GCSE Physics OCR Gateway - P6 REDO after Exam using notes for better quality
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Doesn't have dangers of radiation, how to handle radiation and also which radaiation occurs in different scenarios + safety precautions against radiation)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Isotope
A form of an element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What happens when a nucleus is unstable?
The nuclei becomes radioactive
How does a nucleus become more stable?
Emit ionising radiation
What are the three types of radiation?
alpha, beta, gamma
What is an alpha particle and how fast does it move relative to light?
two protons and two neutrons (helium nucleus; moves at 10% of the velocity of light
Properties of alpha radiation
- stopped by paper
- least penetrating
- most ionising because it has a large mass and a double positive charge
-slow
What is a beta particle and how fast does it move relative to light?
fast moving electron; Neutrons split into a proton and electron; electron can't stay in the nucleus and gets shot out as a (Beta particle/Electron)
Properties of beta radiation
- stopped by 3mm of aluminium foil
- fairly penetrating and ionising
- has a charge so can cause ionisation
What is a gamma wave and how fast does it move relative to light
high energy electromagnetic radiation
Properties of gamma radiation
- reduced by several cm of lead or several metres of concrete
- most penetrating
- least ionising as it has no charge
What could also be released during radiation?
a neutron
Alpha equation
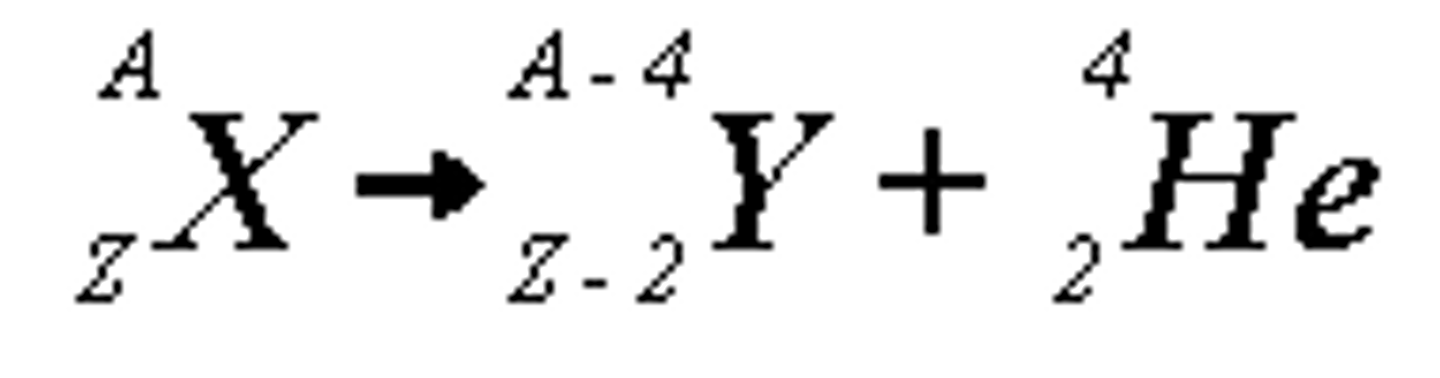
Beta equation
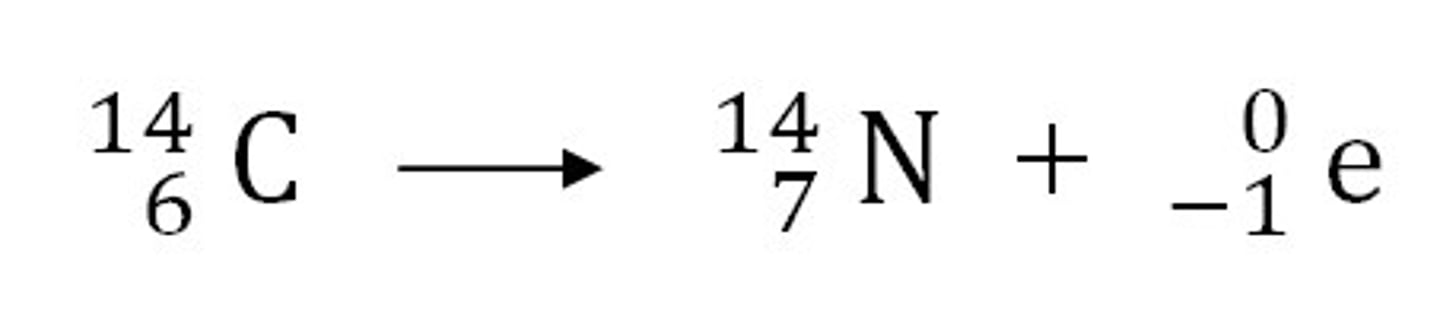
Gamma equation
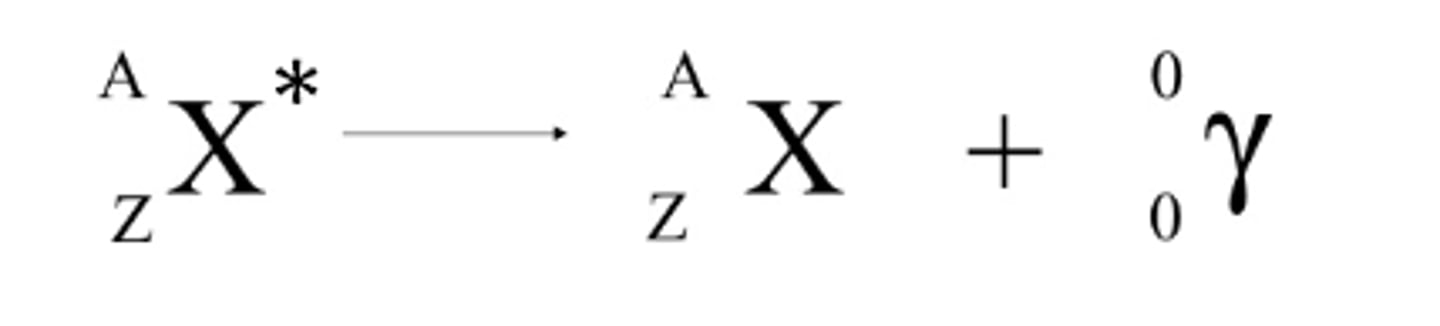
Neutron equation
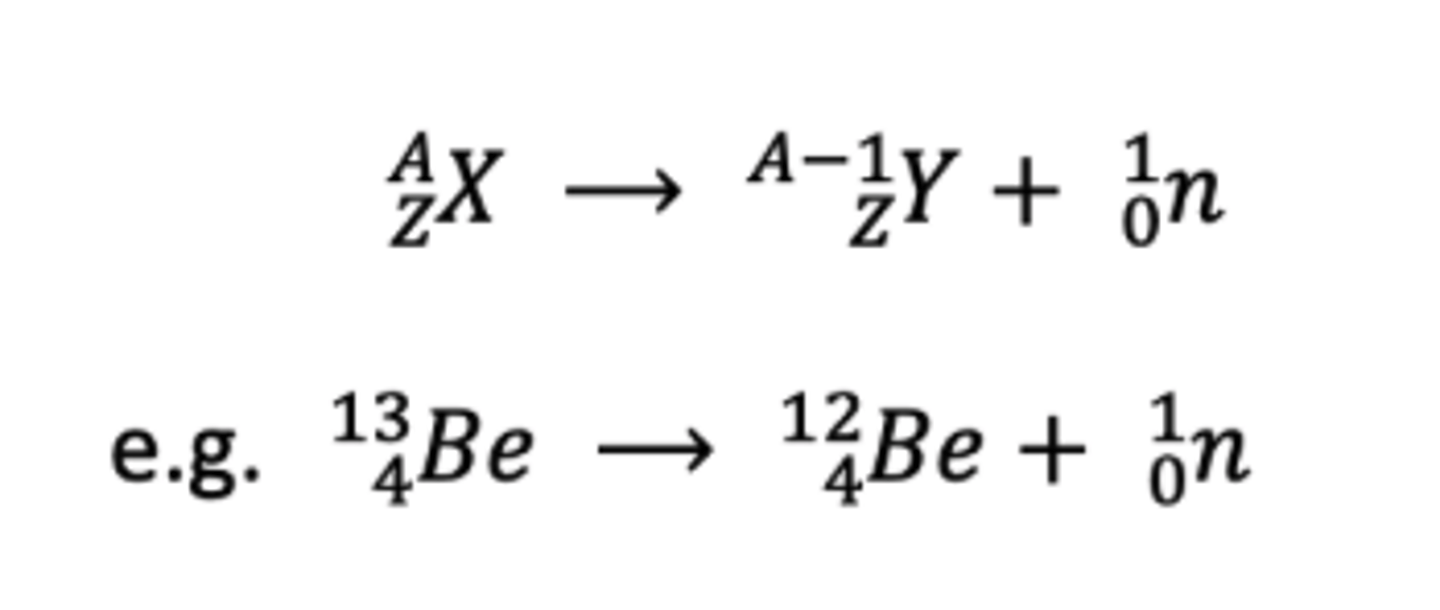
What experiment could you conduct to see what kind of radiation is emitted from a source?
Use a GM tube and ratemeter and some materials to check what kind of radiation is being released
What apparatus wold you need for this test?
Source, source holder, GM tube, ratemeter, long tongs, paper, 3mm of aluminium
How can radioactive decay be described?
random and spontaneous
Half-life
The average time taken for half of the radioactive, unstable nuclei to decay.
Irradiation
To expose something to ionising radiation
Examples of irradiated objects that we use
- Surgical instruments to sterilise them
- Food to kill bacteria and prolong shelf life
- When human cells are irradiated, they ionise and can cause sickness and increase the chance of getting cancer
Contamination
Occurs when a radioactive substance itself is transferred onto a person or into the environment.
How can contamination occur?
- Use of nuclear weapons e.g. Nagasaki
- Malfunction at a nuclear station e.g. Chernobyl
Medical tracers
- A radioactive substance has to emit gamma or beta radiation to be detected by a medical tracer
- Alpha particles cannot be detected because 1) can't penetrate through skin and are highly ionising and would be too dangerous to put in the body
- Radioactive substances must be injected or ingested
- Geiger Muller (GM) tubes are used to detect the flow of Radioactive substances
- A shorter half life is batter as it stops irradiating the body more quickly
Smoke alarms
- Release alpha radiation
- Have long half lives so you don't have to change batteries much
- When no smoke is detected, alpha sources causes ionisation which causes an electric current to flow inside the detector
- When smoke is detected, the smoke particles disrupt the process and reduce the ionisation and the amount of current flowing, which triggers an alarm to sound
Carbon Dating
- In radioactive carbon, there is normally 6 protons and 8 neutrons
- Radioactive carbon has a half life of 5700 years
- The amount of carbon in our atmosphere replenishes because of the carbon cycle (biology)
- When a living thing dies, the amount of radioactive carbon-14 reduces as the nuclei decay
What fuel is used in nuclear power station?
Uranium
Nuclear fission
A nuclear reaction in which a massive nucleus splits into smaller nuclei with the simultaneous release of energy
How does nuclear fission occur?
A neutron is fired at a uranium nucleus. The nucleus absorbs the neutron, becomes unstable, and then splits into two smaller nuclei, releasing two or three neutrons.
Nuclear fission causes mass to be converted into energy.
What happens to the two/three neutrons released from the first fission?
Sets up a chain reaction for more nuclear fissions to occur.
How are the reactions conrtolled?
* Moderator - slows down the fission neutrons
*Control rods - lowered into the reactor to absorb neutrons
What is nuclear fusion and how does it occur?
Nuclear fusion occurs when two small nuclei fuse together to form a larger nucleus. The process converts mass into energy.
Nuclear fusion requires very high pressures and temperatures to overcome the repulsive forces between the positively charged nuclei.
What si the equivalent of an electron shell in physics?
Energy level
Excitation
When an electron in the lowest energy level absorbs some electromagnetic radiation (also called a photon), the electron becomes excited and moves to a higher energy level.
De-excitation
When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, it emits electromagnetic radiation (photon)
Absorption spectra and stars
- Stars produce electromagnetic radiation.
- As these waves or photons of radiation travel through the star's atmosphere, some radiation is absorbed by electrons as they move to higher energy levels.
- This radiation is missing from the light we receive from a star.
Emission spectra
emission of light from electronically excited gas atoms
How does GM tube work
Ions created by radiation in the GM tube are counted by Geiger counter.
Activity:
Rate at which unstable nuclei from a source of radiation decays
Count Rate:
No. Decays recorded each second by a detector
Difference between Count rate + Activity
Activity is rate at which unstable nuclei decay
Count rate is rate at which radioactive emissions are detected