Physics I Lesson 2: Newton's Laws
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
A ball is dropped off of a skyscraper. When it hits the ground, it is clocked as travelling at 467 m/s. How long was the ball falling from the top skyscraper?
(A) 47.65 s
(B) 124.89 s
(C) 563.92 s
(D) 988.20 s
(A) 47.65 s
Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Change in Time
9.8 (gravity) = 467 / Change in Time
Change in Time = 467 / 9.8
Change in Time = ~ 47 s (actual: 47.65)
CRB True or false? Terminal Velocity was reached right before the ball hit the ground, since the ball after that moment started decelerating.
False. Terminal Velocity was clearly not reached right before the ball hit the ground, since the ball was still accelerating right before it hit the ground.
CRB Which of the following statements about Terminal Velocity are true?
I. Terminal Velocity can differ for the same free-falling object, depending on the medium it falls through.
II. Terminal Velocity is characterized by oscillating accelerations, leading to a constant velocity.
III. Terminal Velocity is only possible on Earth.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and II only
(D) I, II and III
(A) I only
Terminal Velocity is when the forces of gravity and resistance through the medium being traveled through are equal and opposite, leading to a constant velocity.
CRB True or false? Air Resistance is the sole type of Drag Force seen in nature. If false, provide a counterexample.
False. There are many types of resistance that can result in Drag Force. For a counterexample, Drag Forces can be seen in the circulatory system due to viscous friction of the blood!
What is the equation for displacement in terms of average velocity?
Displacement = Vav * t
(derived from the equation for Vav)
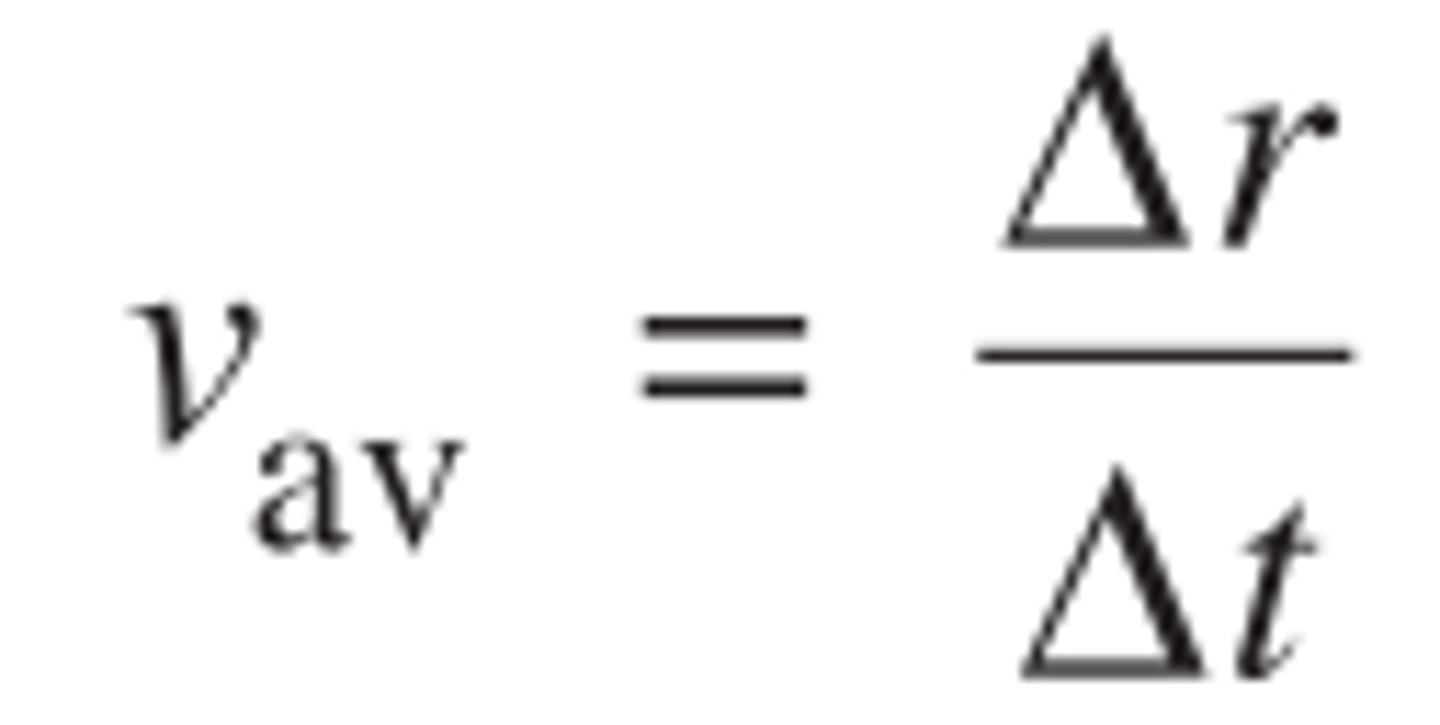
If Johnny starts his car and floors it, he accelerates constantly until he reaches a velocity of 62.44 m/s, which takes about 46.7 seconds. How far does he travel in that time?
(A) 326 m
(B) 867 m
(C) 1231 m
(D) 1458 m
(D) 1458 m
Average velocity = (62.44 + 0)/ 2 = ~30 m/s (actual 31.22 m/s)
Displacement = (Vav) x (Time)
Displacement = (30) x (46.7)
Displacement = 30 × 50
Displacement = ~1500 (actual: 1457.97)
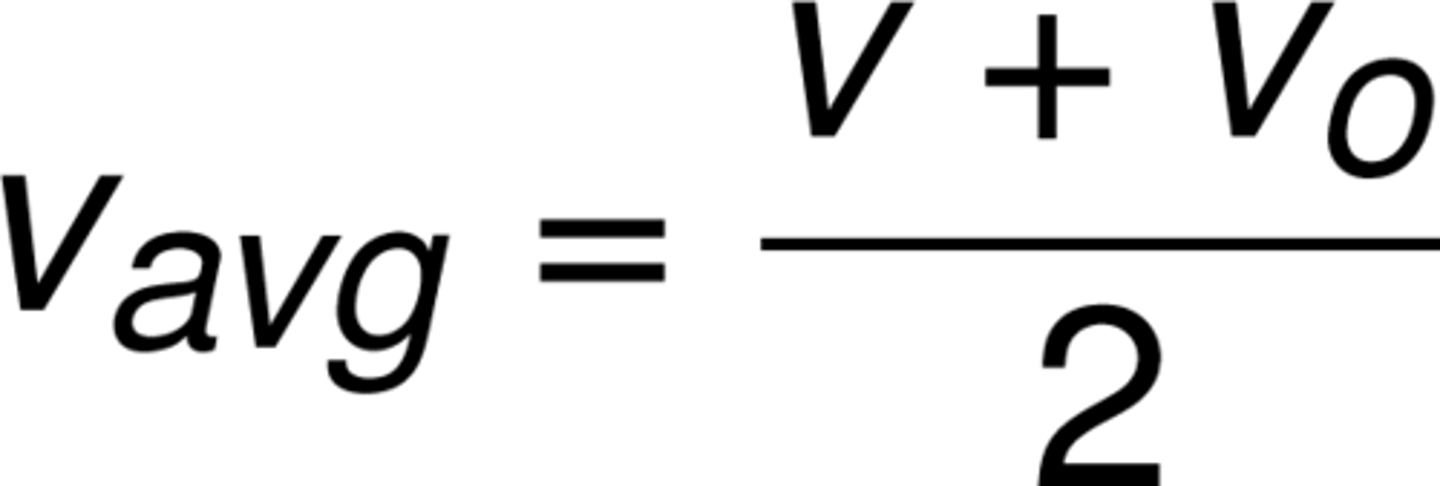
What is the equation for final velocity in terms of initial velocity and acceleration?
(Final Velocity) = (Initial Velocity) + ((Time)x(Acceleration))

Johnny got tired of running so fast (3 m/s), so he started slowing down at a rate of (0.2 m/s^2). What was his final velocity after 7 seconds of this deceleration?
(A) 4.4
(B) 1.2
(C) 1.6
(D) 2.0
(C) 1.6
(Final Velocity) = (Initial Velocity) + ((Time)x(Acceleration))
Final Velocity = (3 m/s) + ((-0.2 m/s^2)(7 s))
Final Velocity = 1.6 m/s

Sally is pushing a box along the floor to the right with a constant velocity of 4.23 m/s. Which of the following is true?
I. Sally is exerting a force on the box.
II. The box is experiencing a net force of zero.
III. The box is falling with a constant acceleration.
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) I and II Only
I. Sally is exerting a force on the box
II. The box is experiencing a net force of zero. (Frictional force = force exerted by Sally, so the box is moving at a CONSTANT velocity and is not accelerating)
III. The box is falling with a constant acceleration - gravity is opposed by the equal and opposite normal force
What is Newton's first law of motion?
When Fnet = 0, an object will stay at rest or continue to move at a constant velocity unless it is acted on by an unbalanced force

CRB Newton's First Law is often referred to as the Law of Inertia. Define Inertia.
Inertia is the tendency to resist change, whether that is moving uniformly straight or being at rest
CRB True or false? Inertia dictates the velocity of an object if the acceleration of that object is zero.
True. Inertia dictates the velocity of an object if the acceleration of that object is zero.
True or False? Speed will always be changed by an unbalanced force acting on the object.
False. An unbalanced force can change the direction, speed, or both. The correct sentence is "VELOCITY will always be changed by an unbalanced force acting on the object."
What is the equation that represents Newton's Second Law of Motion?
Force = mass x acceleration

CRB Two students, Ryan and Akeem, were fighting over if an object can have forces acting on it and not accelerate. Ryan argued that forces are directly related to acceleration, so any object with a force or forces acting on it must be accelerating in some direction. Is Ryan correct? If not, provide a counterexample.
Ryan is incorrect, because he is forgetting about vector addition and the possibility of opposing forces. If the vectors for each force add up to 0 magnitude, then there will be no "net force", and there will be no acceleration.
CRB True or false? If there is a non-zero (or unbalanced) net force, there must be acceleration.
True. If there is a non-zero (or unbalanced) net force, there must be acceleration (think of Fnet = ma)
Johnny was running away from some bullies at school. His friend was running with him and wanted to help him run faster, so he started pushing him forward with a force of 11.23 Newtons. If Johnny has a mass of 48.9 kg, what was Johnny's acceleration?
(A) 4.35 m/s^2
(B) 0.230 m/s^2
(C) 0.537 m/s^2
(D) 549 m/s^2
(B) 0.230 m/s^2
Force/mass = acceleration
11.23/48.9 = acceleration
acceleration = approx. 0.2 m/s^2 (actual: .23)
True or False? An object at rest will never move until it is acted on by an unbalanced Force.
True
What is Newton's Third Law of Motion?
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, or the forces of two bodies on each other are equal and opposite in direction.
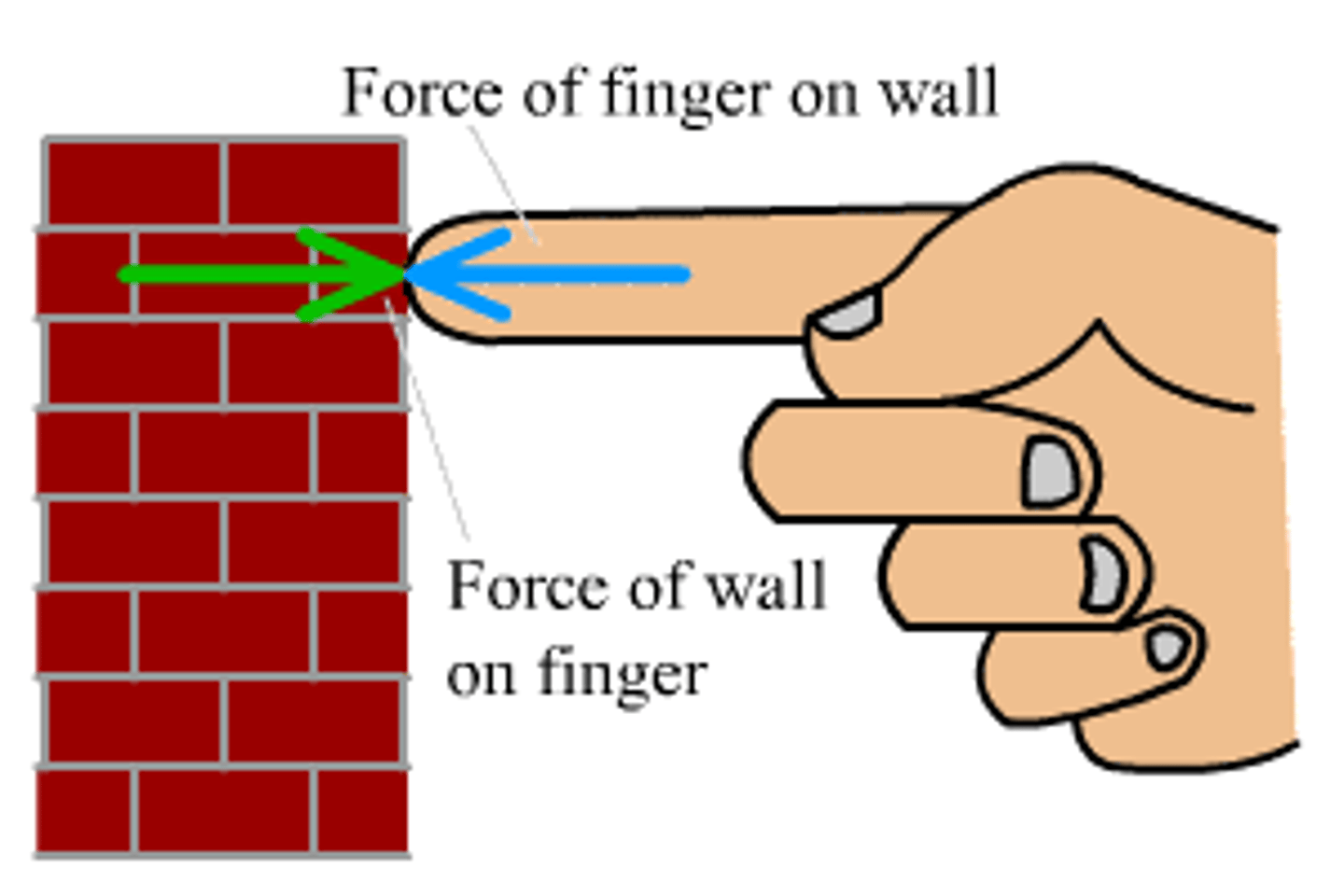
CRB True or false? Newton's First Law could be seen as a special case of Newton's Third law, where the reaction is equal to zero.
False. Newton's First Law could be seen as a special case of Newton's Second law, where Fnet and acceleration are 0
CRB Benny "The Jet" hit a baseball so hard one day that it broke a window. Benny was shocked that the ball and glass both went inside the building, thinking that the equal forces in opposite directions should have made one land inside the building and the other land outside. Where did Benny go wrong in this logic?
Those equal forces in opposite directions do occur! The force of the baseball striking the window provides a force towards the inside of the building, explaining the glass. The glass also exerts the same force going away from the building on the baseball; however, since the baseball was traveling at a high velocity, this force only decelerates it, and doesn’t change the direction of its velocity entirely.
CRB True or false? The baseball still traveling in a direction opposing the net force acting upon the baseball can be attributed to inertia.
False. Inertia would apply if there is no net force acting on the baseball. There clearly is a force exerted on the baseball by the window.
CRB In order to solve problems involving acceleration, velocity, and displacement, you need to know the 4 Linear Motion (Kinematics) equations. Write them out.
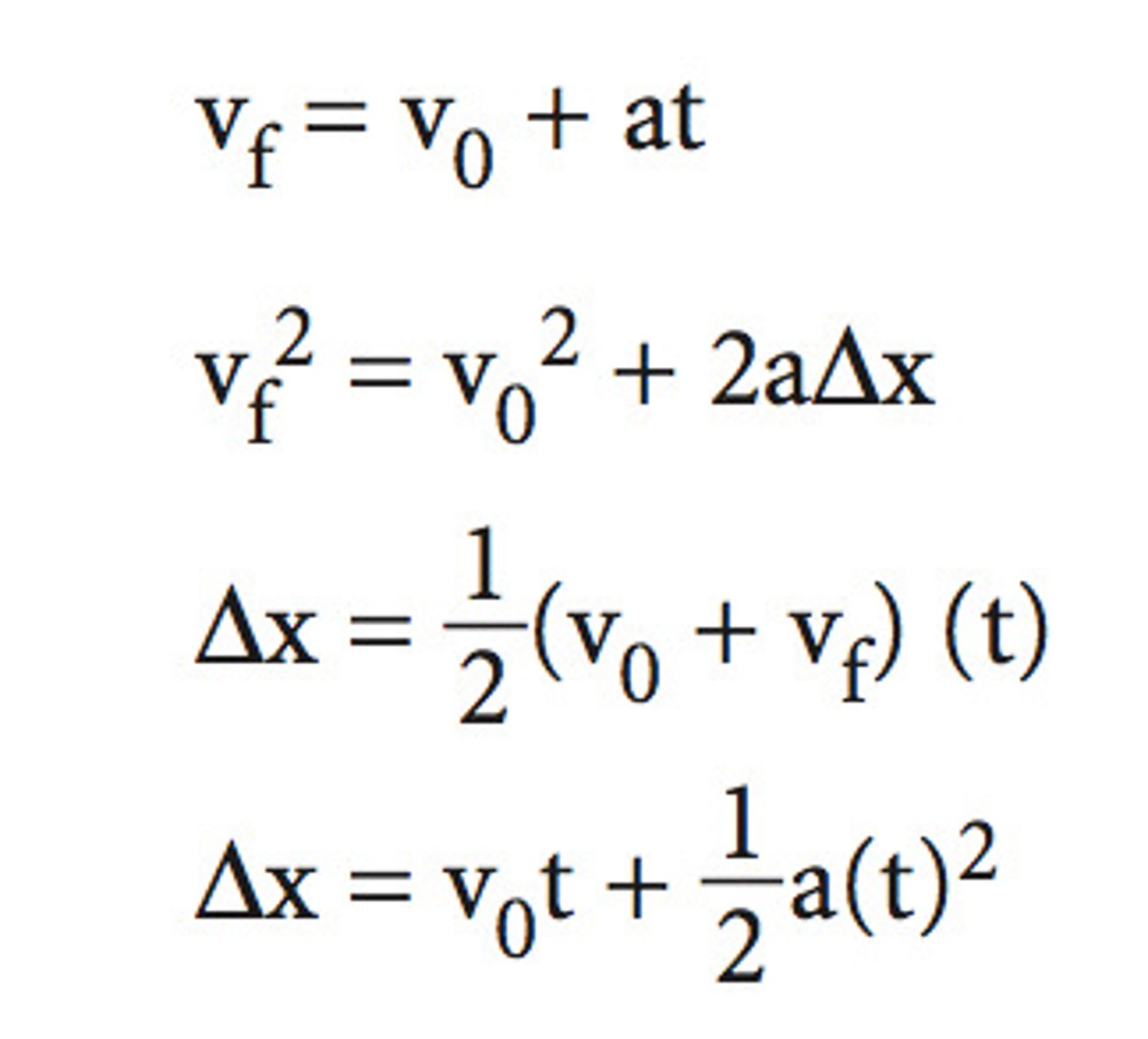
True or False? The Center of Mass is located at the very center of an object that has a mass.
False. The Center of Mass is located at the mean position of mass in a body/system. It is where gravity can be assumed to act on the object.
What will happen if a force acts on an object, but not on its center of mass?
The object will rotate around the center of mass.
Why do high jumpers arch their backs as they jump over the bar?
This allows their center of mass to be lower than the bar (outside their body!)
CRB Newton is also known for his Law of Gravitation. What is his law of Gravitation?
Fgrav= G x (M x m) / r^2
Fgrav = Force of Gravity
G = 6.7 x 10^-11 N m^2/ kg^2
M = Mass of object 1
m = mass of object 2
r = distance between centers of objects
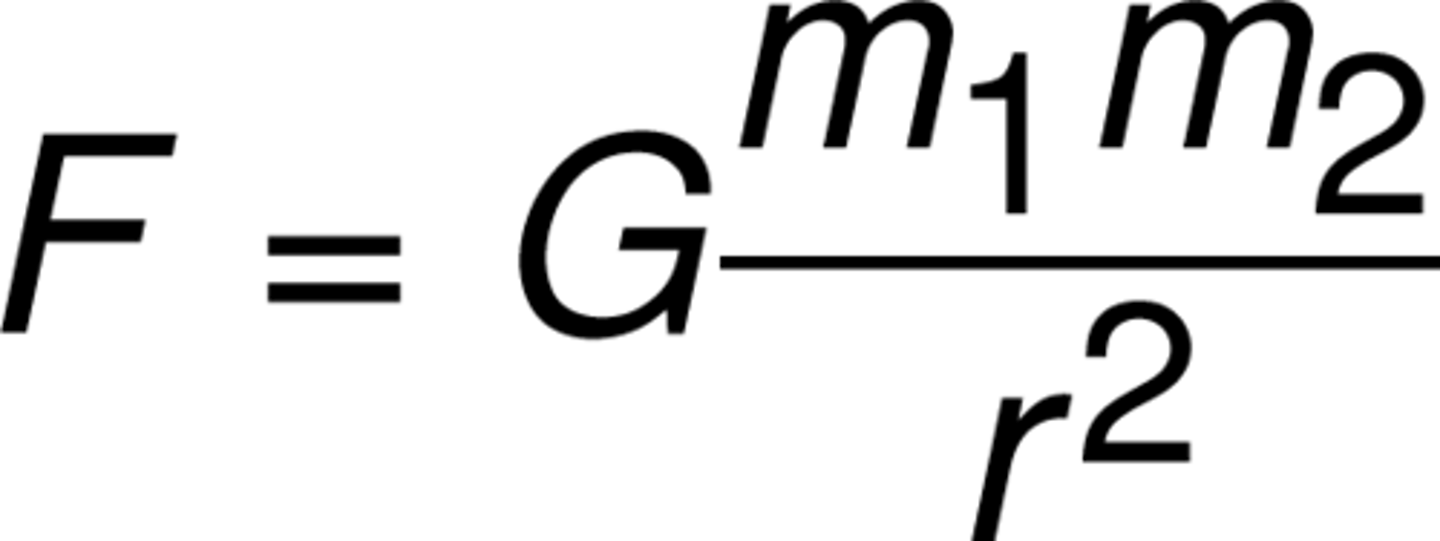
CRB On exam day, it is less likely that they would test that Force of Gravity equation directly. However, they may ask how the force of gravity changes if you quadruple the distance between the two objects' centers. How would it change?
(A) Gravity is 1/16 as strong
(B) Gravity is 1/8 as strong
(C) Gravity is 1/4 as strong
(D) Gravity is 4 times stronger
(A) Gravity is 1/16 as strong
Distance is squared and in the denominator, so as distance increases, the force of gravity will decrease. Four squared is equal to 16, so the force of gravity will be a sixteenth of its original value