Chemistry HL - Unit 10 Organic Chemistry
1/69
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
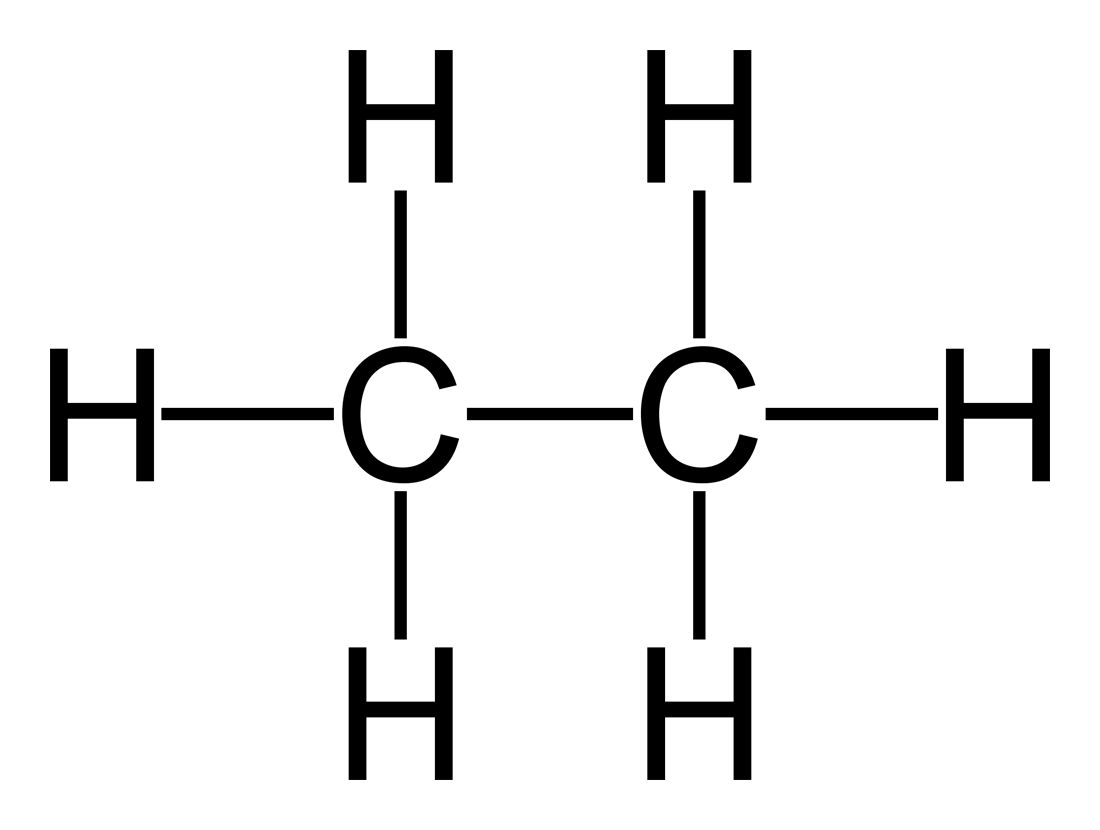
Class, functional group
Alkane, Alkyl
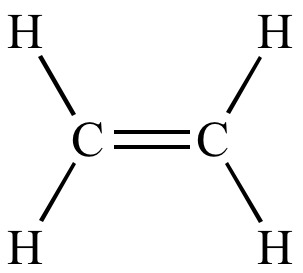
Class, functional group
Alkene, Alkenyl
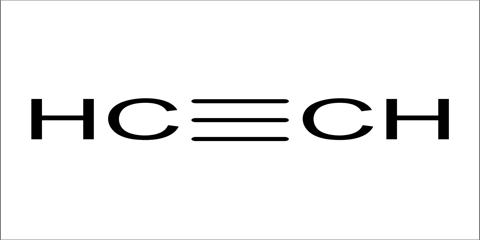
Class, functional group
Alkyne, Alkynyl
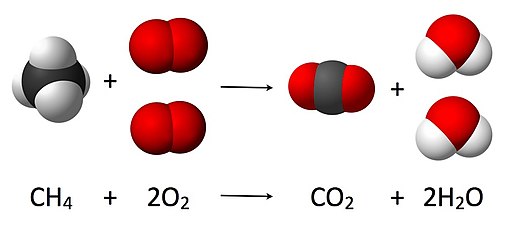
Reaction
Combustion
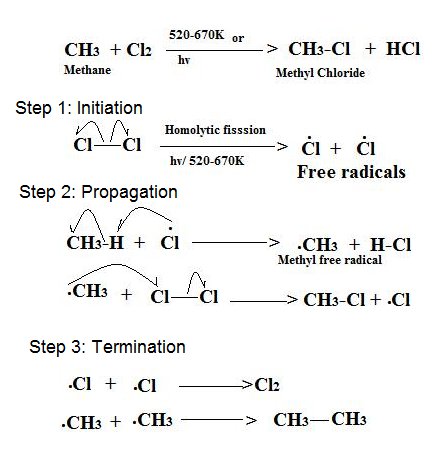
Reaction, reagents
Free radical substitution, UV light
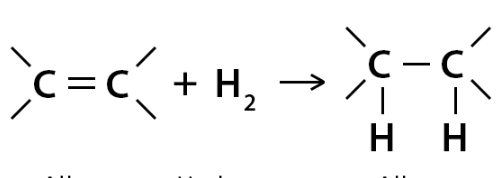
Reaction
Hydrogenation
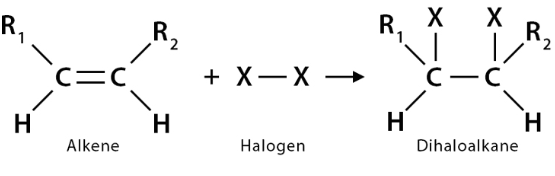
Reaction
Halogenation
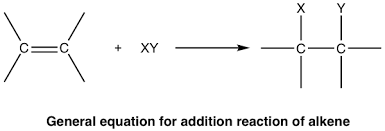
Reaction
Hydrogen Halide
Markovnikovs’s rule
The H will bond to the carbon with the greater amount of bonded hydrogens
Reaction
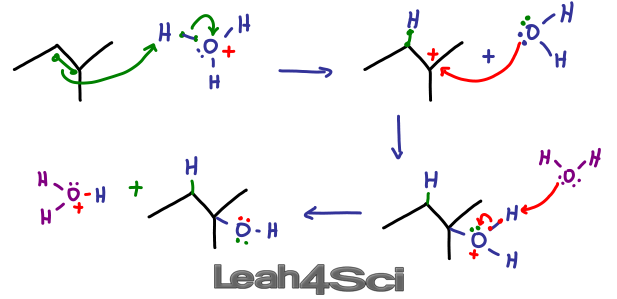
Hydration
Reaction
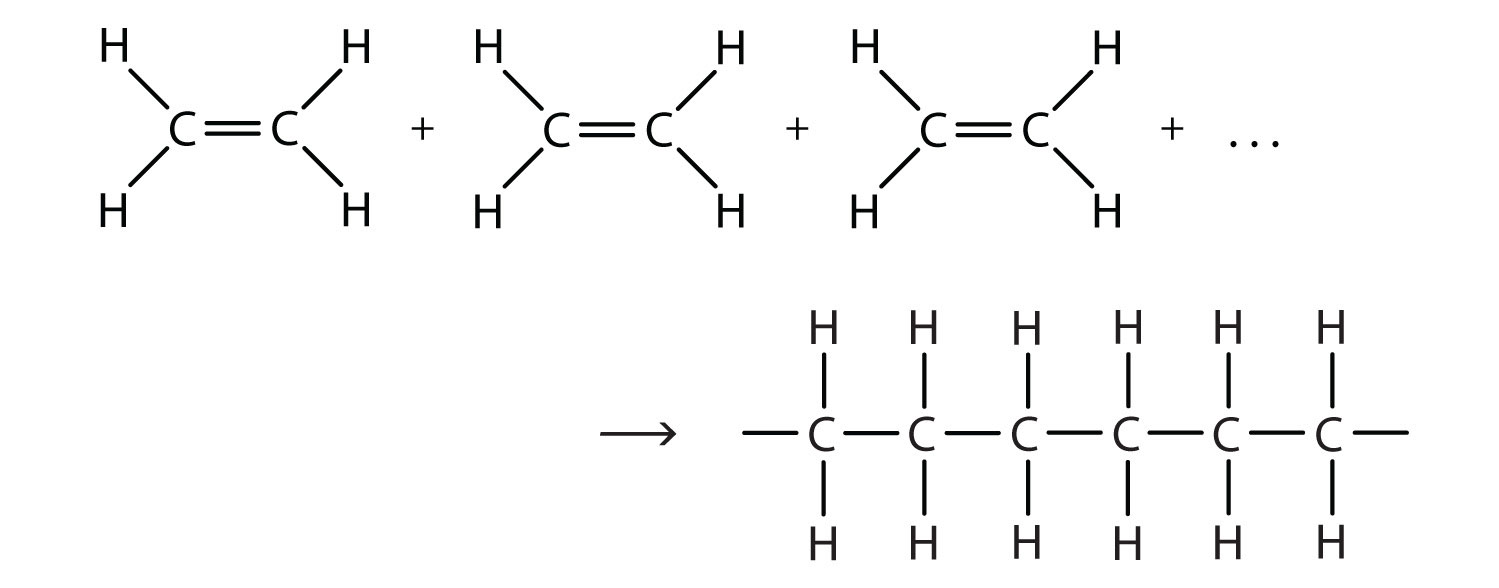
Polymerization
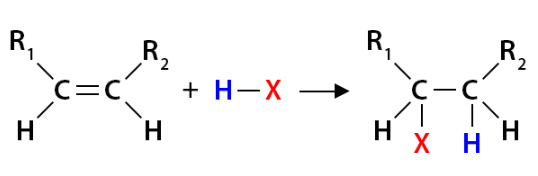
Reaction
Electrophillic addition
Class,functional group
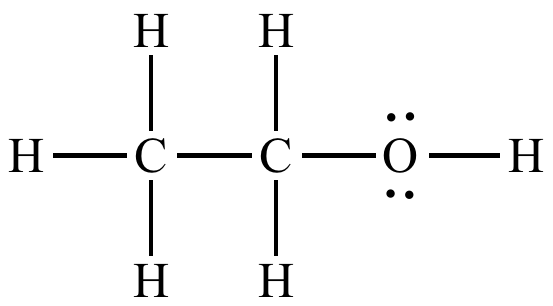
Alcohol, hydroxyl
Formation of an alcohol, reagents and conditions
H2O(g) and concentrated H2SO4 + Heat
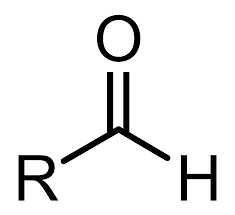
Class, functional group
Aldehyde, Carbonyl
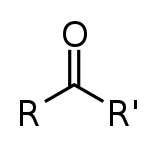
Class, functional group
Ketone, Carbonyl
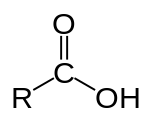
Class, functional group
Carboxylic acid, Carboxyl
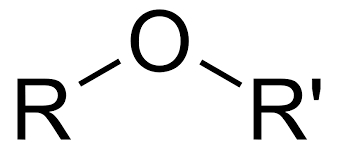
Class, functional group
Ether, Ether
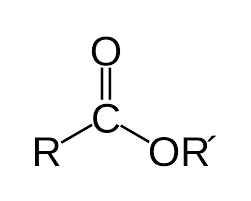
Class, functional group
Ester, Ester
Formation of Esters reaction
Esterization (Condensation)
Products of Esterization
Ester and H2O
Reactants of Esterization
Alcohol + Carboxylic Acid
Reagents/reactants to make an Aldehyde
Primary Alcohol, Acidified/H+ Cr2O72-, Heat/distillation
Reagents to make Carboxylic acid from an Aldehyde + color in product
H+/Cr2O72- + Reflux, Green
Products/color of tertiary alcohol + H+/Cr2O72- and reflux
NO REACTION, Orange
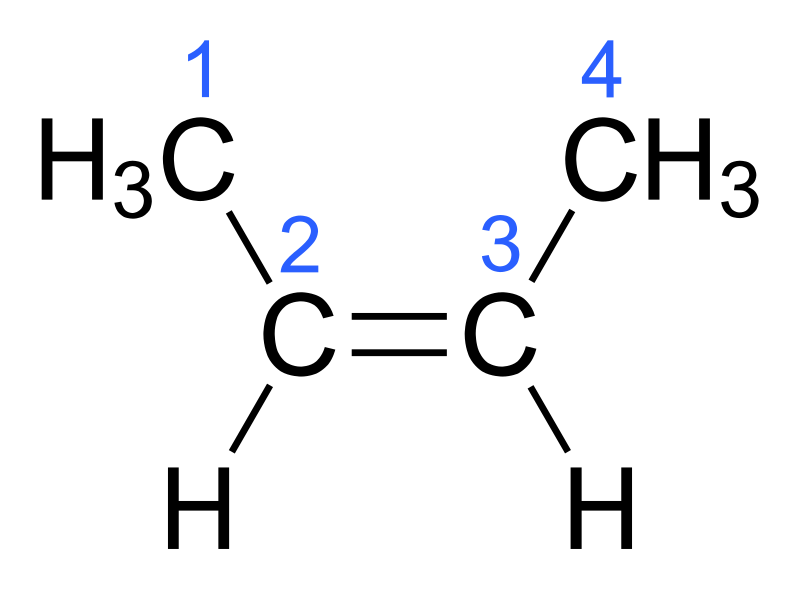
Notation for this Alkene
Cis-
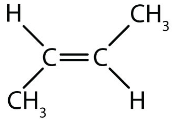
Notation for this Alkene
Trans-
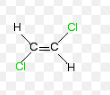
Notation for this alkene
E-
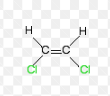
Notation for this Alkene
Z-
Homolytic fission:
Each species takes the same amount of electrons from a bond
Products of a combustion on an Alkane with very limited oxygen
C (s) and H2O
Saturated =
no double bonds
Un saturated =
Double bonds
Products of a combustion on an Alkane with limited Oxygen
CO and H2O
3 steps in a free radical substitution
Initiation, Propagation, Termination
When does electrophillic addition occur
an alkane reacts with a diatomic halogen molecule or a hydrogen halide molecule
Alkane suffix
-ane
Alkene suffix
-ene
Alkyne suffix
-yne
Alcohol suffix
-ol
Aldehyde suffix
-al
Ketone suffix
-one
Carboxylix acid suffix
-oic acid
Reducing reaction
removal of a carbonyl to return to an alcohol by using a reducing agent and heat
Reducing agents used for a reducing rxn
NaBH4, (doesn’t work on carboxylic acid), LiAlH4
Ether naming (R-O-R’)
___oxy___
Ester naming
R’ ___anoate
Miscible definiton
Soluble liquids
Immiscible definition
Not soluble
Conditions to form a Ketone, Color of the product
H+/Cr2O72- + Reflux, Green
Conditions to form a carboxylic acid from a primary Alcohol
MnO4- + H+/Cr2O72- and reflux
Conditions of polymerization
Pressure and heat
Conditions/reagents of Hydrogenation
Ni catalyst and heat
Conditions of Halogenation
Spontaneously at room temperature
Conditions of Hydrogen Halides
Happens spontaneously
Reagents of esterization
Heat + concentrated H2SO4
Why are Alkenes more reactive than Alkanes
The pi bond is relatively weaker, therefore easier to break
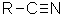
Class
Nitrile
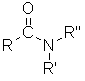
Class
Amide
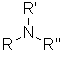
Class
Amine
Nitrile suffix
-nitrile
Amine suffix
-amine
Amide suffix
-amide
Nucleophile definition
Electron donor
Sn1
Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular
Sn2
Substitution nucleophilic bimolecular
Step 2 of an Sn1
Carbocation intermediate
Class, functional group
Benzene, arene
Reagent for Sn1 mechanism
Polar protic solvent
Reagent for Sn2 mechanism
Polar aprotic solvent