Physics- Topic 21 (Alternating Currents)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Period of a current time graph
Is the time taken for one complete oscillation in the graph
T = 1/f
Peak Value
Is the maximum value in a graph
It can be determined from the amplitude of the graph
Sinusoidal Alternating Current or Voltage
General form= X=X0sin(ωt )
where X0 is the peak value and ω is the angular frequency.
Root mean square values
Xrms = X0/ √2, representing the effective value of an alternating current or voltage.
Mean Power in a Resistive Load
P=IV = I2R = V2R
I0=√2 Irms
Ppeak=I02R = (√2 Irms)2R = 2Pmean
Pmean = Ppeak / 2
Rectification
Is the process of converting alternating current and the voltage into direct current and voltage
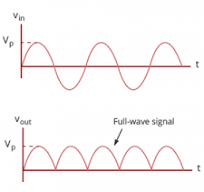
Full- wave Rectification Graph
The graph of the voltage Vout against time is a sine curve where the positive cycle and the negative cycle are both curved bumps

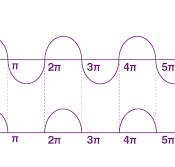
Half- wave Rectification graph
The graph of output voltage Vout against time is a sine curve where the positive cycles are curved bumps and the negative cycles are straight lines

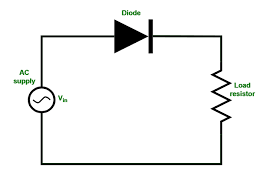
Half wave rectification

Consists of a single diode
AC supply is in series with diode and a resistor
The diode will only conduct during the positive cycles of the ac supply
Current is only present when there is a positive cycle
No negative cycles
Half of the time, the voltage is Zero
Power available from a half-wave rectified circuit is reduced
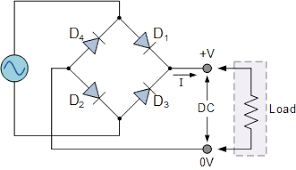
Full- Wave Rectification

Requires a bridge rectifier circuit
During Positive cycles:
If one terminal is positive and the other supplies negative
Two diodes opposite each other will conduct
The other two diodes do not conduct
This causes the current to flow through the positive direction of the resistor
Vice versa for the negative cycle
Current is constant, and more power is supplied compared to half wave rectified circuit
Smoothing
The reduction in variation of the output in voltage or current
This is done using a smoothing capacitor
The single capacitor is connected in parallel with a load resistor
The capacitor charges up from the input voltage and maintains the voltage at a high level
As it discharges gradually through the resistor when rectified voltage drops but the voltage then rises again and the capacitor charges up again
Graphs before and after smoothing
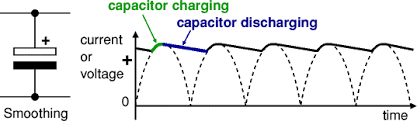
Gives a ripple shape

Effects of single capacitor in smoothing
The slower the capacitor discharges, the more the smoothing
This can be using:
A capacitor with greater capacitance
A resistor with a high resistance
Recall t = RC
hence the time constant of the capacitor must be greater than the time interval between adjacent peaks of the output voltage