Amino acids, peptides and proteins 1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
How are proteins linked to disease?
Protein dysfunction is a common cause of disease
3 reasons why we care about proteins in pharmacy

What are proteins made up of?
Alpha-amino acid monomers which built proteins allowing it to be reactive and have functional polymers governed by chemical properties
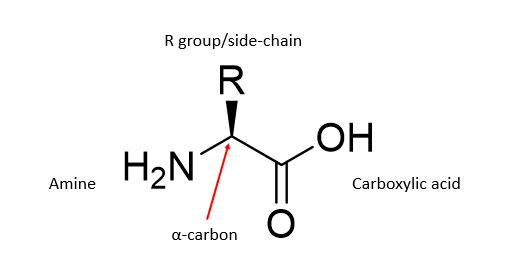
What in the structure of an amino acid defines it?
The R group
What are the 6 different types of proteinogenic amino acids?
aliphatic are hydrophobic or lipohpilic
polar are hydrophilic and have electronegative atons
basic contain bases
acidic contains acids
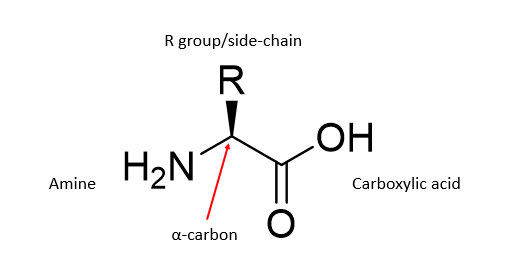
Amino acids can exist in how many different ionisation states and which type of ionisation states at different pHs?
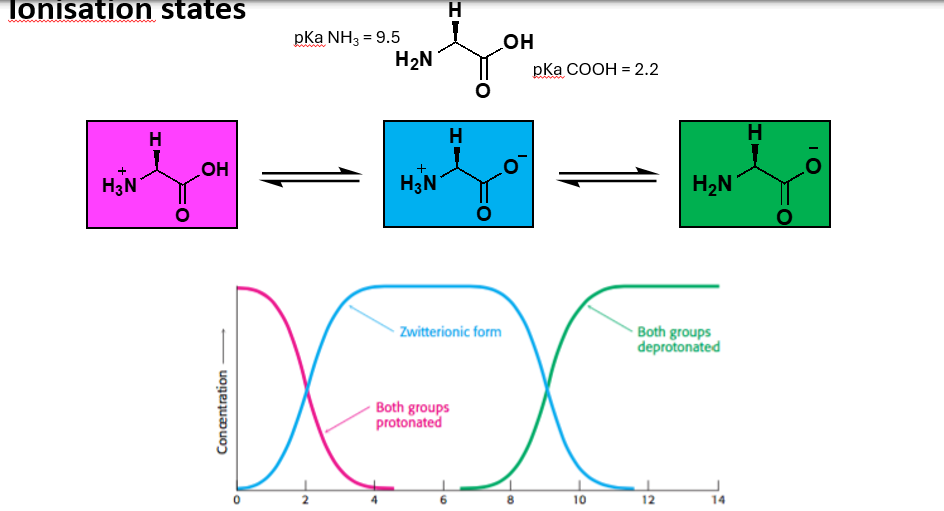
What are zwitterions?
A molecule with functional groups, of which at least one has a positive and one has a negative charge. The net charge of the molecule is zero.
What is the isoelectric point (pl)?
The pH at which a particular molecule carries no net charge, each amino acid has a different pl
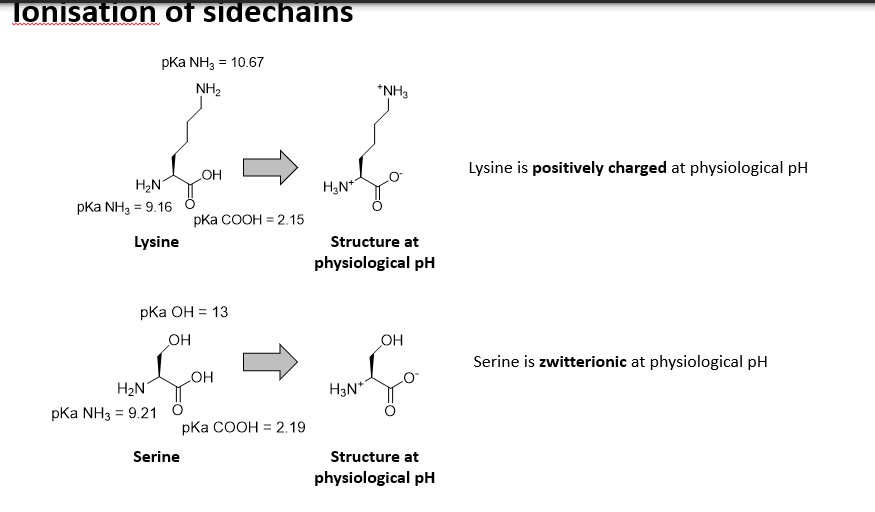
Can the sidechains of amino acids be ionised?
Yes
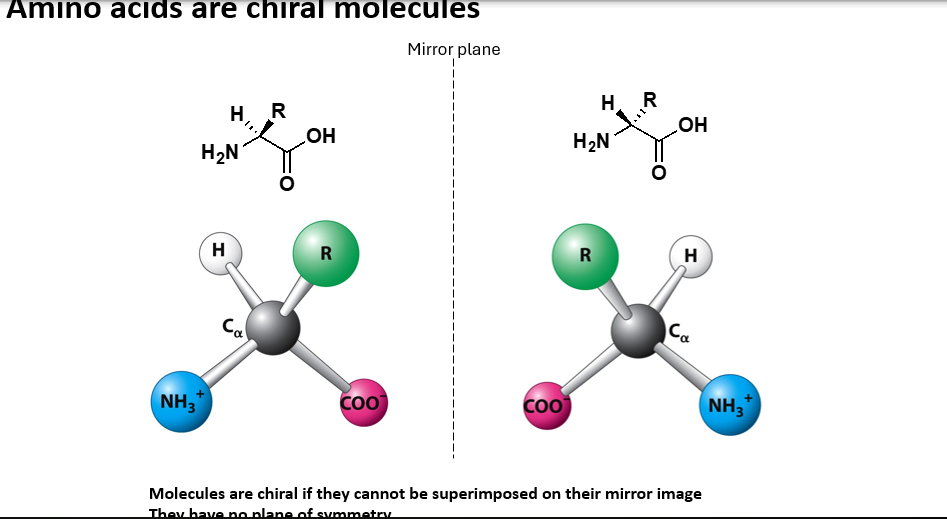
Can amino acids be chiral?
Yes
What is protein function usually dictated by?
It’s shape
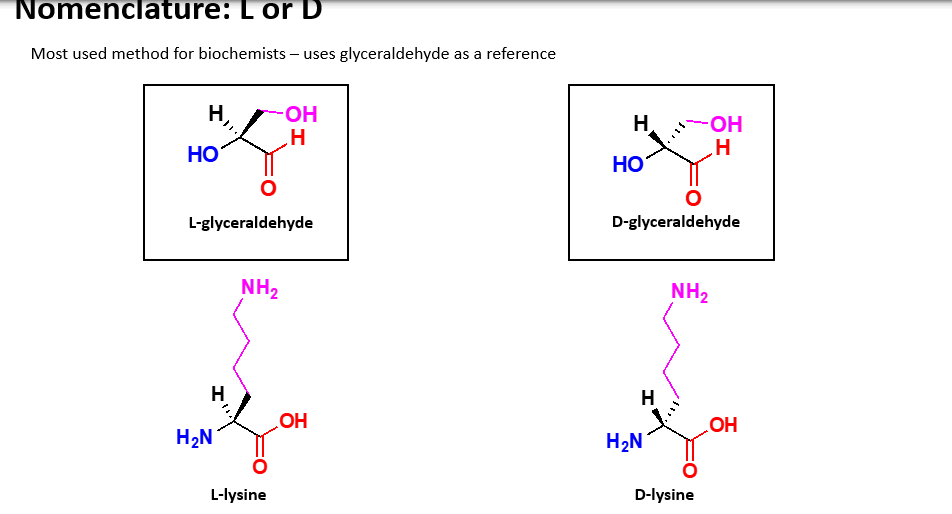
What is the common nomenculture used for amino acids?
L or D
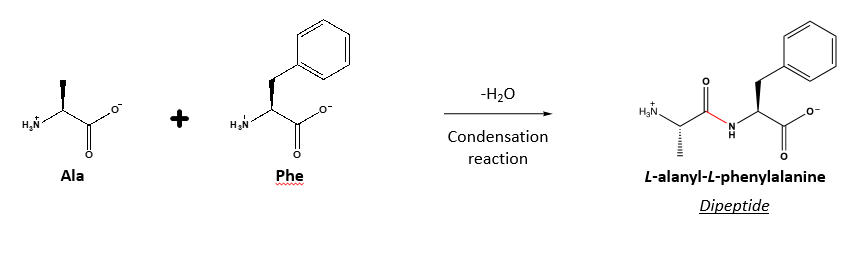
What bond forms chains of amino acids to form proteins and how do the bonds form?
Peptide bonds and they are formed from the reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group of another.
What is needed for the synthesis of peptide bonds in cells?
A catalyst and cellular machinery
Are peptide bonds stable (without a catalyst)?
Yes
What are 3 important things about the structure of peptides (short chain of amino acids)?
Named N to C terminus
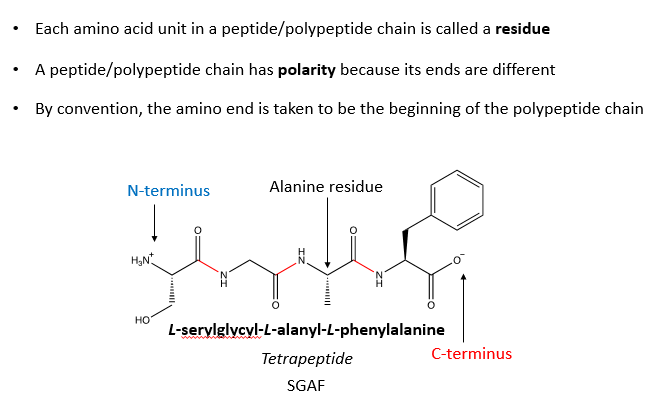
Why is it important that when we name peptides we name them from the N to C terminus?
As they have different properties and activities even though they have the same chemical formula and same side chains present
Proteins have regular repeating…
… backbones or main chains with varying distinctive side chains
Why is it important that peptide bonds remain uncharged?
As this would allow them to form tightly packed globular structures
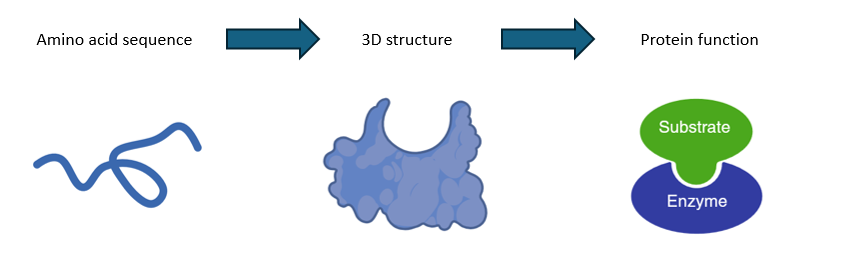
Overall sequence for proteins to function
What property explains how the two alpha carbon atoms are positioned about the peptide bond?
As peptide bonds can have two configurations or geometric isomers (Cis or Trans)
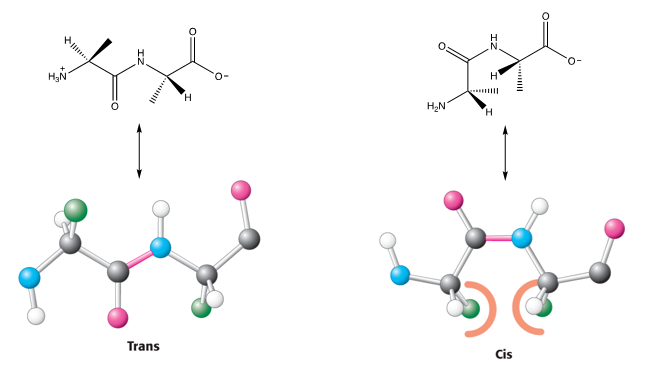
Why do peptide bonds in proteins prefer the trans conformation?
Due to unfavourable steric clashes in the cis form
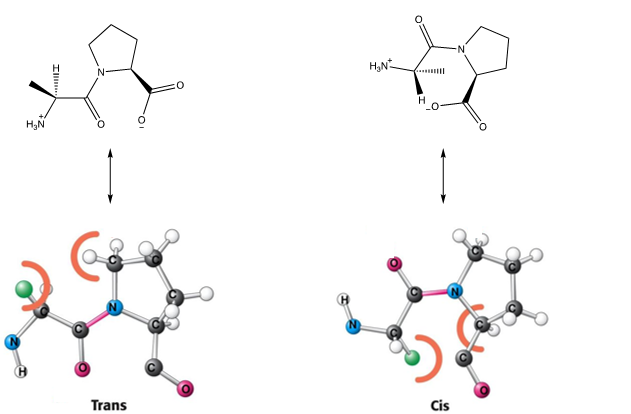
What is excluded from the trans conformation rule?
Proline as both trans and cis isomers have steric clashes so you can observe both conformations in proteins regularly
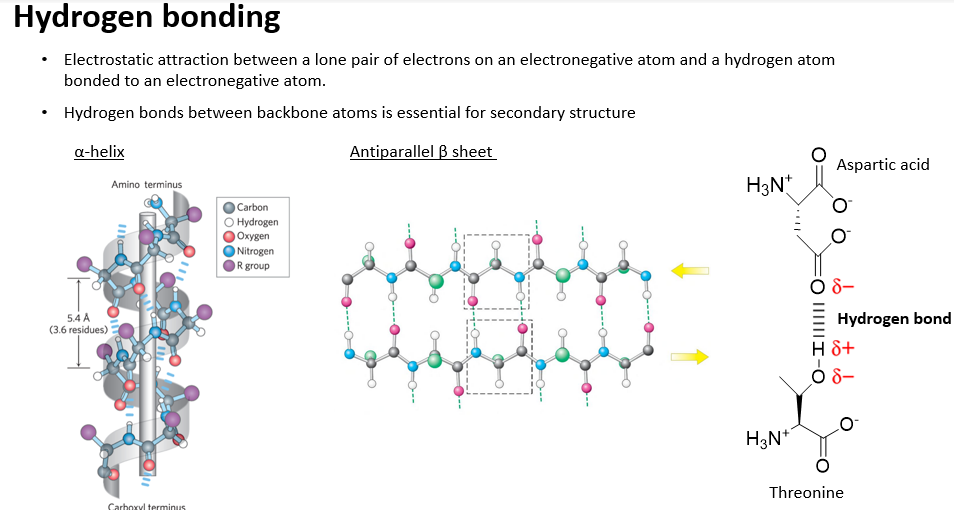
Hydrogen bonding
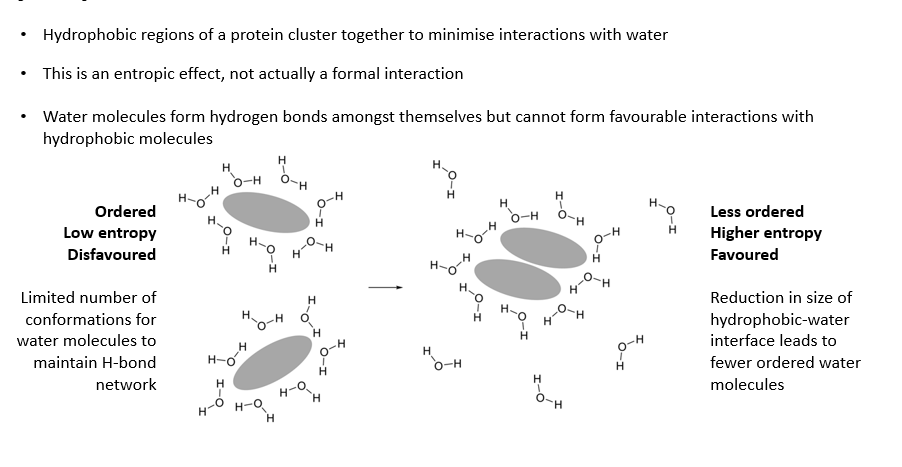
Hydrophobic effect
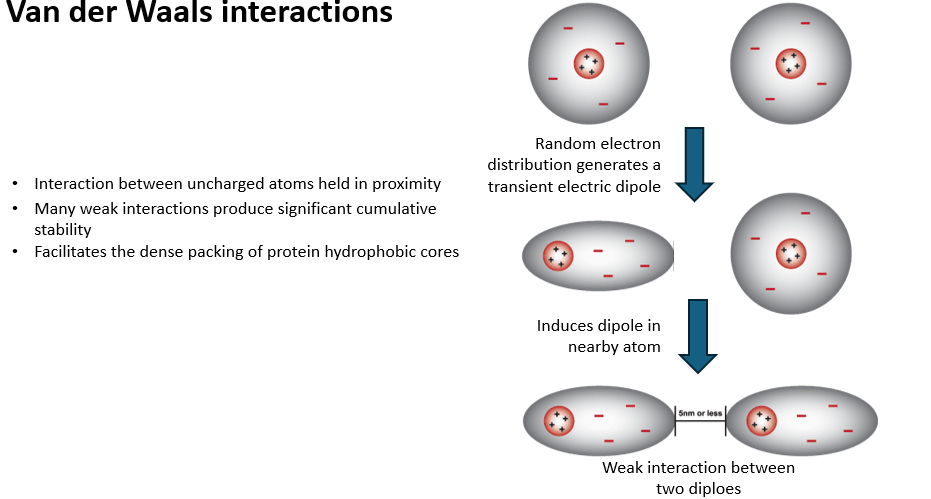
VDW interactions
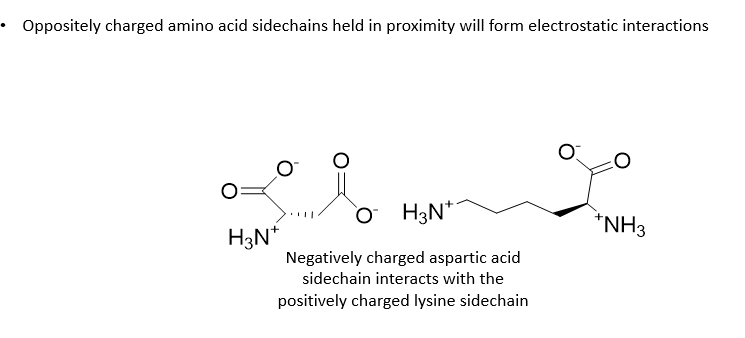
Ionic interactions
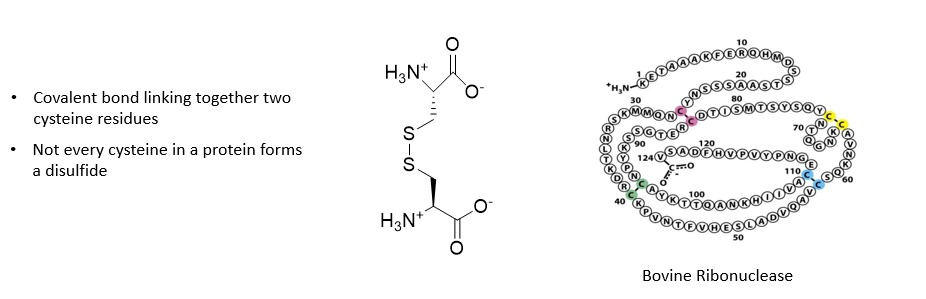
Disulfide bonds
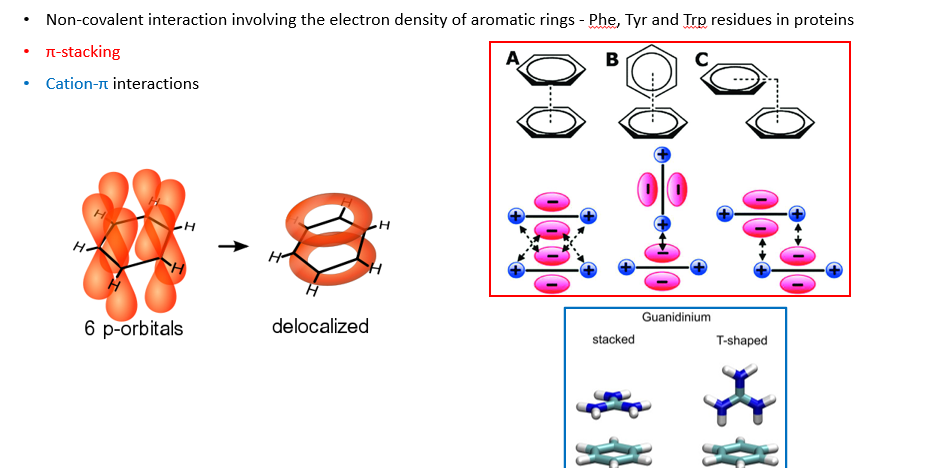
Pie interactions
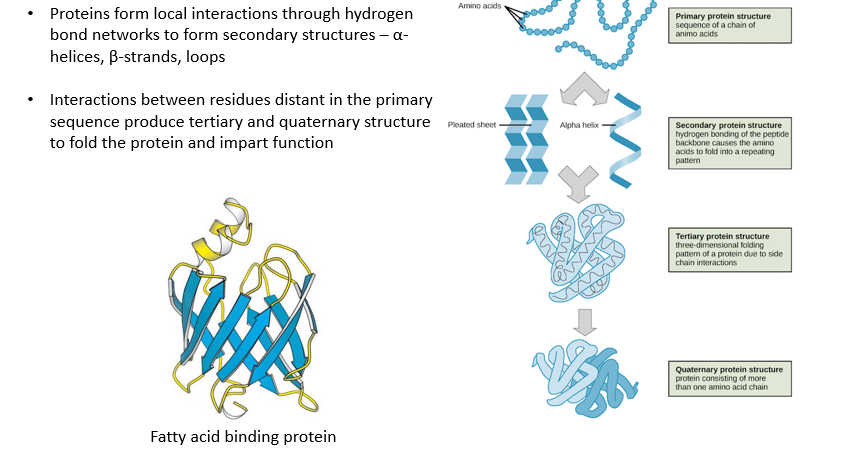
Protein folding 1
Protein folding 2
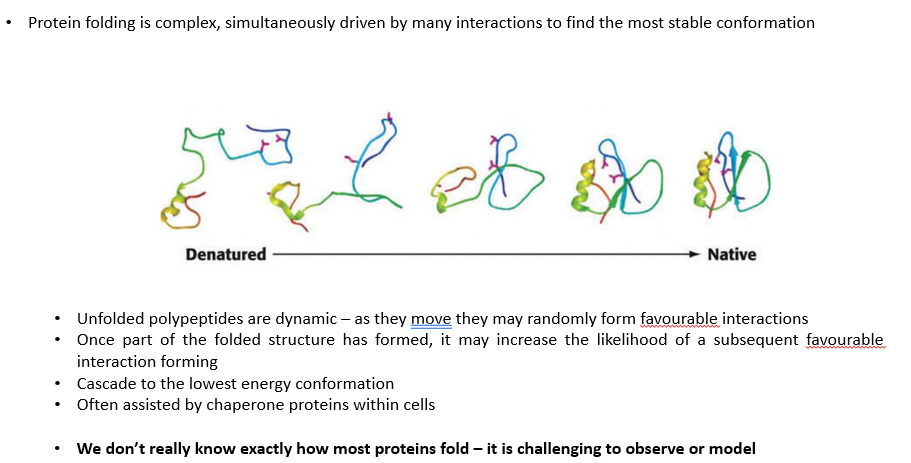
The cumulative effect of all interactions within a protein lead it to a…
… particular folded structure
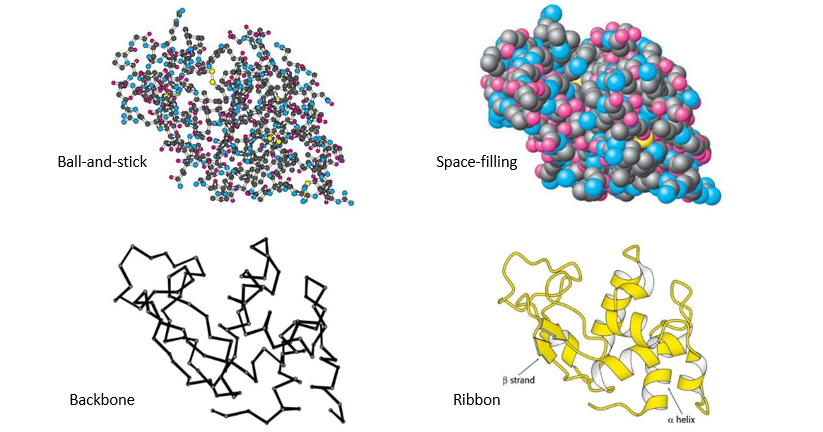
What are the 4 representations of proteins?
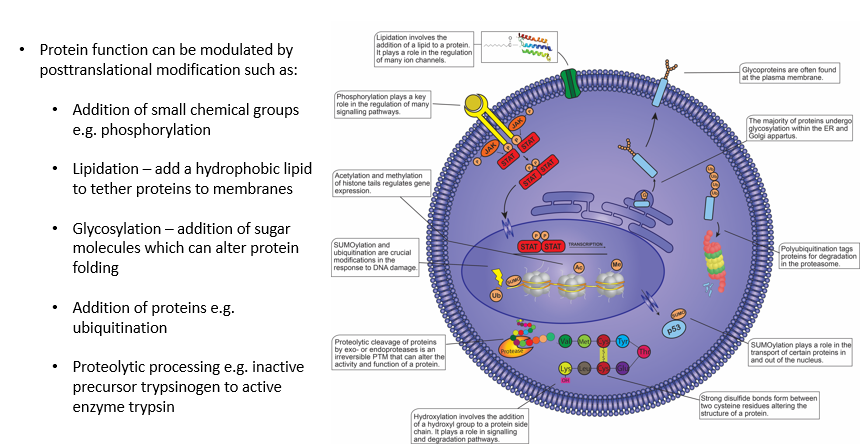
What are posttranslational modifications? (PTMs)
PTMs are chemical changes which occur after a protein has been synthesised, they are typically reversiable and the change in protein structure alters the function, stability or cellular localisation
Examples of PTMs
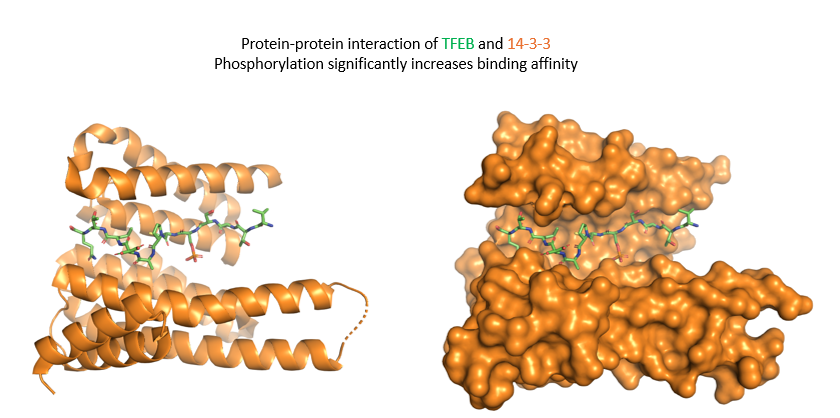
TFEB phosphorylation example of PTMs 1
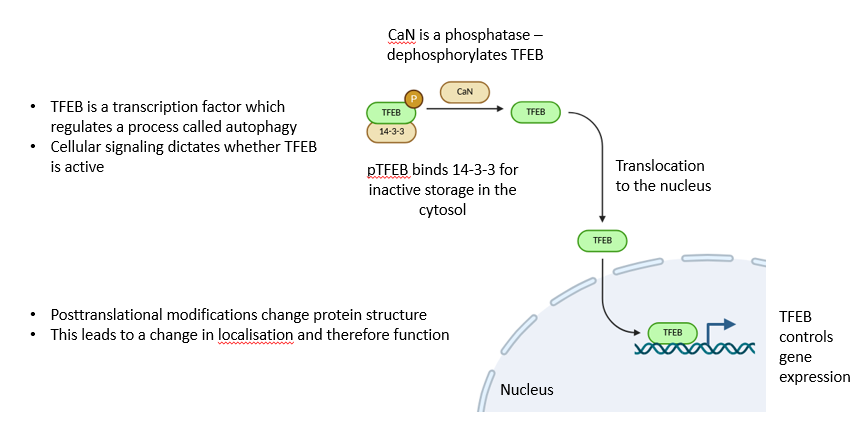
TFEB phosphorylation example of PTMs 2