OCR A A-Level Chemistry Module 2 - Foundations in Chemistry
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/121
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
1
New cards
Define isotope.
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses.
2
New cards
Define relative isotopic mass.
The mass of an atom of an isotope relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
3
New cards
Define relative atomic mass (Ar).
The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
4
New cards
Define relative molecular mass (Mr).
The weighted mean mass of a molecule of a compound compared to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
5
New cards
Define relative formula mass.
The weighted mean mass of the formula unit of a compound compared with 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
6
New cards
Define amount of substance.
The quantity whose unit of the mole, used as a means of counting any species such as atoms, ions and molecules.
7
New cards
Define mole.
The amount of any substance that contains as many elementary particles as there are carbon atoms in exactly 12g of the carbon-12 isotope, that is, 6.02x10²³ particles.
8
New cards
Define avagadros constant.
The number of atoms per mole of the carbon-12 isotope.
9
New cards
Define molar mass.
The mass per mole of a substance.
10
New cards
Define molar gas volume.
The volume per mole of gas molecules at a stated temperature and pressure.
11
New cards
Define empirical formula.
The formula that shows the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound.
12
New cards
Define molecular formula.
The formula that shows the number and type of atoms of each element present in a molecule.
13
New cards
Define anhydrous.
No water of crystallisation.
14
New cards
Define hydrated.
A crystalline compound containing water molecules.
15
New cards
Define water of crystallisation.
Water molecules that are bonded into a crystalline structure of a compound.
16
New cards
Define atomic orbital.
A region around the nucleus that can hold up to two electrons with opposite spins.
17
New cards
Define ionic bonding.
The electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions.
18
New cards
Define covalent bond.
The strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
19
New cards
Define dative covalent bond.
A covalent bond in which the shared pair of electrons has been supplied by one of the bonding atoms only.
20
New cards
Define electronegativity.
The ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond.
21
New cards
Define polar covalent bond.
A bond with a permanent dipole, having delta+ and delta- partial charges on the bonded atoms.
22
New cards
Define non-polar.
With no charge separation across a bond or in a molecule.
23
New cards
Define hydrogen bond.
A strong dipole-dipole attraction between an electron deficient hydrogen atom of -NH, -OH or -FH on one molecule and a lone pair of electrons on a highly electronegative atom containing N, O or F on a different molecule.
24
New cards
Define simple molecular lattice.
A three-dimensional structure of molecules, bonded together by weak intermolecular forces.
25
New cards
What is the equation for percentage yield?
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
26
New cards
What is the equation for atom economy?
total Mr of desired products/ total Mr of all products x 100
27
New cards
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl₃ + 3H₂. In terms of electron transfer, explain whether aluminium is being oxidised or reduced.
Oxidised, because aluminium has lost 3 electrons.
28
New cards
A salt used as a fertiliser has the empirical formula H₄N₂O₃. Suggest the formulae of the ions present in this salt.
NH4⁺ and NO₃⁻
29
New cards
State and explain 2 anomalous properties of ice caused by hydrogen bonding.
- Ice is less dense than water, as the molecules in ice are held apart in an open lattice by hydrogen bonds.
- Ice has a relatively high melting point, as hydrogen bonds are relatively strong.
- Ice has a relatively high melting point, as hydrogen bonds are relatively strong.
30
New cards
Silicon dioxide, SiO₂, has the same structure and bonding as diamond. State the structure and bonding in SiO₂.
Giant covalent lattice. Covalent bonding.
31
New cards
Describe and explain the electrical conductivity of sodium oxide, Na₂O and sodium in their solid and molten states.
- Sodium conducts electricity in solid and molten state. This is because in both solid and liquid state sodium has delocalised electrons.
- Sodium oxide conducts when molten but not solid. This is because molten sodium oxide has ions which are mobile. Solid sodium oxide has ions in a fixed position in an ionic lattice.
- Sodium oxide conducts when molten but not solid. This is because molten sodium oxide has ions which are mobile. Solid sodium oxide has ions in a fixed position in an ionic lattice.
32
New cards
One form of naturally occurring carbon is graphite.
- Electrical conductivity - good conductor.
- Hardness - soft.
- Melting point - very high.
Describe the bonding and structure in graphite. Explain, in terms of bonding and structure, the properties of graphite shown.
- Electrical conductivity - good conductor.
- Hardness - soft.
- Melting point - very high.
Describe the bonding and structure in graphite. Explain, in terms of bonding and structure, the properties of graphite shown.
- It has a giant covalent lattice with layers.
- It is a good conductor because it has delocalised electrons.
- It has a high melting point due to strong covalent bonds.
- It is soft due to weak London forces between the layers.
- It is a good conductor because it has delocalised electrons.
- It has a high melting point due to strong covalent bonds.
- It is soft due to weak London forces between the layers.
33
New cards
Write a balanced equation to show how ammonium sulfate could be formed by the reaction between aqueous ammonia and sulfuric acid.
2NH₃ + H₂SO₄ → (NH₄)₂SO₄
34
New cards
Explain what is meant by the term salt.
When the H⁺ ion in an acid is replaced by a metal ion.
35
New cards
What does the (v) represent in chloric(v) acid?
The oxidation number of chlorine.
36
New cards
Mg + H₂SO₄ → MgSO₄ + H₂. Use oxidation numbers to identify which element has been oxidised. Explain why.
Element oxidised: Magnesium. Why: Oxidation number increases by 2.
37
New cards
Explain why down the group halogens increase in boiling point.
- London forces are stronger.
- Number of electrons increases.
- Down the group more energy needed to break the London forces.
- Number of electrons increases.
- Down the group more energy needed to break the London forces.
38
New cards
Describe how London forces arise.
- Uneven distribution of electrons.
- Creates instantaneous dipole.
- Causes induced dipole in neighbouring molecules.
- Creates instantaneous dipole.
- Causes induced dipole in neighbouring molecules.
39
New cards
Suggest why there are only London forces in solid sulphur.
Only one type of atom.
40
New cards
Aluminium +660. Silicon +1410. Phosphorus +44. ← These are the melting points of three group 3 elements. Explain the trend in terms of bonding and structure.
- Aluminium has metallic bonding.
- Silicon has covalent bonding.
- Phosphorus has London forces.
- Aluminium and Silicon are both Giant.
- Phosphorus is Simple Covalent.
- More energy is needed to overcome the bonds in aluminium and silicon than in phosphorus.
- Silicon has covalent bonding.
- Phosphorus has London forces.
- Aluminium and Silicon are both Giant.
- Phosphorus is Simple Covalent.
- More energy is needed to overcome the bonds in aluminium and silicon than in phosphorus.
41
New cards
What term is given to the xH₂O part of the formula?
The number of waters of crystallisation.
42
New cards
Explain why magnesium has a higher melting point than sodium.
- Magnesium ions have a greater charge.
- Magnesium has more delocalised electrons.
- Magnesium has stronger attraction between ions and delocalised electrons.
- Magnesium has more delocalised electrons.
- Magnesium has stronger attraction between ions and delocalised electrons.
43
New cards
Usually as the atomic number increases, the relative atomic mass also increases. Explain why this isn't true for cobalt and nickel.
- The mass of the atom depends on the sum of its protons and neutrons.
- The relative atomic mass includes the contribution of all the isotopes present.
- Cobalt has a heavy isotope which causes its relative atomic mass to exceed that of nickel.
- The relative atomic mass includes the contribution of all the isotopes present.
- Cobalt has a heavy isotope which causes its relative atomic mass to exceed that of nickel.
44
New cards
Sulfur exists as S₈ molecules and chlorine as Cl₂ molecules. Use this information to explain the different in their melting points.
- Both molecules have intermolecular forces.
- S₈ has stronger intermolecular forces.
- S₈ has stronger intermolecular forces.
45
New cards
What is the trend with group 2 carbonates and thermal stability?
- As the charge density of the metal ions decreases, there is less distorting effect on the carbonate ions.
- This decrease in distortion means more energy is required to break the bonds within the carbonate ion to form carbon dioxide.
- This results in an increase in thermal stability as you go down Group 2.
- This decrease in distortion means more energy is required to break the bonds within the carbonate ion to form carbon dioxide.
- This results in an increase in thermal stability as you go down Group 2.
46
New cards
Explain the properties of ionic compounds.
Melting and boiling point:
- Strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions in giant ionic lattice, therefore high melting and boiling point to overcome.
- Melting points higher for those with lattices containing ions with greater ionic charges, due to stronger attraction between ions.
Solubility:
- Solubility decreases as ionic charge increases as the ionic charge may be too strong for water to break down the lattice.
- Many dissolve in water as polar water molecules break down the lattice and surround each ion in solution.
Electrical conductivity:
- In solid state cannot conduct electricity as the ions are in a fixed position in the giant ionic lattice - there are no mobile charge carriers.
- In molten state can conduct electricity as the solid ionic lattice breaks down.
- The ions are now free to move as mobile charge carriers.
- Strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions in giant ionic lattice, therefore high melting and boiling point to overcome.
- Melting points higher for those with lattices containing ions with greater ionic charges, due to stronger attraction between ions.
Solubility:
- Solubility decreases as ionic charge increases as the ionic charge may be too strong for water to break down the lattice.
- Many dissolve in water as polar water molecules break down the lattice and surround each ion in solution.
Electrical conductivity:
- In solid state cannot conduct electricity as the ions are in a fixed position in the giant ionic lattice - there are no mobile charge carriers.
- In molten state can conduct electricity as the solid ionic lattice breaks down.
- The ions are now free to move as mobile charge carriers.
47
New cards
What is a double covalent bond?
The electrostatic attraction between two shared pairs of electrons and the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
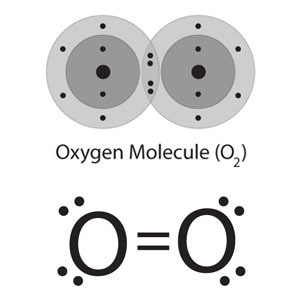
48
New cards
What does the larger the value of the average bond enthalpy suggest.
The stronger the covalent bond.
49
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 4 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Tetrahedral - 109.5°
50
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 3 bonded pairs and 1 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Pyramidal - 107°
51
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 2 bonded pairs and 2 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Non-linear - 104.5°
52
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 2 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Linear - 180°
53
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 3 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Trigonal planar - 120°
54
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 5 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Trigonal bipyramidal - 120°, 90°
55
New cards
What is the name of the shape of molecule with 6 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs and what is the bond angle?
Octahedral - 90°
56
New cards
Describe the relative repulsions between lone pairs and bonded pairs by increasing repulsion.
bp-bp → bp-lp → lp-lp
57
New cards
Why do lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs?
The lone pair of electrons is closer to the nucleus compared to the bonded pair and therefore repel other lone pairs greater than bonded pairs.
58
New cards
Explain the properties of simple molecular substances.
Melting point and boiling point:
- Low melting point and boiling point due to weak intermolecular forces.
Solubility:
- Non-Polar - Non-polar simple molecular substances tend to be soluble in other non-polar solvents as intermolecular forces form between the molecules and the solvent, interactions weaken the intermolecular forces in the simple molecular lattice and the intermolecular forces break and the compound dissolves.
- Non-polar tend not to be soluble in polar solvents as there is little interaction between the molecules in the lattice and the solvent molecules, the intermolecular bonding within the polar solvent is too strong to be broken.
- Polar - Polar covalent substances may dissolve in polar solvents as the polar solute molecules and polar solvent molecules can attach each other.
Electrical conductivity:
- There are no mobile charge particles in simple molecular structure.
- There is therefore nothing to conduct.
- Low melting point and boiling point due to weak intermolecular forces.
Solubility:
- Non-Polar - Non-polar simple molecular substances tend to be soluble in other non-polar solvents as intermolecular forces form between the molecules and the solvent, interactions weaken the intermolecular forces in the simple molecular lattice and the intermolecular forces break and the compound dissolves.
- Non-polar tend not to be soluble in polar solvents as there is little interaction between the molecules in the lattice and the solvent molecules, the intermolecular bonding within the polar solvent is too strong to be broken.
- Polar - Polar covalent substances may dissolve in polar solvents as the polar solute molecules and polar solvent molecules can attach each other.
Electrical conductivity:
- There are no mobile charge particles in simple molecular structure.
- There is therefore nothing to conduct.
59
New cards
Suggest why ice has a higher melting point than solid ammonia.
- Ice has stronger hydrogen bonds.
- Oxygen has 2 lone pairs of electrons and Ammonia has 1.
- Oxygen has 2 lone pairs of electrons and Ammonia has 1.
60
New cards
Describe the intermolecular forces present in hydrogen chloride gas.
- Permanent dipole-dipole intermolecular forces because of the difference in electronegativity.
- London forces because of the movement of the electrons.
- London forces because of the movement of the electrons.
61
New cards
Describe the intermolecular forces present in hydrogen gas.
London forces because of the movement of the electrons only, because the bond is non-polar.
62
New cards
Describe the intermolecular forces present in ammonia gas.
- Permanent dipole-dipole intermolecular forces because of the difference in electronegativity.
- London forces because of the movement of the electrons.
- London forces because of the movement of the electrons.
63
New cards
What is the formula for a sulphite?
SO₃²⁻
64
New cards
What is the formula for a nitrite?
NO₂⁻
65
New cards
What does the 'p' stand for in pV = nRT and what is the unit?
Pressure (Pa)
66
New cards
What does the 'V' stand for in pV = nRT and what is the unit?
Volume (m³)
67
New cards
What does the 'n' stand for in pV = nRT?
Number of moles
68
New cards
What does the 'R' stand for in pV = nRT?
Gas constant (8.31)
69
New cards
What does the 'T' stand for in pV = nRT and what is the unit?
Temperature (K)
70
New cards
What is 0 degrees celsius in Kelvin?
+273K
71
New cards
dm³ to m³
divide by 1000
72
New cards
KPa to Pa
x1000
73
New cards
What is number of particles equal to?
Avagadro's constant x number of moles.
74
New cards
Why does a giant ionic structure have a high boiling point?
- Strong electrostatic attraction.
- Many bonds to break.
- Many bonds to break.
75
New cards
What atoms do covalent bonds form between?
Non-metal
76
New cards
What atoms do ionic bonds form between?
Non-metal + Metal
77
New cards
How many orbitals and electrons in a s-subshell?
1 orbital and 2 electrons.
78
New cards
How many orbitals and electrons in a p-subshell?
3 orbitals and 6 electrons.
79
New cards
How many orbitals and electrons in a d-subshell?
5 orbitals and 10 electrons.
80
New cards
How many orbitals and electrons in a f-subshell?
7 orbitals and 14 electrons.
81
New cards
What is the shape around the carbon atoms in graphene?
trigonal planar
82
New cards
Fullerenes, graphite and diamond are all forms of carbon. Fullerenes dissolve in petrol, but diamond and graphite do not. This is because?
Diamond and graphite are giant structures but fullerenes are molecular.
83
New cards
Why does a carton of milk expand when freezing?
Hydrogen bonds in ice hold H₂O molecules further apart than in water.
84
New cards
Why does water have a concentration of approx. 56 mol dm⁻³?
n(H₂O) in 1dm³ = 1000/18 = 56 mol
85
New cards
How could a student be confident all waters of crystallisation are removed in an experiment?
Heat to constant mass.
86
New cards
Which of these ions has a different number of electrons from the other 3 ions.
Ga³⁺/Cl⁻/S²⁻/Ca²⁺
Ga³⁺/Cl⁻/S²⁻/Ca²⁺
- Ga³⁺ has 28
- The rest have 18
- The rest have 18
87
New cards
The burette readings from a titration are shown below:
- Final reading/ cm³ = 24.95
- Initial reading/ cm³ = 5.00
The burette had an uncertainty of ₊₋0.05cm³ in each reading.
What is the percentage uncertainty of the reading titre?
- Final reading/ cm³ = 24.95
- Initial reading/ cm³ = 5.00
The burette had an uncertainty of ₊₋0.05cm³ in each reading.
What is the percentage uncertainty of the reading titre?
0.05x2/19.95 = 0.501%
88
New cards
The electron configuration of element X is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁴.
What is the formula of a compound formed when sodium reacts with element X?
What is the formula of a compound formed when sodium reacts with element X?
Na⁺, X²⁻
Na₂X
Na₂X
89
New cards
What is the number of oxygen atoms in 88g of CO₂?
2.41 x10²⁴
90
New cards
What is the oxidation number of Fe in K₂FeO₄?
+6
91
New cards
A phosphate (V) ion has the formula PO₄³⁻. What is the formula for copper(I) phosphate?
Cu₃PO₄
92
New cards
Which element has atoms with the greatest number of singly occupied orbitals C/Cl/Ca/Ga?
C
93
New cards
Which compound has polar molecules OCl₂/BCl₃/CCl₄/SCl₆?
OCl₂ as it has a non-linear shape so dipoles don't cancel out.
94
New cards
Which element has the highest boiling point and why?
Silicon/Phosphorus/Sulfur/Chlorine.
Silicon/Phosphorus/Sulfur/Chlorine.
Silicon because it is macromolecular with strong covalent bonds and the others are simple molecular with weak intermolecular forces.
95
New cards
Ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH, is the main dissolved acid in vinegar. Ethanoic acid is a weak acid.
What is meant by acid and weak acid?
What is meant by acid and weak acid?
- Acid is a proton donor.
- Weak acid is an acid that only partially dissociates into ions in solution.
- Weak acid is an acid that only partially dissociates into ions in solution.
96
New cards
Several students titrate 25.00cm³ of the same solution of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid. One student obtains a smaller titre than the other students. Which procedure explains the smaller titre?
a) The burette readings are taken from the top of the meniscus instead of the bottom.
b) The conical flask is rinsed with water before carrying out the titration.
c) An air bubble is released from the jet of the burette during the titration.
d) The pipette is rinsed with water before filling with NaOH.
a) The burette readings are taken from the top of the meniscus instead of the bottom.
b) The conical flask is rinsed with water before carrying out the titration.
c) An air bubble is released from the jet of the burette during the titration.
d) The pipette is rinsed with water before filling with NaOH.
d.
97
New cards
Which statement gives the numerical value of the Avogadro constant?
a) The number of moles in 12g of carbon-12.
b) The number of electrons lost by 20.5g of calcium when it reacts with oxygen.
c) The number of molecules in 16g of oxygen.
d) The number of atoms in 1 mole of chlorine molecules.
a) The number of moles in 12g of carbon-12.
b) The number of electrons lost by 20.5g of calcium when it reacts with oxygen.
c) The number of molecules in 16g of oxygen.
d) The number of atoms in 1 mole of chlorine molecules.
b.
98
New cards
0.8g of element X is reacted with 0.4g of O₂ to form an oxide with the formula X₂O₃. What is the identity of element X?
Titanium.
99
New cards
Explain what is meant by the term weighted mean mass.
The average mass taking into account the relative abundances of isotopes.
100
New cards
Which statement describes electronegativity?
a) A measure of the reactivity of an element.
b) The ability of an atom to attract an electron to become a 1- ion.
c) The attraction of a bonded atom for the electrons in a covalent bond.
d) The attraction of an atom of for a lone pair of electrons.
a) A measure of the reactivity of an element.
b) The ability of an atom to attract an electron to become a 1- ion.
c) The attraction of a bonded atom for the electrons in a covalent bond.
d) The attraction of an atom of for a lone pair of electrons.
c.