9. ECG Interpretation: Electrical Axis and Deviation
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the fundamental question addressed by the QRS Axis?
In what general direction or toward which lead axis is the QRS complex predominantly oriented?
What does the QRS axis represent in the frontal plane?
This is a MEAN axis of all depolarization vectors in the FRONTAL plane.
What happens on an ECG when a wave of depolarization spreads toward the positive pole of a lead?
An upward (positive) deflection occurs.
What happens on an ECG when a wave of depolarization spreads toward the negative pole of a lead?
A downward (negative) deflection occurs.
What is the degree associated with the positive pole of Lead I and how does it divide the frontal plane?
The positive pole of lead I is 0˚; all points below the lead I axis are positive and all points above are negative.

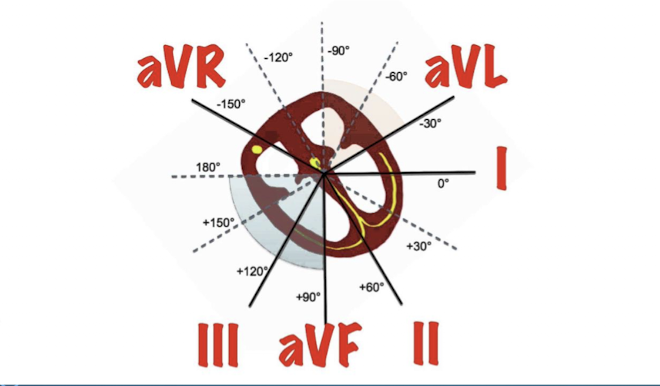
What crucial tool is used in determining the electrical axis?
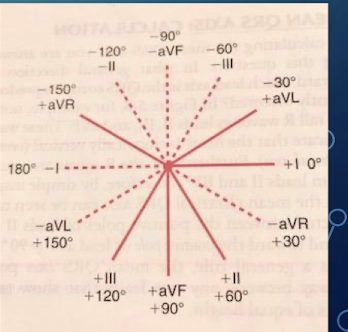
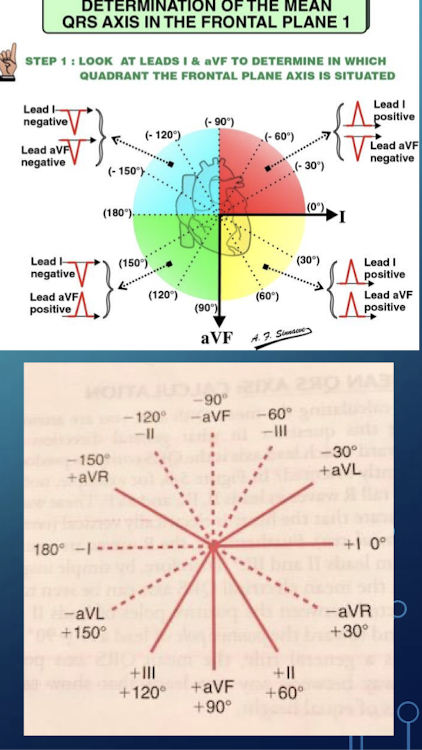
The Hexaxial Reference System is a crucial tool in determining axis.
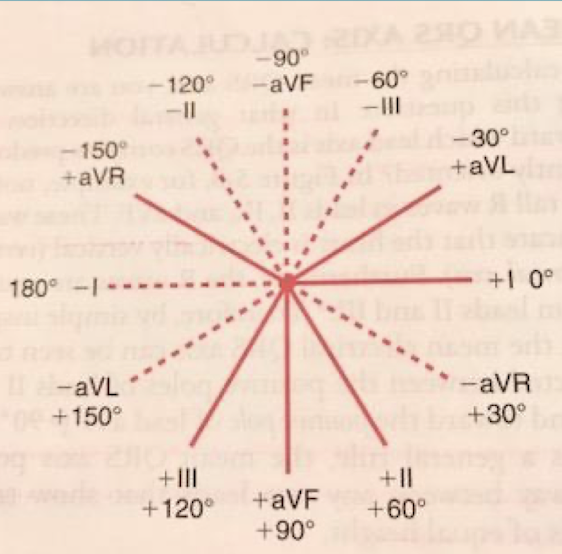

What leads comprise the Hexaxial Reference System?
It is a combination of the three standard limb leads found in Einthoven’s triangle (I; II; III) and lines of derivation of the three unipolar limb leads (aVR; aVL; aVF).


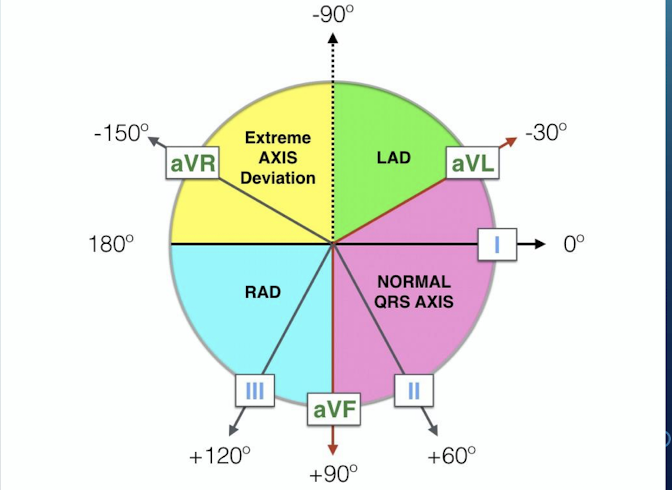
What range defines a Normal QRS Axis?
Between -30˚ and +90˚.
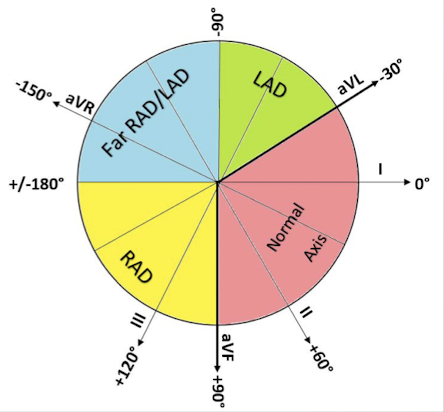
What range defines Left Axis Deviation (LAD)?
Less than -30˚.

What range defines Right Axis Deviation (RAD)?
Greater than or equal to +90˚.

What range defines Extreme Axis Deviation?
Between -90˚ and 180˚ (Can be right or left).

What is the utility of the Quadrant Method (Method I) for determining QRS axis?
It does NOT give the actual axis; it just puts the axis in the ballpark.
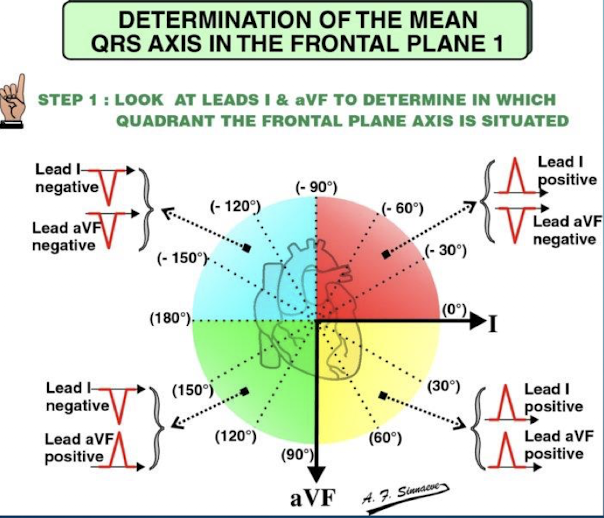
Which two leads are utilized when applying the Quadrant Method for QRS axis determination?
Lead I and Lead aVF.


A 45-year-old patient presents with an ECG showing a predominantly positive QRS complex in Lead I and a predominantly negative QRS complex in Lead aVF. What axis deviation is suggested by the Quadrant Method?
Lead I positive and Lead aVF negative indicates the axis is in the quadrant between 0˚ and -90˚; which suggests Left Axis Deviation (LAD).
What is the first step in calculating the specific QRS axis using Method II?
Identify the limb lead that is isoelectric (or has the smallest amplitude).
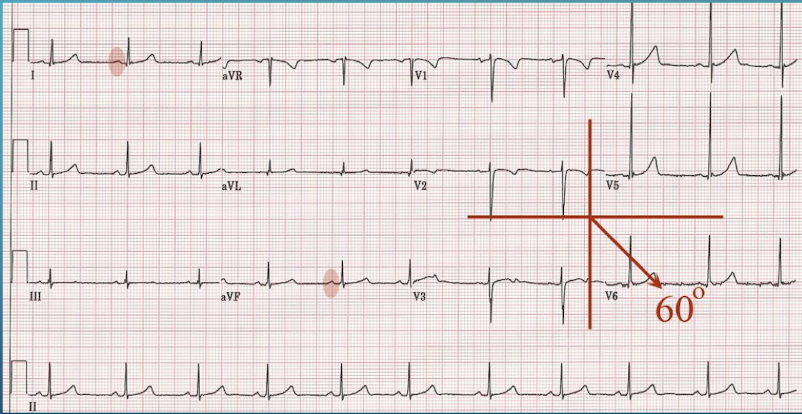
After identifying the isoelectric lead, what is the second step in calculating the specific axis?
Determine the limb lead that is oriented 90 degrees to this lead

If the QRS complex in the 90˚-oriented lead is predominantly upward which degree is assigned as the electrical axis?
Use the degrees assigned to the positive pole


If the QRS complex in the 90˚-oriented lead is predominantly downward which degree is assigned as the electrical axis?
Use the degrees assigned to the negative pole


On an ECG Lead aVL is observed to be isoelectric and Lead II is predominantly positive. What is the approximate specific QRS axis?
The axis is approximately +60˚; which is the positive pole of Lead II (90˚ away from aVL)

Electrically what does Left Axis Deviation (LAD) denote regarding the heart's orientation?
It denotes a more electrically horizontal heart
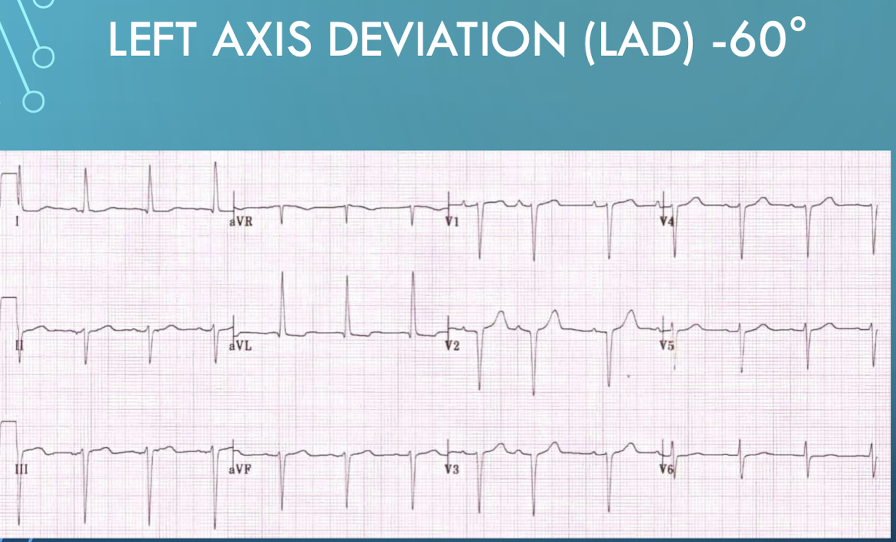
Name the common cardiovascular and mechanical causes of Left Axis Deviation (LAD).
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH); Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB); Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome; Mechanical Shifts (High diaphragm from pregnancy; ascites).
Electrically what does Right Axis Deviation (RAD) denote regarding the heart's orientation?
It denotes an electrically more vertical heart
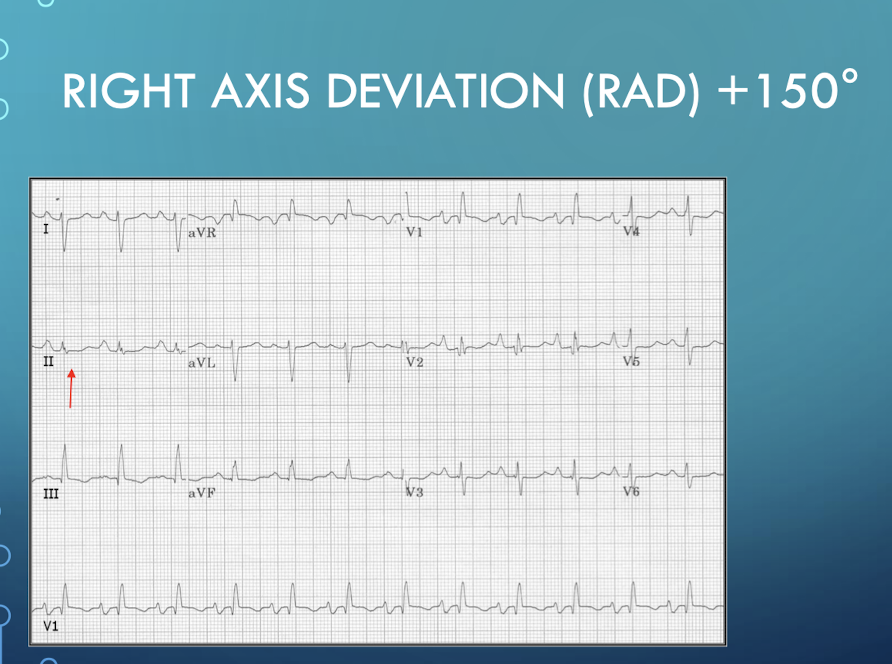

Name the common cardiovascular and pulmonary causes of Right Axis Deviation (RAD).
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH); Dextrocardia; Chronic Lung Disease (chronic bronchitis; emphysema); Acute PE; Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB); Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome.
A 68-year-old patient with a history of severe emphysema presents with an ECG showing a QRS axis of +120˚. What primary etiology is associated with this Right Axis Deviation (RAD)?
Chronic Lung Disease (chronic bronchitis; emphysema).
How is a normal P wave typically oriented in Lead aVR and Lead II during normal sinus rhythm and what is the approximate normal P wave axis?
A normal P wave is negative in lead aVR and positive in lead II; axis is approximately 60
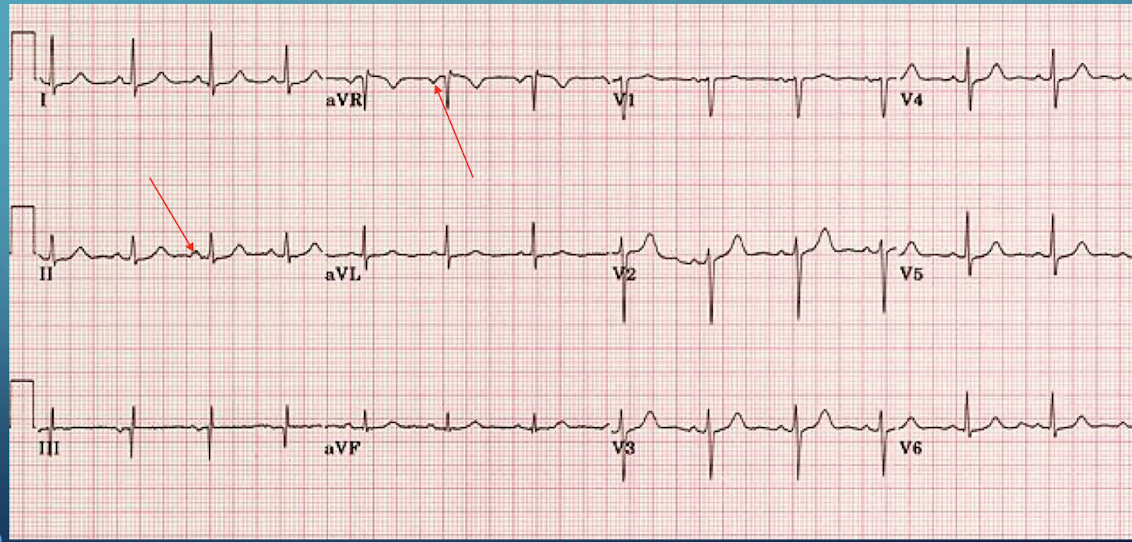
Describe the P wave orientation in leads aVR and II if an ectopic rhythm originates in the lower atria or AV junction.
The atria are stimulated in a retrograde fashion (depolarization toward lead aVR and away from lead II); therefore; the P wave is now positive in aVR and negative in lead II; axis is approximately -150˚.