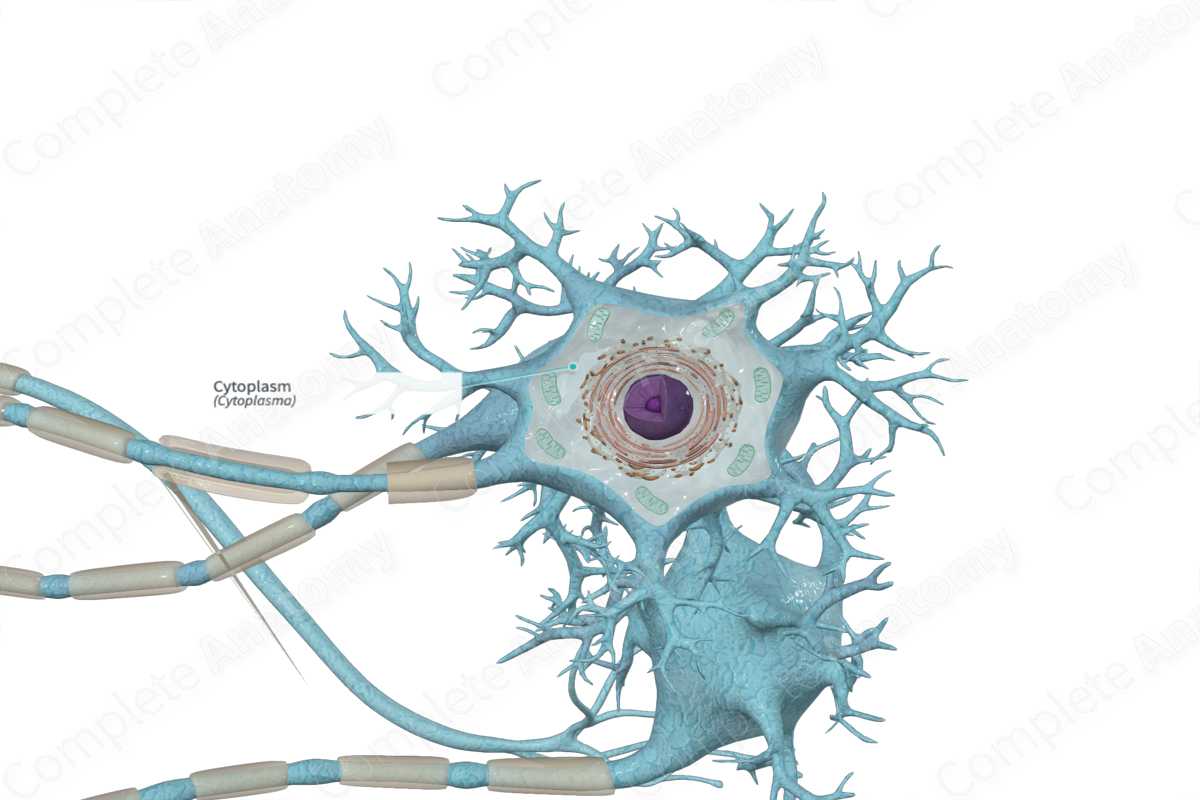
Cytoplasm of the axon
Axoplasm
Axoplasm contains
neurofibrils, neurotubles, enzymes and organelles
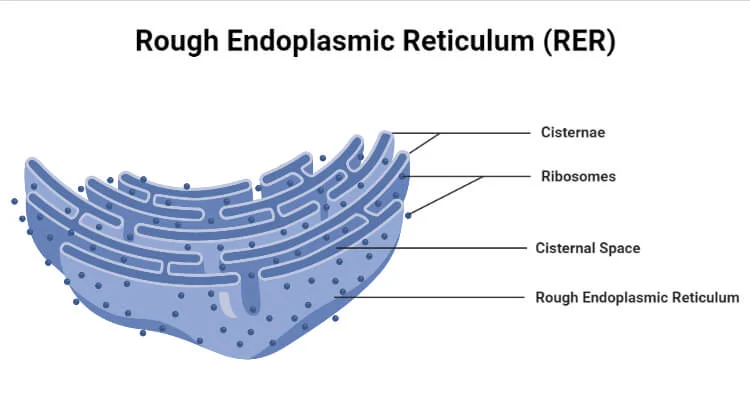
Dense areas of RER (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) and ribosomes in perikaryon
Nissel bodies
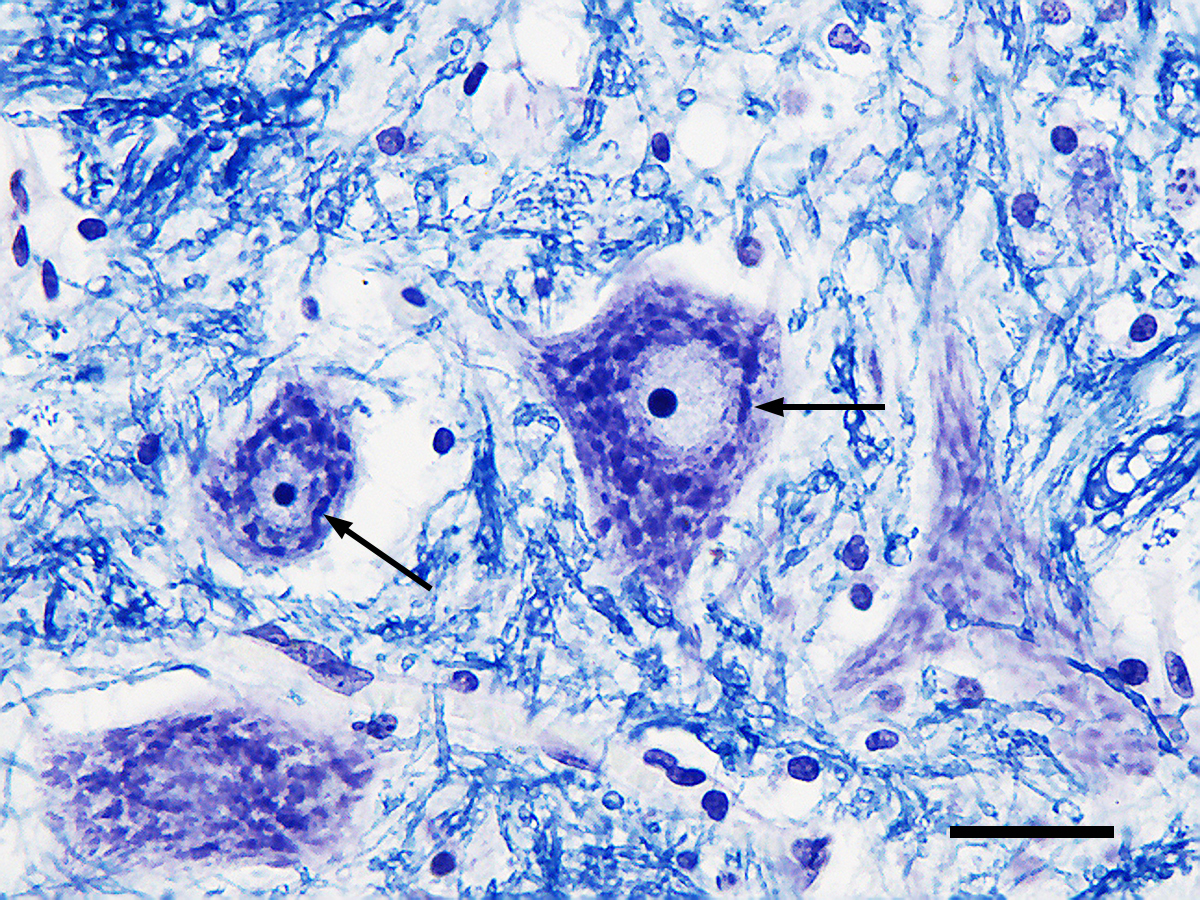
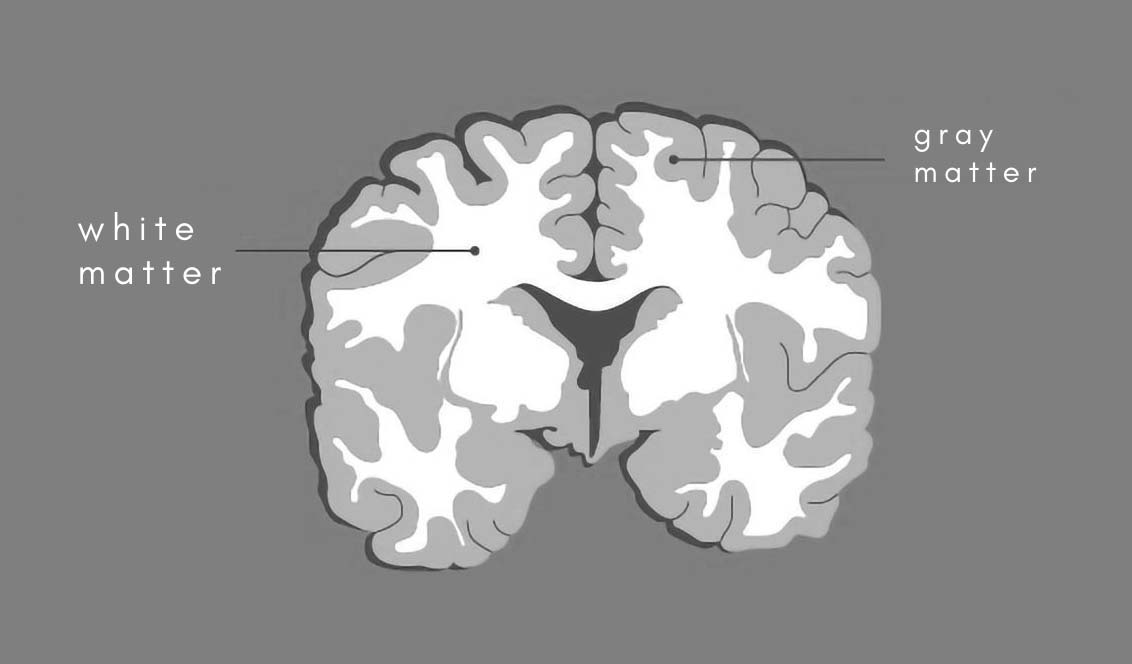
Nissel bodies make nervous tissue appear in
gray matter
Neurofilaments and neurotubules are similar to
filament and microtubules
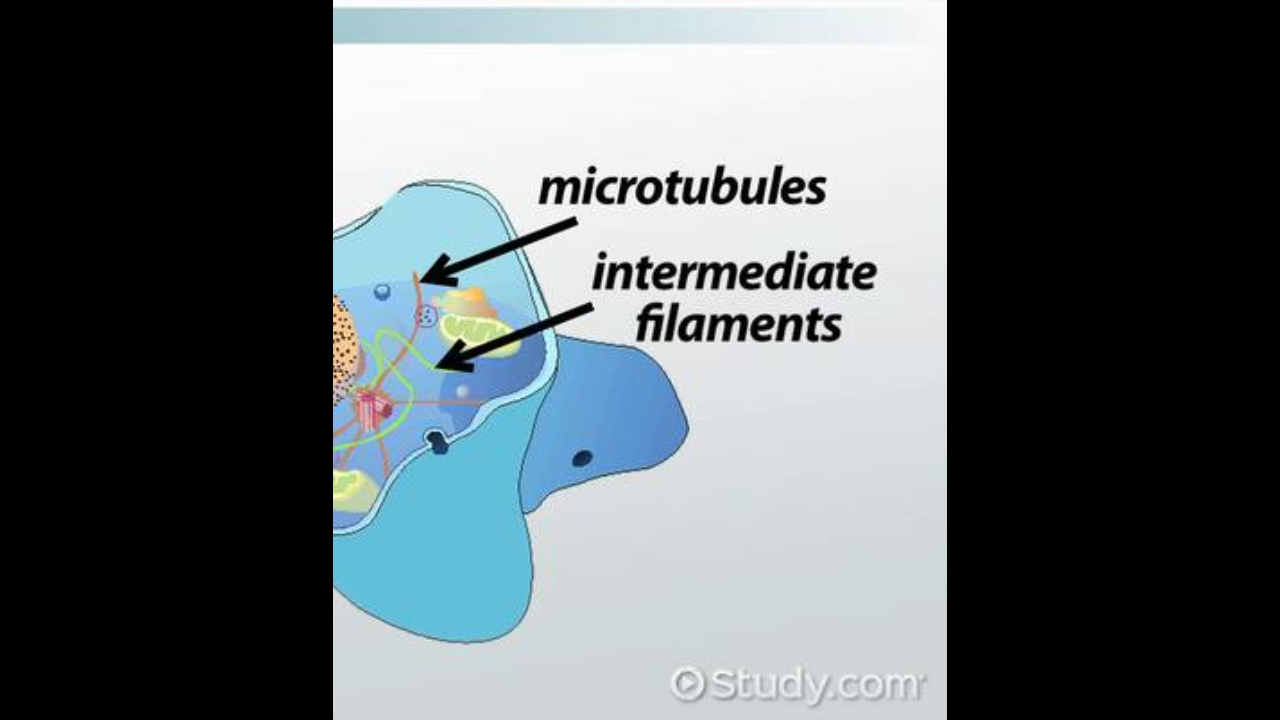
Bundles of neurofilaments that provide support for dendrites and axon
Neurofibrils
Plasma membrane of the axon
Axolemma
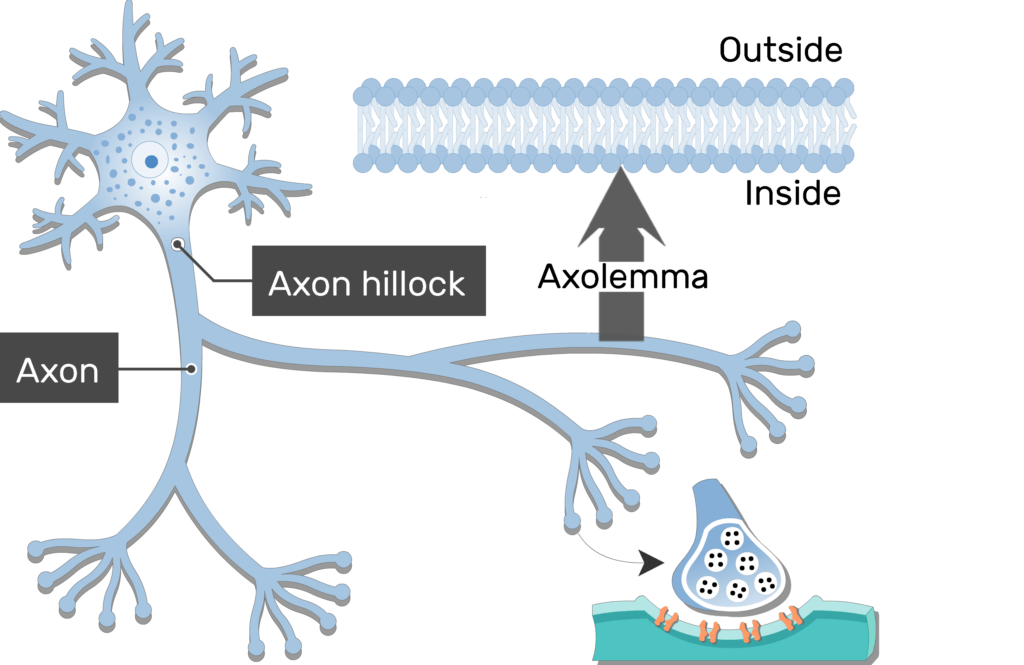
What covers does the Axolemma cover
the axoplasm
base of axon
Initial segment
thick region that attaches initial segment to cell body
Axon hillock
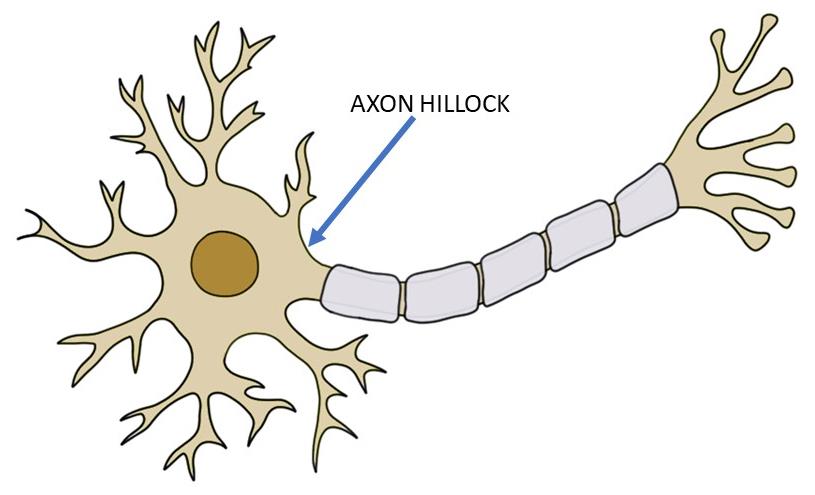
–Which is the direction of the action potential (nerve impulse or electrical signal)?
A) Cell body>>>axon>>>Telodendria>>>>>axon terminal>>>Other cells
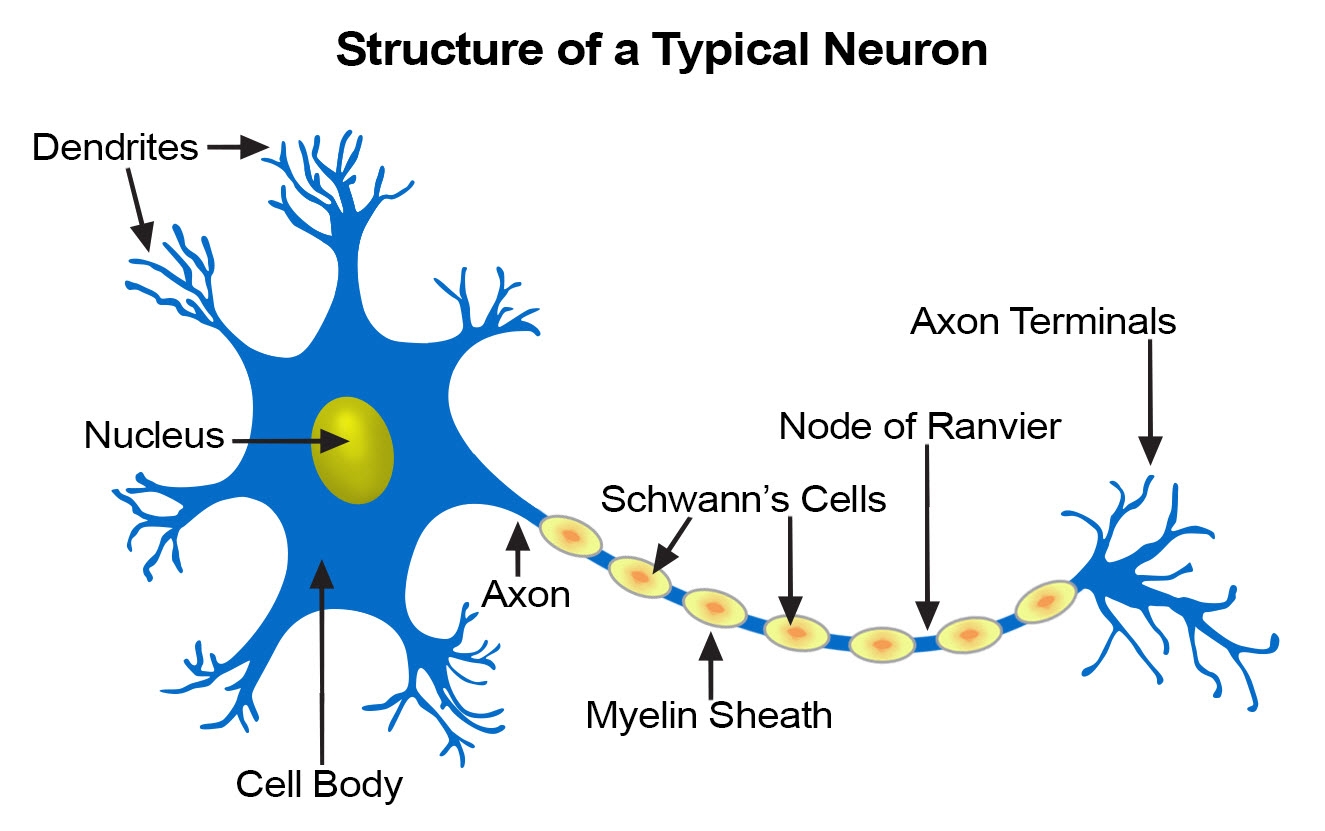
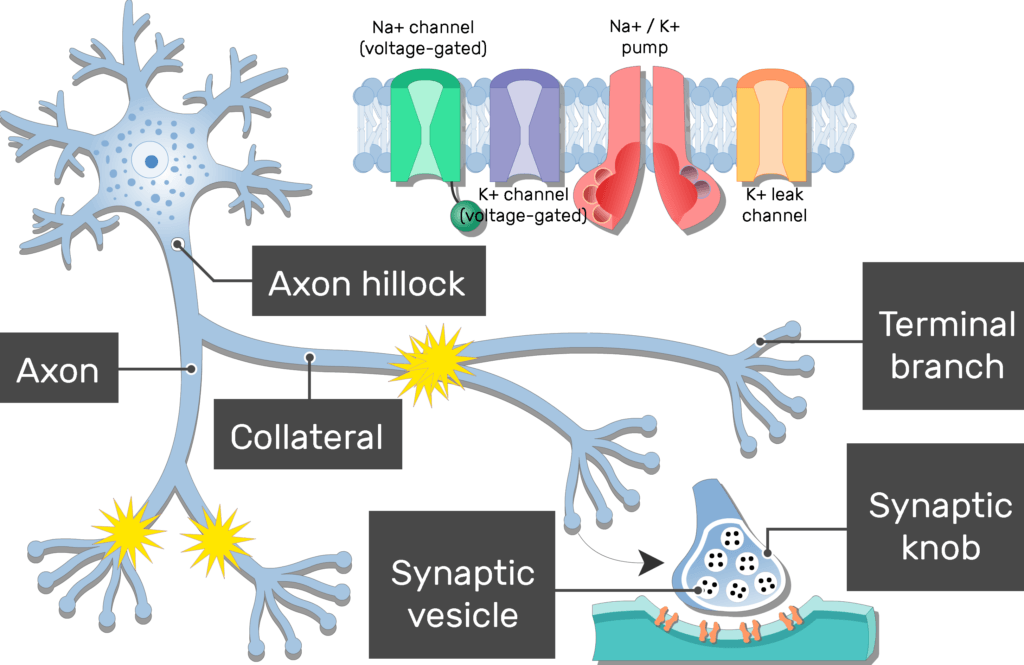
The structures of an Axon are
Collaterals, Telodendria, and Axton terminals
Collaterals
branches of the axon
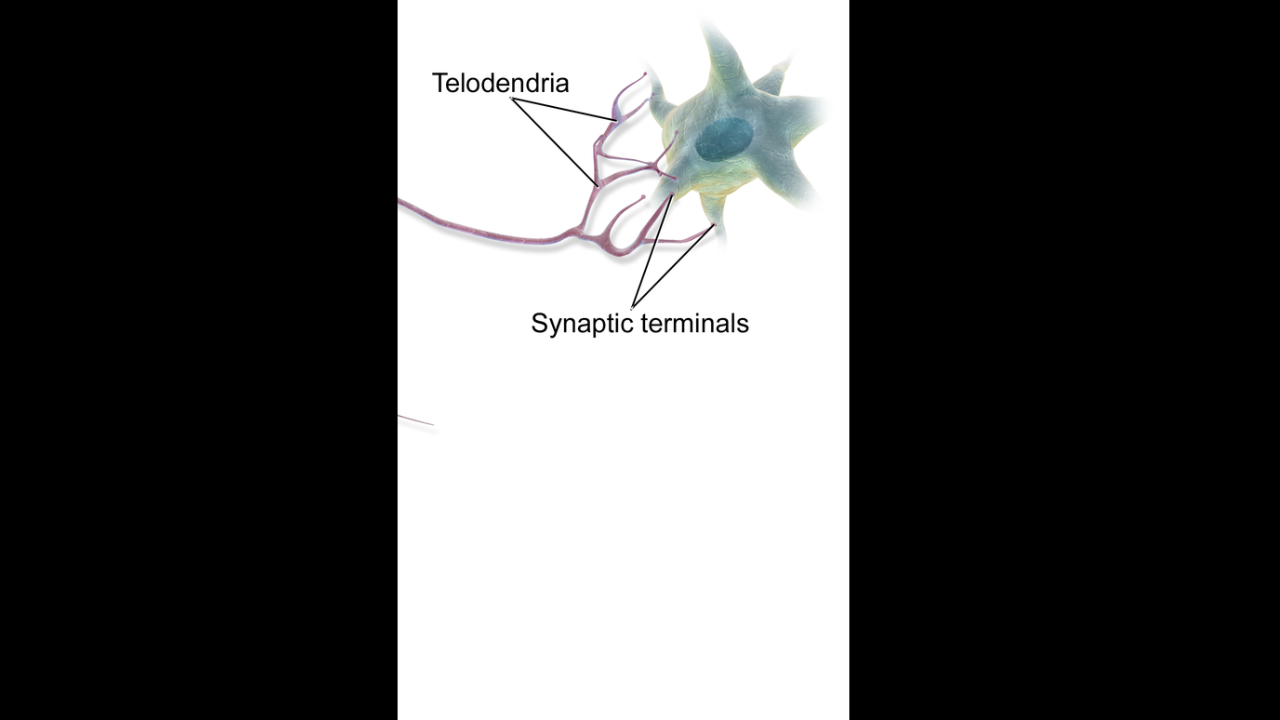
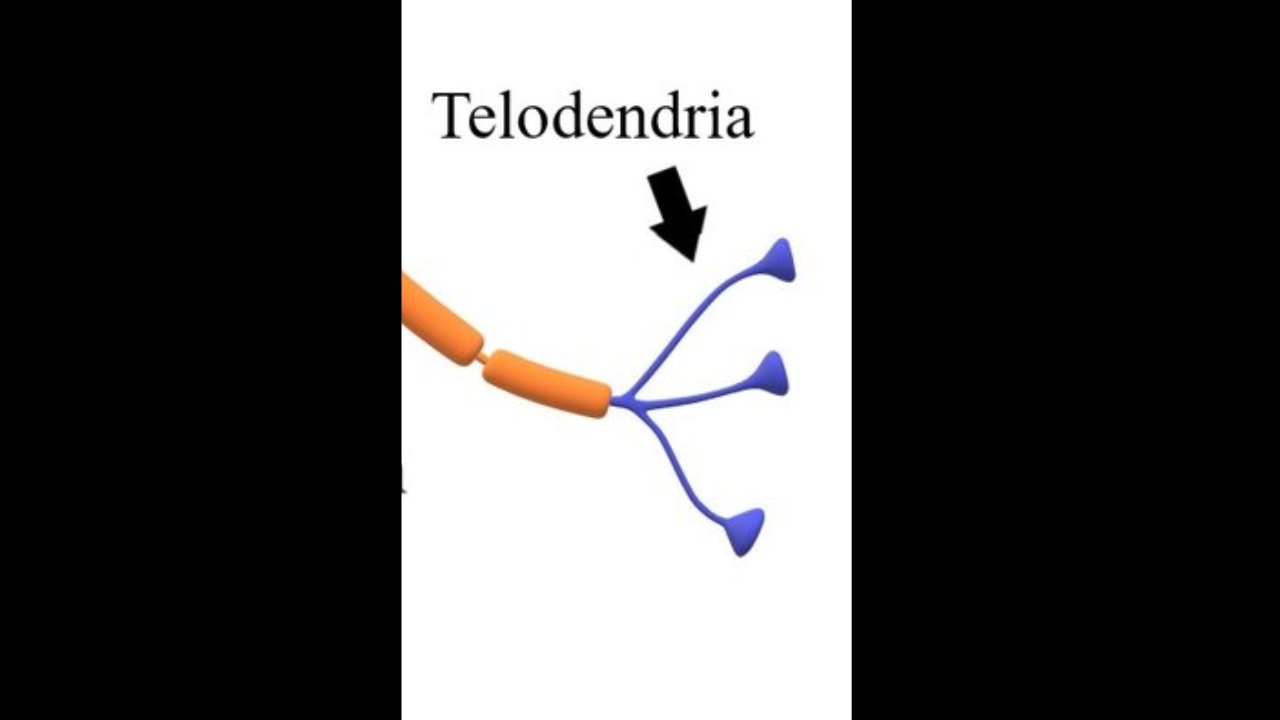
telodendria
fine extensions of distal axon
axon terminals (synaptic terminals)
tips of telodendria
cell body and axon terminals
movement of materials
materials move along
neurotubles within axon
powered by
mitochondria, kinesin, and dynein
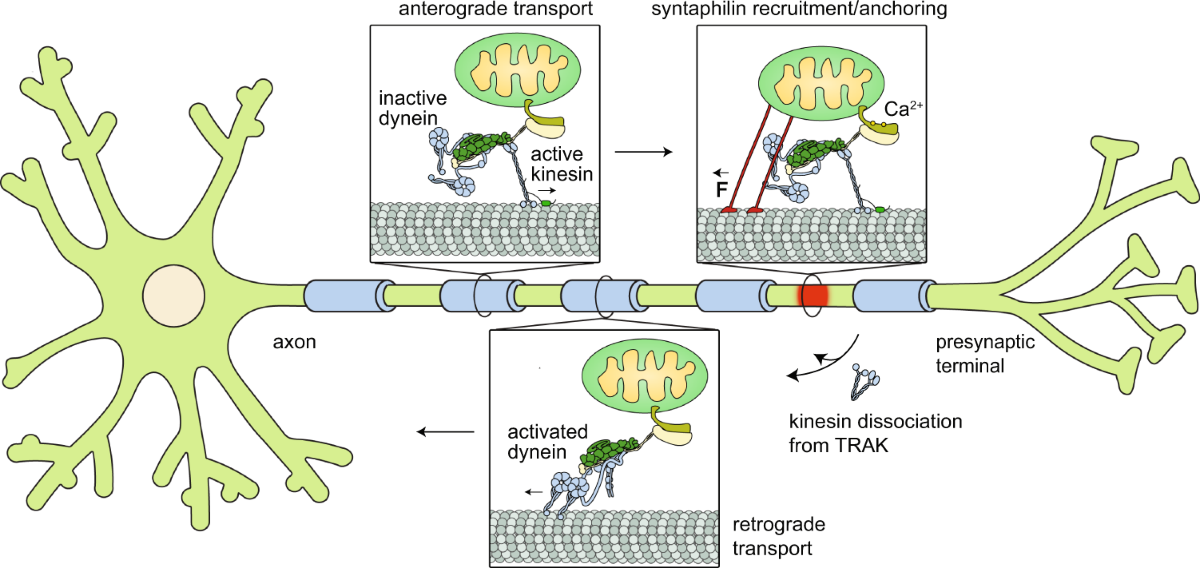
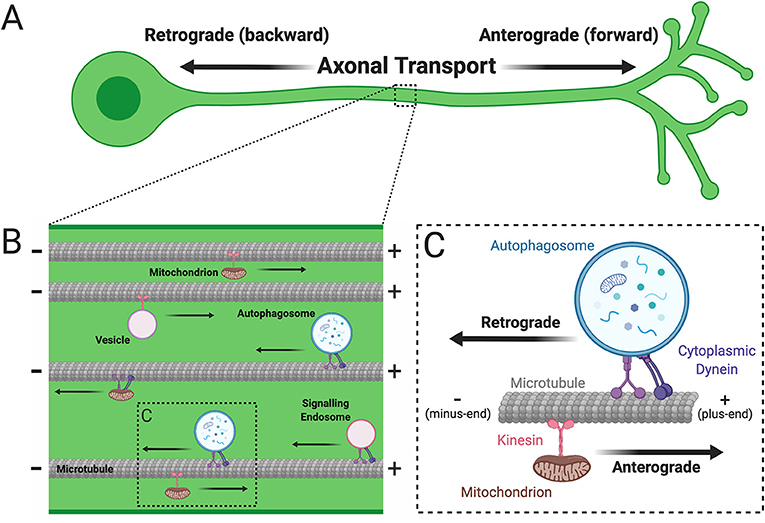
Anterograde transport
transport from the cell body to the terminal axon
Retrograde transport
rabies virus, varicella zoster
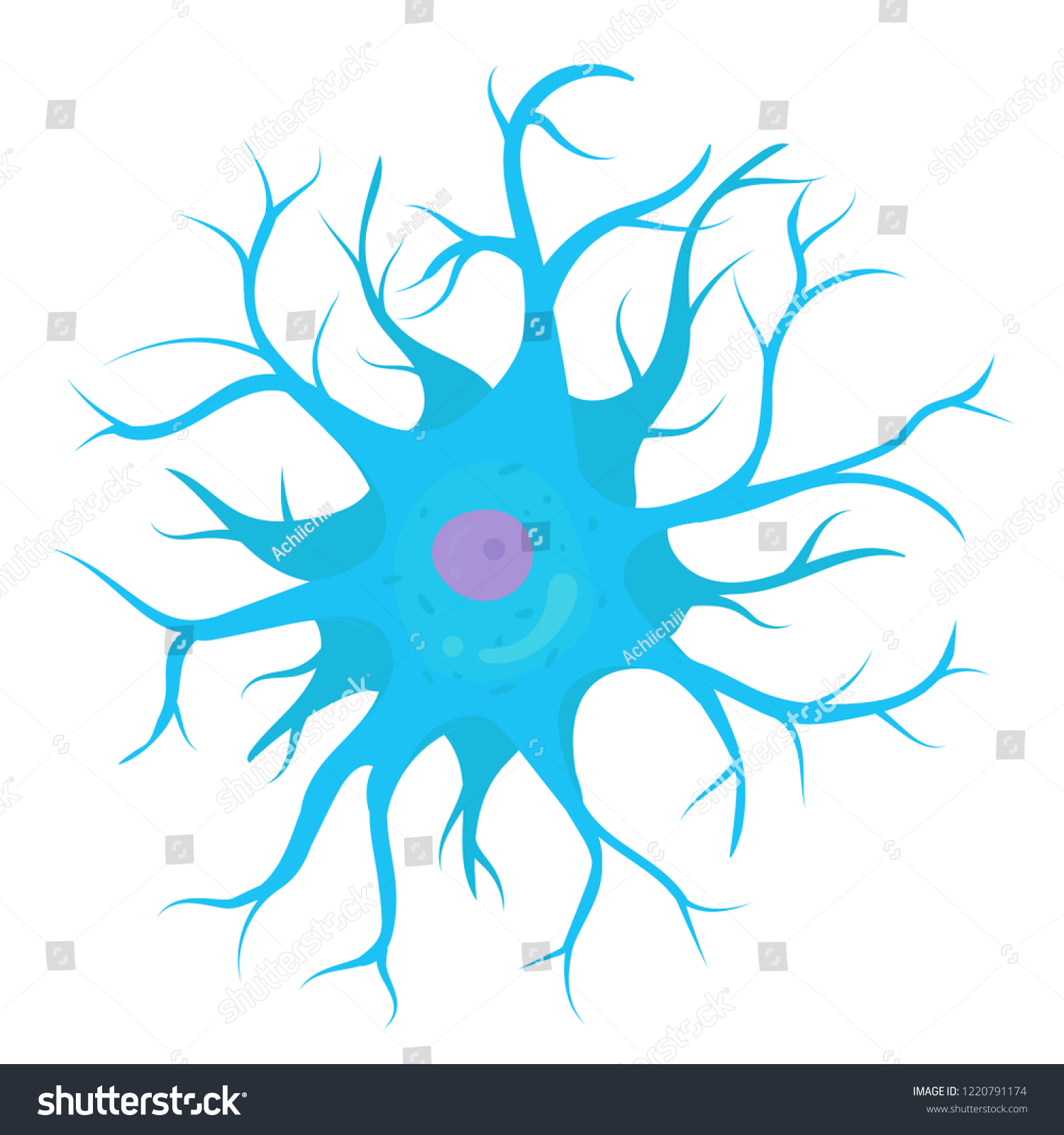
Anaxonic neuron
in brain and special senses
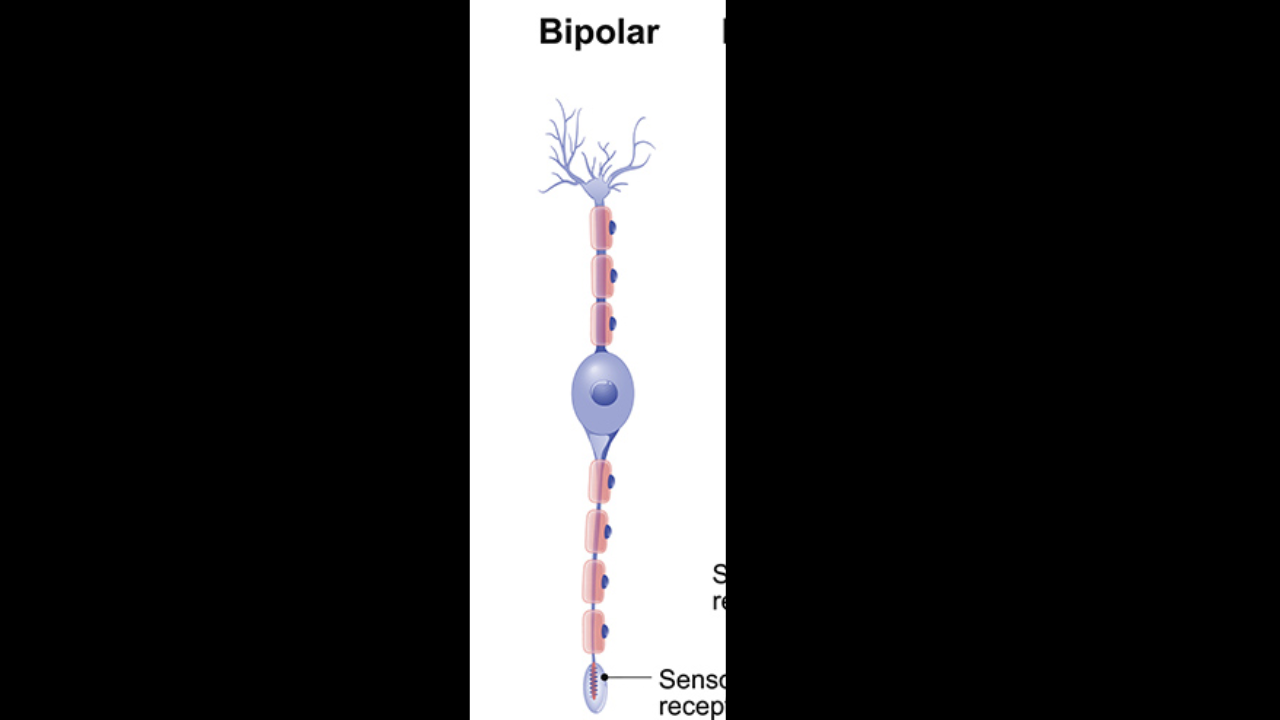
Bipolar neuron
found in special sense organs (sight, smell, hearing)
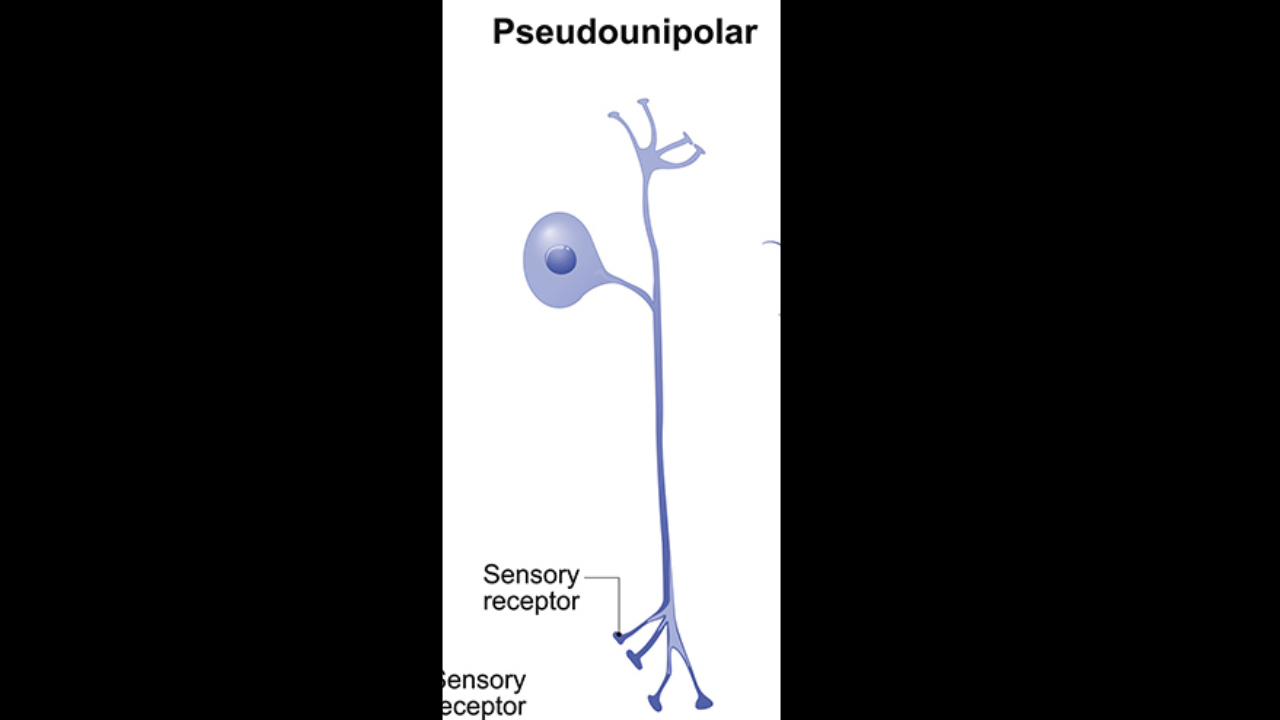
Unipolar neuron
most sensory neurons of PNS; Sensory ganglia (dorsal root ganglia)
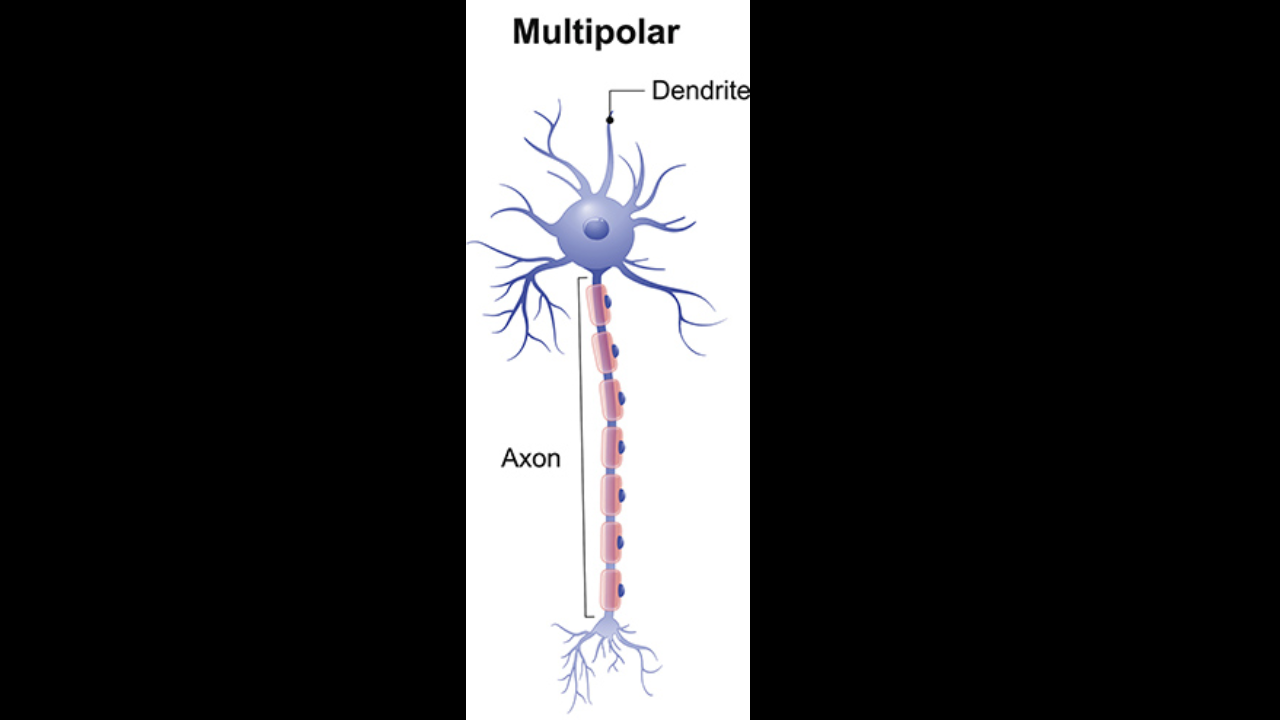
Multipolar neuron
Common in the CNS all motor neurons that control skeletal muscles
Small, All cell processes look similar, found in brain and special sense organs
Anaxonic neurons
small and rare. one dendrite and one axon. found in special sense organs (sight, smell, hearing)
Bipolar neurons
Axon and dendrites are fused
Unipolar neurons (pseudo unipolar neurons)
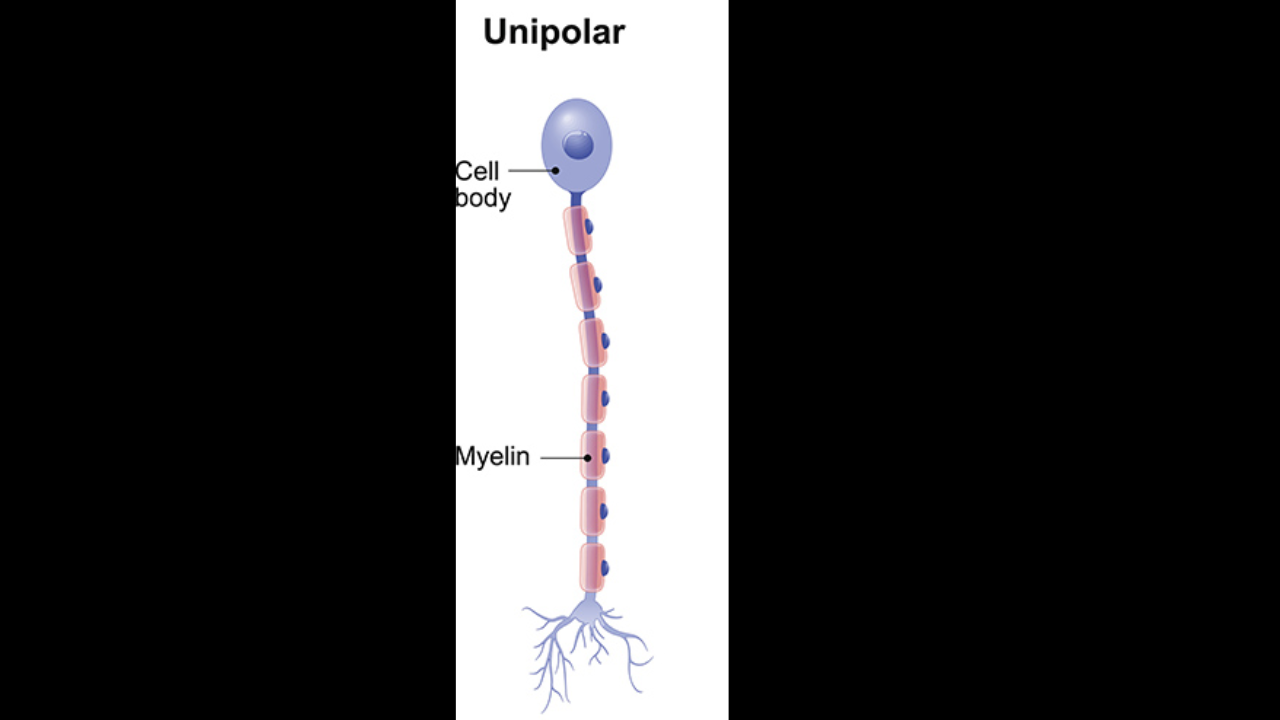
Cell body to
one side
Most sensory neurons of
PNS
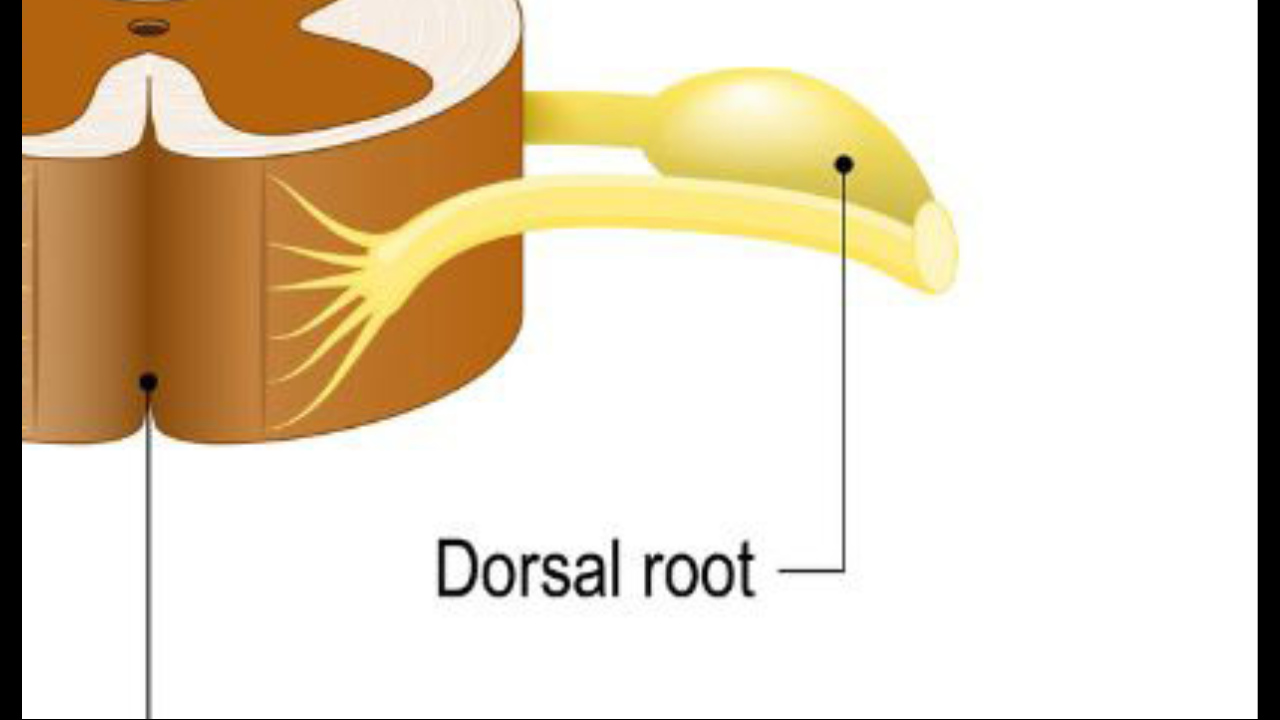
Sensory ganglia
(dorsal root ganglia)
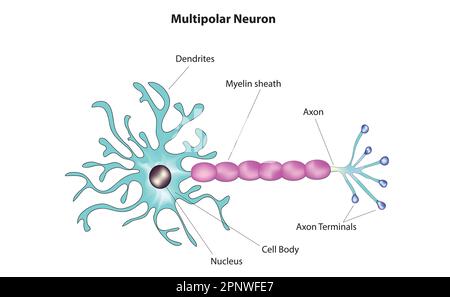
Multipolar neurons
have one long axon and two or more dendrites
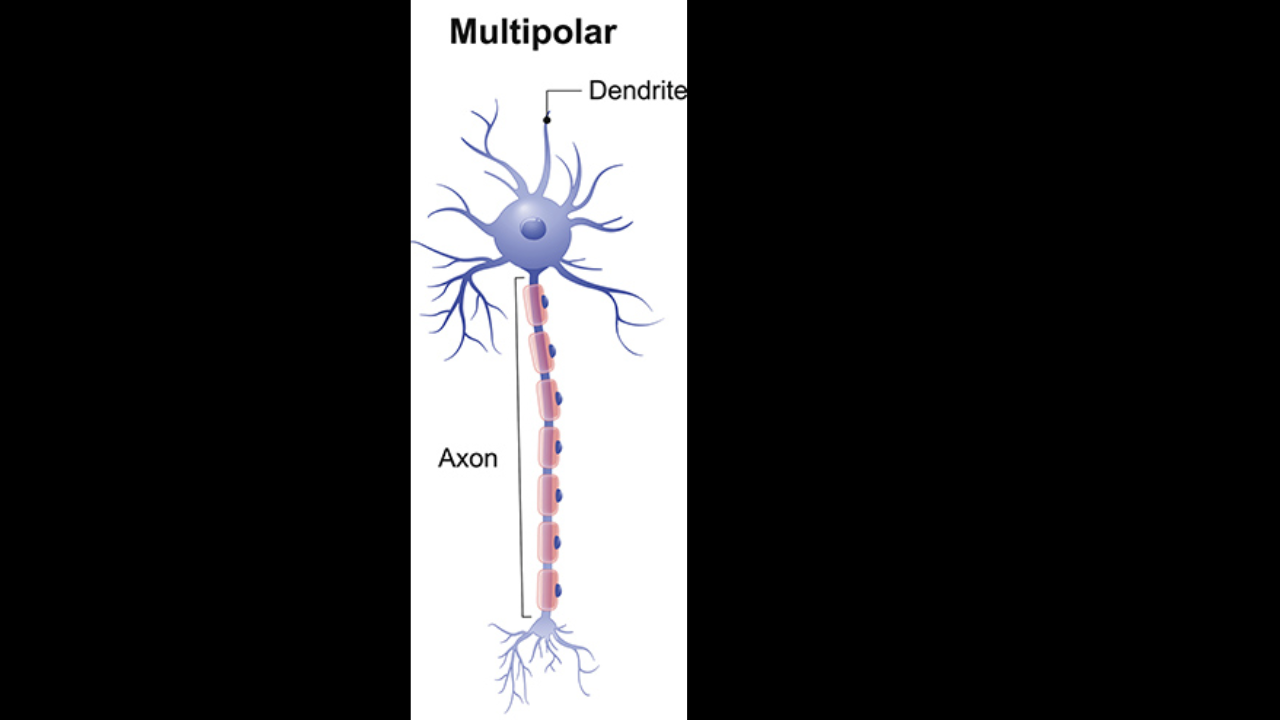
Multipolar neurons are common in the
CNS (Central Nervous System)
All motor neurons that control
skeletal muscles
Sensory neurons
receive information
Motor neurons
send motor command to effectors
Interneurons
in between sensatory and motor neurons
Sensory neurons
afferent neurons
Sensory neurons can be
unipolar
Cell bodies are grouped in the
sensory ganglia
Sensory neurons processes (afferent fibers) extend from sensory receptors to the
CNS (central nervous system)
Monitor external environment
Somatic sensory neurons
Visceral sensory neurons
Monitor internal environment
What are the types of sensory receptors
Interoceptors, Exteroceptors, and Proprioceptors
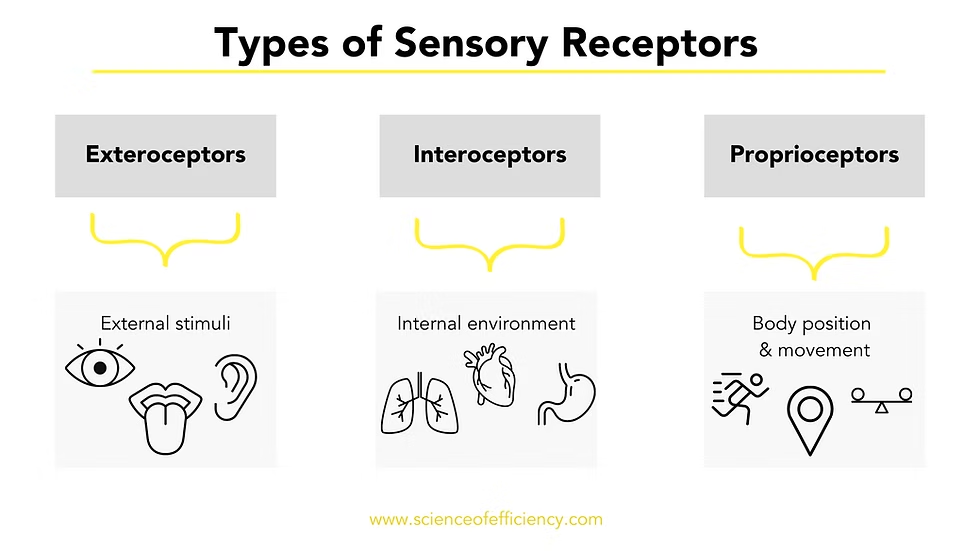
Interoceptors
Monitor internal systems (EG digestive, urinary)
Exteroceptors
monitor external environment (e.g. temperature)
Complex senses (e.g. sight smell, hearing
Monitor position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints
Proprioceptors
Carry instructions from CNS to peripheral effectors.
multiple neurons.
Via efferent fibers (axons)
Motor neurons (efferent neurons)
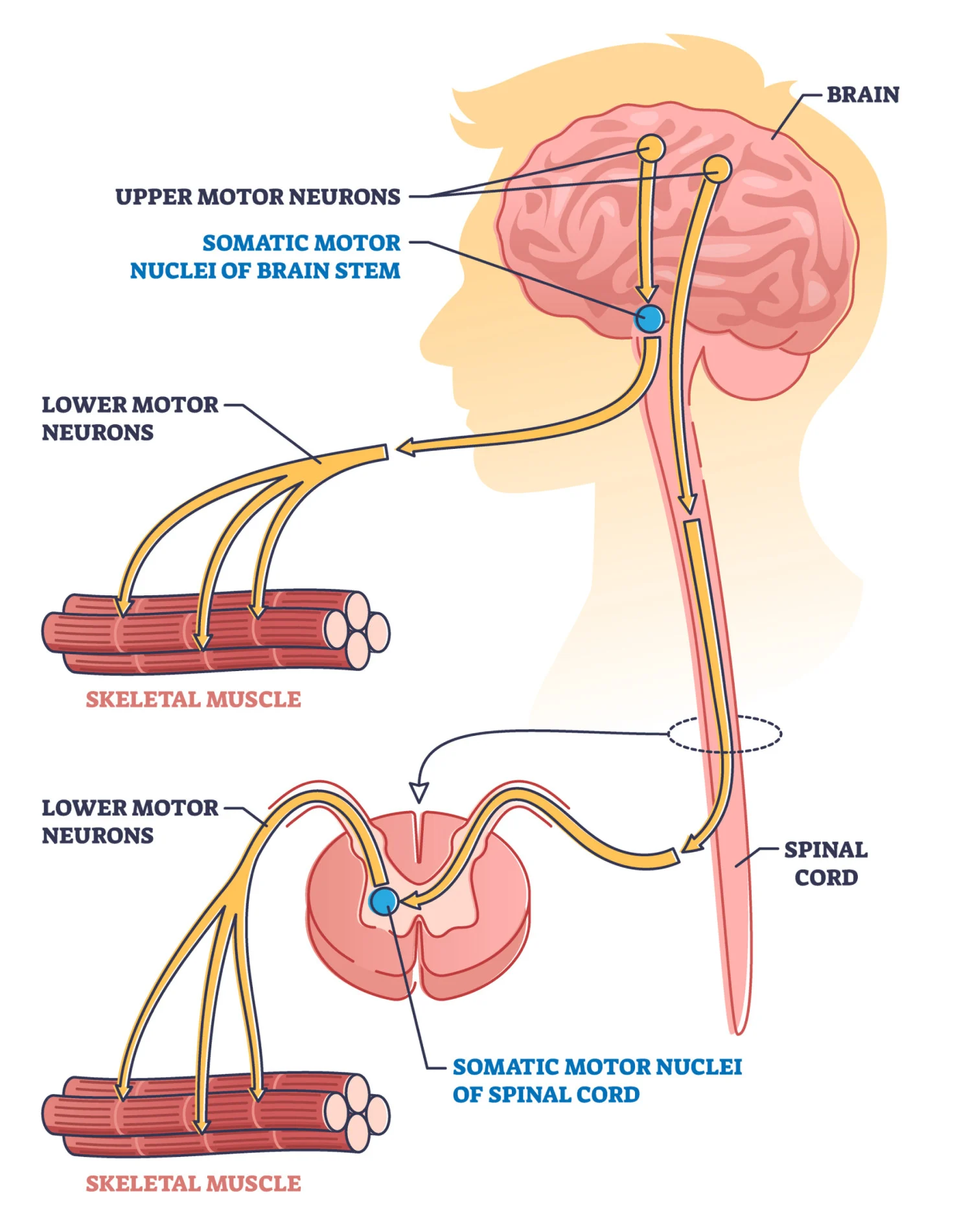
Somatic motor neurons of the SNS
innervate skeletal muscles
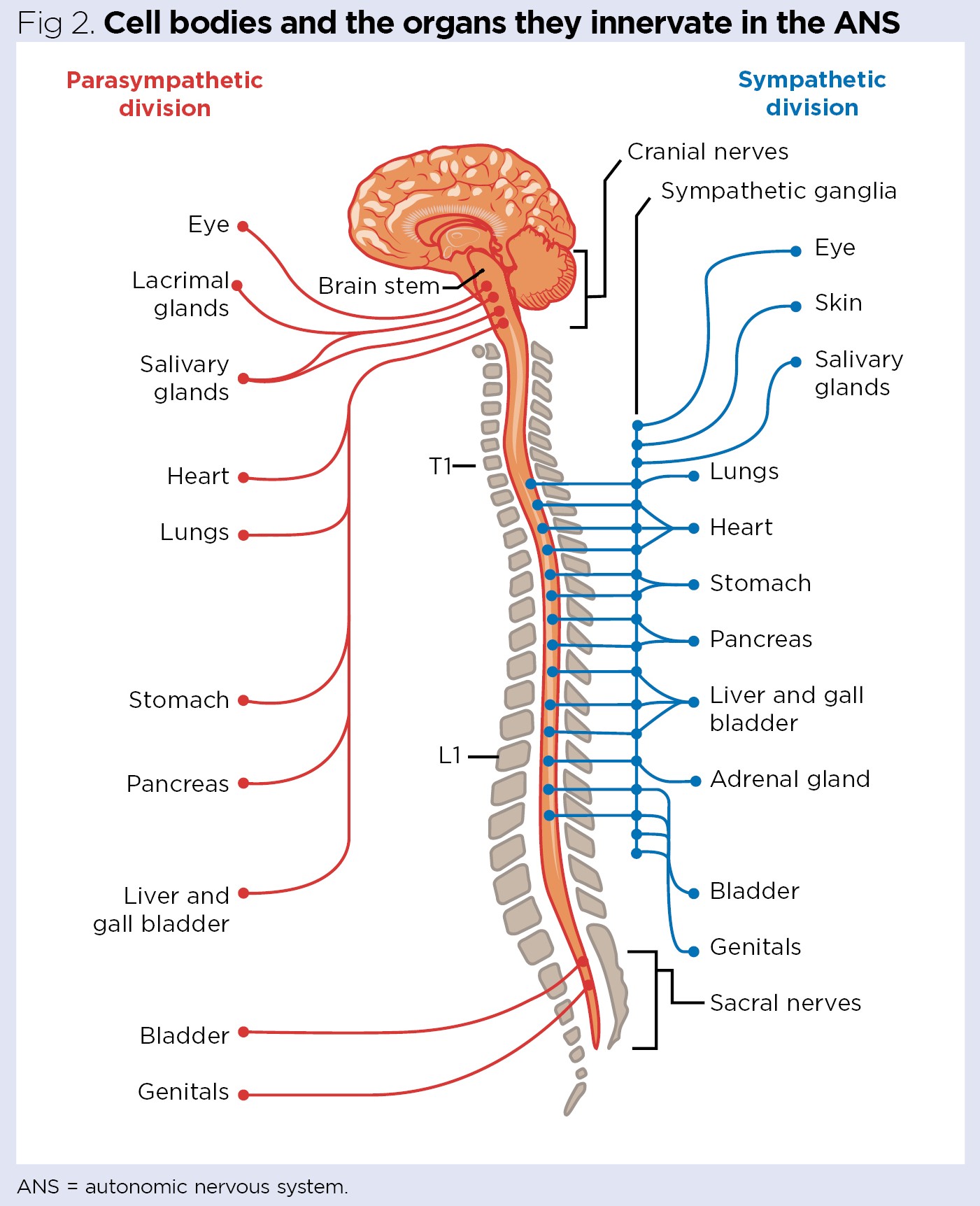
ANS (automatic Nervous System)
Visceral motor neurons