AP Microeconomics Unit 2 Test Study Guide
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Demand
The different quantities that consumers are WILLING and ABLE to buy at different prices.
Law of Demand
There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. (As one increases, other decreases)
Why does the Law of Demand occur? 1. The Substitution Effect
If the price goes up for a product, then consumers will be more likely to by a substitute more. (Lucky Charms vs. Marshmellows and Stars)
Why does the Law of Demand occur? 2. The Income Effect
As a products price decreases, a consumer's purchasing power increases (they can buy more)
Why does the Law of Demand occur? 3. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
The more you buy of any good the less satisfaction you receive.
5 Shifters of DEMAND
1. Tastes & Preferences
2. # of Consumers
3. Price of Related Goods
4. Income
5. Future Expectations
*PRICE ONLY ACCOUNTS FOR MOVEMENT ALONG THE CURVE*
Normal vs. Inferior Goods
Normal Goods
- luxury cars, jewelry
- As income increases, demand increases (positive)
Inferior Goods
- ramen, used clothes
- As income increases, demand decreases (inverse)
Supply
The different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to produce/sell at different prices
Law of Supply
There is a direct/positive relationship between price and quantity supplied (As one increases, so does the other)
5 Shifters of SUPPLY
1. Prices & Availability of resources
2. # of sellers
3. technology
4. Government actions (taxes & subsidies)
5. Expectations of future sales
Surplus
When the quantity supplied > quantity demanded
Shortage
When quantity supplied < quantity demanded
(price will usually increase)
Equilibrium
quantity supplied = quantity demanded
Double Shift Rule
If TWO curves shift at the same time,
EITHER price or quantity will be
indeterminate (ambiguous).
Consumer Surplus
The difference between
what you are willing to pay and what you
actually pay.
CS = Buyer's Maximum - Price
Producer's Surplus
The difference between
the price the seller received and how much
they were willing to sell it for.
PS = Price - Seller's Minimum
Dead weight loss
The lost CS and PS= inefficient
Elasticity
Shows how sensitive quantity is to a change in price
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measurement of CONSUMER'S response to a change in price
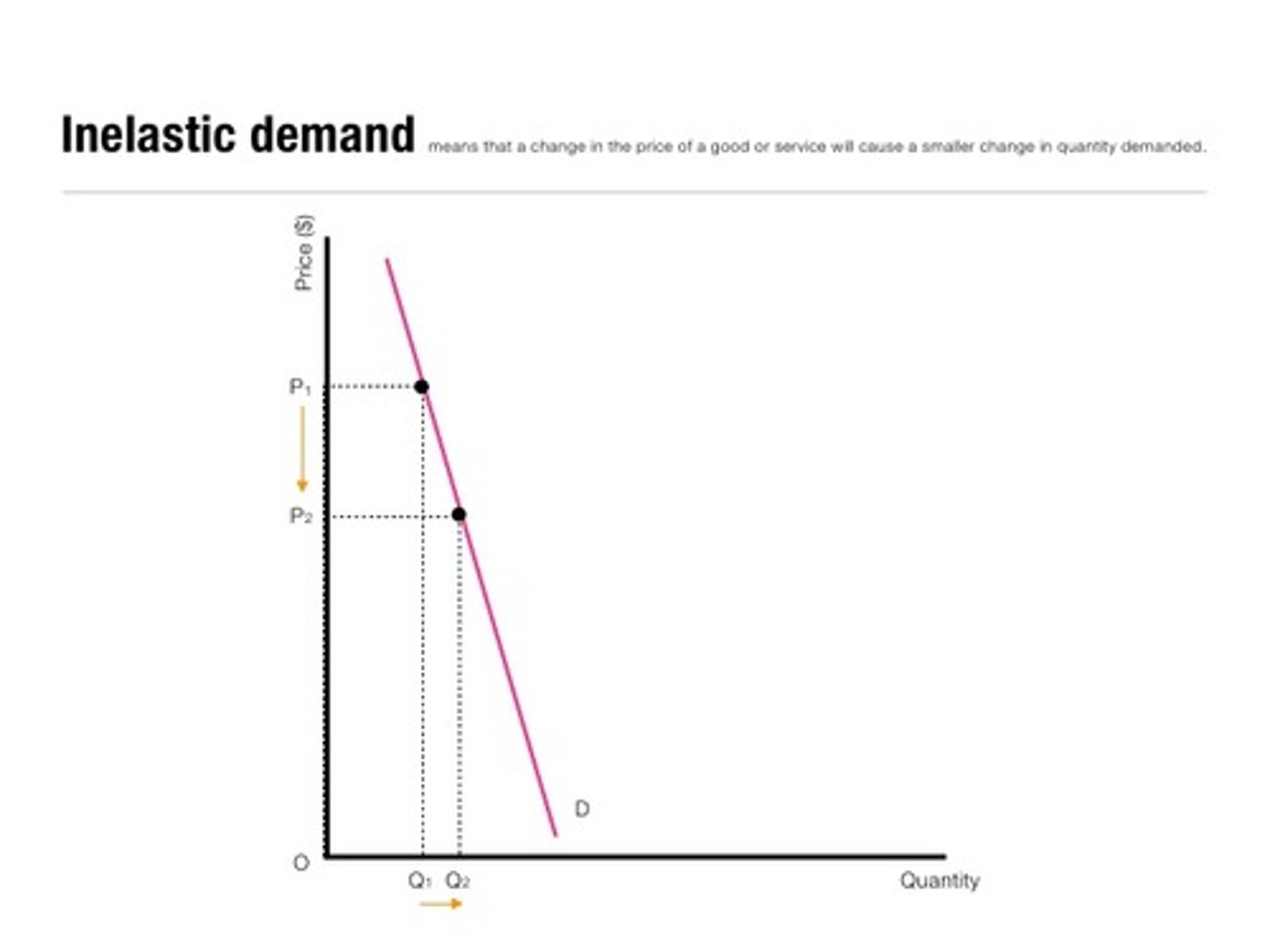
INelastic Demand
- Quantity is INsensitive to a change in price.
- Price increases, quantity demanded decreases a little
- The curve is steep
- Elasticity coefficient < 1
Elastic Demand
- Quantity is sensitive to a change in price
- Curve is flat
- Elasticity coefficient >1
- If price increases a little, quantity demanded decreases a lot
What makes a good inelastic?
- There aren't many substitutes
- It's a necessity
- Required now rather than later
- Small part of income
What makes a good elastic?
- Many subs
- It's a luxury
- There is time to decide if you want it or not
- Large part of income
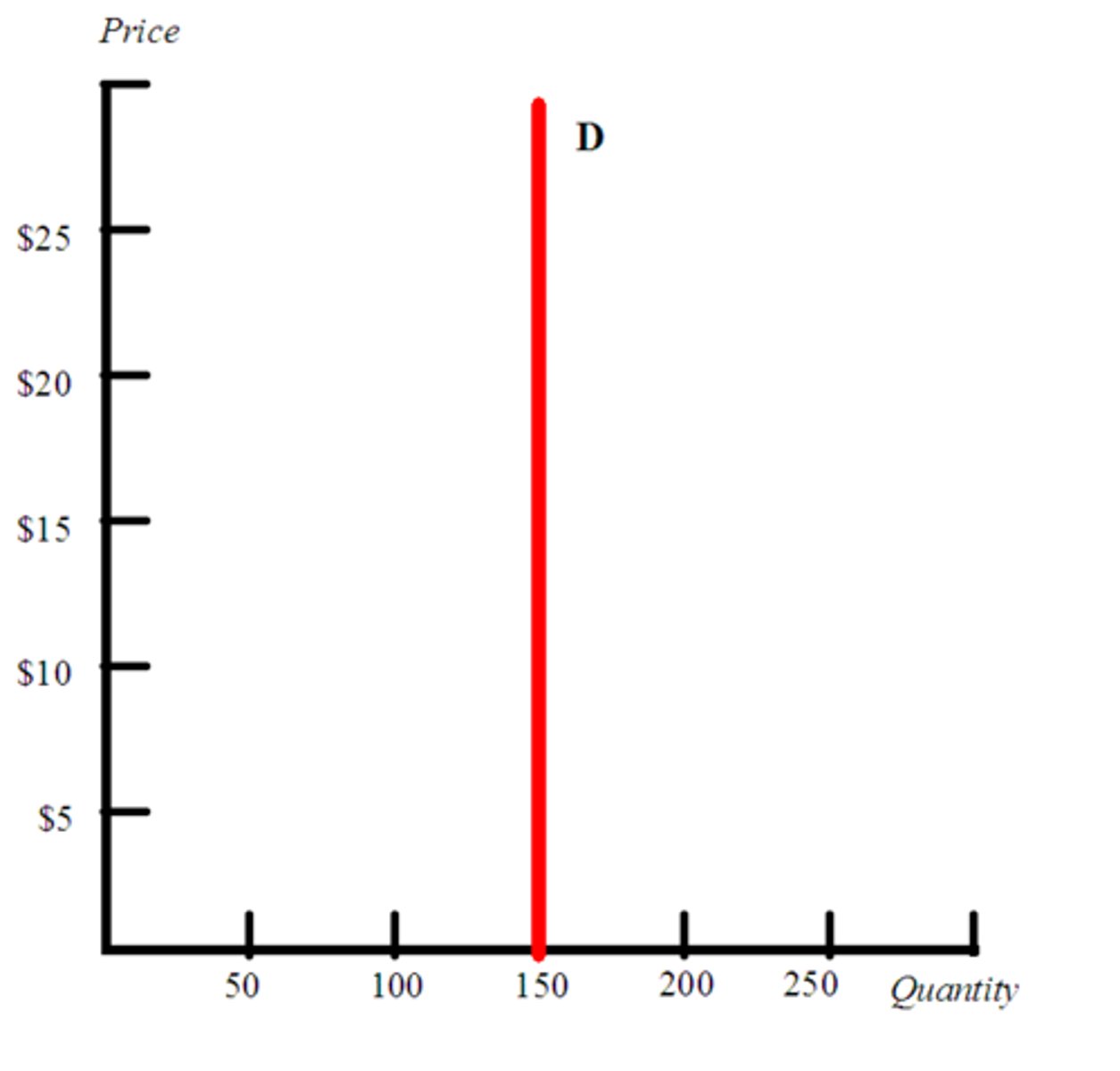
Perfectly INelastic
- The quantity demanded stays the same for any price
- Elasticity coefficient of 0
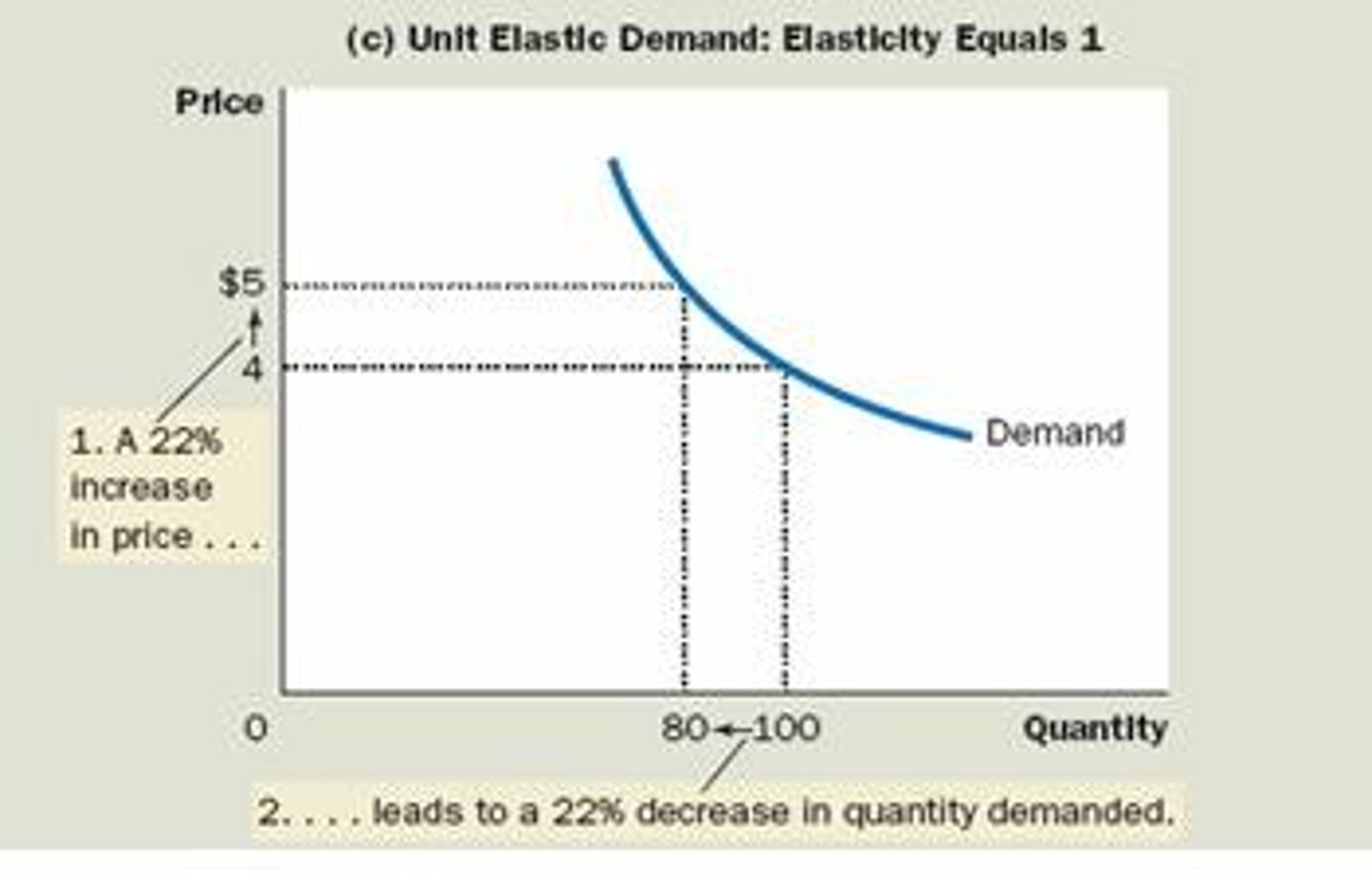
Unit Elastic
- % change in quantity demanded and % change in price are =
- Elasticity coefficient is 1
Perfectly Elastic
- The price stays the same for any quantity
- Coefficient is infinity
Elasticity types and coefficients
Relatively inelastic: <1
Perfectly inelastic: 0
Relatively elastic: >1
Perfectly elastic: infinity
Unit elastic: 1
Total Revenue Test
(Price x Quantity)
Uses elasticity to show how changes in P effect total revenue
Inelastic demand- Price increases, TR increases
Elastic- Price increases, TR decreases
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
Shows how sensitive the price of one good is in relation to the change in price of another
*If the number is positive, they're substitutes
*If the number is negative, they are complements
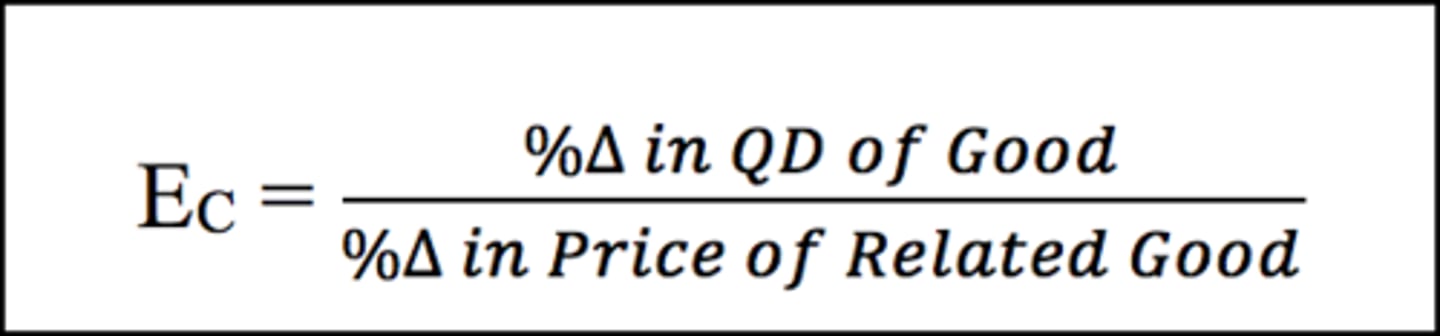
Income Elasticity of Demand
Shows if a product is sensitive to a change in income (If it's normal or inferior)
*If the number is positive, it's normal
*If the number is negative, it's inferior
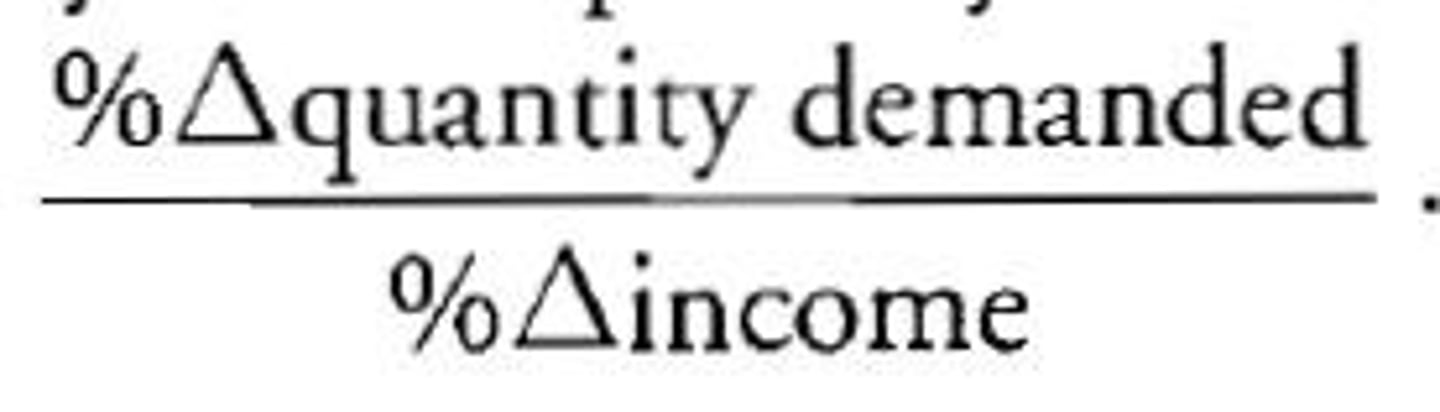
Price Elasticity of Supply
Shows sensitivity of producers to a change in price.
Time based, more time= more produced
Inelastic= steep curve
elastic= flat curve
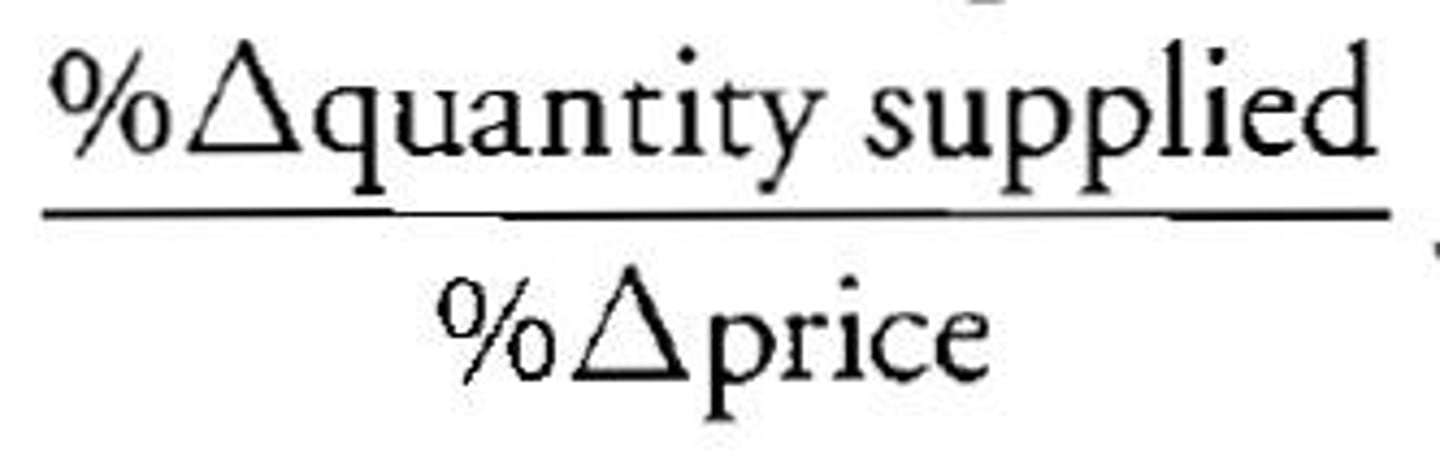
World Price
The price to import a good from another country
Tariff
Tax on imported goods to protect domestic producers from the cheap world price
Quota
Limit on # of imports (to protect domestic producers)
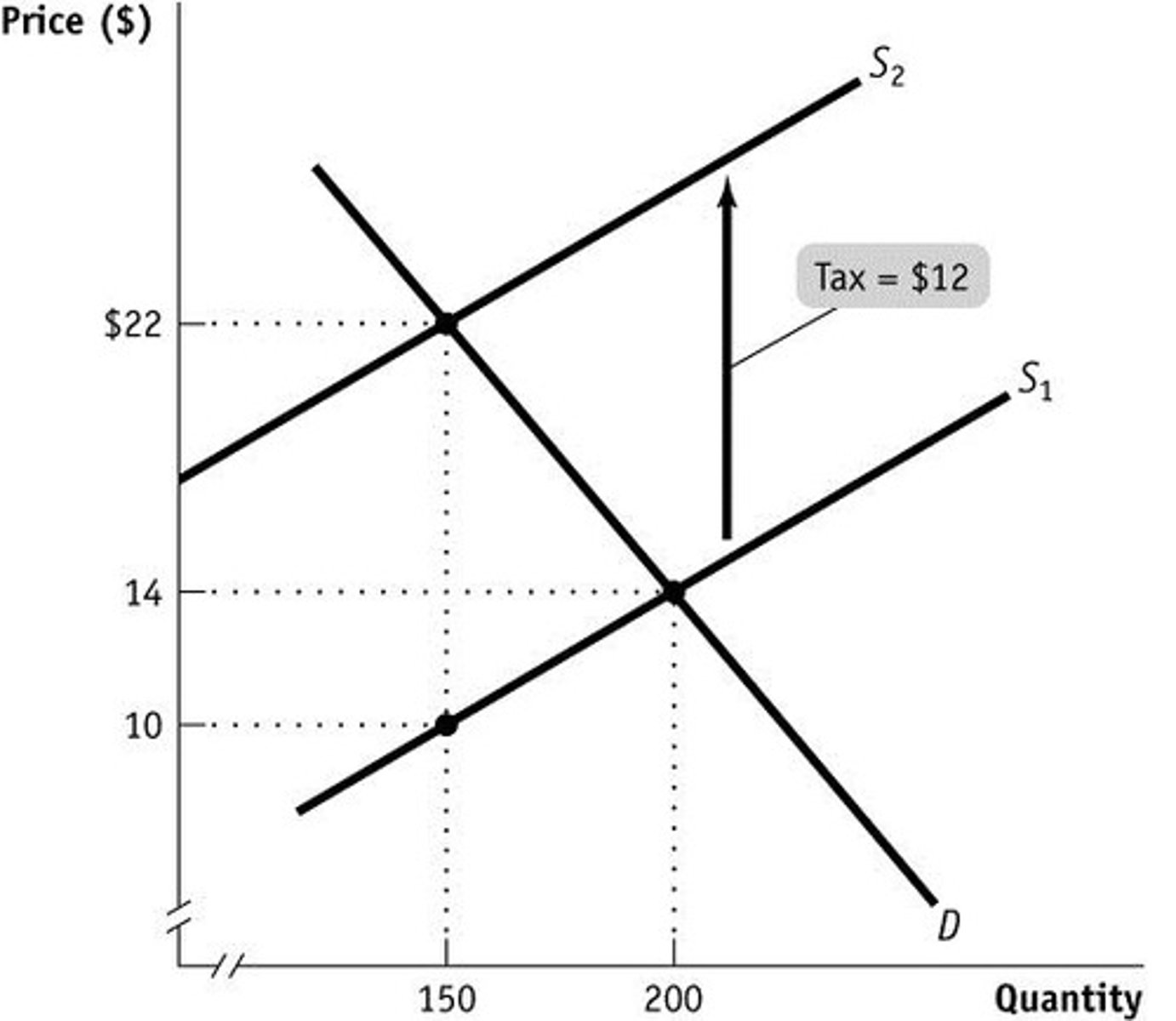
Excise Taxes
- A PER UNIT tax on producers
- goal= to make less of the goods that the government deems unwanted
- The tax is the vertical distance between the two supply lines
Utility Maximizing Rule
MU/P
to find the marginal utility from the total find the difference between the two marginal utilities.
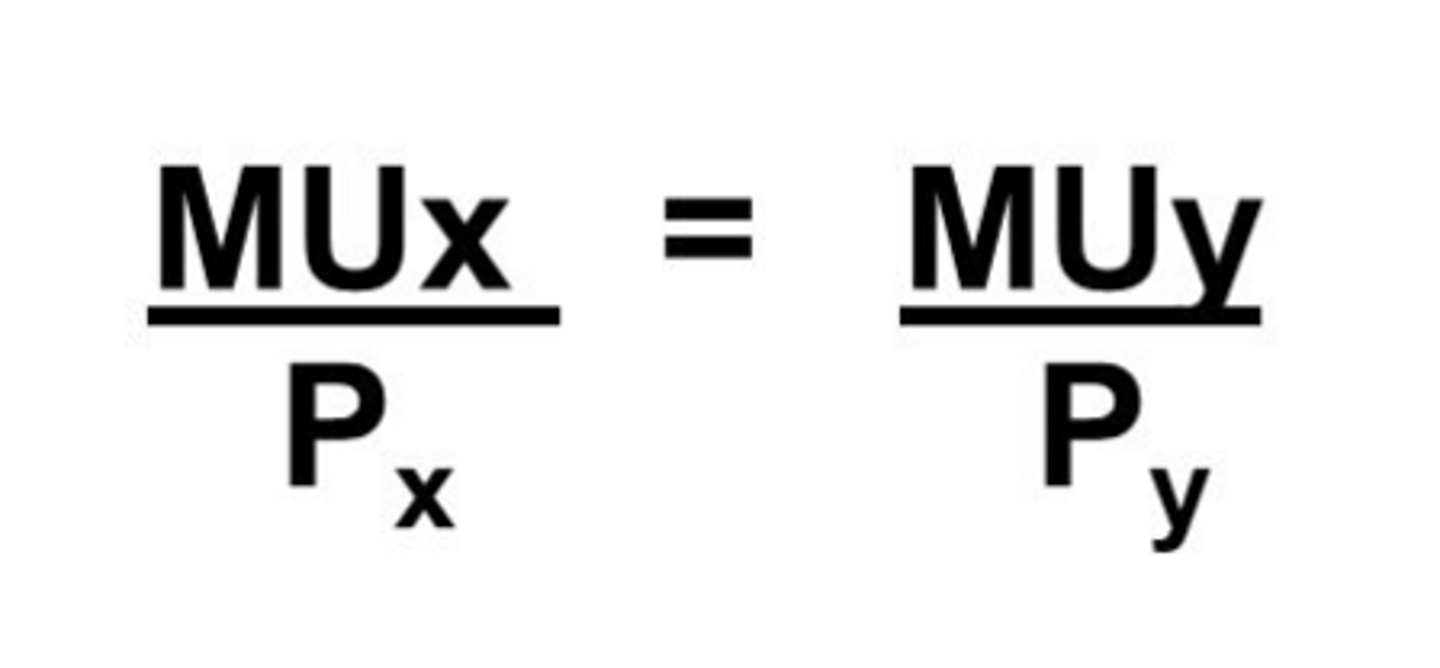
Supply and Demand Sample Graph
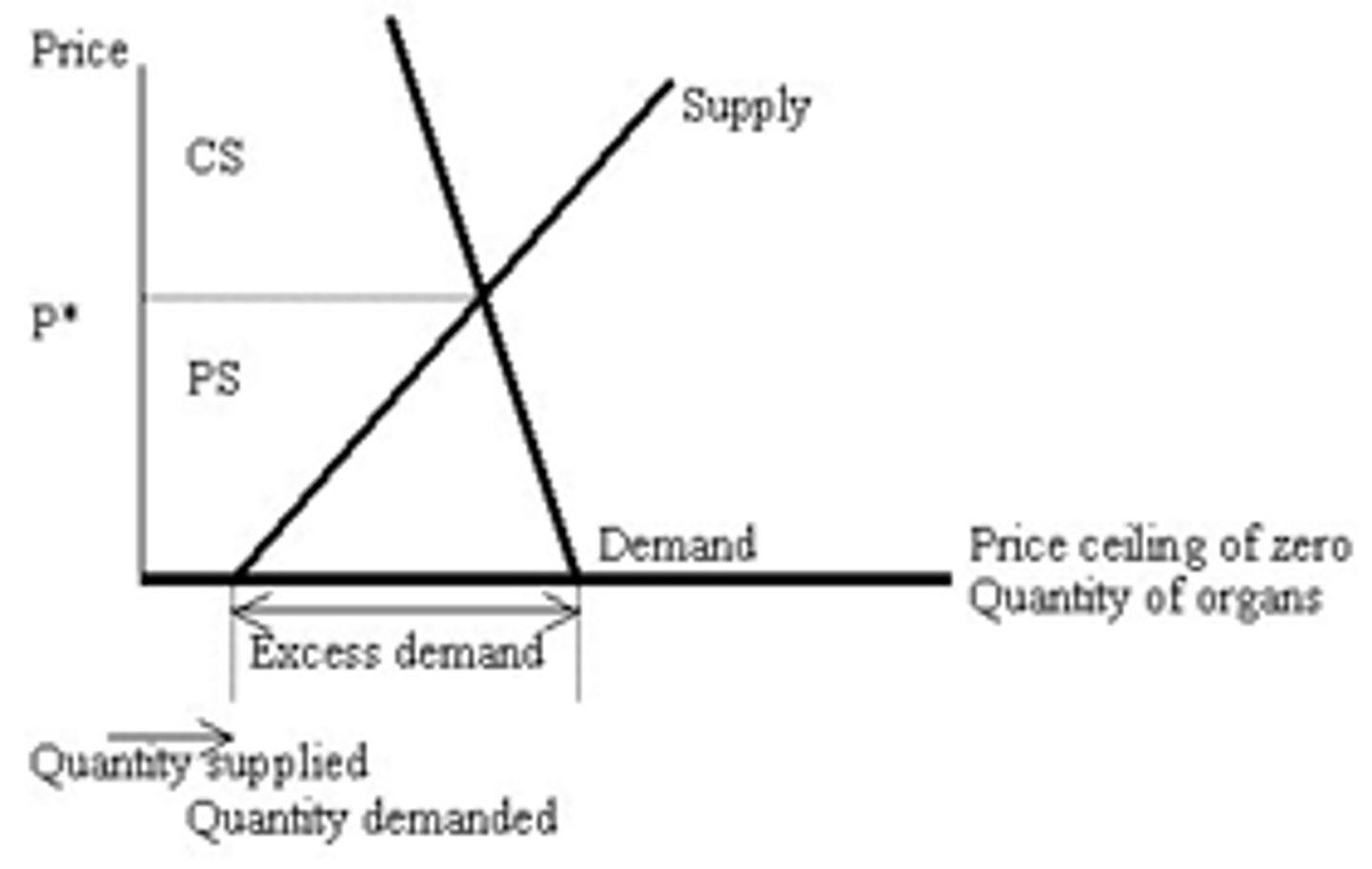
Price ceiling
Maximum legal price a seller can charge for a product
has to be below Eq to be binding
Price Floor
Minimum legal price a seller can sell a product.